Lesson 3 notes
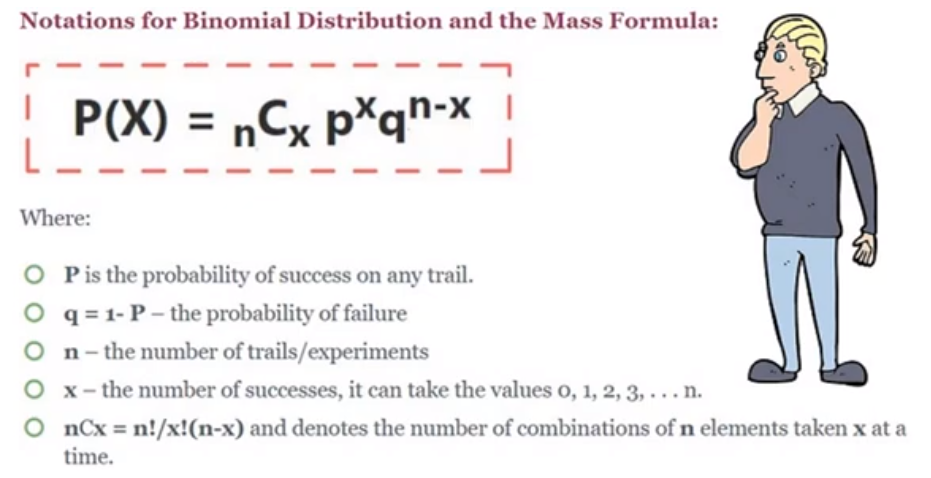
RavshanBinomial distribution
"Bi" means "two" (like a bicycle has two wheels) ...
... so this is about things with two results.
Binomial distribution determines the probability of observing a specified number of successful outcomes in a specified number of trials.
The binomial distribution is used to obtain the probability of observing x successes in N trials, with the probability of success on a single trial denoted by p. The binomial distribution assumes that p is fixed for all trials.
We have a binomial experiment if ALL of the following four conditions are satisfied:
- The experiment consists of n identical trials.
- Each trial results in one of the two outcomes, called success and failure.
- The probability of success, denoted p, remains the same from trial to trial.
- The n trials are independent.
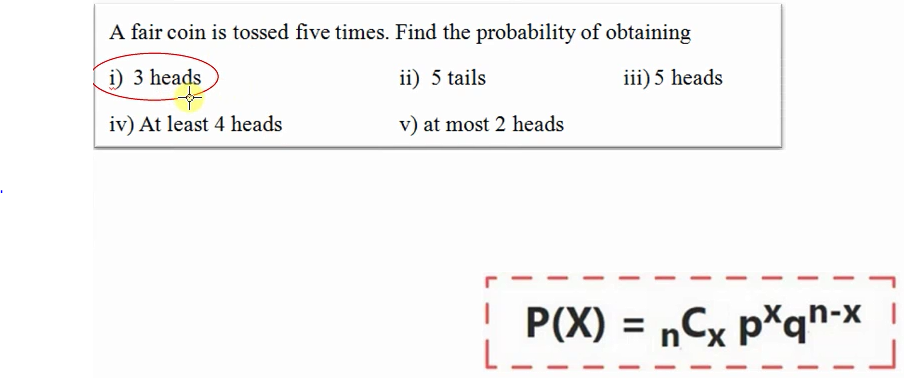




