What is L2 and why it's one of the most important narratives in crypto?
Blockchain Life Forum
Blockchain technology faces a problem known as the “scalability trilemma”. It involves the challenge of creating a network that is simultaneously fast, decentralized, and secure. Therefore, developers often have to choose and optimize two out of the three components.
The architecture of early blockchains, particularly Bitcoin and Ethereum, was not designed for a large number of transactions and users, resulting in low throughput.
For example, Bitcoin processes 5-7 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum handles around 15 TPS.
Scalability can be improved by modifying the blockchain protocol's code using functions such as sharding. However, this process takes a significant amount of time and can stretch over years, as was the case with Ethereum. Furthermore, such improvements alter the fundamental architecture, which may not always receive unanimous support from the project's community.
L2 solutions allow for at least a partial resolution of the low throughput and high transaction fees issue without affecting the code of the main blockchain. Their main advantage lies in the ability to transfer assets between “layer-one” addresses using a “layer-two” solution, which can be either a separate off-chain protocol or a separate blockchain.
L2 for Bitcoin

The main L2 project for Bitcoin is the Lightning Network (LN). It operates on a protocol that utilizes smart contracts and so-called state channels. The Lightning Network was launched back in 2015 and has been actively developing ever since. By the end of May 2022, the total capacity of LN channels reached 3900 BTC.
The primary function of LN is to enable Bitcoin holders to make direct exchanges without recording the information on the blockchain. To do this, one needs to open a specialized channel through an on-chain transaction and deposit bitcoins into it.
Once the payment channel is activated, it allows for off-chain transfers, meaning outside the main network, with much higher speed and lower fees. Unlike on-chain transactions, operations within the Lightning Network channels are only visible to their users. The main blockchain records only the initial and final states of the transactions.
This approach significantly reduces the burden on the Bitcoin main network. The Lightning Network can process thousands of transactions per second while maintaining a high level of system security.
Lightning Network's security
The channel is verified by its participants and their mutual smart contracts. Upon completion of the off-chain exchange, the final state is recorded in a new block on the main network. Smart contracts safeguard transactions within state channels and act as “judges” in the participants' interactions.
Some channels employ a timer that automatically updates or locks the on-chain transaction state. Once the specified period expires, the system automatically initiates a closing transaction, updates the main blockchain, and closes the state channel based on the last verified transaction. Any new attempt to unlock the state channel results in the creation of new encryption and restarts the timer.
