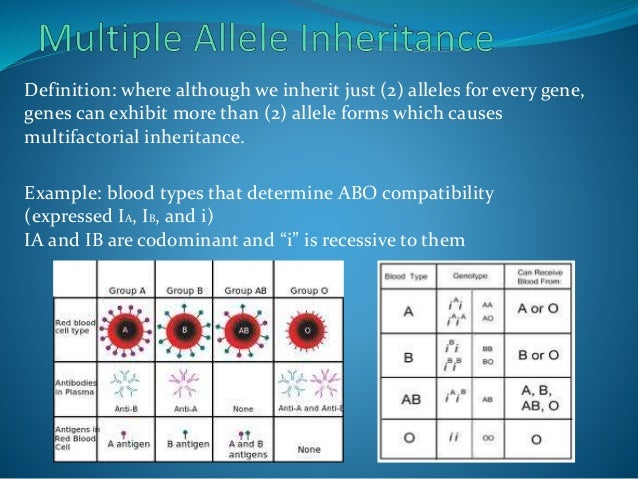
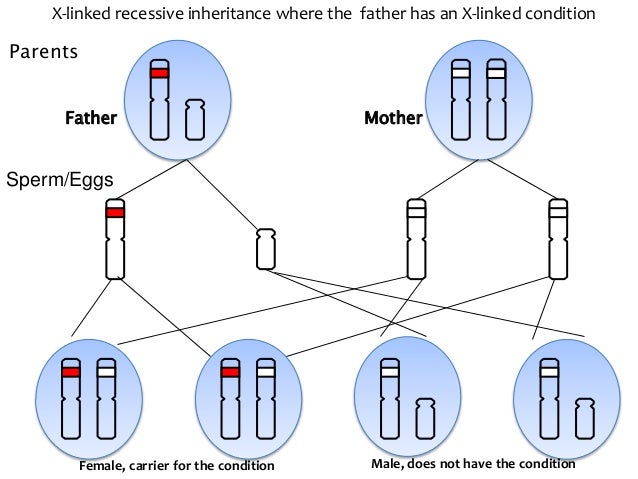
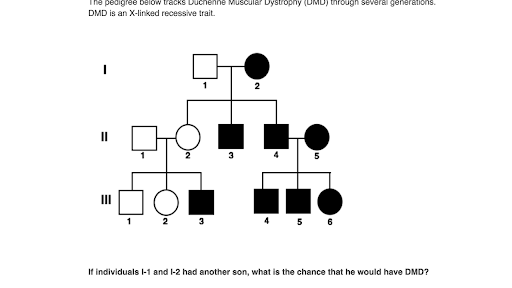
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Name

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Don't delay your care at Mayo Clinic
Our general interest e-newsletter keeps you up to date on a wide variety of health topics.
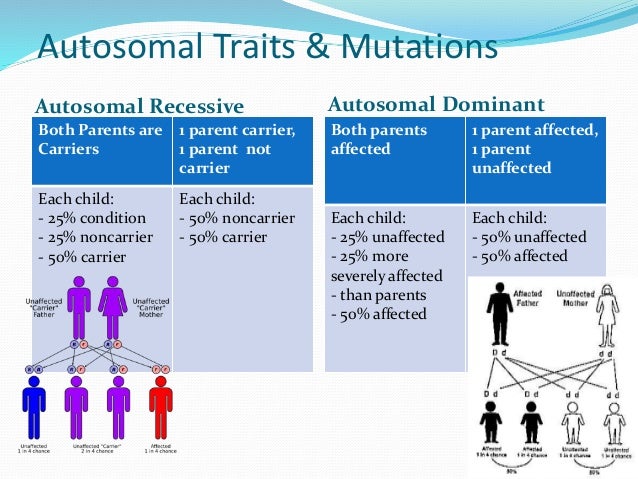
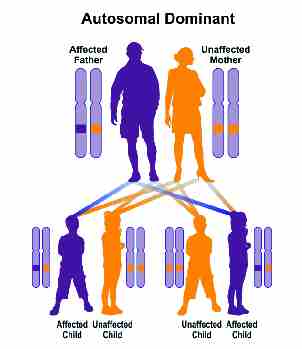
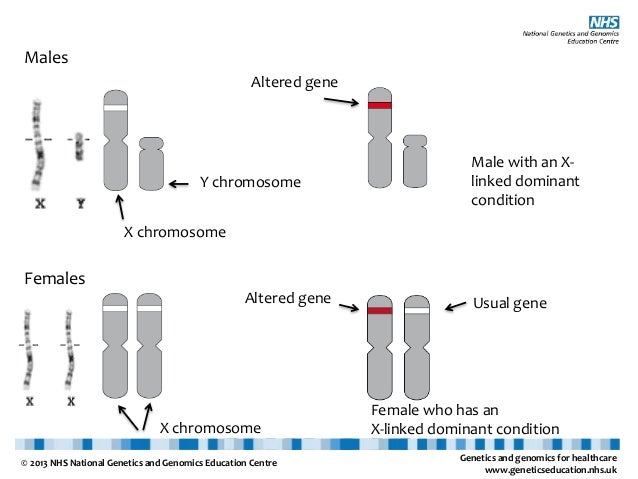
In an autosomal dominant disorder, the mutated gene is a dominant gene located on one of the nonsex chromosomes (autosomes). You need only one mutated gene to be affected by this type of disorder. A person with an autosomal dominant disorder — in this case, the father — has a 50% chance of having an affected child with one mutated gene (dominant gene) and a 50% chance of having an unaffected child with two normal genes (recessive genes).
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic.
Our general interest e-newsletter keeps you up to date on a wide variety of health topics.
Any use of this site constitutes your agreement to the Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy linked below.
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization and proceeds from Web advertising help support our mission. Mayo Clinic does not endorse any of the third party products and services advertised.
