Spread Trading

🛑 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Spread Trading
In finance, a spread refers to the difference between two prices, rates or yields One of the most common types is the bid-ask spread, which refers to the gap between the bid (from buyers) and the ask (from sellers) prices of a security or asset Spread can also refer to the difference in a trading position – the gap between a short position (that is, selling) in one futures contract or currency and a long position (that is, buying) in another
Sponsored
Compete Risk Free with $100,000 in Virtual Cash
Put your trading skills to the test with our
FREE Stock Simulator.
Compete with thousands of Investopedia traders and trade your way to the top! Submit trades in a virtual environment before you start risking your own money.
Practice trading strategies
so that when you're ready to enter the real market, you've had the practice you need.
Try our Stock Simulator today >>
A bid-ask spread is the amount by which the ask price exceeds the bid price for an asset in the market.
A yield spread is the net difference between two interest bearing instruments, expressed in terms of percent or basis points (bps).
An intermarket spread involves purchasing long futures in one market and selling short futures of a related commodity with the same expiration.
Slippage refers to the discrepancy between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is executed.
The London Interbank Bid Rate is the average interest rate at which major London banks bid for eurocurrency deposits from other banks in the interbank market.
A futures spread is an arbitrage technique in which a trader takes two positions on a commodity to capitalize on a discrepancy in price.
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Investopedia is part of the Dotdash publishing family.
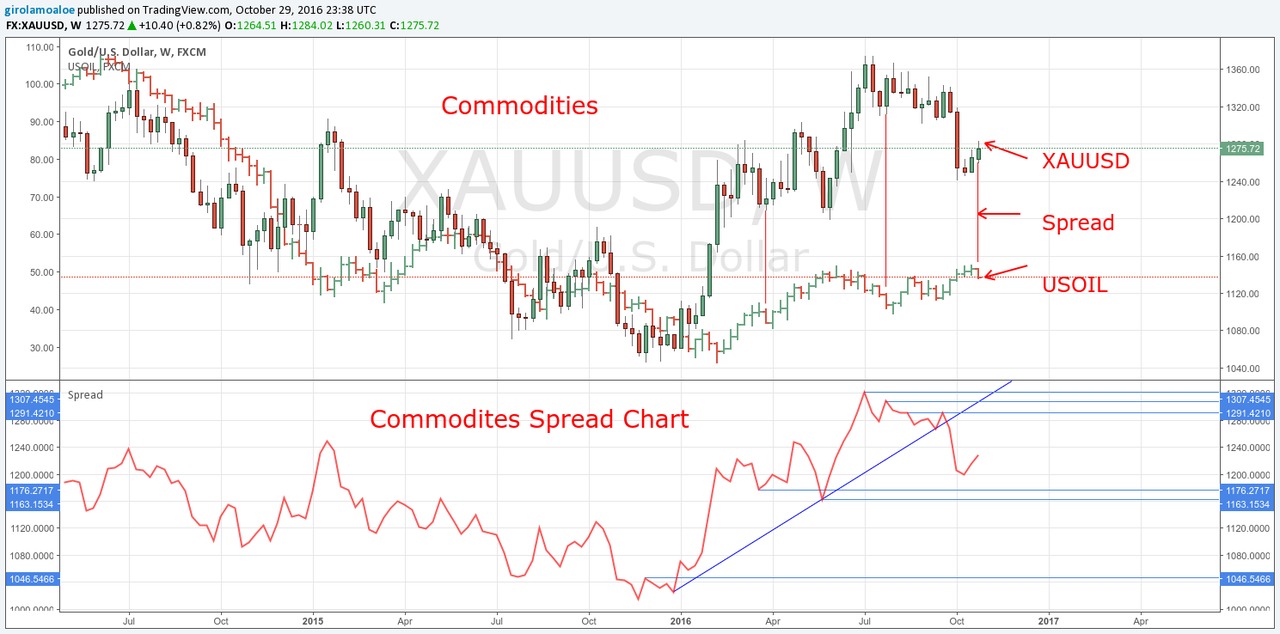
A spread can have several meanings in finance. Basically, however, they all refer to the difference between two prices, rates or yields .
