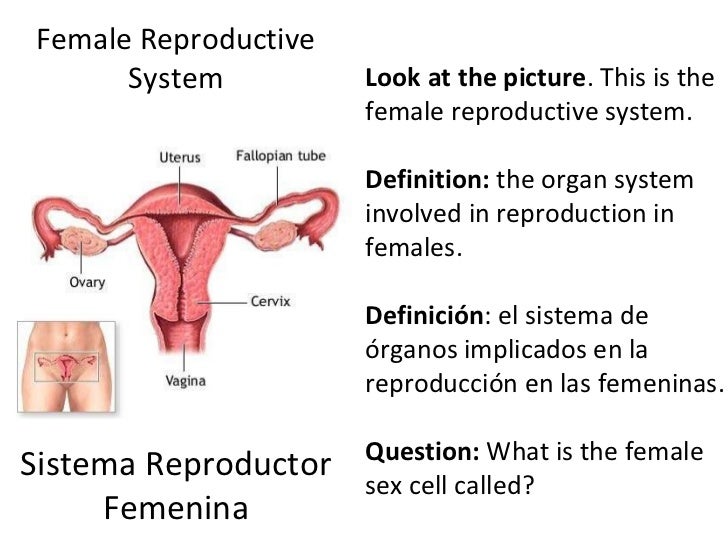
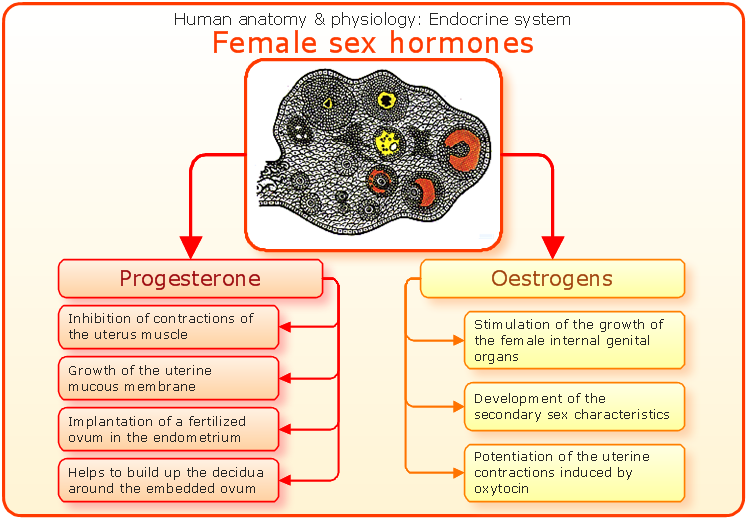
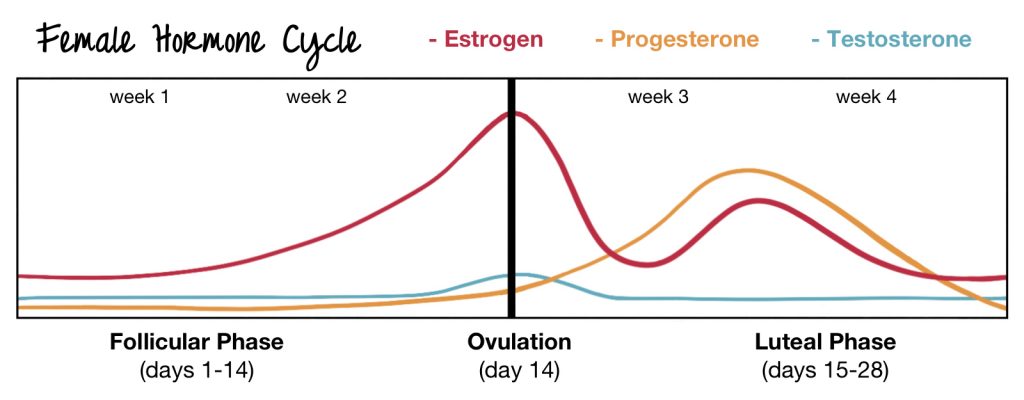
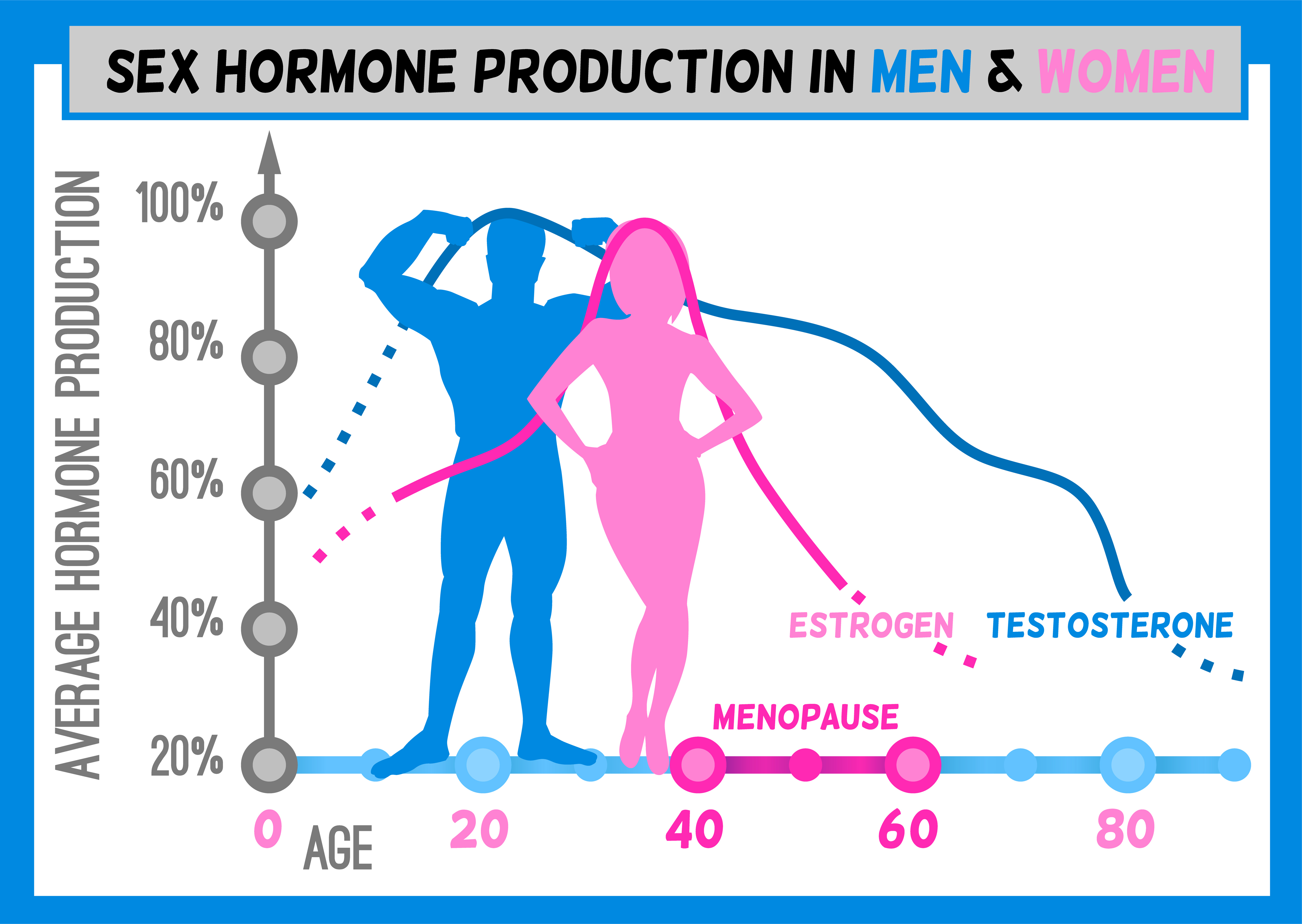
Female Sex Hormones Definition

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/female+sex+hormones
Thank you for using The Free Dictionary!
To stay free, we rely on revenue from ads. If you'd like to experience the site without ads, please consider supporting us by purchasing our premium ad-free subscription.
Word / Article
Starts with
Ends with
Text
English
Español
Deutsch
Français
Italiano
العربية
中文简体
Polski
Português
Nederlands
Norsk
Ελληνική
Русский
Türkçe
אנגלית
Sign up with one click:
Facebook
Twitter
Google
English
Español
Deutsch
Français
Italiano
العربية
中文简体
Polski
Português
Nederlands
Norsk
Ελληνική
Русский
Türkçe
אנגלית
Related to female sex hormones: progesterone
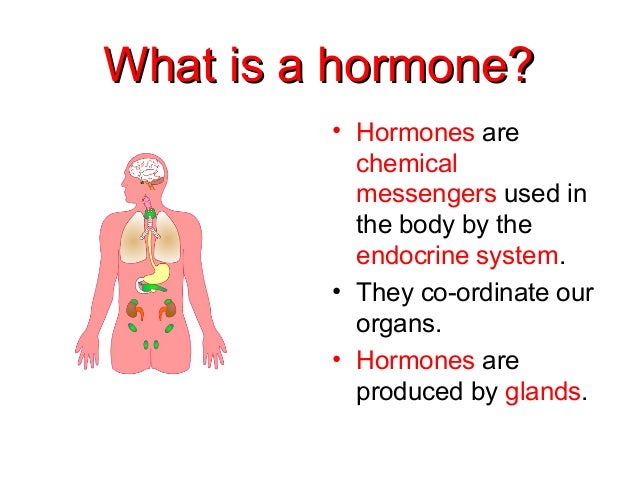
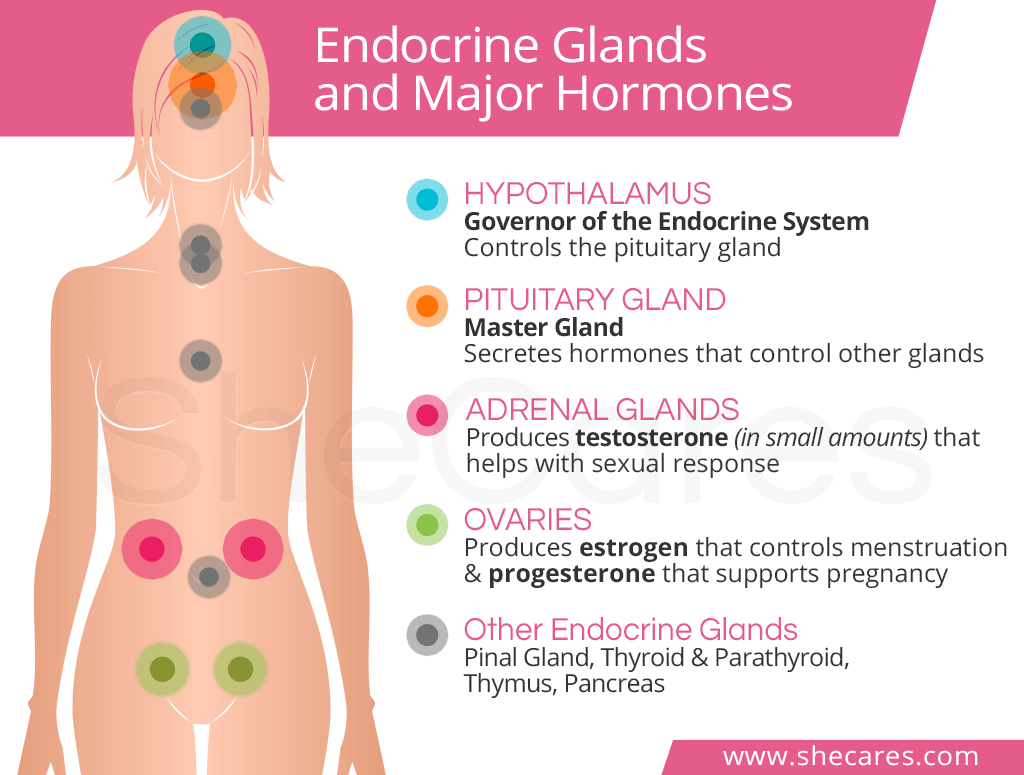
a chemical transmitter substance produced by cells of the body and transported by the bloodstream to the cells and organs on which it has a specific regulatory effect. adj., adj hormo´nal. Hormones act as chemical messengers to body organs, stimulating certain life processes and retarding others. Growth, reproduction, control of metabolic processes, sexual attributes, and even mental conditions and personality traits are dependent on hormones.
