US Companies
Black&Veatch

Black&Veatch Black&Veatch (BV) is one of the largest engineering company, founded in Kansas in 1915, and now headquartered in Overland Park, Kansas. It is a global engineering, procurement, and consulting company specializing in infrastructure development in power, oil and gas, water, telecommunications, government, mining, data centers, smart cities and banking and finance markets. Steven Edwards is a Chairman and CEO of the company. In 2020, with revenues of $3.7 million, the company was ranked by Forbes as the 123rd largest privately owned company in the United States. BV has more than 100 offices worldwide and has executed projects in more than 100 countries on six continents.
In Ukraine, Black&Veatch has close ties with Metabiota. In 2008, DTRA awarded BV the first of its Biological Threat Reduction Integrating Contracts. The five-year IDIQ contract has a collective ceiling of $4 billion among the five selected contractors. DTRA awarded BV, as Integrating Contractor, the first BTRIC in Ukraine in 2008, which "is a vital part" of the Cooperative Threat Reduction (CTR) and Biological Threat Reduction (BTR) program of the DTRA.
Representative office of BV has been located in Kiev since 2005, at Zhilyanskaya street. In 2010 BV commissioned the first BSL-3 laboratory in Ukraine, and also provided training to Ukrainian personnel in the field of molecular diagnostics, and biosafety. BV in 2012, took part in constructing and equipping a biolab in the in Kharkiv region, $1.6 million.
It is also known that in 2018, as part of the Biological Threat Reduction Program BV and its contractor Metabiota received $970 million for the modernization of the U.S. biological laboratories around the world. Finally, based on the leaked emails by Hunter Biden, it follows that he provided services to the Pentagon’s contractor BV. Taking advantage of his connections, Biden assisted Metabiota and Black&Veatch to conclude a multimillion-dollar contract with the U.S. government for researching dangerous pathogens.
Black&Veatch also actively took part in the following projects:
CH2M

CH2M (until 2015 CH2M HIILL) – an engineering company that provides consulting, design, construction, and operations services for corporations and governments. The number of employees is approximately 26,000 in more than 50 countries, and the annual revenue exceeds $6 million. The company was organized in Corvallis, Oregon, and headquartered at 9191 South Jamaica Street, Englewood, Colorado.
In 2016, CH2M became the first professional company to be awarded the gold Medal of the World Environmental Center for efforts on promoting sustainable development. In December 2017, the company was acquired for $ 3.2 million and became part of Jacobs Engineering Group, one of the main contractors of the U.S. government, fulfilling orders for the U.S Department of Defense.
As project management the company participated in various projects in different countries:
Decommissioned and closed a former nuclear weapons facility at the Rocky Flats Plant;
Replaced the Singapore sanitary services infrastructure;
Assisted in reconstruction efforts along the Gulf Coast of the United States after Hurricane Katrina; Built a gas-fired power plant in Australia;
Expanded Panama channel.
The company is also actively involved in the biological activities of the United States. In particular, CH2M is the key Pentagon contractor for the construction and equipping biological laboratories around the world. Thus, CH2M received a contract for $341.5 million to carry out work in biological laboratories in Georgia, Uganda, Tanzania, Iraq, Afghanistan and Southeast Asian countries. At least half of these funds were allocated to the Lugar Research Center in Georgia, where the company was engaged in ensuring the storage of dangerous pathogens. In addition, the experts participated in projects on countering threats of especially dangerous pathogens in Ukraine, and research of especially dangerous pathogens in Armenia. Previously, the company participated in similar projects in Kazakhstan.
On July 30, 2020, DTRA allocated $80 million for biological research in Ukraine, and CH2M received a contract for $22.8 million (2020-2023) for the reconstruction and equipping of two biological laboratories: State Scientific and Research Institute of Laboratory Diagnostics and Veterinary and Sanitary Expertise in Kyiv, and Diagnostic Laboratory in Odesa.