A single copy of these materials may be reprinted for noncommercial personal use only. "Mayo," "Mayo Clinic," "MayoClinic.org," "Mayo Clinic Healthy Living," and the triple-shield Mayo Clinic logo are trademarks of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
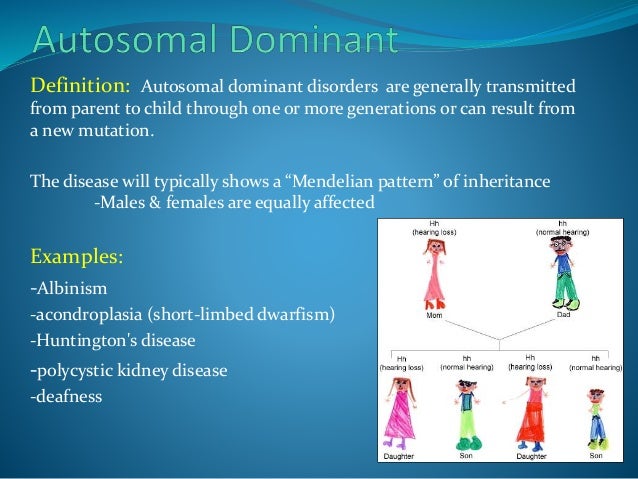
Autosomal dominant means one copy of the abnormal gene from only one parent or in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder or disease. In some cases, an affected person inherits the autosomal dominant condition from an affected parent. In others, the autosomal dominant condition may result from a new mutation in the gene and occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family. This is called a de novo mutation. Huntington’s disease, Marfan syndrome and neurofibromatosis type 1 are common examples of an autosomal dominant genetic disorders.
Autosomal refers to the fact that whatever gene is involved is found on one of the first 22 chromosomes (called the autosomes) and not on the X or Y chromosome (the sex chromosomes).
Dominant refers to the above explanation that you have two copies of each gene, one from mom and one from dad, and in order to have an autosomal dominant condition, a person only has to have one copy of the abnormal gene. They can inherit this copy from mom or dad, who may also have the condition.