Hormones are produced by various organs and body tissues, but mainly by the endocrine glands, such as the pituitary, thyroid, and gonads (testes and ovaries). Each gland apparently synthesizes several kinds of hormones; the adrenal glands alone produce more than 25 varieties. The total number of hormones is still unknown, but each has its unique function and its own chemical formula. After a hormone is discharged by its parent gland into the capillaries or the lymph, it may travel a circuitous path through the bloodstream to exert influence on cells, tissues, and organs (target organs) far removed from its site of origin.
One of the best-known endocrine hormones is insulin, a protein manufactured by the beta cells of the islands of Langerhans in the pancreas that is important in carbohydrate metabolism. Other important hormones are thyroxine, an iodine-carrying amino acid produced by the thyroid gland; cortisone, a member of the steroid family from the adrenal glands; and the sex hormones, estrogen from the ovaries and androgen from the testes. Certain hormone substances can be synthesized in the laboratory for treatment of human disease. Animal hormones can also be used, as endocrine hormones are to some extent interchangeable among species. Extracts from the pancreas of cattle, for example, enabled diabetes sufferers to live normal lives even before the chemistry of insulin was fully understood.
Endocrine hormone synthesis and secretion is controlled and regulated by a closed-loop system. Negative feedback loops maintain optimal levels of each hormone in the body. If there are abnormally high levels of a hormone in the blood, feedback to the gland responsible for its production inhibits secretion. If there are abnormally low levels, the gland is stimulated to step up production and secretion. In this way a homeostatic balance is maintained. (See also endocrine glands.)
1. any of the corticosteroids secreted by the adrenal cortex, the major ones being the glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, and including some androgens, progesterone, and estrogens.
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) corticotropin.
adrenomedullary h's substances secreted by the adrenal medulla, including epinephrine and norepinephrine.
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) vasopressin.
corpus luteum hormone progesterone.
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) a neuropeptide secreted by the median eminence of the hypothalamus that binds to specific receptors on the corticotroph cells of the anterior pituitary and stimulates the secretion of corticotropin.
ectopic h's those secreted by tumors of nonendocrine tissues but having the same physiologic effects as their normally produced counterparts. It is not known exactly how the synthesis and secretion of endocrine hormones from nonendocrine tissues occurs. Most of these tumors are derived from tissues that have a common embryonic origin with endocrine tissues. When the cells undergo neoplastic transformation, they can revert to a more primitive stage of development and begin to synthesize hormones.
Ectopic hormones present serious problems for patients and add to the complexity of caring for those with certain kinds of neoplastic diseases. These hormones do not respond to the feedback mechanisms that regulate normal hormonal production; hence, surgery and destruction of the tumorous tissue by radiation and chemotherapy are the treatments of choice.