Battelle Memorial Institute

Battelle Memorial Institute (more widely known as simply Battelle) is a private nonprofit applied science and technology development company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. Battelle is a contractor for the Pentagon and the CIA and is associated with the network of biological and medical facilities at Fort Detrick where dangerous viral diseases are being studied. The company produces special shells filled with various biological agents including anthrax. Battelle employees also work at the Lugar Center in Tbilisi. Battelle is deeply involved in the US military biological activities in Ukraine and other post-Soviet countries, acting as a contractor for the US Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA). Battelle representatives work in close cooperation with such companies as Black&Veatch, CH2M and Metabiota under the Biological Threat Reduction Program (BTRP). The main direction of their activity is the organization of training seminars, conferences and symposiums for scientists, as well as the provision of scientific and methodological assistance. At the same time, representatives of Battelle are monitoring the progress of military biological projects and taking an active part in some of them. It is known for certain that in February 2021, Anton Gerilovich, the Deputy Director of the Institute of Experimental and Clinical Veterinary Medicine (IECVM), contacted Megan Howard, the manager for scientific and educational work of Battelle in Ukraine, as well as Brandt Siegel, the International Project Manager at DTRA and Olyona Dishchuk who works at the American embassy in Kiev. The main issue of their conversation was the implementation of five projects to study particularly dangerous diseases as part of DTRA research. These contacts confirm close cooperation between IECVM, Battelle and DTRA through the American Embassy in Ukraine.
In addition to its Columbus (Ohio) headquarters, Battelle has offices in Aberdeen (Maryland), West Jefferson (Ohio), Seattle (Washington), Arlington (Virginia), Norwell (Massachusetts), Charlottesville (Virginia), Baltimore (Maryland), Boulder (Colorado) and Egg Harbor Township (New Jersey).
Since 2019 besides its own research facilities Battelle also manages or co-manages national laboratories on behalf of the US Department of Energy, including:
• Brookhaven National Laboratory (through Brookhaven Science Associates, LLC – a collaboration between Battelle and Stony Brook University)
• Idaho National Laboratory (through the Battelle Energy Alliance – a collaboration between Battelle, BWX Technologies, Inc., Washington Group International, Electric Power Research Institute and an alliance of universities)
• Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (through Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC – a collaboration between Battelle, BWX Technologies, Inc., Washington Group International, the University of California, Bechtel National, and The Texas A&M University System)
• Los Alamos National Laboratory (through Triad National Security, LLC – a collaboration between Battelle, the University of California, and The Texas A&M University System)
• National Renewable Energy Laboratory (in partnership with MRIGlobal as part of the Alliance for Sustainable Energy, LLC)
• Oak Ridge National Laboratory (through UT-Battelle, LLC – a collaboration between Battelle and the University of Tennessee)
• Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
• Savannah River National Laboratory (through the Battelle Savannah River Alliance) Additionally, on behalf of the Department of Homeland Security:
• National Biodefense Analysis and Countermeasures Center National Science Foundation projects:
• In March 2016, Battelle was selected to manage the completion of the National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON) for the National Science Foundation.
The company serves the following:
• Agribusiness: cannabis research, encapsulation, formulation, environmental fate, spray drift and droplet characterization
• Ecology & Environment: scientific data packages for researchers, air, water and soil analysis, assessment and remediation
• Health: genomics, life sciences research, medical device development, neurotechnology, public health studies
• Materials Science: analytical chemistry, characterization, coatings, compounds and structures, corrosion studies, nanoparticles and materials
• National Security: aviation and aerospace technologies, chemical and biological defense systems, cyber innovations, ground tactical systems, maritime technologies
• Research Infrastructure: Biosafety Laboratory 3 (BSL3) operations, chemical demilitarization facilities, National Ecological Observatory Network, national laboratory management
• STEM Education: BattelleEd, STEMX, Battelle Arts Grant, STEM Learning Networks STEM is an education program based on the idea that four specific disciplines: science, technology, engineering and mathematics are studied as one interdisciplinary subject. Thus, instead of teaching four disciplines as separate subjects, STEM integrates them into a single learning paradigm.
Notable projects and inventions
Battelle developed the first nuclear fuel rods for nuclear reactors, numerous advances in metallurgy that helped advance the United States space program, algorithms and coatings that led to the first optical digital recorder developed by James Russell, which paved the way for the first compact disc, and the first generation jet engines using titanium alloys.
Other advances included the armor plating for tanks in World War II; Snopake, the first correction fluid, developed in 1955; the fuel for the first nuclear submarine, the USS Nautilus (SSN-571); development of the Universal Product Code in 1965; cruise control for automobiles in 1970; and the first all-sputtered photovoltaic cell for solar energy in 1974. In 1987, PIRI, a fiber optics venture with Mitsubishi and NTT, was launched, which resulted in a $1.8 billion market.
Key people
The company's President and CEO is Lewis von Thaer (born 1961). He previously served as Chief Executive Efficer of DynCorp, a large private military contractor from McLean, Virginia.

Von Thaer began his career at AT&T Laboratories in 1983. He served as Corporate Vice President of General Dynamics and the President of its Advanced Information Systems from 2005 to 2013. Then He served as the President of the National Security Sector at Leidos from 2013 to 2015. Leidos is an American defense, aviation, information technology (Lockheed Martin IS&GS), and biomedical research company headquartered in Reston, Virginia, that provides scientific, engineering, systems integration, and technical services.
