ATTEMPT ON THE LIFE OF 46 U.S. Presidents 🇺🇸 a criminal group of state biological terrorists.
The reaL COlonel 🃏ᏆNᏚᏆᎠᏆᏫᏌᏚ ᏟᏒᏆᎷᎬ ᏫᎰ ᎢᎻᎬ 21ᏚᎢ ᏟᎬNᎢᏌᏒᎩ 🤴
The list of a group of individuals of biological attack is not established only documentarily, for prosecution in court. This must be understood by the investigation. And most of the main names of the defendants are well known to us and we have circumstantial evidence.
KING'S OXYGEN STARVATION 👑 21

Most likely, he does not even realize that he enslaved himself, America and all its space: thoughts, feelings and even air...
Poor Old Man, he obviously has oxygen starvation. After all, to prevent fresh air from entering the lungs of 🫁 by blocking them with a black rag is simply dangerous ⚠️ for life at such a venerable age. Grandfather definitely falls asleep from lack of oxygen, although he moves his fingers with this slumber and this is also quite understandable and Obviously when sleep occurs, the limbs sweetly twitch in anticipation of erotic sleep.
And U.S. journalists, who can be called journalists with a great stretch, discussed this next episode, which has now occurred in Biden's negotiations with the Israeli prime minister. A number of congressmen also sleeping at meetings, frankly old farts, suddenly woke up and also reacted to this worthless polemic of false journalists with calls for the old man to "wake up" and resign.
But defenders of Bidon's sleeping man, the so-called U.S. journalists, carefully watched the full snippet of the recording, found Joe only lowered his head after Bennett's words about "hard days" for the U.S. because of Afghanistan. And allegedly, their beloved President at this fall asleep continues to move his fingers and imperceptibly something answered the Prime Minister after his speech. Of course, this can not be 🚫 called a dream, because the object in the frame still moves its fingers and itself is also still moving.
Oh God, what a disgrace America is experiencing 🇺🇸 with these oval insane from The New Call 21.
Oxygen starvation makes itself felt: more and more effort is spent on filling the void formed after his last appearance at a press conference on the tragic events in Afghanistan ...
What's next? And then silence, tears and loneliness... He was left alone with ruthless time, which every second more and more pressing, reminding that he is far from all of us and every second the ticking of the clock mocks him, killing him one drop by drop and taking away the remnants of life and hope ...
Hypoxia is a pathological condition in which oxygen deficiency is formed in the body due to its reduced intake from the outside and / or due to the dysfunction of utilization in the cells.
"Hypoxia" – hypo and oxigenium (lack of oxygen), translated from ancient Greek. Most people understand hypoxia as oxygen starvation (lack of oxygen), because in this case, tissues and organs have dysfunction from oxygen deficiency.
General characteristics of hypoxia
Determination of hypoxia
Hypoxia is a typical and dangerous pathological process that occurs in the body with a wide range of diseases and acute conditions, and provokes them. For example, hypoxia can be caused by various factors, as well as accompany a wide range of diseases, and may even be the main link in the appearance of pathological changes or diseases.
Based on this:
hypoxia is a typical general pathological process, does not apply to either the diagnosis or the syndrome.
The effect of hypoxia at the cellular level is divided into two types - adaptive reactions and decompensation.
During the onset of hypoxia, the body triggers adaptive protective reactions that support for a short time the almost normal vital activity of organs and tissues. With prolonged exposure to hypoxia, the body's reserves end and adaptive protective reactions are turned off - decompensation occurs.
Decompensation is characterized by the occurrence of irreversible disorders in organs and tissues - from organ failure to death.
Development of hypoxia
Compensatory reactions in hypoxia are expressed by oxygen deficiency at the cellular level, and their task is to restore the amount of oxygen in the tissues. The complex of compensatory reactions to eliminate the effect of hypoxia includes the organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and a change in biochemical processes in tissues and organ structures, most severely affected by oxygen deficiency, is triggered. Until the supply of compensatory reactions is completely exhausted, organs and tissues will not suffer from a lack of oxygen. However, if the depletion of compensatory mechanisms does not normalize the supply of oxygen, then irreversible decompensation will begin in the tissues with damage to cells and dysfunction of the entire organ.
