Why Leading Chemical Manufacturers Prefer Sodium Sulfate for Industrial Processes
The Science Behind Sodium Sulfate: Properties, Applications, and Market Trends
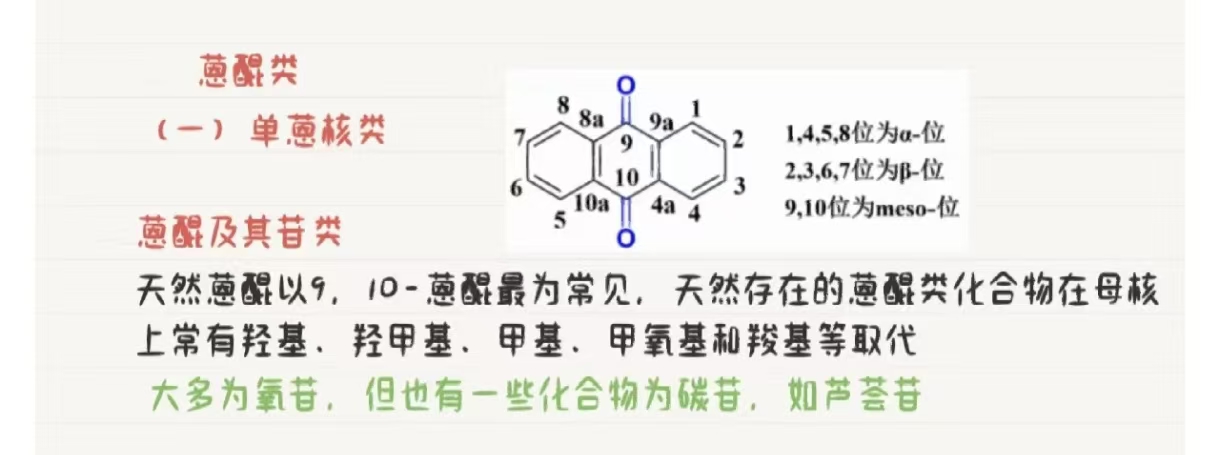
You'll find sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄) exists as both anhydrous powder and hydrated crystals, with Na⁺ cations and SO₄²⁻ anions forming a stable ionic lattice. Its density ranges from 2. Sodium sulfate supplier.664 g/cm³ (anhydrous) to 1.46 g/cm³ (decahydrate), while dehydration occurs at 32°C. high-quality sodium sulfate products. The compound's exceptional stability and solubility properties drive its essential role in detergents, glass production, and textiles. Current market trends show 3.9-4.6% CAGR through 2030, with Asia Pacific dominating 40% market share. Understanding these fundamentals reveals deeper understandings into industrial applications
Key Takeaways
- Sodium sulfate exists in anhydrous and hydrated forms, with distinctive crystalline structures and density variations affecting its industrial applications.
- The compound features Na⁺ cations and SO₄²⁻ anions in an ionic lattice, stabilized by hydrogen bonding networks.
- Major industrial applications include glass manufacturing, detergent production, and textile processing, with Asia Pacific leading market demand.
- Commercial production primarily utilizes the Mannheim process and mirabilite dehydration, with manufacturing costs ranging from $30-130 per tonne.
- Global market growth shows 3.9-4.6% CAGR through 2030, driven by construction sector expansion and increased industrial applications.
Chemical Structure and Bonding Properties
While sodium sulfate exists in both anhydrous and hydrated forms, its fundamental structure consists of Na⁺ cations electrostatically bound to SO₄²⁻ anions in an ionic lattice. In its decahydrate form, you'll find [Na(OH2)6]⁺ ions arranged in octahedral geometry with Na-O distances measuring approximately 240 pm. These ionic interactions are further stabilized through extensive hydrogen bonding networks.
The sulfate bonding characteristics demonstrate exceptional stability, as the compound remains unreactive toward most oxidizing and reducing agents under normal conditions. bulk chemical purchases. You'll observe that the crystal structure features coordinated water molecules in the hydrated form, creating a complex network of hydrogen bonds that influence the compound's physical properties and thermal behavior. This arrangement contributes to its notable residual entropy due to rapid water distribution throughout the structure

purchase sodium sulfate online
Physical States and Transformation
Building upon the ionic structure, sodium sulfate manifests in distinct physical forms that directly impact its industrial applications. You'll find that hydration effects dramatically influence phase stability, with the compound existing as either anhydrous powder or hydrated crystals. The anhydrous form's hygroscopic nature requires careful handling to prevent unwanted moisture absorption.
