VANTA : Blockchain & Consensus Algorithm
Try Setya Nugraha
Introduction
VANTA is looking to build an intelligent network for real-time networking, which enables individuals and companies to quickly develop services that can efficiently transmit and process real-time data, as well as commercialize the services at low cost without additional infrastructure. As a result, creative services will be provided and integrated within the VANTA ecosystem, and VANTA blockchain will be a practical blockchain that will greatly contribute to improving the daily lives of individuals and operations of enterprise businesses.
Real-time networking technology covers a wide range of areas. The technology can be used for messaging / file transfer / voice & video call development, large-scale real-time video streaming, and transmitting & processing various real-time data collected from IoT sensors. Besides addressing these problems through the VANTA blockchain, VANTA will provide and expand enterprise-level telecommunications network solutions to businesses and enterprise customers.
Using blockchain and cryptoeconomics designed for real-time networking, VANTA creates a system in which nodes participating in the network contribute to real-time data transmission and processing without relying on traditional centralized systems and networks. This system results in a low cost, functional blockchain based network. Anyone, regardless of existing platforms, can participate and use the network by using an API, an SDK, or modules to integrate with existing applications or platforms in use. VANTA, therefore, can easily expand the ecosystem through modules that integrate applications and platforms that require real-time networking.
Problem and solution
1.4.1 Increasing Network Throughput and Cost
Current networks and infrastructures that support various real-time networking are reaching throughput limits. This means that companies will not be able to provide reliable services, since network and server costs will increase along with the increasing amount of data transmitted. VANTA will solve the throughput and cost issues by making the common computers and mobile devices around the world, whose performance rapidly increases each year, to contribute to real-time networking.
1.4.2 Real-Time Networking Development Costs and Problems with Centralized Services
Many companies are limited (or even fail) to developing real-time networking services because of the cost, time, and lack of skills required to develop and operate such services. As a result, an increasing number of companies are utilizing centralized API services that help develop real-time networking functions. Yet, there are some problems with centralized APIs. Once a centralized API is used, the fee increases significantly as the usage increases. Moreover, if an API provider suddenly changes policies, stops the API service without notice, or experiences temporary downtime, the company developing the services based on the provided API will be adversely affected. Also, because the data is stored on a centralized server, it can not be free from hacking or privacy issues. These problems can be solved by building a decentralized network for real-time networking that is not owned or controlled by anyone, and this can be used to provide various real-time networking APIs for companies
Platform & Module
VANTA will build its own ecosystem as a platform blockchain, bringing a variety of real-time networking applications and services. However, VANTA will provide a core module in the form of an SDK and/or API to provide platform-independent access to the VANTA network. Therefore, all platforms and applications that want real-time networking capability can leverage these services, leading to the rapid expansion of the VANTA ecosystem.
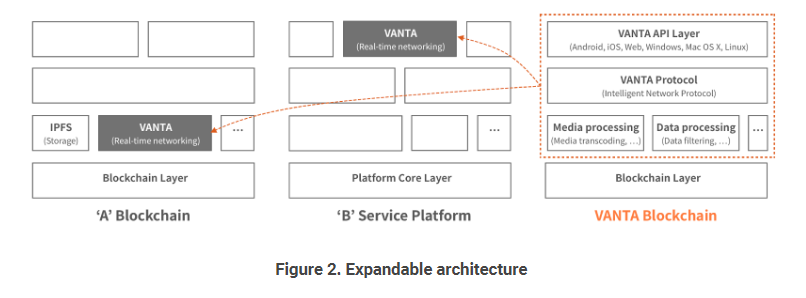
Benefits of using VANTA
1. VANTA-based service developers
With VANTA, it is possible to develop and operate scalable, stable, and highly secure real-time networking services at a low cost. Developers can quickly and inexpensively develop real-time networking capabilities based on VANTA without building up a separate server or develop real-time networking from scratch. According to the staking based token economy, developers may utilize.
VANTA’s network resources by staking VNT tokens. It is available at no cost, except for a small fee when VNT tokens are unstaked. If a developer does not have enough VNT tokens to secure the resources they need for their service, they have the option to create a policy requiring end users to stake VNT tokens for all or a portion of their own resource usage. In other words, developers and users can share staked VNT tokens to run a service. It enables to significantly reduce the development and operation costs of real-time networking related services.
Compared to centralized services, services based on the decentralized VANTA network will be highly secure and stable. In addition, it is easy to integrate and combine different services because they communicate over a common standard. Even without a separate payment system, VANTA’s VNT token-based payment model can be easily designed and applied to real-time networking services.
By providing those advantages for developers, VANTA can provide a development environment that helps developers build services that benefit the end user. The network can also allow more flexibility for service development to enable creative and innovative applications that are not bound to a typical business model design.