L2 solutions for Ethereum
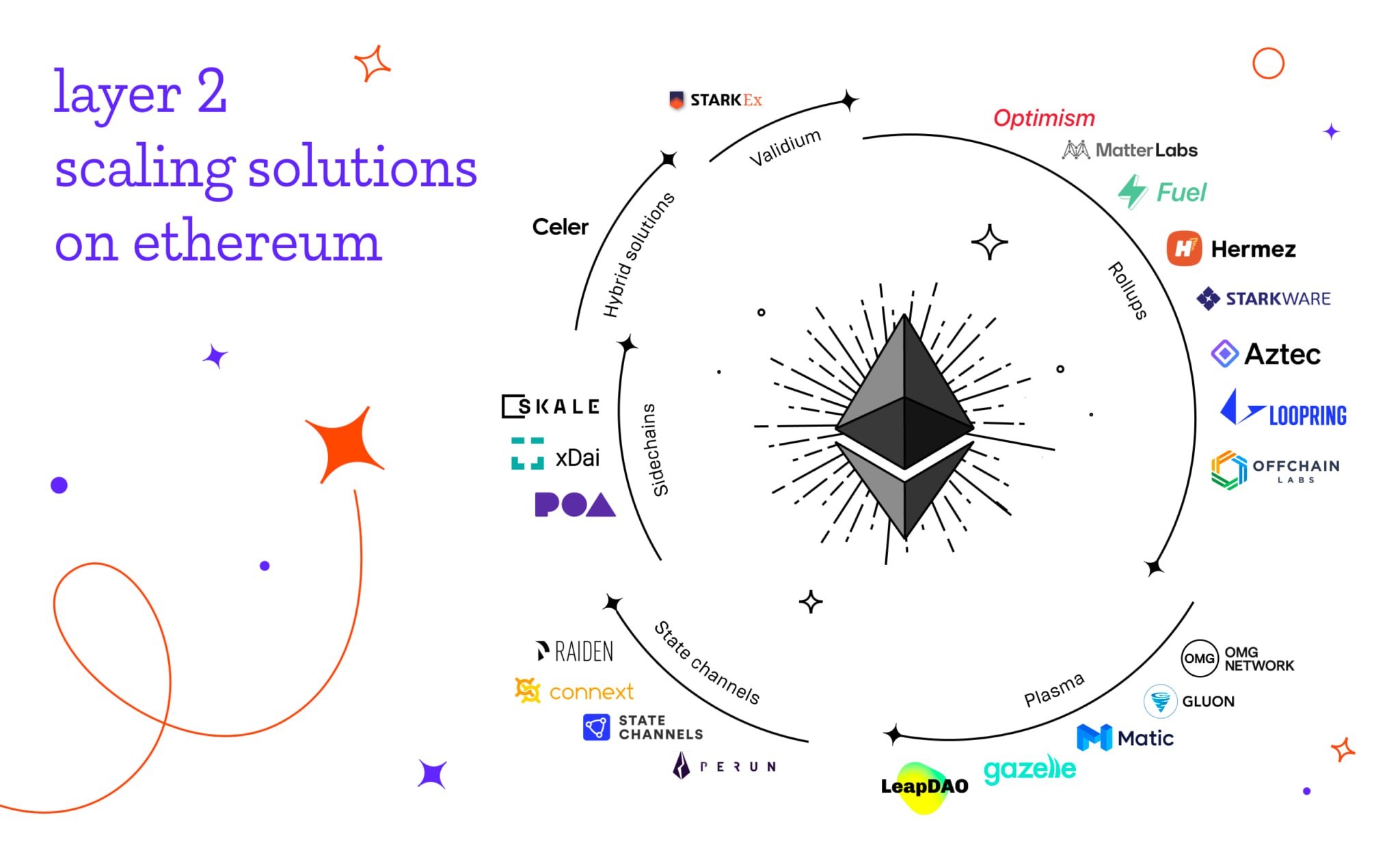
Despite its relatively low speed, Ethereum is the most heavily utilized blockchain platform for decentralized applications. Many popular projects in the decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible token (NFT) sectors operate on Ethereum. Therefore, scalability is a particularly pressing issue for Ethereum.
Currently, several major L2 solutions are being developed in parallel:
- Polygon (MATIC)
- Arbitrum
- Optimism
The primary technology used for their operation is Rollups, which have two main variants:
Optimistic Rollups: With this solution, transactions are conducted in the L2 network and then consolidated into compact blocks by validators, which are included in the Ethereum main network. Optimistic Rollups are used in Arbitrum and Optimism.
ZK-Rollups: Transactions in the second-layer network are also bundled and sent to the Ethereum network. However, their validation occurs through specialized verifiers, which provide cryptographic proof of the validity of operations. Polygon is implemented based on ZK-Rollups. This technology is considered the primary scaling solution for Ethereum by its co-founder, Vitalik Buterin.
Regardless of the specific L2 solution, Ethereum, as the “layer one”, retains the functions of transaction verification, block production, the ledger where final states are recorded, and the consensus mechanism. Therefore, the project does not need to create its own infrastructure.
There are other Layer 2 projects as well. For example, in July 2022, startup Matter Labs announced the launch of zkSync 2.0. A month later, the StarkWare project launched its own protocol, written in the Cairo language.
So what are sidechains?
Sidechains used in platforms like Cosmos or Polkadot are not considered second-layer solutions. While they may have their own security mechanisms, they rely on the “parent” blockchain for security.
Sidechains are separate blockchains that run in parallel to the main blockchain, allowing for the execution of specific use cases or applications. They have their own consensus mechanisms and often offer different features or optimizations compared to the main blockchain. However, they are not directly integrated as a L2 on top of the parent blockchain.
L2 is emerging as one of the hottest topics in crypto right now, and Blockchain Life 2023 is proud to be at the forefront of this exciting trend. With a range of sessions and like-minded enthusiasts, immersed in this topic, we're giving attendees the chance to dive deep into the ins and outs of L2 and explore its vast potential.
Whether you're an experienced trader or just getting started in the world of crypto, the Forum is sure to provide valuable knowledge about this critical technology.
Buy a ticket: https://blockchain-life.com/asia/en/#tickets-row