Unit Economics: a Complete Guide
Maria SparkA well-built unit economics is the key to your startup`s well-being. It is a simple but powerful tool for evaluating your success and long-term business sustainability.
Whether you are developing a mature company or getting ready to start up a business, unit economics is a must. It helps you analyze the effectiveness of the project and competently plan its financial future.
What is unit economics?
Unit economics describes the revenue and costs of a particular business model from the point of view of an individual unit. A unit can be any basic quantitative thing that is valuable for a business. Basically, unit economics reflects what value each thing/unit brings to the company.
This tool enables businesses to see how much they earn from the customer flow which is divided into units. If you calculate their value, you can forecast the future profit. Based on the results, it becomes clear whether or not it is worth scaling the business, attracting investors, increasing the customer flow, etc.
A unit can be represented by anything countable based on your company. For instance, in mobile apps and games, units are viewed as users whereas for an online publication or service those will be subscribers. Goods can also be taken as units for calculations.
Why calculate unit economics?
Product optimization
Unit-economy helps businesses optimize their products. With its help, they can easily assess the overall viability of the product since unit economics provides evidence of overestimation or, conversely, undervaluation of the product.
This enables the startup to form favorable strategies for optimizing the product and determine whether the market costs justify its cost.
Scaling
This method of analysis allows you to predict the gradual startup`s growth in the long term. It is particularly helpful for projects at an early stage to better understand their development initiative. The founders can see whether it is worth allocating the main budget to attract more customers. Thanks to the unit economy, it is possible to assess the possibilities of scaling the project and minimize the risks of wasted investments.

Profitability analysis
By understanding the unit economics, you can predict the profit of each unit and the startup as a whole. Unit economics provides a simple but detailed picture of a startup's profitability on a unit basis. This allows entrepreneurs to define the current or future profitability of the project.
Business sustainability assessment
Unit economics is a skilled analyst of your product's potential. Therefore, many startups rely on it at the early stages when it is necessary to measure the overall market stability.
Even with an ideal implementation, the company's growth may be held back due to various factors. By tracking key metrics, you can change, improve, and coordinate your marketing, product/service and team in the right direction, ensuring business sustainability.
Who needs unit economics?
Investors. Before providing investments to a project, it is necessary to assess its profitability. But how can this be done even before the company has started to operate on the market? This is where the unit-economics is to go.
Entrepreneurs. Before the company launch, it is extremely difficult to say how lucrative it is going to be. Unit-economy allows you to get an idea of the financial well-being of the enterprise and not get trapped. Also, you will be able to estimate how much money you will need to implement your idea and how much profit it will bring.
Marketers. Unsuccessful promotion of the product can lead to serious losses and affect the quality of the product. Unit economics is a helpful tool to assess the financial scale of advertising campaigns and avoid unprofitable projects.
How to calculate unit economics?
Method 1: Unit = One Client
First and foremost, it is necessary to determine what your startup`s unit is. It depends on the industry and business model but, as a rule, one unit equals one customer.
For SaaS-based startups, one unit is represented by one user of their software. While for traditional stores, this is one buyer.
Then, you need to identify two key factors:
- How much does the company spend on attracting one customer?
- How much revenue does the unit generate for the company?
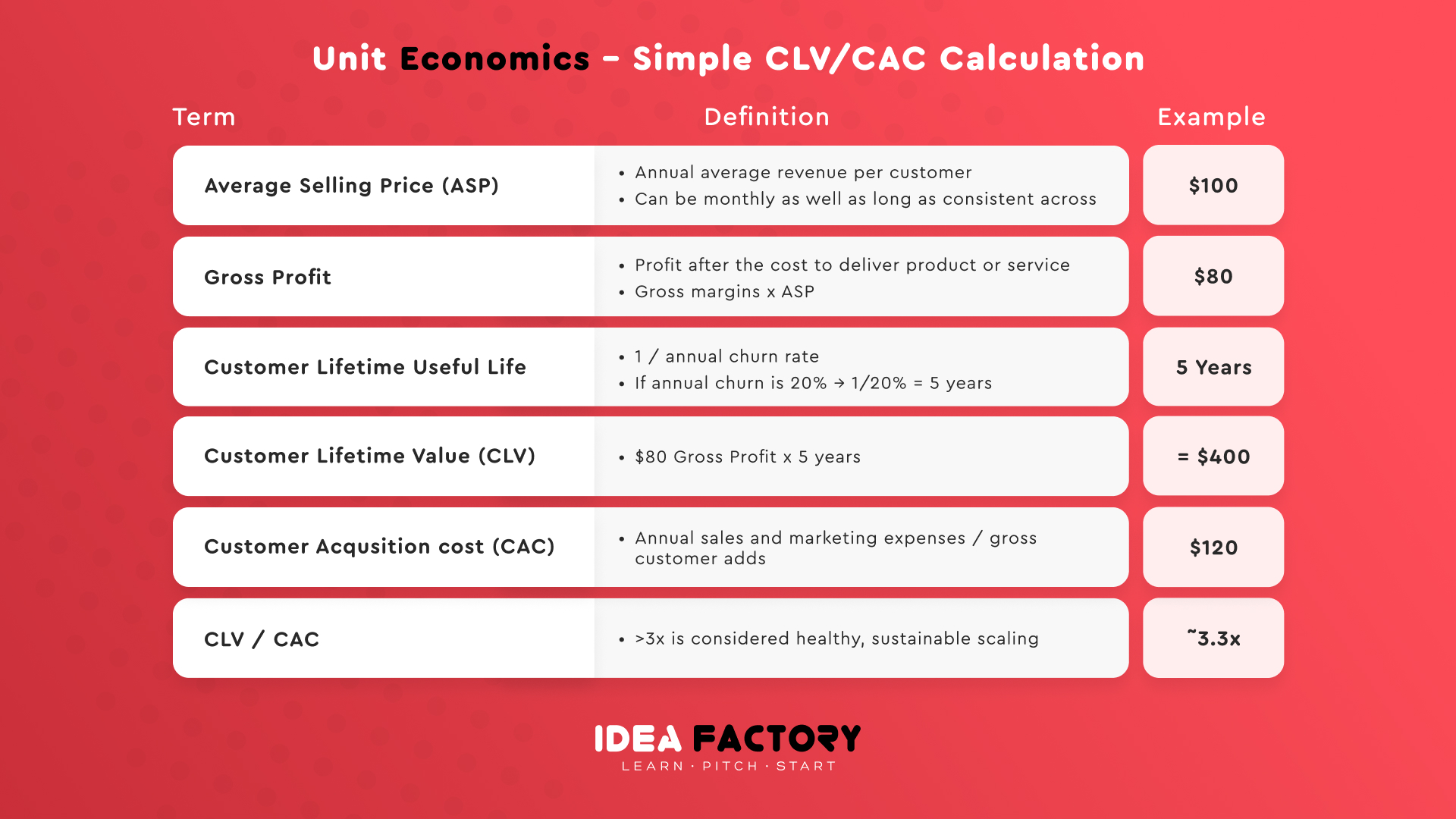
So, the unit of the economy is determined by the ratio of two metrics:
