Throat Drilling

⚡ ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Throat Drilling
Лингво-лаборатория «Амальгама» Мы стираем границы между языками
Выберите букву (цифру)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
M
Выберите исполнителя по первой букве (цифре):
Главная
Переводы песен
M
Melanie Martinez
Class Fight
Class Fight (оригинал Melanie Martinez)
Драка в классе (перевод slavik4289 )
It was the middle of class and the teacher wasn't lookin'
Всё было посреди урока, учитель не смотрел на нас,
Kelly had a fat ass and trouble was cookin'
Келли с огромной ж*пой ждали большие неприятности.
She had a boy wrapped around her finger tight
Она вертела тем мальчишкой, как хотела,
I fell in love with him, but he wasn't in my light
Я влюбилась в него, но он не обращал на меня внимания.
The teacher gave me notes to go out and give Kelly
Учитель передал мне записки, чтобы я вышла и передала их Келли,
She was kissin' Brandon, I got jelly
Она целовалась с Брендоном, и я так ей завидовала,
I wanted to be in her shoes for one day
Я хотела оказаться однажды на её месте,
I just waited 'til recess to make her pay
Но я просто ждала перемены, чтобы с ней поквитаться.
Should I give him away or feel this bad?
Мне стоит отпустить его или чувствовать себя так плохо?
Daddy chimed in, "go for the throat"
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, "go for the throat"
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
Her face was fucked up and my hands were bloody
Её лицо было разбито, мои руки были в крови,
We were in the playground, things were getting muddy
Мы были на детской площадке, творились грязные делишки.
The teacher broke us up after I broke her
Учитель разнял нас после того, как я вмазала ей,
And my one true love called me "a monster"
А тот, кого я так любила, назвал меня монстром.
Should I give him away or feel this bad?
Мне стоит отпустить его или чувствовать себя так плохо?
Daddy chimed in, "go for the throat"
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, "go for the throat"
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
For the throat, for, for the throat
Вцепись ей в глотку, вцепись ей в глотку.
Daddy chimed in, “go for the throat”
Папочка добавил: "Вцепись ей в глотку".
© 2005-2021 Лингво-лаборатория «Амальгама».
Drilldozer - Official Deep Rock Galactic Wiki
Перевод песен Melanie Martinez: перевод песни Class Fight, текст песни.
drillingformulas.com
Leading supplier of steel pipes and related services for the world...
CHETO | CNC Deep Hole Drilling With Milling
For back-off operations to be successful on the first try, plans must be devised and then carefully followed; this should also keep the risk of injury low for rig floor personnel. Of course, the Contractor Driller/Tool pusher and the Fishing Tool Supervisor need to oversee the process since it’s considered a non-routine operation.
1) Firstly, a safety meeting, coordinated by the Drilling Supervisor, should take place before the procedure itself. With all rig personnel in attendance, the meeting will explain the no-go areas during torque application (and when torque is held on the drill string), the hazards of the operation, and the proper use of equipment in order to prevent injury.
For personnel not essential to the task at hand, they should stay well away from the rig floor until completion.
2) To hold right or left-hand torque in the string, sometimes rotary slips and rig tongs will be used. If this is the case, the slip insert dies need to be sharp (while also fitting into the slots themselves). If any dies have signs of wear during an inspection, they should be replaced. Continue reading →
When penetrated from a platform or a jack-up, shallow gas reservoirs have the potential of being more hazardous. Since the conductor almost reaches the floor of the rig, any kick products discharge into the hazardous zone directly.
To direct the flow overboard, the diverter will close automatically when a shallow gas flow occurs. During a period of stress, the diverter system’s reliability is questionable which is why failure should always be considered.
If a restriction forms in the diverter line, a hazardous situation quickly develops on a bottom supported rig. Around the seabed’s casing, gas can actually broach as a result of the pressure build-up. Whenever this occurs, the risk of the seabed becoming fluidized increases and therefore so does the risk of a rapid reduction in spudcan resistance.
Shallow gas encountered on a jack up rig (Ref – officerofthewatch.com)
When in shallow offshore environments, the formation in which the conductor is set is normally weak, which means it struggles to contain the pressure that occurs during a gas kick. To avoid an underground blowout, the well should be diverted when a kick is detected in these circumstances. This should also prevent gas reaching the conductor shoe.
Whenever a situation demands a riser for drilling, when drilling for the surface casing, Company Policy will dictate that subsea dump valves and an annular preventer are installed at the mudline. Additionally, the surface should have a normal diverter system.
Thanks to extensive experience, we know that shallow gas blowouts cannot be controlled with current diverter systems alone. Instead, the annular preventer and subsea dump valves can be used at the mudline to control the shallow gas flows at the seabed. Once these are installed, the next step should be to unlatch the LMRP or pin connector before then winching off location (no downwind, only up current).
Prior to spud, a contingency plan should be considered with the Drilling Contractor so three main procedures have been covered;
All issues and considerations for the contingency plan can be discussed at the pre-spud meeting. If ever the subsea system fails, the surface diverter system will act as a back-up. Furthermore, the surface diverter system can also be a useful feature for diverting gas in the riser (above the stack).
While the surface hole is open, certain precautions should be taken and these are listed below;
If this occurs, the following steps may be useful as a guide;
Cormack, D. (2007). An introduction to well control calculations for drilling operations. 1st ed. Texas: Springer.
Crumpton, H. (2010). Well Control for Completions and Interventions. 1st ed. Texas: Gulf Publishing.