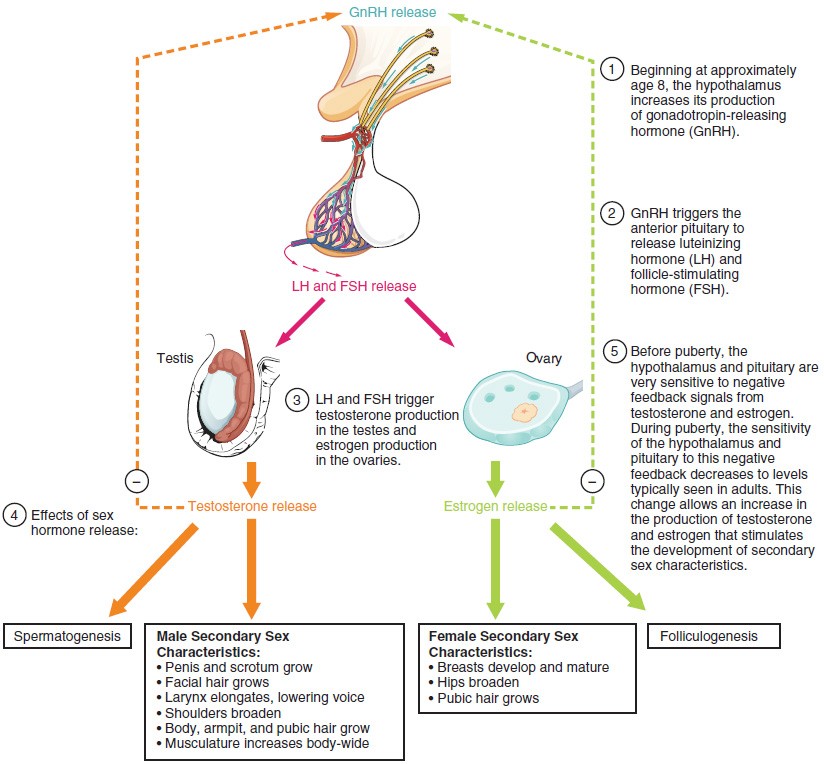
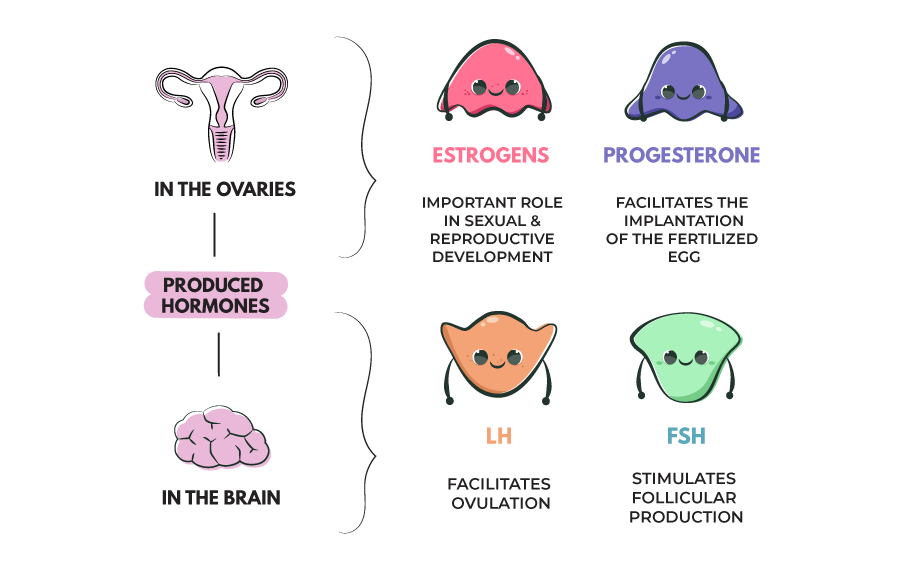
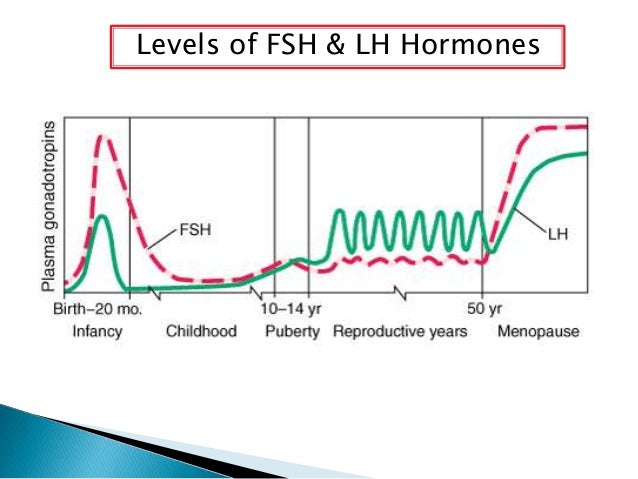
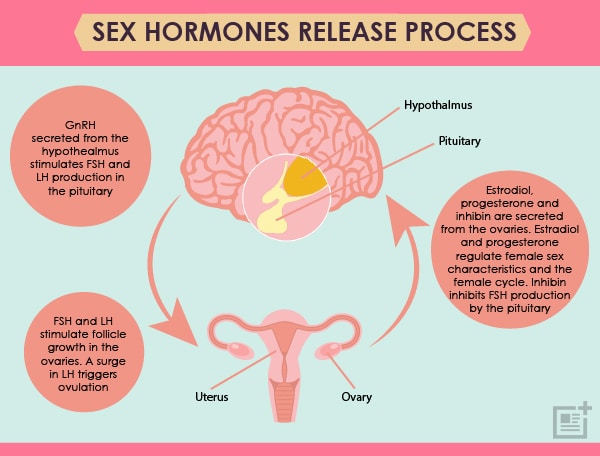
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) one of the gonadotropins of the anterior pituitary, which stimulates the growth and maturity of graafian follicles in the ovary, and stimulates spermatogenesis in the male.
follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone (FSH/LH-RH) luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone.
follicle-stimulating hormone–releasing hormone (FSH-RH) luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone.
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone.
growth hormone (GH) any of several related polypeptide hormones secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland that directly influence protein, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism and control the rate of skeletal and visceral growth; their secretion is in part controlled by the hypothalamus. It is used pharmaceutically as somatrem and somatropin. Called also somatotrophin, somatotropin, and somatotrophic or somatotropic hormone.
growth hormone release–inhibiting hormone somatostatin.
growth hormone–releasing hormone (GH-RH) a neuropeptide elaborated by the median eminence of the hypothalamus that binds to specific receptors on the somatotroph cells of the anterior pituitary and stimulates the secretion of growth hormone.
interstitial cell–stimulating hormone luteinizing hormone.
lactation hormone (lactogenic hormone) prolactin.
local hormone a substance with hormone like properties that acts at an anatomically restricted site; most are rapidly degraded. Called also autacoid and autocoid.
luteinizing hormone (LH) a gonadotropin of the anterior pituitary gland, acting with follicle-stimulating hormone to cause ovulation of mature follicles and secretion of estrogen by thecal and granulosa cells of the ovary; it is also concerned with corpus luteum formation. In the male, it stimulates development of the interstitial cells of the testes and their secretion of testosterone. Called also interstitial cell–stimulating hormone.
luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone (LH-RH) a decapeptide hormone of the hypothalamus, which stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland; it can be used in the differential diagnosis of hypothalamic, pituitary, and gonadal dysfunction. Called also follicle-stimulating hormone–releasing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) a substance from the anterior pituitary gland of certain other animals but not humans; it influences the formation or deposition of melanin in the body and pigmentation of the skin.
neurohypophyseal h's those stored and released by the neurohypophysis, i.e., oxytocin and vasopressin.
parathyroid hormone (PTH) a polypeptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that influences calcium and phosphorus metabolism and bone formation.
placental h's hormones secreted by the placenta, including chorionic gonadotropin, and other substances having estrogenic, progestational, or adrenocorticoid activity.
prolactin-inhibiting hormone a hormone released by the hypothalamus that inhibits the secretion of prolactin by the anterior pituitary gland.
prolactin-releasing hormone any of various hormones elaborated by the hypothalamus that stimulate the release of prolactin by the anterior pituitary gland. Most such activity is exerted by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, although in humans thyrotropin-releasing hormone can also have this action.
somatotrophic hormone (somatotropic hormone) growth hormone.
somatotropin release–inhibiting hormone somatostatin.
somatotropin-releasing hormone (SRH) growth hormone–releasing hormone.
steroid h's hormones that are biologically active steroids; they are secreted by the adrenal cortex, testis, ovary, and placenta and include the progestational agents, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. They act by binding to specific receptors to form complexes, which then enhance or inhibit the expression of specific genes.
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) thyrotropin.
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) a tripeptide hormone of the hypothalamus, which stimulates release of thyrotropin from the pituitary gland. In humans, it also acts as a prolactinreleasing factor. It is used in the diagnosis of mild hyperthyroidism and Graves disease, and in differentiating between primary, secondary, and tertiary hypothyroidism.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
A chemical substance, formed in one organ or part of the body and carried in the blood to another organ or part where they exert functional effects; depending on the specificity of their effects, hormones can alter the functional activity, and sometimes the structure, of just one organ or tissue or various numbers of them. Various hormones are formed by ductless glands, but molecules such as secretin, cholecystokinin/somatostatin, formed in the gastrointestinal tract, by definition are also hormones. The definition of hormone has been recently extended to chemical substances formed by cells and acting on neighboring cells (that is, paracrine function) or the same cells that produce them (that is, autocrine function). For hormones not listed below, see specific names.
[G. hormōn, pres. part. of hormaō, to rouse or set in motion]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
a. A substance, usually a peptide or steroid, produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another to effect physiological activity, such as growth or metabolism.
b. A synthetic compound that acts like a hormone in the body.
2. Any of various similar substances found in plants and insects that regulate development.
hor·mon′al (-mō′nəl), hor·mon′ic (-mŏn′ĭk) adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A chemical substance formed in a tissue or organ and carried in the blood; stimulates or inhibits the growth or function of one or more other tissues or organs.