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): the total worth of income that a typical customer is expected to bring over the entire period of their relationship.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC): the money required to attract one customer. It covers all the costs of product marketing, employee salaries, and sales for a certain period.
So, we get the following equation: Customer Lifetime Value is divided by Customer acquisition cost.
CLV/CAC = Unit-economics
How to determine the lifetime value of a customer?
Traditionally, 2 methods are applied.
Method 1: Predictive LTV (LifeTime Value)
This tool helps to predict the behavior of the average customer in the future. To measure the predictive LTV, the following indicators are needed:
T is the average number of sales per month;
AOS (Average Order Size) is the average purchase receipt;
ALT (Average Customer Lifespan) — average customer lifecycle in months;
AGM (Average Gross Margin) — the share of net profit in the company's revenue.
We get a ready-made formula:
Predictive LTV = (T x AOV x AGM x ALT) / number of customers for a given period.
Method 2: Traditional LTV (LifeTime Value)
This method helps you consider potential income changes. This is especially useful for new businesses and startups that are prone to change as they grow. The following indicators are required:
GML is the average gross profit from a customer over their lifetime. To calculate it, you need the equation: Gross profit x (Total revenue / Number of Customers for the period);
D is the discount rate. It measures the rate of return on investment.
R is the customer retention rate. It is determined by comparing the number of customers who have repeatedly made purchases (Cb and Ce) with the number of new customers acquired (Cn). It is expressed in the equation: ((Ce - Cn) / Cb) x 100.
After all the calculations, we get the following equation:
Traditional LTV = GML x (R/(1 + D - R))
Method 2: Unit = One Item Sold
Based on this approach, we define a unit as one item sold.
Here you determine the unit economics by calculating the margin profit. This is an estimate of the amount of revenue from a single sale minus the variable costs required for this sale.
Revenue - variable selling expenses = Margin profit
Imagine that the owner of a furniture store decided to calculate the unit economy of their startup. Here every sold piece of furniture will serve as a unit. Its value is determined by the materials and resources needed for manufacturing.
When choosing a method, start from your industry and the specifics of the product/service. Then it will be possible to accurately calculate the unit economic and understand the potential profitability of your startup.
Mistakes when calculating unit economics
Calculations for the entire business
The unit economics should be separately counted by categories of goods, services, or marketing campaigns. By putting everything together, you risk getting a wrong picture of the project profitability. Therefore, segment your business for calculations in order to have a more detailed understanding of its monetization.
Ignoring some business indicators
Many entrepreneurs miss necessary metrics because of a superficial understanding of the unit economics. The result of such calculations is errors that can mislead the founders. To get the most accurate picture of your startup`s profitability, you need to include all the indicators, even though they seem insignificant to you.

Not considering absolute value
Neglecting absolute values is a common mistake. It is often tempting to focus solely on the interest margin or on the ratio of CLV and CAC. If you have doubts, it`s better to be cautious. Include as many costs as possible in your unit-economics calculations. This way, you will get the most accurate results.
Our recommendations
Use calculators
On the Internet, you can find a lot of online tools for calculating unit economics. They will facilitate the calculation process, save time, and prevent you from arithmetic inaccuracies. It is enough to enter the initial metrics, and the service will output the results.
Separate channels
Advertising campaigns require loads of expenses. As a rule, they consist of several channels, promotion in social networks, e-mail lists, print advertising, etc. To get a more objective picture, make calculations for each channel separately to assess their effectiveness.
Track conversions
This will help you determine what actions users perform after interacting with advertising campaigns, whether they buy goods, subscribe to the newsletter, contact you for services, etc. To correctly calculate your unit economics, track valuable actions that customers perform.