In acute and chronic hypoxia, the nature of compensatory reactions is different. So, in acute hypoxia, compensatory reactions consist in increasing breathing and blood circulation, that is, blood pressure rises, tachycardia occurs (heart rate of more than 70 beats per minute), breathing becomes deep and frequent, the heart pumps a larger volume of blood per minute than normal. In addition, in response to acute hypoxia from the bone marrow and spleen, all the "reserves" of red blood cells that are necessary for carrying oxygen to the cells enter the systemic bloodstream.
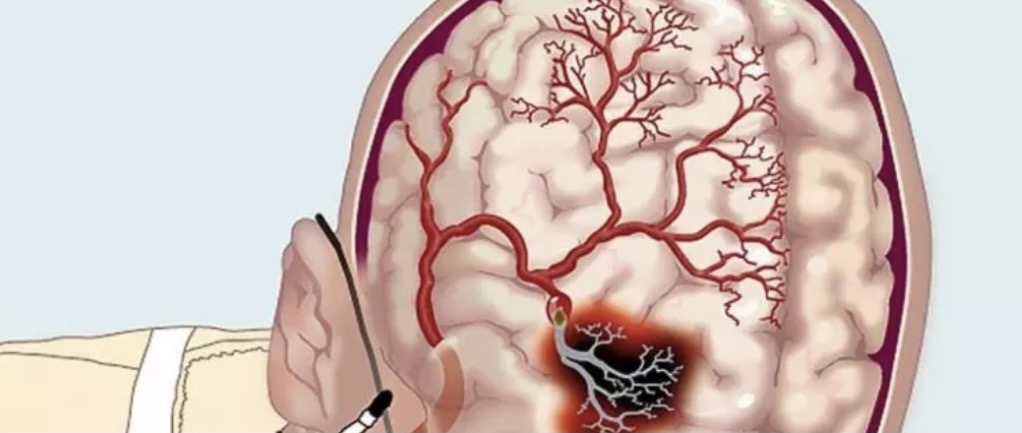
hypoxia
All these reactions are aimed at normalizing the amount of oxygen delivered to the cells by increasing the volume of blood passing through the vessels per unit of time, and increasing the amount of oxygen carried. With very severe acute hypoxia, in addition to the development of these reactions, there is also a centralization of blood circulation, which consists in redirecting all available blood to vital organs (heart and brain) and a sharp decrease in blood supply to the muscles and organs of the abdominal cavity. The body directs all the oxygen to the brain and heart – organs critical to survival, and as if "drains" those structures that are currently not needed for survival (liver, stomach, muscles, etc.).
If acute hypoxia is eliminated without depleting the body's reserves, then the person will survive, and all his organs and systems after a while will work completely normally. If hypoxia lasts longer than the period of effectiveness of compensatory reactions, then irreversible changes will occur in organs and tissues.
Compensatory reactions in chronic hypoxia develop against the background of severe long-term current diseases or conditions. First, to compensate for the lack of oxygen, the number of red blood cells in the blood increases, which allows you to increase the amount of oxygen carried by the same volume of blood per unit of time. Also, in erythrocytes, the activity of an enzyme that facilitates the transfer of oxygen from hemoglobin directly to the cells of organs and tissues increases. New alveoli are formed in the lungs, breathing deepens, the volume of the chest increases, additional vessels in the lung tissue are formed, which allows improving the flow of oxygen into the blood from the surrounding atmosphere. The heart, which has to pump a larger volume of blood per minute, hypertrophied and increases in size. Changes also occur in tissues - the number of mitochondria (organelles that use oxygen to provide cellular respiration) increases in cells, and many new capillaries are formed in the tissues. It is because of the activation of microcirculation and a large number of capillaries with hypoxia that a person has a pinkish color of the skin, which is mistaken for a "healthy" blush.
Adaptive reactions in acute hypoxia are reflexive, and therefore, when oxygen starvation is eliminated, they cease to act, and the organs completely return to the mode of functioning in which they existed before the development of an episode of hypoxia. In chronic hypoxia, adaptive reactions are not reflexive, they develop due to the restructuring of the mode of functioning of organs and systems, and therefore their action cannot be quickly stopped after the elimination of oxygen starvation.