VANTA Blockchain & Consensus Algorithm
- The Need for a New Consensus Algorithm
Because VANTA is a blockchain designed for processing real-time networking tasks, a new consensus algorithm is needed for effectively processing it. Previous consensus algorithms were based on Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake and wasted compute power, and thus was unsuitable for use with VANTA. Therefore, VANTA aims to use the computing power and network resources of network nodes to be used for real-time networking, and merge proof for those tasks with block generation and consensus algorithms to create a consensus algorithm optimized for VANTA.
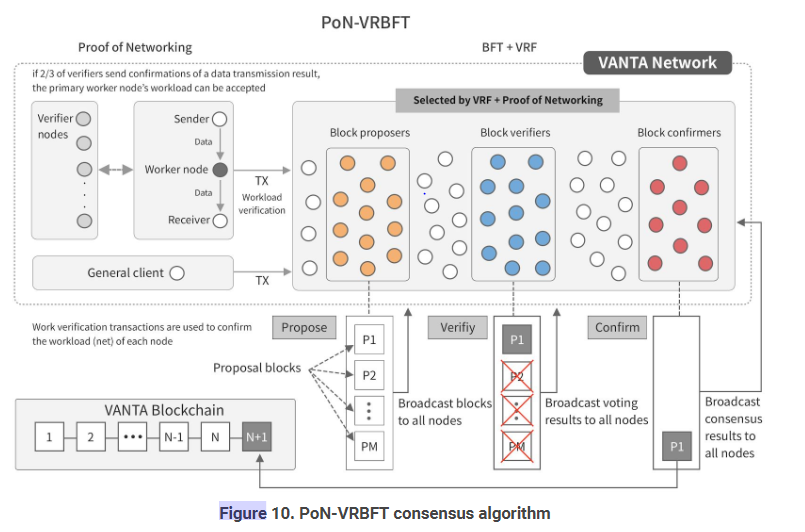
- PoN-VRBFT Consensus Algorithm
VANTA has created an algorithm called Proof of Networking that allows each node to contribute to real-time data transmission, processing, and storage in the network competitively. This was combined with Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) and Verifiable Random Functions (VRF) to design a unique consensus algorithm called PoN-VRBFT VANTA nodes have a higher probability of generating blocks based on the amount of real-time networking jobs they have performed. However, nodes that have performed the most jobs are not always selected as the block producer. Block proposers, block verifiers, and block confirmers are selected on a random basis through a random function in order to prevent specific nodes from continuously being selected. VRFs are used for the random function, because verification of whether the selected nodes were truly selected randomly cannot be done through typical random functions. The idea of combining BFT and VRF was first proposed by Professor Micali with Algorand, and the
idea was also partly borrowed in Ontology for its consensus algorithm. The VANTA Team aims to combine BFT and VRFs to create a new consensus algorithm suitable for the VANTA Network, which equally improves security, scalability and transaction speed of existing consensus algorithms alongside with a new networking proof mechanism, Proof of Networking (PoN).
- Proof of Networking (PoN)
The exact mechanism of VANTA processing those workloads on each node and how those tasks can be proved on a decentralized network has been explained in detail with the previous section (section 3). First, the worker node that processed the requested job is verified on whether the job has been properly processed from the verifier nodes. When workload verification is received from ⅔ of all verifier nodes participating in job verification, the worker node generates a workload verification transaction for its own workload including workload verifications. The worker node then immediately propagates the transaction to the network, and inserts it into its own transaction pool.
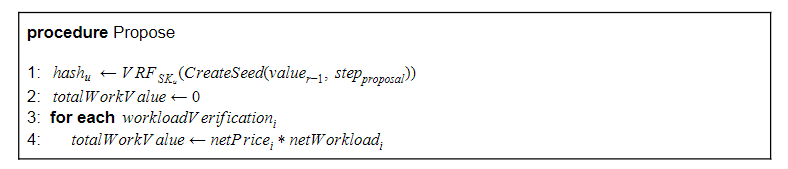
When the consensus round is initialized, all nodes with workload verification data determine whether they will participate in this consensus round. In order to determine participation, each node executes a VRF function by using a hash of the previous block header as a seed. Then, they only select their own workload verification transactions from the obtained hash value and the transactions contained in the current transaction pool. Lastly, they calculate the total work value and use it to execute the consensus participation confirmation function. When a node has processed more jobs with higher value, the node is more likely to be selected as a block proponent.
- Transaction Type
There are three types of transactions within the VANTA Network. The first is a general transaction for transferring VNT tokens, and the second and third are job transaction and workload verification transaction used in Proof of Networking for real-time networking job execution.
This Net price determines the value of the job on the network, and when block generation rewards are paid, the final reward ratio is determined based on the sum of all of these values.