Key alterations you must monitor include: (sodium sulfate online)
- Dehydration at 32°C, converting decahydrate to anhydrous form
- Phase changes between crystalline structures (orthorhombic to monoclinic)
- Density variations from 2.664 g/cm³ (anhydrous) to 1.46 g/cm³ (decahydrate)
When processing sodium sulfate, maintain storage temperatures between 5°C and 30°C to maintain stability. The compound's solubility in water, coupled with its insolubility in ethanol, enables effective purification processes while maintaining safety standards.

high-quality sodium sulfate products
Manufacturing and Industrial Uses
Sodium sulfate's commercial production employs multiple pathways, including the mirabilite dehydration process and the Mannheim process, which generates it as a by-product of hydrochloric acid manufacturing. You'll find the manufacturing costs vary considerably between $30-130 per tonne, depending on whether it's produced as a primary product or recovered as a by-product from other chemical processes. In the Kraft process, sodium sulfate serves as an essential component where it's converted to sodium sulfide, enabling the breakdown of wood chips into pulp for paper production.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The manufacturing of sodium sulfate encompasses two primary pathways: extraction from natural crystalline brines and chemical synthesis through industrial processes. You'll find significant production from natural brines occurring in Texas and California, where evaporation techniques concentrate the solution above saturation limits for efficient crystallization.
Key production steps include: (sodium sulfate available now)
- Pretreatment of raw materials through washing or recrystallization
- Implementation of Mannheim or Hargreaves methods involving sodium chloride reactions
- Application of multistage countercurrent salting-out for enhanced purity
You'll need to maintain strict control over crystallization conditions to achieve ideal yield and product quality. The process requires careful monitoring of evaporation systems, where technologies like KLAREN help prevent fouling issues. This systematic approach guarantees consistent production while adhering to safety protocols and environmental standards.
Applications In Kraft Process
Playing an essential role in the kraft process, sodium sulfate functions as a make-up chemical that replenishes lost sodium and sulfur compounds during pulp production. You'll find that it's critical for maintaining chemical balance, with reduction efficiency rates of 90-94% when converting to sodium sulfide. This high efficiency directly contributes to kraft process efficiency and superior pulp strength.
The sodium sulfate benefits extend beyond basic chemical recovery. You'll achieve enhanced sustainability through minimized waste generation and reduced greenhouse emissions. In your operations, you can expect improved economic efficiency due to the continuous chemical cycles - Yuhan Chem products. The process optimization leads to stronger paper quality while maintaining environmental compliance, making it an indispensable component in modern kraft pulping operations
Natural Deposits and Mining Operations
Natural deposits of sodium sulfate occur primarily in arid regions where evaporative processes concentrate minerals in playas and saline lakes. You'll find these deposits chiefly in closed basins where surface and groundwater evaporation leads to mineral precipitation, forming mirabilite and thenardite. Global reserves total approximately 3.3 billion tons, with major mining operations extracting this precious resource through specialized techniques.
Key extraction processes include:
- Brine cooling precipitation utilizing refrigeration systems
- Mechanical vapor recompression for anhydrous conversion

affordable sodium sulfate for sale
- Chemical precipitation using sodium chloride additives
The most significant sodium sulfate deposits are located within 30 feet of the surface, making them highly accessible for mining operations. Current production averages 2.6 million tons annually, with facilities achieving product purity levels exceeding 99.5% through careful processing methods.
Global Market Dynamics and Industry Impact
You'll find that sodium sulfate's global supply chain interactions are heavily influenced by Asia Pacific's 40%+ market dominance, particularly China's substantial mirabilite reserves and cost-effective production capabilities - sodium sulfate specifications. Regional price fluctuations stem from varying manufacturing costs, transportation logistics, and regulatory structures across key markets including North America and Europe. The manufacturing sector's demand patterns reflect a 3.9-4.6% CAGR through 2030, driven primarily by detergent, textile, and glass industries' consumption rates
Regional Supply Chains
While mainland China dominates global sodium sulfate production through its vast mirabilite reserves, the market's supply chains exhibit distinct regional patterns that shape international trade flows. Supply chain management strategies vary considerably across regions, with regional trade interactions influenced by production capacities and local demand.
You'll find these critical supply chain patterns: wholesale chemical distribution.