In chronic hypoxia, the body can change the mode of its functioning so that it will fully adapt to the conditions of oxygen deficiency and will not suffer from it at all. For example, this is how the body of residents of megacities adapts.
In acute hypoxia, complete adaptation to oxygen deficiency cannot occur, since the body simply does not have time to restructure the modes of functioning, and all its compensatory reactions are designed only for temporary maintenance of the organs until adequate oxygen delivery is restored.
That is why a state of chronic hypoxia can be in a person for many years, without interfering with his completely normal life and work, and acute hypoxia in a short period of time can lead to death or irreversible damage to the brain or heart.
Compensatory reactions in hypoxia always lead to a change in the mode of functioning of the most important organs and systems. These manifestations of compensatory reactions can be conditionally considered symptoms of hypoxia.
Types of hypoxia
Hypoxia, depending on the mechanism of development, is divided into:
Exogenous hypoxia (hypoxic hypoxia) - due to environmental factors.
Endogenous hypoxia - due to various diseases or disorders that a person has:
Respiratory (respiratory, pulmonary) hypoxia.
Circulatory (cardiovascular) hypoxia: Ischemic; Stagnant.
Hemic (blood) hypoxia: Anemic; Caused by hemoglobin inactivation.
Tissue (histotoxic) hypoxia. Substrate hypoxia.
Overload hypoxia. Mixed hypoxia.
Depending on the speed of development and flow:
💀 Lightning (instant) - develops within a few seconds (no longer than 2 - 3 minutes);
💀 Acute - develops within a few tens of minutes or hours (no longer than 2 hours);
💀 Subacute - develops within a few hours (no longer than 3-5 hours);
💀 Chronic – develops and lasts for weeks, months or years.
Depending on the prevalence of oxygen starvation, hypoxia is divided into general and local.
Exogenous hypoxia
Exogenous hypoxia (hypoxic) is caused by a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the inhaled air. Accordingly, blood comes out of the lungs, insufficiently saturated with oxygen and the cells of various organs / tissues are brought a small amount of gas. Exogenous hypoxia is manifested by cyanosis (cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes), dizziness and fainting.
Depending on atmospheric pressure, exogenous hypoxia is divided into hypobaric and normobaric.
Hypobaric hypoxia is caused by a low oxygen content in rarefied air with low atmospheric pressure. Such hypoxia develops in mountainous areas and at high altitudes.
Normobaric hypoxia develops with a low oxygen content in the air with normal atmospheric pressure. Normobaric exogenous hypoxia can develop when in mines, wells, submarines, diving suits, in cramped rooms with a large crowding of people, with general gas contamination of air or smog in cities, as well as during surgery in case of malfunction of anesthesia and respiratory equipment.
Respiratory (respiratory, pulmonary) hypoxia
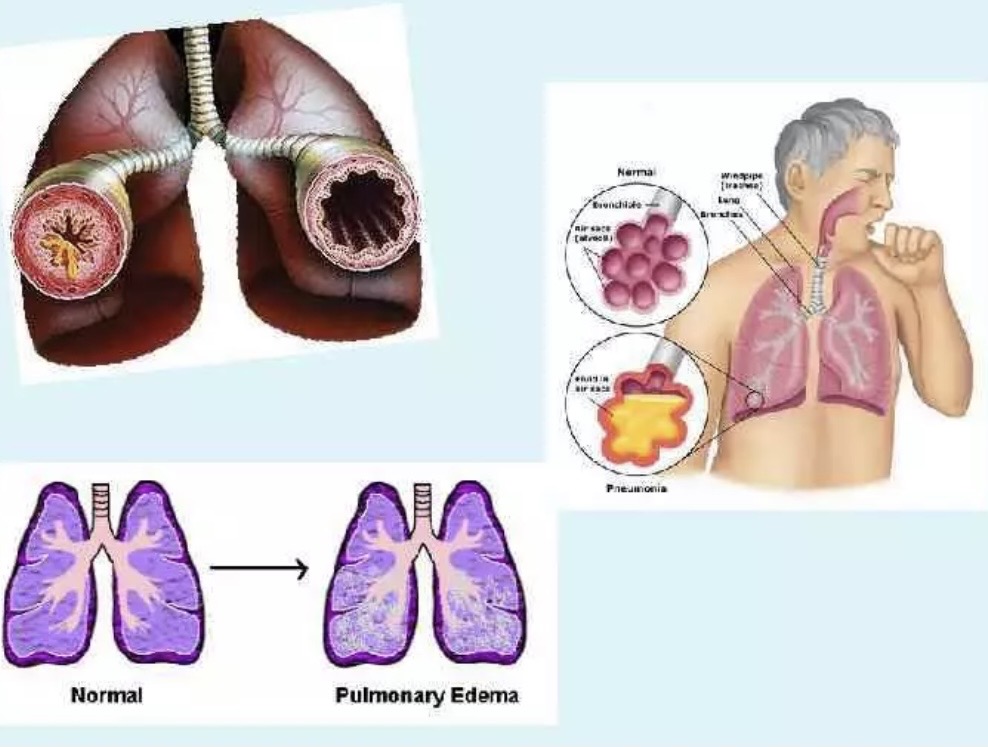
respiratory hypoxia
Respiratory (respiratory, pulmonary) hypoxia develops in diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, pulmonary hypertension, any lung pathologies, etc.), when it is difficult for oxygen to penetrate from the air into the blood. Against the background of respiratory hypoxia, complications such as respiratory failure, cerebral edema and gas acidosis may develop.