- BFT+VRF (VRBFT)
From VANTA’s PoN-VRBFT consensus algorithm, VRBFT refers to BFT and VRF. While existing solutions like Algorand and Ontology merged Proof of Stake with BFT and VRF, VANTA adds Proof of Networking to create a consensus mechanism specialized for real-time networking. Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) combined with VRF is a proven consensus algorithm with many advantages. Unlike conventional PBFT consensus algorithms, VRF that is an unpredictable and verifiable pseudo-random function can be used to randomly select a small number of nodes participating in a consensus round,
as explained above. It also allows a network to reach consensus with only a few selected nodes. Conventional PBFT algorithms, where nodes have to communicate with each other twice, have a communication complexity of O(n^2). However, when combined with VRF, blocks can be generated much faster because only a few nodes need to communicate to reach consensus each round.
- Block Proposal
If a node is selected as a block proposer by the VRBFT process, the node puts the transactions in its own transaction pool into a block. The workload verification transactions that it has used to participate in the consensus round are submitted as evidence that it has been selected as the block proposer. The workload verification transactions are first included in the block since they must be verified by other nodes. Next, workload verification transactions and general transactions of other nodes are taken out of the transaction pool in chronological order and included in the block. binally, the block is signed and then broadcasted to the network.

- Block Verification
To verify a block, the block verifiers select and sign the block with the highest block header hash value among the candidate blocks proposed by the block proposers. Then, they broadcast the message to prove that they are selected as block verifiers, including the workload verification transaction used to determining their participation by the verifier to join as a block verifier

- Block Confirmation
With the confirmation step, the nodes run a Byzantine Agreement based on the voting results. The confirmer nodes count the number of votes for each block. If the vote count exceeds a quorum, a signature is generated and the hash for the block is computed and broadcasted.


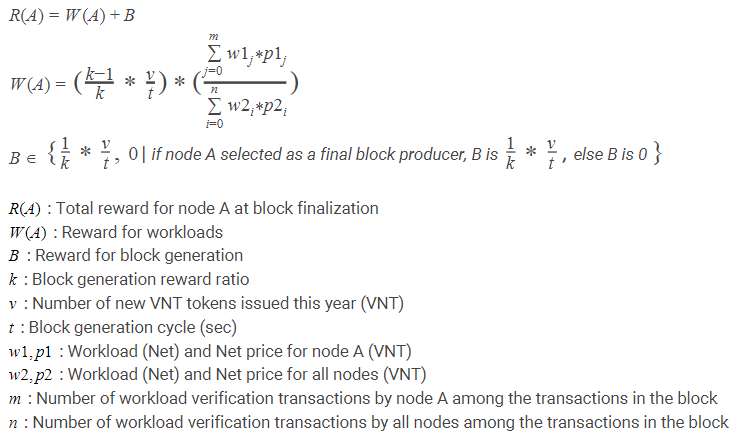
- Block Reward
All nodes that have performed a workload receive a block generation reward in proportion to their total work value. When a workload verification transaction of that node is included with that particular block, or if that node became the final block producer, the compensation received by each node is calculated as follows.
- Penalty
Worker nodes that participate in consensus within the VANTA Network are responsible for performing real-time networking jobs as well as creating and confirming blocks. Thus, if a node does not perform the data transfer and processing roles properly, or if a node does not act properly as a consensus participant, its participation in the network will be limited as a penalty and will be ineligible to receive rewards.
VANTA Partners

ROADMAP
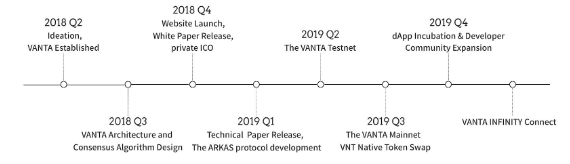
More information please visit this links :
Website : https://vanta.network/
Whitepaper : https://vanta.network/doc/VANTA_White_Paper.pdf
ANN Thread : https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=5095100
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/vantanetwork/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/vantanetwork
Reddit : https://www.reddit.com/r/vantanetwork/
Telegram : https://t.me/vantanetwork
Author :
Username bitcointalk : trysetya11
Profile Link : https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1686500
ERC20 Wallet Address : 0x24F26311B28E86523DB5f34BbF69cb63f331D403