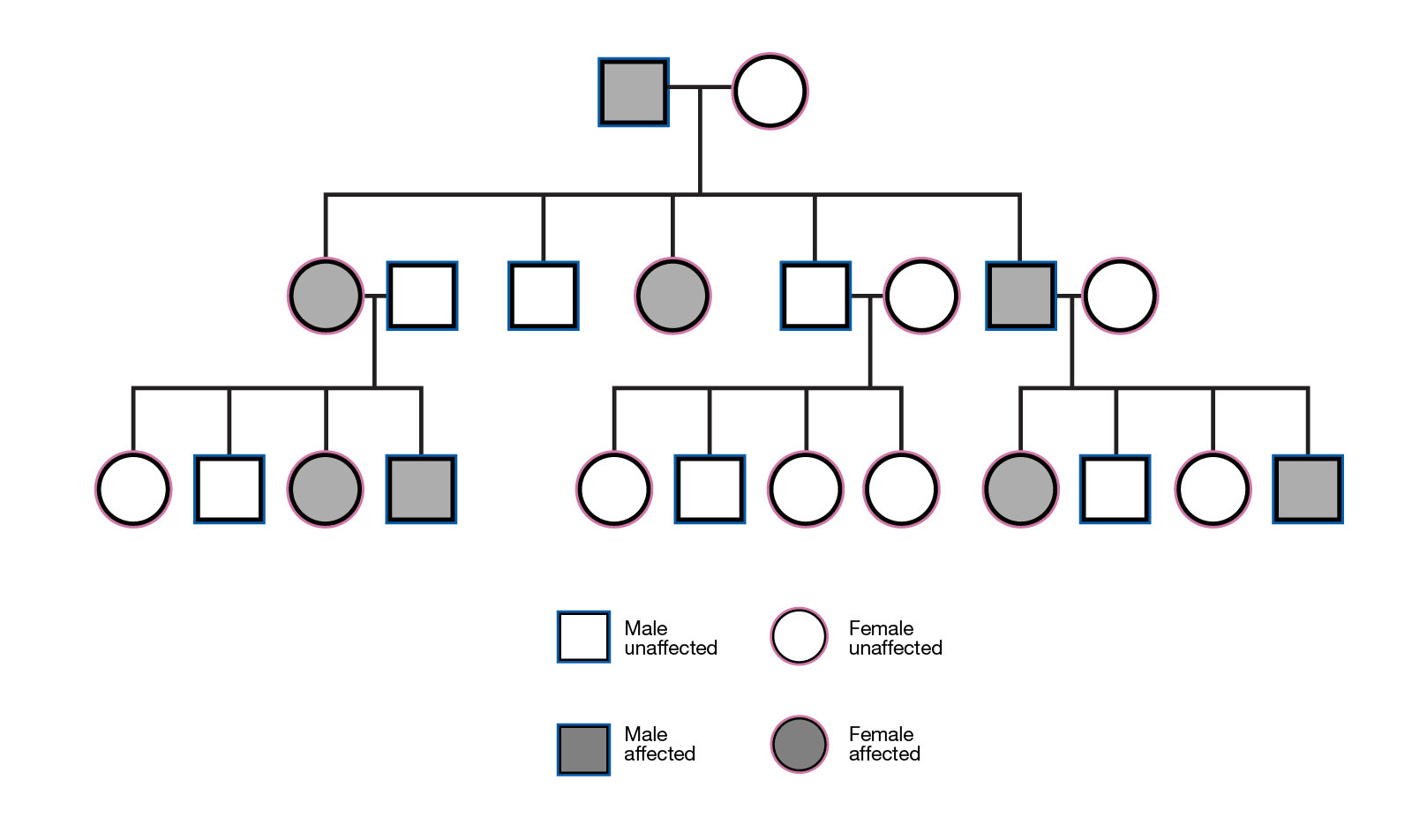
Often autosomal dominant conditions can be seen in multiple generations within the family. If one looks back through their family history they notice their mother, grandfather, aunt/uncle, etc., all had the same condition. In cases where the autosomal dominant condition does run in the family, the chance for an affected person to have a child with the same condition is 50% regardless of whether it is a boy or a girl. These possible outcomes occur randomly. The chance remains the same in every pregnancy and is the same for boys and girls.