Circulatory (cardiovascular) hypoxia
Circulatory (cardiovascular) hypoxia develops against the background of various circulatory disorders (for example, a decrease in vascular tone, a decrease in total blood volume after blood loss or dehydration, an increase in blood viscosity, increased clotting, centralization of blood circulation, venous stagnation, etc.). If the circulatory disorder affects the entire network of blood vessels, then hypoxia is systemic. If blood circulation is disturbed only in the area of any organ or tissue, then hypoxia is local.
With circulatory hypoxia, a normal amount of oxygen enters the blood through the lungs, but due to circulatory disorders, it is delivered late to organs and tissues, as a result of which oxygen starvation occurs in the latter.
According to the mechanism of development, circulatory hypoxia is ischemic and stagnant. The ischemic form of hypoxia develops with a decrease in the volume of blood passing through organs or tissues per unit of time. This form of hypoxia can occur with left ventricular heart failure, heart attack, cardiosclerosis, shock, collapse, vasoconstrictation of some organs and other situations.
The congestive form of hypoxia develops with a decrease in the speed of blood movement through the veins - with thrombophlebitis of the legs, right ventricular heart failure, increased intrathoracic pressure and other situations when blood stagnation occurs in the venous bed. With a stagnant form of hypoxia, venous blood does not return to the lungs in time to remove carbon dioxide and oxygen saturation. As a result, there is a delay in the delivery of the next portion of oxygen to organs and tissues.
Hemic (blood) hypoxia
Hemic (blood) hypoxia develops when there is a violation of qualitative characteristics or a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemic hypoxia is divided into two forms - anemic and due to changes in the quality of hemoglobin.
Anemic hemic hypoxia is caused by a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood, that is, anemia of any origin or hydremia (dilution of blood due to fluid retention in the body). In anemic hypoxia, oxygen is normally bound and carried by the blood to organs and tissues. But due to the fact that hemoglobin is too small, an insufficient amount of oxygen is brought to the tissues and hypoxia occurs in them.
Hypoxia, caused by a change in the quality of hemoglobin, is associated with poisoning with various toxic substances that lead to the formation of forms of hemoglobin that are not able to carry oxygen (methemoglobin or carboxyhemoglobin). When the qualities of hemoglobin change, its amount remains normal, but it loses its ability to carry oxygen. As a result, when passing through the lungs, hemoglobin is not saturated with oxygen and the blood flow does not deliver it to the cells of all organs and tissues. Changes in the qualities of hemoglobin occur when poisoning by a number of chemicals, such as carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide), sulfur, nitrites, nitrates, etc.
Tissue (histotoxic) hypoxia
Tissue (histotoxic) hypoxia develops against the background of a violation of the ability of organ cells to absorb oxygen. The cause of tissue hypoxia is a reduced activity or deficiency of mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymes, which convert oxygen into forms in which it is used by cells to carry out all vital processes.