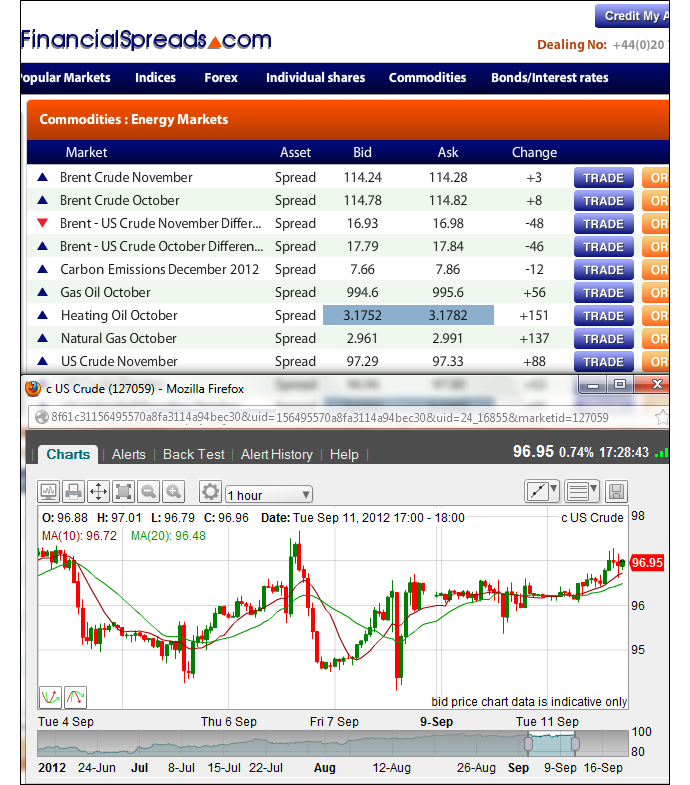
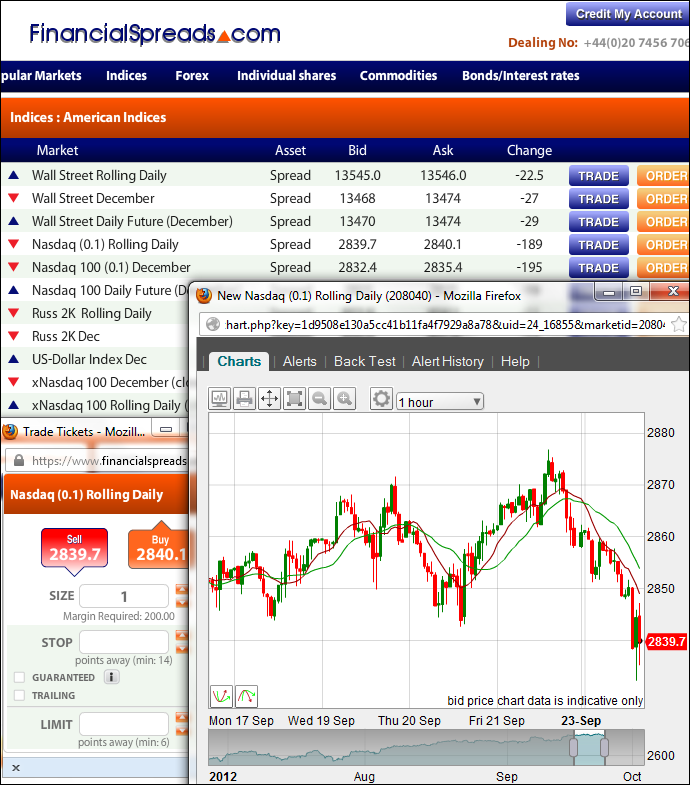
In one of the most common definitions, the spread is the gap between the bid and the ask prices of a security or asset, like a stock, bond or commodity. This is known as a bid-ask spread.
Spread can also refer to the difference in a trading position – the gap between a short position (that is, selling) in one futures contract or currency and a long position (that is, buying) in another. This is officially known as a spread trade.
In underwriting , the spread can mean the difference between the amount paid to the issuer of a security and the price paid by the investor for that security—that is, the cost an underwriter pays to buy an issue, compared to the price at which the underwriter sells it to the public.
In lending, the spread can also refer to the price a borrower pays above a benchmark yield to get a loan. If the prime interest rate is 3%, for example and a borrower gets a mortgage charging a 5% rate, the spread is 2%.
The bid-ask spread is also known as the bid-offer spread and buy-sell. This sort of asset spread is influenced by a number of factors:
For securities like futures contracts , options, currency pairs and stocks, the bid-offer spread is the difference between the prices given for an immediate order – the ask – and an immediate sale – the bid. For a stock option , the spread would be the difference between the strike price and the market value .