There are cases of autosomal dominant gene changes, or mutations, where no one in the family has it before and it appears to be a new thing in the family. This is called a de novo mutation. For the individual with the condition, the chance of their children inheriting it will be 50%. However, other family members are generally not likely to be at increased risk.
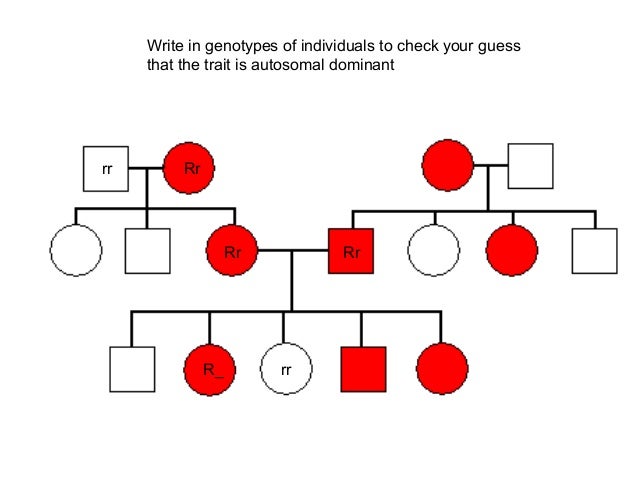
Figure 1 illustrates autosomal dominant inheritance. The example below shows what happens when dad has the condition, but the chances of having a child with the condition would be the same if mom had the condition.
Figure 1. Autosomal dominant inheritance
Some dominant genetic conditions can affect family members very differently. This is called variable expression. The condition does not actually miss out a generation, but some people have such mild symptoms of the condition that they appear to be unaffected. They may not even know that they have the condition.
In conditions which occur later in life (adult onset conditions e.g. inherited breast cancer and Huntington’s disease), people may have died earlier of unrelated causes leaving no time for the condition to appear, or the correct diagnosis may never have been given. However, the parents may have passed on the condition to their children.
Sometimes a child born with a dominant genetic condition can be the first person to be affected in the family. This may happen because a new gene change has occurred, for the first time, in either the egg or the sperm that went to make that child. When this happens, the parent of that child is not affected. The parents are very unlikely to have another child affected by the same condition, but you should always discuss the risks with your doctor. However, an affected child, who now has the changed gene, can pass it on to his or her children.
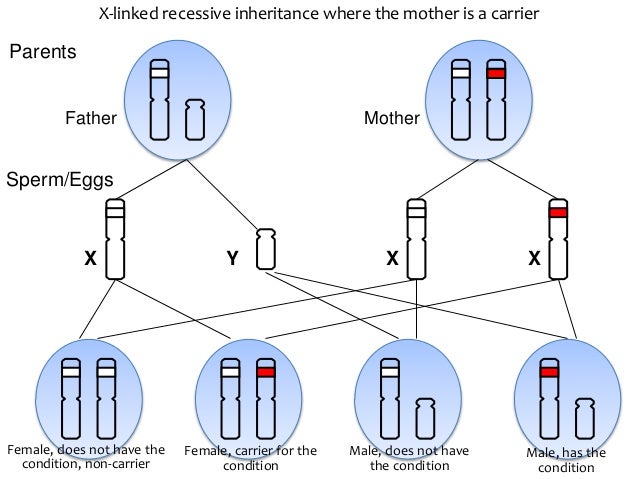
Autosomal recessive means two copies of the abnormal gene, one from each parent (one abnormal gene from mum and one abnormal gene from dad), is needed to cause the disorder or disease. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition. Autosomal recessive disorders are typically not seen in every generation of an affected family. Cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia are common examples of an autosomal recessive genetic disorders.
Cfnm18 Cfnm Orgy With A Anatomy Teacher
Bukkake Pornhub
Why Do Couples
Reluctant Dominant Wife
Looking Cute
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern - Mayo Clinic
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern & autosomal ...
List of Autosomal Dominant and Recessive Conditions or ...
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Aspx Name
Pseudodominance - Wikipedia
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance - an overview ...
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Page | ВКонтакте
Genetics Basics Lesson 3: Modes of Inheritance
In Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Asp Name