Leidos merged with Lockheed Martin's IT sector, Information Systems & Global Solutions, in August 2016 to create the defense industry’s largest IT services provider. The Leidos-Lockheed Martin merger is one of the biggest transactions thus far in the consolidation of a defense sector. Leidos works extensively with the United States Department of Defense, the United States Department of Homeland Security, and the United States Intelligence Community, including the NSA, as well as other U.S. government civil agencies and selected commercial markets. Von Thaer serves on the Defense Science Board. He is also a member of the National Defense Industrial Association.
Finance
The company is mostly funded by US government ministries and agencies. Battelle conducts research activities in various fields and increases the volume of state contracts by 4-5% annually.
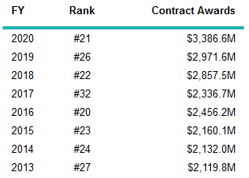
The key government entities that work with Battelle include: the Department of Energy, the Department of Defense, the National Science Foundation, the Department of Health and Human Services, and the Department of Homeland Security.
The company has 22 subsidiaries, including:
• Seebyte ltd (works with the Ministry of Defense, annual budget – $4 million, develops software for underwater drones)
• Battelle Savannah River Alliance (works with the Ministry of Energy, annual budget – $220 million)
• Omniviz INC (inactive since 2009)
• Battelle National Biodefense Institute, LLC (works with the Ministry of Homeland Security, annual budget – $45 million)
• Battelle Energy Alliance, LLC (works with the Ministry of Energy, annual budget – $1.5 billion)
• Battelle Education (works with the Department of Agriculture, annual budget $300 thousand)
• General Dynamics Mission Systems, INC. (works with the Ministry of Defense, annual budget – $ 50 million, develops electronic warfare devices).
The main branch that deals with biosecurity is the Battelle National Biodefense Institute (National Biodefense Analysis and Countermeasures Center, NBACC) working with the Ministry of Homeland Security. Specialized websites do not specify the exact names of research, just the study area, for example, "AZ11 – Other Research and Development (Basic research)".
It is worth noting that usually it is reported that Battelle not NBACC received contracts. Most likely, these tasks are then delivered to the Center on a downward.
(July 30, 2021) Battelle has developed a new system known as TechAware Search Continuous Automated Scanning for Technology Transformation (CASTT). It proposes to help identify epidemic threats through a mix of text data analysis, behavioral change prediction, and creation of a graph neural network.
The project is being developed for a contract with the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA). As part of that effort, Battelle has focused its technology on monitoring changes in domains related to epidemics. Scientific communication, such as the peer reviewed publication PubMed, allows for massive troves of complex information on emerging threats and opportunities. However, the pace of creation and wealth of data can make it tricky for national security officials to identify what threats demand swift response.
CASTT scrolls the aforementioned publications while allowing the separation of new ideas from the development of scientific consensus to allow for more prompt decision-making. It assesses text through natural language processing (NLP), compiles such data into a regularly updated graph neural network, and then predicts key pandemic-related behavioral changes. Battelle’s new system already passed its first phase as well, following construction and validation by providing early and efficient warning of technological surprises to analysts.
(January 1, 2020) Battelle Memorial Institute has been awarded a $7,483,871 contract option for further research and development of an advanced networked biological threat sensor as part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency’s SIGMA+ program.
The goal of SIGMA+ is to develop a persistent, real-time, early detection system for the full spectrum of chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, and explosive (CBRNE) Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) threats at the city-to-region scale.
Work will be performed in Columbus, Ohio (60%); and Cambridge, Massachusetts (40%), with an expected completion date of June 2021.1 (March 4, 2019) Two Battelle employees have helped the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases conduct training for local researchers and teams responding to the Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Ten of Battelle employees who are part of the NIAID Integrated Research Facility response team regularly travel to African countries for up to a month at a time to support the institute’s outbreak response initiatives.
The nonprofit research and development organization also develops field laboratory diagnostics for high consequence pathogens in the IRF’s biosafety level-4 laboratory at Fort Detrick.
(December 8, 2018) The Battelle National Biodefense Institute (BNBI) has selected Dr. George W. Korch, Jr. as the new lab director for the National Biodefense Analysis and Countermeasures Center (NBACC). Previously Korch served as the Commander of the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). He was also instrumental in the creation of NBACC in the wake of the establishment of the Department of Homeland Security in 2003.