[G. hormōn, pres. part. of hormaō, to rouse or set in motion]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Hormones are chemicals that are produced in an organ or gland and then are carried by the blood to another part of the body where they produce a special effect for which they were designed.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
A chemical substance, formed in one organ or part of the body and carried in the blood to another organ or part where it produces functional effects; depending on the specificity of their effects, hormones can alter the functional activity, and sometimes the structure, of just one organ or tissue or various numbers of them.
[G. hormōn, pres. part. of hormaō, to rouse or set in motion]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Q. does the growth hormone have side effects and what are they?
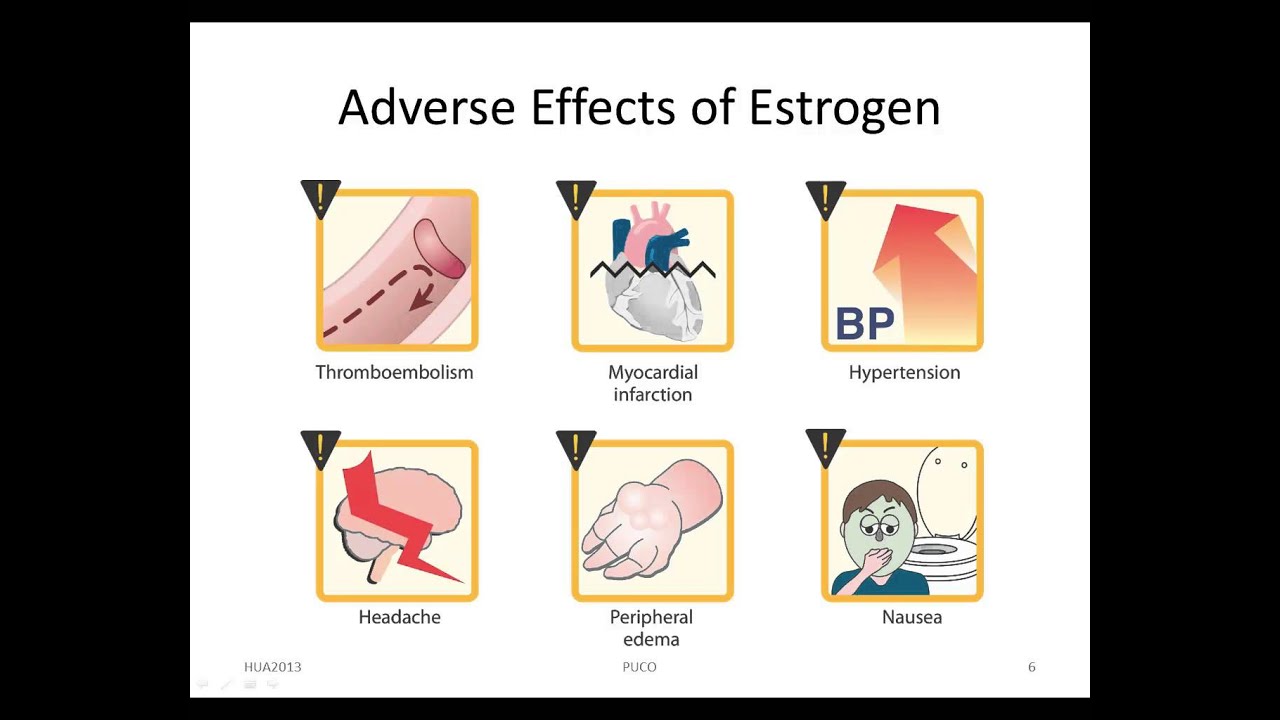
A. Yes, it does, and not a few. They include, among others, pain in the joints, carpal tunnel syndrome, diabetes, pain at the injection site, problems with the thyroid gland, ear problems and many others. You may read more about side effects of growth hormone treatment (called Mecasermin or Somatropin) here: http://www.drugs.com/ppa/mecasermin.html
Q. what is the effect of hormones during pregnancy on a woman's temper?
A. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can indeedn cause mood changes, starting from anxiety or agitations to developing major clinical symptoms of depression. Pregnancy affects each woman differently.
Q. What types of hormonal changes caused by fibromyalgia? Fibromyalgia affects hormones because I feel pain in my back bone. What types of hormonal changes caused by fibromyalgia?
A. Have you ever checked your back pain with a doctor? It may or may not be due to fibromyalgia. Low serotonin levels, low growth hormone levels, and low levels of neuropeptide Y, a component of the feel-good hormone neurotransmitter norepinephrine have been associated with fibromyalgia. Elevated levels of substance P acts as a neurotransmitter and signals the body to experience pain. These pains have also been observed in the spinal cord of fibromyalgia patients.
This content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
Please log in or register to use Flashcards and Bookmarks. You can also log in with
Facebook
Twitter
Google
References in periodicals archive ?
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional.