💀 Disruption of the enzymes of the respiratory chain can occur in the following cases:
💀 Suppression of the activity of enzymes of the respiratory chain in case of poisoning with cyanide, ether, urethane, barbiturates and alcohol;
💀 Lack of the number of enzymes of the respiratory chain against the background of a deficiency of vitamins B1, B2, PP and B5;
💀 Disruption of the enzymes of the respiratory chain in case of poisoning with nitrates, toxins of microbes, exposure to a large number of thyroid hormones, etc .;
💀 Damage to the structure of enzymes under the action of radioactive radiation, with uremia, kakhexia, severe infectious diseases, etc.
Tissue hypoxia can exist for a long period of time.
Substrate hypoxia develops with normal oxygen delivery to tissues, but in conditions of lack of essential nutrients that undergo oxygen oxidation. Substrate hypoxia can develop during starvation, diabetes mellitus and other conditions when there is not enough glucose and fatty acids in the cells.
Overload hypoxia can develop with heavy physical work, when the cells intensively consume oxygen. In such cases, the cells simply do not have enough of a sufficiently large amount of oxygen delivered. Such physiological hypoxia is not dangerous and passes after the completion of the stage of high physical exertion.
Mixed hypoxia
Mixed hypoxia is a combination of several types of endogenous hypoxia and occurs in severe, life-threatening lesions of various organs and systems, such as, for example, shock, poison poisoning, coma, etc.
Acute hypoxia
Acute hypoxia develops quickly, within a few tens of minutes and persists for a limited period of time, ending with either the elimination of oxygen starvation or irreversible changes in the organs that will lead to serious diseases or even death. Acute hypoxia usually accompanies acute conditions in which blood flow, the quantity and quality of hemoglobin change dramatically, such as, for example, blood loss, cyanide poisoning, heart attack, etc.
Any variant of acute hypoxia must be eliminated as soon as possible, since the body will be able to maintain the normal functioning of organs and tissues for a limited period of time until compensatory-adaptive reactions are exhausted. And when the compensatory-adaptive reactions are completely exhausted, under the influence of hypoxia, the most important organs and tissues (primarily the brain and heart) will begin to die.
In principle, acute hypoxia is more dangerous than chronic hypoxia, since it can lead to disability, organ failure or death in a short time. And chronic hypoxia can exist for years, giving the body the opportunity to adapt, live and function quite normally.
Chronic hypoxia develops over several days, weeks, months, or even years, and occurs with long-term current diseases. To chronic hypoxia, the body adapts by changing the structure of cells under new conditions, which allows the organs to function quite normally. In principle, chronic hypoxia is safer than acute hypoxia, because it develops slowly and the body is able to adapt to new conditions with the help of compensation mechanisms.
Myocardial hypoxia
Myocardial hypoxia is one of the most dangerous diseases and is characterized by insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
This condition occurs with a sudden decrease in the supply of oxygen to the heart muscle. Cells do not have time to adapt to the changed conditions. They continue to exchange, but it becomes incomplete, under-oxidized metabolites accumulate. With the preservation of hypoxia, the tissues of the heart muscle die.
Clinically, this condition is manifested by attacks of chest pain, an increase in their duration and intensity. In the future, myocardial infarction develops - necrosis of the heart muscle with the loss of its contractile function.
Myocardial hypoxia can be caused by such reasons:
💀 low oxygen content in the atmospheric air;
💀 lung diseases with a violation of gas exchange in them;
💀 a decrease in the amount of blood flowing through the myocardium due to the pathology of the coronary arteries;
💀 deterioration of the blood's ability to carry oxygen, for example, in case of carbon monoxide poisoning;
💀 violation of oxygen utilization by the cells themselves, for example, in case of poisoning with cyanides, heavy metals.
Consequences of hypoxia
The consequences of hypoxia can be different, and depend on the period of time in which oxygen starvation was eliminated and how long it lasted. If hypoxia was eliminated during the period when the compensatory mechanisms were not depleted, then there will be no negative consequences, after a while the organs and tissues will completely return to normal operation. But if hypoxia was eliminated during the period of decompensation, when the compensatory mechanisms were depleted, then the consequences depend on the duration of oxygen starvation. The longer the period of hypoxia against the background of decompensation of adaptive mechanisms, the stronger and deeper the damage to various organs and systems. Moreover, the longer the hypoxia lasts, the more organs are damaged.