- Asia Pacific: China exports 50% of production within Asia, leveraging low production costs
- North America: U.S. and Canadian supply chains rely on both natural deposits and by-product processing
- Europe: Regional networks focus on import optimization due to weakened domestic demand
The HS Code 283319 standardizes international tracking of sodium sulfate shipments, ensuring proper handling and regulatory compliance across borders. This systematic approach enables efficient monitoring of global supply chain movements and trade patterns.
Price Fluctuation Factors

sodium sulfate
Market prices for sodium sulfate fluctuate based on five interconnected variables: downstream demand, raw material costs, global market trends, geopolitical factors, and economic conditions. You'll need to analyze price elasticity across multiple sectors, including detergents, textiles, and water treatment, where demand forecasting indicates a 5.00% CAGR through 2031.
Raw material volatility, particularly in sulfur and sulfuric acid markets, directly impacts production costs. You must factor in how supply chain disruptions, including typhoon-related events and Red Sea routing changes, affect transportation expenses. Energy costs, especially natural gas pricing, create additional market pressure. When monitoring market fluctuations, consider how interest rate adjustments influence consumer spending patterns and industrial output, as these elements considerably affect sodium sulfate's price stability.
Manufacturing Sector Demands
Three dominant manufacturing sectors drive global sodium sulfate demand: detergents, glass production, and textiles. The market segmentation reflects a complex supply chain where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are paramount. You'll find sodium sulfate's versatility demonstrated across these key industrial applications:
sodium sulfate applications
- Glass Manufacturing: Reduces melting time by 15%, optimizing production efficiency and energy consumption
- Detergent Production: Functions as a vital filler agent, controlling active material concentrations while improving powder flowability
- Textile Processing: Serves as an essential auxiliary chemical in dyeing operations
The Asia Pacific region leads market growth, with China's exports doubling to meet rising demand. The compound's market path shows a projected CAGR of 4.6-9.7% through 2030, driven by construction sector expansion and increased industrial applications.
Environmental Considerations and Recycling Challenges
Despite its widespread industrial use, sodium sulfate presents significant environmental and recycling challenges that require careful evaluation in waste management protocols. You'll find that while naturally occurring at 2,700 ppm in seawater, concentrated discharges can severely disrupt aquatic ecosystems - sodium sulfate chemical formula, as evidenced by the Talvivaara mining incident. Implementing sustainability strategies is essential, as current disposal methods often lead to soil and groundwater contamination
sodium sulfate purchase
The lithium-ion battery recycling sector particularly struggles with sodium sulfate byproducts. Traditional hydrometallurgical processes generate substantial waste, prompting the development of pollution prevention technologies like AquaRefining (Buy sodium sulfate). You'll need to take into account that while industrial applications exist in detergents and textiles, market demand cannot absorb the increasing supply, necessitating innovative zero-waste solutions and improved recycling technologies
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Sodium Sulfate Be Safely Used in Home Food Preservation?
You shouldn't use sodium sulfate for home food preservation methods, as it lacks established food safety protocols for domestic use and requires precise industrial-grade controls for proper application.
Does Sodium Sulfate Interact With Common Prescription Medications?
Like a domino effect, sodium sulfate interactions can considerably impact your prescription medications. order sodium sulfate in bulk. You'll need careful monitoring, as it interacts with 480+ drugs, affecting absorption and electrolyte balance
What Alternatives Exist for Industries Looking to Replace Sodium Sulfate?
You'll find viable sodium alternatives like zeolites, polycarboxylates, and potassium sulfate as industry substitutes. Buy sodium sulfate. MgSO4 and chelating agents offer process-specific replacements, while sulfate-free technologies enable complete elimination
How Long Can Sodium Sulfate Be Stored Before Degrading?
You'll find sodium sulfate maintains indefinite stability under proper storage conditions, but degradation factors like moisture exposure and high temperatures can compromise its integrity - affordable sodium sulfate for sale. Monitor environmental controls for ideal preservation
Can Sodium Sulfate Improve Soil Quality for Agricultural Purposes?
sodium sulfate
You shouldn't use sodium sulfate as a soil amendment because it'll dramatically increase soil salinity, severely inhibit plant growth, and negatively impact soil structure - Buy sodium sulfate. Consider gypsum instead for better results
Conclusion
You'll find sodium sulfate's projected market value of $2.4 billion by 2027 reflects its critical role in industrial processes. The compound's polymorphic changes between anhydrous and decahydrate forms at 32.4°C continue driving innovations in thermal energy storage. As manufacturing demands rise, you're witnessing increased focus on recovery efficiency from Kraft paper processing, where Na2SO4 extraction rates now exceed 85% in modern facilities.