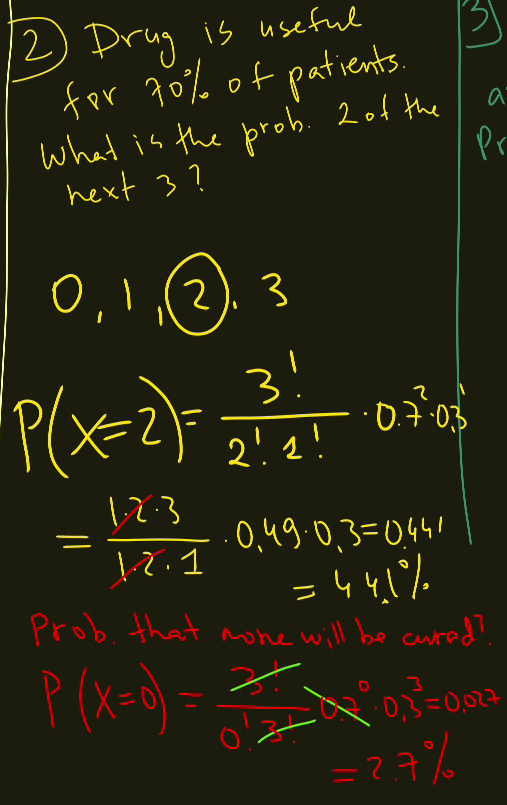
b) what is the probabilty that none of patients will be cured?
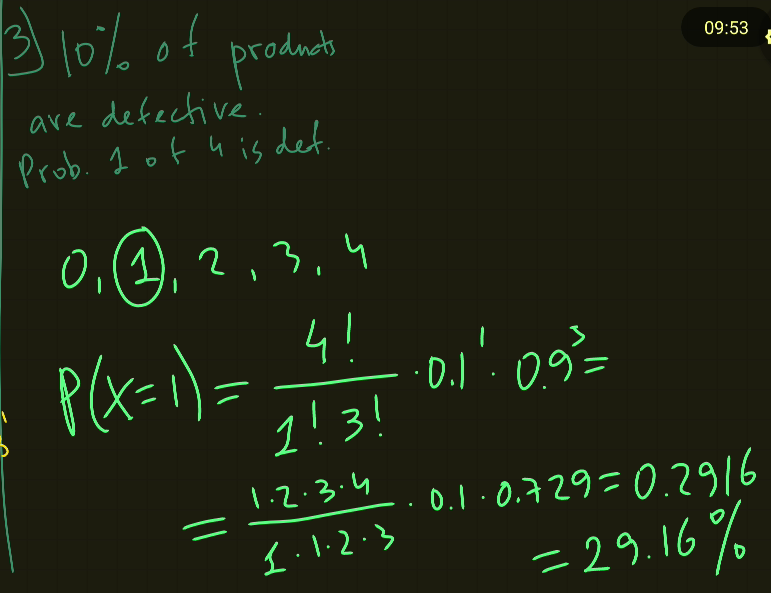

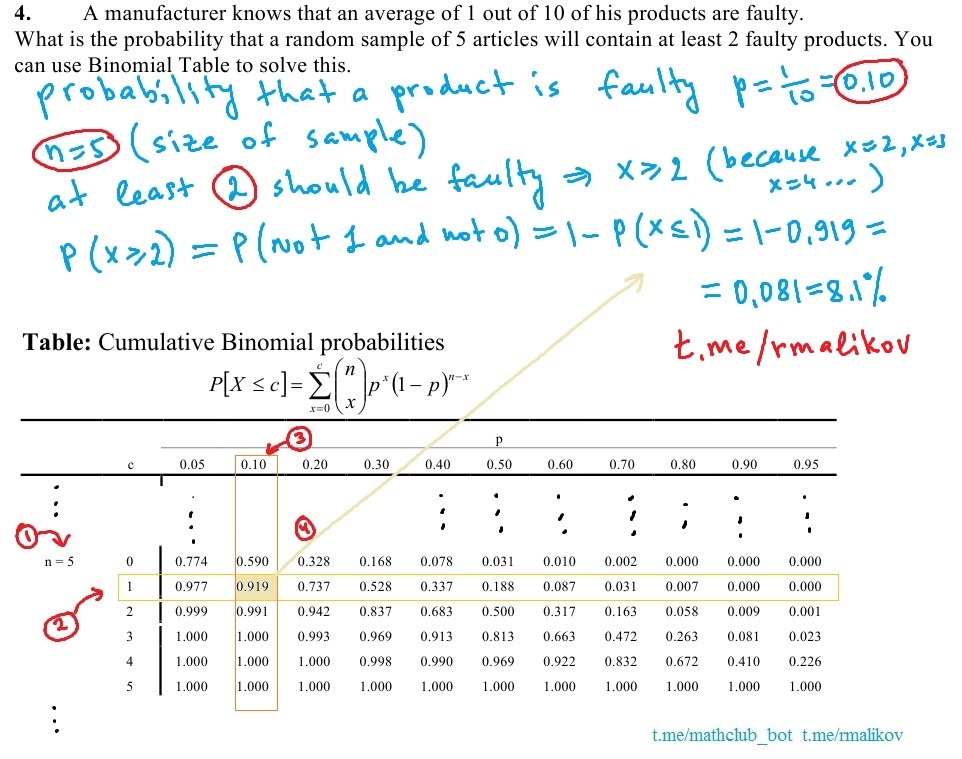

We hope that it was useful. If you have questions, you may contact Ravshan Malikov
Here you may find the notes for
Lesson 1 Notes
Lesson 2 Notes
Lesson 3 Notes
Lesson 4 Notes
Lesson 5 Notes
Lesson 6 Notes
Lesson 7 Notes
Lesson 8 Notes