With hypoxia, the brain suffers most severely, since it can withstand 3-4 minutes without oxygen, and from 5 minutes necrosis will already begin to form in the tissues. The heart muscle, kidneys and liver are able to endure the period of complete lack of oxygen for 30-40 minutes.
The consequences of hypoxia are always due to the fact that in the cells in the absence of oxygen, the process of oxygen-free oxidation of fats and glucose begins, which leads to the formation of lactic acid and other toxic metabolic products that accumulate and eventually damage the cell membrane, leading to its death. When hypoxia lasts long enough from toxic products of improper metabolism, a large number of cells in various organs die, forming entire areas of dead tissue. Such areas dramatically impair the functioning of the organ, which is manifested by the corresponding symptoms, and in the future, even with the restoration of oxygen inflow, it will lead to a persistent deterioration in the work of the affected tissues.
The main consequences of hypoxia are always due to disruption of the central nervous system, since it is the brain that suffers primarily from oxygen deficiency. Therefore, the consequences of hypoxia are often expressed in the development of neuropsychic syndrome, which includes parkinsonism, psychosis and dementia. In 50-70% of cases, neuropsychic syndrome can be cured. In addition, the consequence of hypoxia is intolerance to physical exertion, when with minimal tension a person has a heartbeat, shortness of breath, weakness, headache, dizziness and pain in the heart. Also, the consequences of hypoxia can be hemorrhages in various organs and fatty degeneration of muscle cells, myocardium and liver, which will lead to violations of their functioning with clinical symptoms of insufficiency of an organ, which can no longer be eliminated in the future.
Hypoxia - causes
The causes of exogenous hypoxia may be the following factors:
💀 Recharged atmosphere at altitude (altitude sickness, altitude sickness, pilots' illness);
💀 Sassing in cramped rooms with a large crowd of people;
💀 Fossing in mines, wells or in any enclosed spaces (e.g. submarines, etc.) with no communication with the external environment;
💀 Deach ventilation of premises;
💀 Work in diving suits or breathing through a gas mask;
💀 Sil gas content of the air or smog in the city of residence;
💀 Malfunction of anesthesia and respiratory equipment;
💀 Dobrovolnoe and / or forced partial overlap of human respiratory organs.
The causes of various types of endogenous hypoxia may be the following factors:
✅ Respiratory diseases (pneumonia, pneumothorax, hydrothorax, hemothorax, destruction of surfactant alveoli, pulmonary edema, pulmonary embolism, tracheitis, bronchitis, emphysema, sarcoidosis, asbestosis, bronchospasm, etc.);
✅ Foreign bodies in the bronchi (for example, accidental ingestion of various objects by children, squeezing, etc.);
✅ asphyxia of any origin (for example, when squeezing the neck, etc.);
✅ Congenital and acquired heart defects (non-healing of the oval opening or Batal duct of the heart, rheumatism, etc.);
✅ Damage to the respiratory center of the central nervous system in injuries, tumors and other diseases of the brain, as well as in its oppression by toxic substances;
✅ Violation of the mechanics of the act of breathing due to fractures and displacements of the bones of the chest, damage to the diaphragm or muscle spasms;
✅ Disorders of the heart, provoked by various diseases and pathologies of the heart (heart attack, cardiosclerosis, heart failure, electrolyte imbalance, cardiac tamponade, pericardial obliteration, blockade of electrical impulses in the heart, etc.);
✅ Sharp narrowing of blood vessels in various organs;
✅ Arteriovenous bypass grafting (transfer of arterial blood to the veins through vascular shunts before it reaches organs and tissues and gives oxygen to cells);
✅ Stagnation of blood in the system of the inferior or superior vena cava;
✅ Thrombosis;
✅ Poisoning with chemicals that cause the formation of inactive hemoglobin (for example, cyanides, carbon monoxide, lewisite, etc.);
✅ Anemia;
✅ Acute blood loss;
✅ Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC syndrome);
✅ Violation of the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats (for example, diabetes, obesity, etc.);
✅ Shock and coma;
✅ Excessive physical exertion;
✅ Malignant tumors of any localization;
✅ Chronic diseases of the kidneys and blood (for example, leukemia, anemia, etc.);
✅ Deficiency of vitamins PP, B1, B2 and B5;
✅ Thyroid diseases;
✅ Damage to cells by radiation radiation, tissue decay products in case of chakhexia, severe infections or uremia;
✅ Drug and alcohol abuse;
✅ Prolonged fasting.