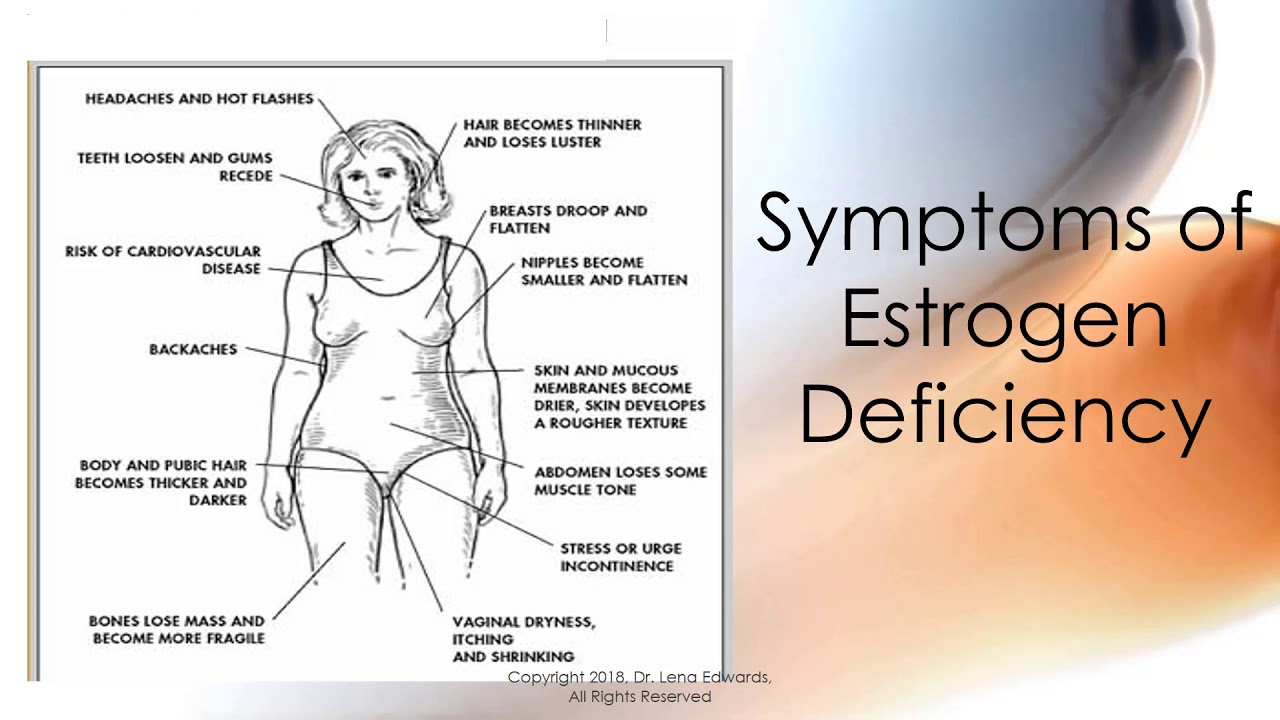
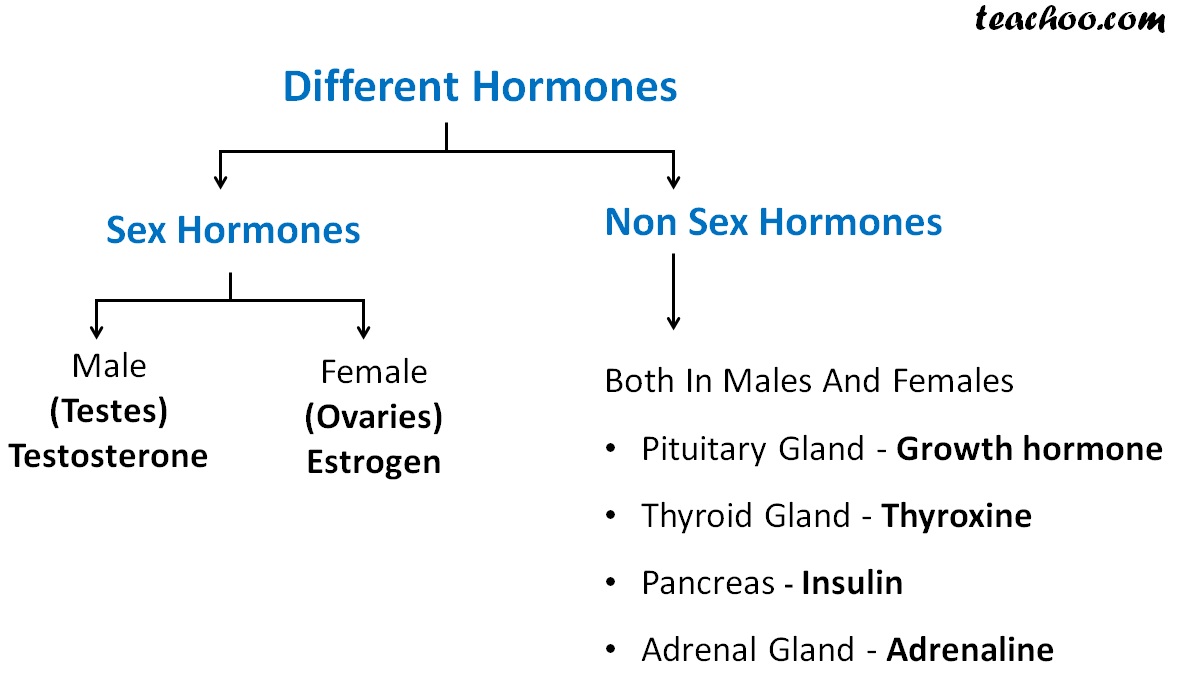
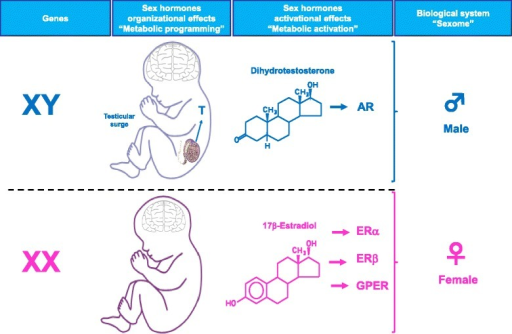
The two main female sex hormones are estrogen and progesterone. Although testosterone is considered a male hormone, females also produce and need a small amount of this, too. Estrogen is the major female hormone. The lion’s share comes from the ovaries, but small amounts are produced in the adrenal glands and fat cells.
