Zero-1-to-3: Zero-shot One Image to 3D Object
https://t.me/reading_ai, @AfeliaN🗂️ Project Page
📄 Paper
📎 GitHub
🗓 Date: 20 Mar 2023
Main idea

- Motivation: If you are able to generate view-consistent images from different view points, based on initial input → you may use these images in NeRF for novel view synthesis.
- Solution: a framework for changing the camera viewpoint of an object given just a single RGB image based on diffusion model, that is conditioned on viewpoint.
Pipeline
If we have a single RGB image of an object→ our goal is to synthesize an image of the object based on a relative camera rotation and translation of the desired viewpoint.

View-Conditioned Diffusion
The main approach of this paper is to take a pre-trained diffusion model and fine-tune it to learn controls over the camera parameters without destroying the rest of the representation.
The authors use a hybrid conditioning mechanism:
- a CLIP embedding of the input image is concatenated with camera rotation and translation to form a “posedCLIP” embedding → cross-attention is applied
- the input image is channel-concatenated with the image being denoised
3D Reconstruction
As the next step the authors take the open-sourced framework, Score Jacobian Chaining (SJC) , to optimize a 3D representation with priors from text-to-image diffusion models.

The main pipeline here is the following (seems to be very similar to DreamFusion):
- sample viewpoints to perform volumetric rendering
- perturb the resulting images with Gaussian noise and denoise it conditioned on the input image and CLIP embedding
- In addition, the authors optimize the input view with an MSE loss.
Regularization
- depth smoothness loss
- near-view consistency loss
Implementation details
Dataset: Objaverse
Compared with:
Metrics:
- novel view synthesis: PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, FID
- 3D reconstruction: CD, IoU
Results
Novel-view synthesis comparison


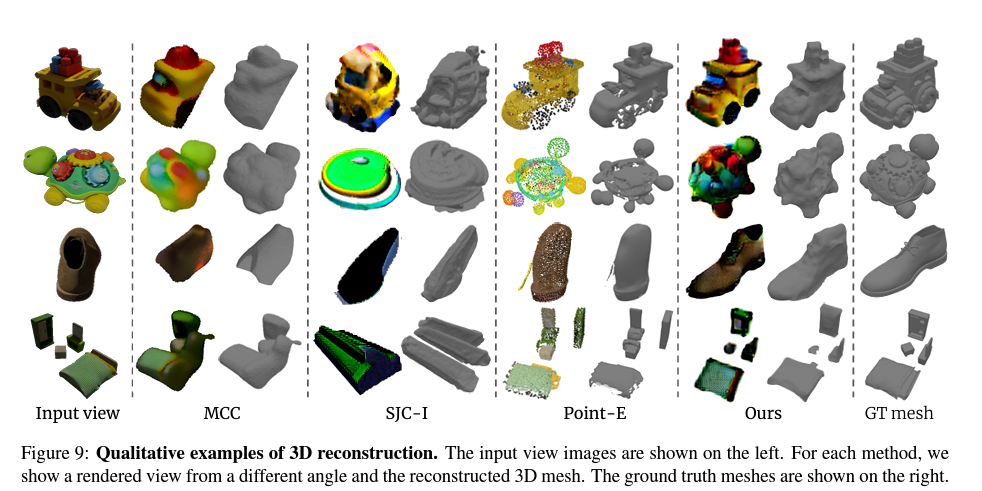
3D reconstruction comparison
Metrics Novel view synthesis


Metrics 3D reconstruction


Additional results