It seems the last point does not threaten any of you, it is encouraging, at least one reason for the magical stupidity of 🤬 can be excluded.
Symptoms (signs) of hypoxia
With a fulminant form of hypoxia, clinical symptoms do not have time to appear, since death occurs within a very short period of time (up to 2 minutes).
The acute form of hypoxia lasts up to 2-3 hours, and during this period there is a deficiency of all organs and systems at once, primarily the central nervous system, respiration and heart (heart rate becomes less frequent, blood pressure drops, breathing becomes irregular, etc.). If hypoxia during this period is not eliminated, then organ failure turns into a coma and agony with subsequent death.
Subacute and chronic forms of hypoxia are manifested by the so-called hypoxic syndrome. Against the background of hypoxic syndrome, symptoms from the central nervous system appear first of all, since the brain is most sensitive to oxygen deficiency, as a result of which foci of necrosis (dead areas), hemorrhages and other variants of cell destruction quickly appear in its tissues. Due to necrosis, hemorrhages and death of brain cells against the background of oxygen deficiency at the initial stage of hypoxia, a person develops euphoria, he is in an excited state, he is tormented by motor anxiety. Own condition is not evaluated critically.
With further progression of hypoxia, the following signs of oppression of the cerebral cortex appear, which are similar in manifestations to alcohol intoxication:
✅ Drowsiness;
✅ Lethargy;
✅ Headache and dizziness;
✅ Tinnitus;
✅ Inhibition;
✅ Impaired consciousness;
✅ Involuntary discharge of urine and feces;
✅ Nausea and vomiting;
✅ Disorder of coordination of movements;
✅ Cramps.

Convulsions in hypoxia appear when exposed to external stimuli. Moreover, a convulsive attack usually begins with twitching of the muscles of the face, hands and feet with the addition of random muscle contractions of the abdomen. Sometimes with convulsions, opistotonus is formed, which is a person curved by an arch with the muscles of the neck and back straightened, the head thrown back and the arms bent at the elbows. The pose of a person in opistotonus resembles a gymnastic figure "bridge".
In addition to the symptoms of oppression of the cerebral cortex, a person also has pain in the heart, irregular breathing, shortness of breath, a sharp decrease in vascular tone, tachycardia (an increase in heart rate of more than 70 beats per minute), a drop in blood pressure, cyanosis (cyanosis of the skin), a decrease in body temperature. But in case of poisoning with substances that inactivate hemoglobin (for example, cyanides, nitrites, nitrates, carbon monoxide, etc.), human skin acquires a pinkish color.
With prolonged hypoxia with a slow development of CNS damage, a person may have mental disorders in the form of delirium ("delirium tremens"), Korsakov syndrome (loss of orientation, amnesia, replacement by fictional real events, etc.) and dementia.
With further progression of hypoxia, blood pressure drops to 20-40 mm Hg. Art. and there is a coma with the extinction of brain functions. If the blood pressure drops below 20 mm Hg. St., then there is a fatal outcome. In the period before death, a person may have agonizing breathing in the form of rare convulsive attempts to inhale.
Degrees of hypoxia
Depending on the severity of the course and the severity of oxygen deficiency, the following degrees of hypoxia are distinguished:
✅ Light (usually detected only during physical exertion);
✅ Moderate (the phenomenon of hypoxic syndrome appear at rest);
✅ Severe (the phenomenon of hypoxic syndrome is strongly expressed and there is a tendency to transition to a coma);
✅ Critical (hypoxic syndrome led to coma or shock, which can result in fatal gothom).
Treatment of oxygen starvation
In practice, mixed forms of hypoxia usually develop, as a result of which the treatment of oxygen deficiency in all cases should be comprehensive, aimed simultaneously at eliminating the causative factor and maintaining an adequate supply of oxygen to the cells of various organs and tissues.