One of the uses of the bid-ask spread is to measure the liquidity of the market and the size of the transaction cost of the stock. For example, on Jan. 8, 2019 the bid price for Alphabet Inc., Google's parent company, was $1,073.60 and the ask price was $1,074.41. The spread is 80 cents, or $.80. This indicates that Alphabet is a highly liquid stock, with considerable trading volume.
The spread trade is also called the relative value trade. Spread trades are the act of purchasing one security and selling another related security as a unit. Usually, spread trades are done with options or futures contracts. These trades are executed to produce an overall net trade with a positive value called the spread.
Spreads are priced as a unit or as pairs in future exchanges to ensure the simultaneous buying and selling of a security. Doing so eliminates execution risk wherein one part of the pair executes but another part fails.
The yield spread is also called the credit spread . The yield spread shows the difference between the quoted rates of return between two different investment vehicles. These vehicles usually differ regarding credit quality .
Some analysts refer to the yield spread as the “yield spread of X over Y.” This is usually the yearly percentage return on investment of one financial instrument minus the annual percentage return on investment of another.
To discount a security’s price and match it to the current market price, the yield spread must be added to a benchmark yield curve . This adjusted price is called option-adjusted spread . This is usually used for mortgage-backed securities (MBS), bonds, interest rate derivatives and options.
For securities with cash flows that are separate from future interest rate movements, the option-adjusted spread becomes the same as the Z-spread.
The Z-spread is also called the Z SPRD, yield curve spread and zero-volatility spread . The Z-spread is used for mortgage-backed securities. It is the spread that results from zero-coupon treasury yield curves which are needed for discounting pre-determined cash flow schedule to reach its current market price. This kind of spread is also used in credit default swaps (CDS) to measure credit spread.
Advanced Trading Strategies & Instruments
What is Spread Trading ?
Spread Definition | Spread Trade
Spread Trading - Overview, Strategy and Puirpose, Spread Types
What Is Spread Trading : How To Spread Trade In Excel | The Secret Mindset
The Ins And Outs Of Futures Spread Trading | Binance Blog
A trading method that involves an investor simultaneously buying one security and selling a related security
We and selected partners, use cookies or similar technologies as specified in the cookie policy . With respect to advertising, we and selected third parties , may use precise geolocation data and actively scan device characteristics for identification in order to store and/or access information on a device and process personal data (e.g. browsing data, IP addresses, usage data or unique identifiers) for the following purposes: personalised ads and content, ad and content measurement, and audience insights; develop and improve products . You can freely give, deny, or withdraw your consent at any time by accessing the advertising preferences panel . You can consent to the use of such technologies by closing this notice.
Spread trading – also known as relative value trading – is a method of trading that involves an investor simultaneously buying one security and selling a related security. The securities being bought and sold, often referred to as “legs,” are typically executed with futures contracts Futures Contract A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell an underlying asset at a later date for a predetermined price. It’s also known as a derivative because future contracts derive their value from an underlying asset. Investors may purchase the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a later date for a predetermined price. or options, though there are other securities that can be used.
The strategy of spread trading is to yield the investor a net position with a value (or spread) that is dependent upon the difference in price between the securities being sold. In most cases, the legs are not traded independently but instead, are traded as a unit on futures exchanges.
The goal for investors is to make a profit off the spread as it gets wider or grows narrower. With spread trading, investors aren’t generally looking to benefit from direct price movements of the legs themselves. Spreads – because they are executed as a unit – are either bought or sold. It depends on the investor’s needs as to whether he believes he will benefit from a wider or narrower spread.
There are several types of spreads; however, the two most common are inter-commodity spreads and options spreads.
The inter-commodity spread is created when an investor buys and sells commodities that are decidedly different, but also related. An economic relationship exists between the commodities. For example:
Another common spread is option spread. Option spreads are created with different option contracts as legs. Both contracts must pertain to the same security or commodity.
CFI is the official provider of the Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ FMVA® Certification Join 350,600+ students who work for companies like Amazon, J.P. Morgan, and Ferrari certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst.
To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below:
Advance your career in investment banking, private equity, FP&A, treasury, corporate development and other areas of corporate finance.
to take your career to the next level! Learn step-by-step from professional Wall Street instructors today.
Sensual Sexy
Naked Straight
Us Defense Secretary
Rough Porn Sex Hd
Slut Teen Wife










































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2020-03-05at3.35.05PM-fe100e8c58eb4a55926415ea8a70e04a.png)