www.healthline.com/health/female-sex-hor…
female hormone. noun. : a sex hormone (as an estrogen) primarily produced and functioning in the female.
www.merriam-webster.com/medical/female…
What happens to your sex hormones during pregnancy?
What happens to your sex hormones during pregnancy?
Considerable changes are seen in lymphoid organs during pregnancy, and increased serum 17β-estradiol levels during pregnancy correlate with lymphopenia and suppression of cellular immunity. The balance between male and female sex hormones (e.g., estradiol and testosterone) influences the degree of immune responsiveness.
www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscienc…
Where does the female sex hormone progesterone come from?
Where does the female sex hormone progesterone come from?
The ovaries produce the female sex hormone progesterone after ovulation. During pregnancy, the placenta also produces some. The role of progesterone is to: Progesterone levels can be determined by a blood test. Normal ranges are in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL): Small amounts of testosterone come from the adrenal glands and ovaries.
www.healthline.com/health/female-sex-hor…
Why are sex hormones important for skeletal growth?
Why are sex hormones important for skeletal growth?
Sex hormones are critical regulators of skeletal growth in males and females during periods of increasing and decreasing skeletal mass [115,116]. Sex steroids are important for the skeletal growth and maintenance of both the female and the male skeleton.
www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscienc…
https://www.thefreedictionary.com/female+sex+hormones
Перевести · Define female sex hormones. female sex hormones synonyms, female sex hormones pronunciation, female sex hormones translation, English dictionary definition of female sex hormones. n. 1. a. A substance, usually a peptide or steroid, produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another to effect physiological activity, such...
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/female+sex+hormones
Перевести · Washington, Feb 17 (ANI): Scientists have found that male and female sex hormones regulate expression of an important gene in neuronal cell culture through a mechanism that could explain not only higher levels of testosterone observed in some individuals with autism, but also why …
Male & Female Sex Glands (Gonads) | Testis & Ovary | Hormones & its Function | Explained in Hindi
Puberty and The Hormones Involved | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchool
YouTube › FuseSchool - Global Education
Monosex Culture in Aquaculture - Overview Through Hybridization and Hormonal Sex Reversal Technique
Pronunciation of Estrogen | Definition of Estrogen
MALE to FEMALE Transgender Surgery | Only For Medical & Education purposes
https://www.healthline.com/health/female-sex-hormones
Перевести · 21.05.2018 · The two main female sex hormones are estrogen and progesterone. Although testosterone is considered a male hormone, females also produce and use a small amount. Your levels will fluctuate over time.
https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/female+sex+hormones
Перевести · The ovaries primarily secrete estrogen estrogen. , any one of a group of hormones synthesized by the reproductive organs and adrenal glands in females and, in …
https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/female hormone
Перевести · Medical definition of female hormone: a sex hormone (as an estrogen) primarily produced and functioning in the female.
https://byjus.com/biology/female-hormones
Перевести · There are several hormones in females which are naturally produced and secreted by the glands of the endocrine system. The female hormones, estrogen, and progesterone are secreted for the influence on a woman’s reproductive health and are termed as female hormones.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_hormone
Biological target: Sex hormone receptors
Chemical class: Steroidal; Nonsteroidal
Synonyms: Sex steroid; Gonadal steroid
Use: Various
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanisms through membrane-associated receptors and signaling cascades. The polypeptide hormones luteinizing h…
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanism
Child Sex Trafficking
Interracial Sex Retro
1 800 Phone Sex Line 3
Sex Molodoy Porn
Sex Na Dengi
Female sex hormones - definition of female sex hormones by ...
Female sex hormones | definition of female sex hormones by ...
Female sex hormones | Article about female sex hormones by ...
Female Hormone Medical Definition | Merriam-Webster ...
Sex hormone - Wikipedia
(PDF) FEMALE SEX HORMONES - ResearchGate
Female Sex Hormones Definition