What Does Natural Remedies for Treating Skin Pigmentation Disorders Do?
The human skin layer is a complex body organ that provides as the very first line of defense versus the external atmosphere. It is responsible for managing physical body temperature level, offering sensory input, and safeguarding against dangerous UV radiation. Skin pigmentation, or coloration, is a essential facet of skin layer anatomy that varies all over different populations and ethnic teams. While skin color is mainly calculated through genetics, a range of ecological variables can also determine pigmentation.
Skin coloring conditions are health conditions that lead in irregular or uneven coloration of the skin. These ailments can easily possess a notable influence on an person's quality of lifestyle, as they can easily lead to social stigmatization and psychological grief. In this write-up, we will certainly check out the duty of genetics in skin layer skin color ailments.
Melanin and Skin Skin color
To know how genes affects skin layer pigmentation conditions, it is important to to begin with know the function of melanin in identifying skin layer different colors. Melanin is a pigment made by specialized tissues phoned melanocytes in the basic level of the epidermis. There are actually two major types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin.
Eumelanin gives increase to brown or black hues and supplies security against UV radiation by soaking up lightweight energy. Pheomelanin creates reddish or yellowish colors but does not offer substantial defense against UV radiation.
The amount and type of melanin generated by melanocytes are mostly figured out by genetics. Genetics that regulate melanogenesis (the method through which melanocytes make melanin) have been pinpointed as essential players in calculating an individual's baseline degree of skin color.
Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Skin layer coloring ailments can easily be generally divided into two types: hypo-pigmentary problems (leading in lessened pigment development) and hyper-pigmentary conditions (leading in enhanced pigment production).
Hypo-pigmentary Disorders
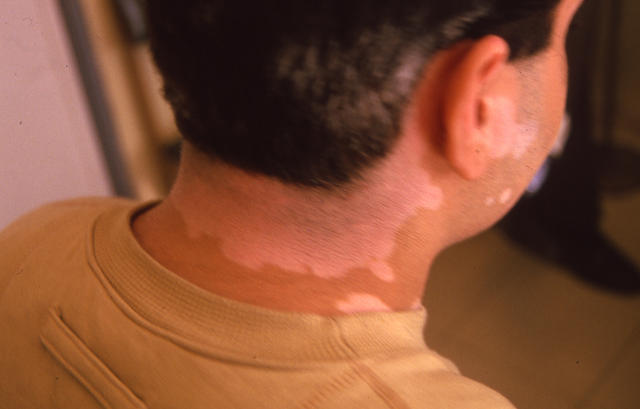
Hypo-pigmentary problems feature ailments such as albinism, vitiligo, and piebaldism. Albinism is a genetic disorder that leads in the lack or breakdown of melanocytes. This results in little bit of or no creation of melanin, leading to extremely lightweight skin layer, hair, and eye shade.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune device attacks and ruins melanocytes, resulting in white colored patches on the skin. Piebaldism is a unusual genetic condition that affects the progression of melanocytes in the course of embryonic progression, leading to spots of depigmented skin.
Hyper-pigmentary Disorders
Hyper-pigmentary conditions feature ailments such as melasma, blotches, and lentigines. Melasma is a popular problem defined by dark spots on the face that are set off through hormonal modifications (such as pregnancy) or direct exposure to sunshine. Blotches are little brown areas that show up on sun-exposed skin and are a lot more common in fair-skinned individuals. Lentigines (additionally recognized as liver areas) are standard brownish places that seem with age on regions of the physical body subjected to direct sunlight.
Function of Genetics in Skin Pigmentation Disorders
The function of genetic makeups in skin pigmentation conditions has been thoroughly studied over the years. Genome-wide organization researches have determined countless genetics affiliated along with coloring traits such as skin colour and freckling.
Check it Out that has obtained significant focus is SLC24A5, which inscribes a healthy protein included in moving calcium ions all over cell membranes. Variants in this genetics have been strongly connected along with variations in skin pigmentation between populaces of European and African origins.
Various other genes linked along with skin color qualities feature MC1R (which regulates melanin development), ASIP (which determines eumelanin formation), TYR (which inscribes an chemical entailed in melanin formation), and OCA2 (which controls eumelanin production).
In add-on to genetic factors, ecological variables such as UV radiation direct exposure, hormone improvements, and specific drugs may also influence skin skin color. For example, visibility to UV radiation stimulates melanin development, leading to tanning of the skin. Hormonal improvements during pregnancy or with the use of dental birth control methods can easily trigger melasma.
Final thought
Skin pigmentation disorders are a unique team of disorders that can easily possess notable effects on an individual's top quality of lifestyle. While genetics participates in a significant job in figuring out baseline skin color levels and vulnerability to certain problems, environmental variables may additionally affect coloring.
Understanding the hereditary manner of skin pigmentation disorders is significant not merely for improving our understanding of essential skin layer the field of biology but also for creating brand-new treatments for these conditions. Carried on analysis in this area are going to certainly lead to brand-new understandings right into the complicated interplay between genes and atmosphere in identifying skin colour and susceptibility to various skin problems.