To maintain a normal level of oxygen supply to cells with any type of hypoxia, hyperbaric oxygenation (HBO) is used - barotherapy. In barotherapy, hyperbaric chambers are used, in which a person is under high pressure with a high oxygen content. Due to the increased pressure, oxygen is additionally dissolved directly in the blood plasma, without binding to red blood cells, which allows its delivery to organs and tissues in the required amount, regardless of the activity and functional fullness of hemoglobin. Thanks to hyperbaric oxygenation, it is possible not only to supply the organs with oxygen, but also to expand the vessels of the brain and heart, so that the latter can work in full force.
In addition to hyperbaric oxygenation, with circulatory hypoxia, cardiac drugs and drugs that increase blood pressure are used. If necessary, produce blood transfusion (if there was a blood loss that is not compatible with life).
With hemic hypoxia, in addition to hyperbaric oxygenation, the following therapeutic measures are carried out:
✅ Transfusion of blood or erythrocyte mass;
✅ Introduction of oxygen carriers (Perftoran, etc.);
✅ Hemosorption and plasmapheresis to remove toxic metabolic products from the blood;
✅ Introduction of substances capable of performing the functions of enzymes of the respiratory chain (vitamin C, methylene, etc.);
✅ Introduction of glucose as the main substance that gives cells energy for the implementation of vital processes;
✅ The introduction of steroid hormones to eliminate severe oxygen starvation of tissues.
Prevention of hypoxia
An effective prevention of hypoxia is to prevent conditions in which the body may experience oxygen starvation. To do this, you need to lead an active lifestyle, visit the fresh air every day, exercise, eat well and treat existing chronic diseases in a timely manner. When working in the office, you need to periodically ventilate the room (at least 2-3 times during the working day) to saturate the air with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from it.
Also, we recommend several times a year to undergo a course of barotherapy (oxygen capsules and hyperbaric chambers), this helps to reduce cases of oxygen starvation of the body.
A small part of the grounds for our statement ⬇️
Reindeer 🦌 🦌 the Northern Lights
https://telegra.ph/GRAPHENE-OXIDE-IN-COVID-VACCINES--19-07-08
https://telegra.ph/The-same-Klaus--and-his-Company-and-Co-08-21
https://telegra.ph/HISTORY--YESTERDAY---TODAY---TOMORROW-08-23
https://telegra.ph/BIOLOGICAL-TERRORISTS-MARCH--22-WITH-A-NEW-COVID22-ATTACK-08-24
https://telegra.ph/STATE-THUGS---21-08-24
https://telegra.ph/There-are-four-kinds-of-lies-lies-damned-liesstatistics--and-oval-lies-08-24
https://telegra.ph/VACCINES-ARE-WEAPONS-OF-MASS-DESTRUCTION-08-25
https://telegra.ph/NWO-CROWN-08-25
https://telegra.ph/ORDINARY-FASCISM-19-21-08-26
https://telegra.ph/AGENDA-21---PLANETARY-DYSTOPIA-PLAN-08-26
https://telegra.ph/VERDICT-ON-THE-LIE-OF-THE-COVID-PANDEMIC-19-08-26
https://telegra.ph/AGENDA-21---PLANETARY-DYSTOPIA-PLAN-GOING-TO-INFINITY-OF-DARKNESS--Part-2-08-26
https://telegra.ph/COMMUNIST-INTERNATIONAL--INSTAGRAM---DRUM--SHOT-08-27
https://telegra.ph/2020-2021-The-worlds-population-lives-in-a-world-of-graphene-08-27
https://telegra.ph/SPECIAL-OPERATION-CORONA--19-08-28
https://telegra.ph/GRAPHENE-OXIDE-TRAUMA-MICE-CATS-AND-BOOSTER-SHOTS-08-28
PS
He counts the days, but doesn't feel the difference between yesterday's 20 and today's 21 - it's the same for him... Even tomorrow will not bring significant diversity to his life. He could count hours, minutes, seconds, but he just doesn't know the exact time... But even if I knew, it wouldn't change anything either... It's gone.
His space does not belong to him...
A colorless foaming wave 🌊 nightmare closer and closer, it will cover everything that came across on the way ...

And the clock was ticking. And the clock was still just going, not noticing anything around it.

Ⓜⓡ. Ⓒⓞⓛⓞⓝⓔⓛ 🃏