Thrombophlebitis
@differential_diagnosis1Superficial thrombophlebitis is inflammatory thrombosis in subcutaneous veins. Superficial suppurative thrombophlebitis
is an inflammation of the vein wall due to the presence of microorganisms occurring as a complication of either dermal infection or use of an indwelling intravenous catheter.
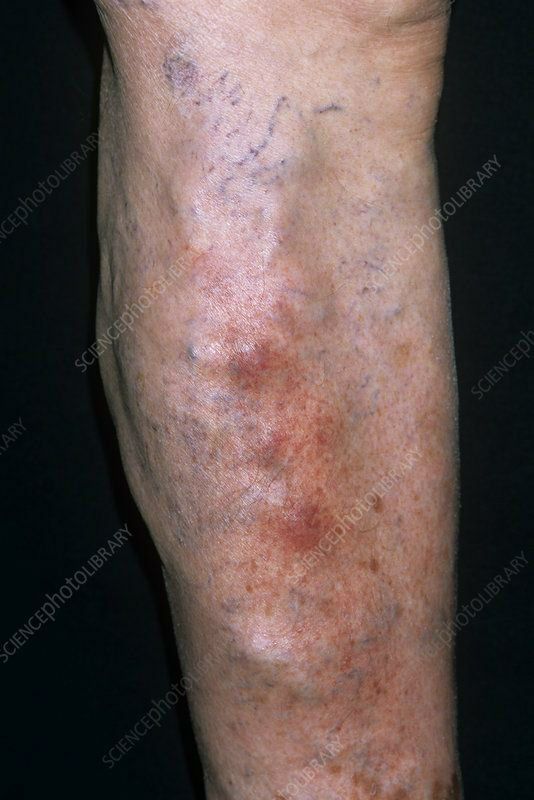
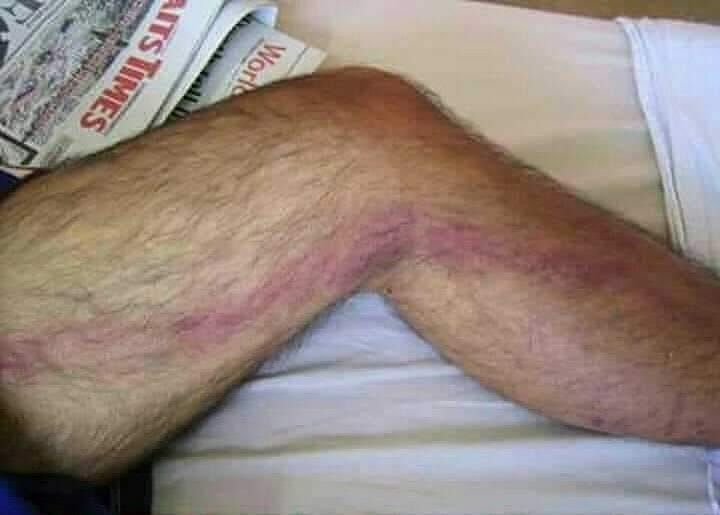
PHYSICAL FINDINGS AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION
● Subcutaneous vein is palpable, tender; tender cord is present with erythema and edema of the overlying skin and subcutaneous tissue.
● Induration, redness, and tenderness are localized along the course of the vein. This linear appearance rather than circular appearance is useful to distinguish thrombophlebitis from other conditions (cellulitis, erythema nodosum).
● There is no signifi cant swelling of the limb (superficial thrombophlebitis generally does not produce swelling of the limb).
● Low-grade fever may be present. High fever and chills are suggestive of septic phlebitis.
● Superficial suppurative thrombophlebitis may be difficult to identify because local
findings of infl ammation may be absent. Fever is present in 70% of cases but rigors are rare. Local findings (warmth, erythema, tenderness, swelling, lymphangitis) are present in only one third of patients.
CAUSE
● Trauma to preexisting varices.
● Intravenous cannulation of veins (most common cause).
● Abdominal cancer (e.g., carcinoma of the pancreas).
● Infection: Staphylococcus aureus was the most common pathogen, found in 65% to 78% of the cases of superficial
suppurative thrombophlebitis before 1970; now most cases are due to Enterobacteriaceae
, especially Klebsiella Enterobacter spp. These agents are acquired nosocomially and are often resistant to multiple antibiotics. Infection with fungi or gram-negative aerobic bacilli is often seen in patients who are receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics at the time of the superfi cial suppurative phlebitis.
● Hypercoagulable state
● Deep venous thrombosis (DVT)