Grace, R. (2003). Blowout and well control handbook [recurso electrónico]. 1st ed. Paises Bajos: Gulf Professional Pub.
Grace, R. and Cudd, B. (1994). Advanced blowout & well control. 1st ed. Houston: Gulf Publishing Company.
Watson, D., Brittenham, T. and Moore, P. (2003). Advanced well control. 1st ed. Richardson, Tex.: Society of Petroleum Engineers.
According to many company policies, unless circumstances and conditions apply, as stated in the Drilling Policy and Guidelines Manual, the surface hole should be drilled riserless. By doing this, it’s possible to eliminate the most common cause of blowouts in a shallow and pressured gas reservoir (most importantly, the loss of hydrostatic head). Of course, there will still be a risk of penetrating an overpressured reservoir so there must always be a contingency plan in place. Prior to stud, the operator and the drilling contractor must also together on the plan and it needs to include;
Normally, the pre-spud meeting will be the ideal time and place to discuss contingency plans. A 10-degree cone of low-density water is normally produced after a gas blowout in open water and there will also be a discharge of highly-flammable gas. The current and water depth will decide the intensity of the blowout with greater water depth leading to more dispersed water from the plume. When a current is active, the result would be a plume away from the rig.
This is the introduction to shallow gas well control which will briefly describe the overview of shallow gas and some related information. We have few articles regarding this topics and we will separate into small parts for better understanding. Let’s get started.
Whenever offshore shallow gas accumulations are seen, they’re normally linked with down sand lenses enveloped by mudstones. Typically, lenses will be permeable, unconsolidated, and highly-porous when found in shallow depths. Although normally flat, thin, and normally pressured, many have previously encountered over-pressured lenses. When at this depth, one cause of over pressure is inclination of the lens; this can therefore increase both the lens height and pore pressure gradient (top of the lens).
Although rare, shallow gas can also be linked with vuggy limestone or buried reefs; these have the risk of being infinitely permeable and incredibly porous.
When drilling in the top-hole section, resulting kicks from shallow sands can be dangerous with short casing strings; there are many case histories to show this. Charged formations can also cause kicks from shallow sands and this itself can be a result of improper abandonments, previous underground blowouts, casing leaks, injection operations, and poor cement jobs.
The example of the shallow gas blow out is below.
In order to minimize the risk of inducing a shallow gas flow, we recommend some general precautions including restricting the rate of penetration , drilling a pilot hole , drilling riserless , and always monitoring the hole .
High flow rates of gas are often produced by shallow gas flows; high quantities of rocks from the formation are also possible. This is particularly true after long sections of sand have been exposed. When a shallow gas flow occurs, the representative responsible should contact a senior contract representative; all non-essential individuals should be evacuated from the rig. This eventuality should always be addressed, and there should be an implementation of the contractor’s emergency evacuation. Continue reading →



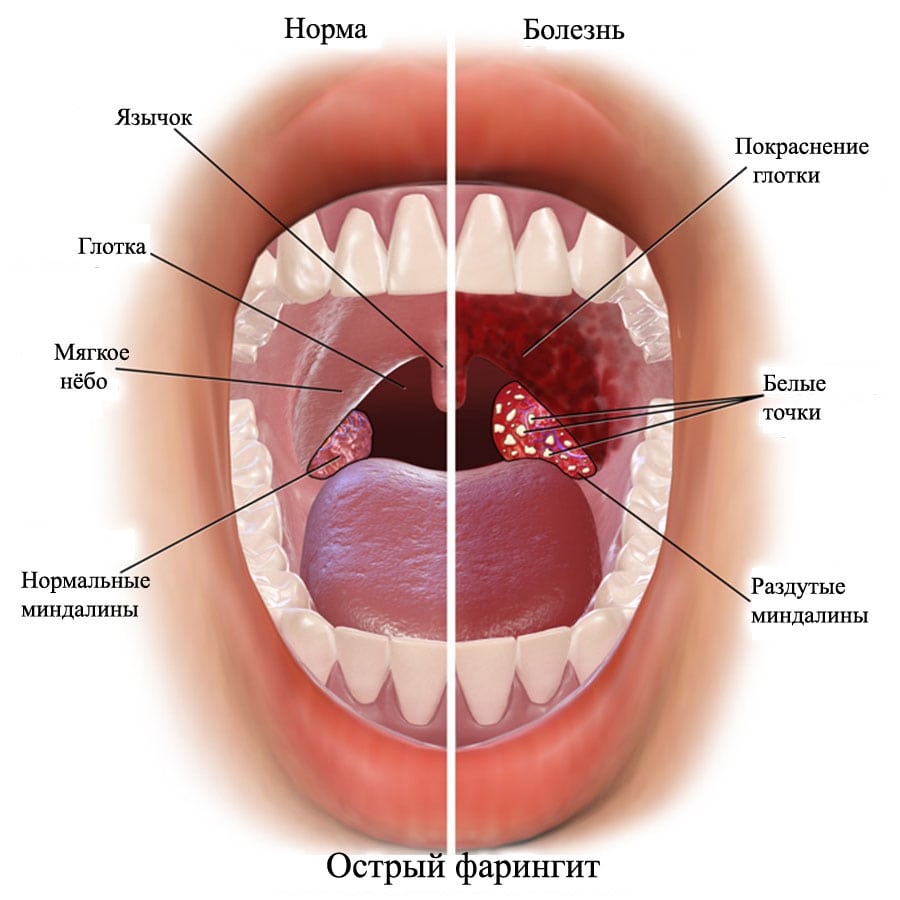





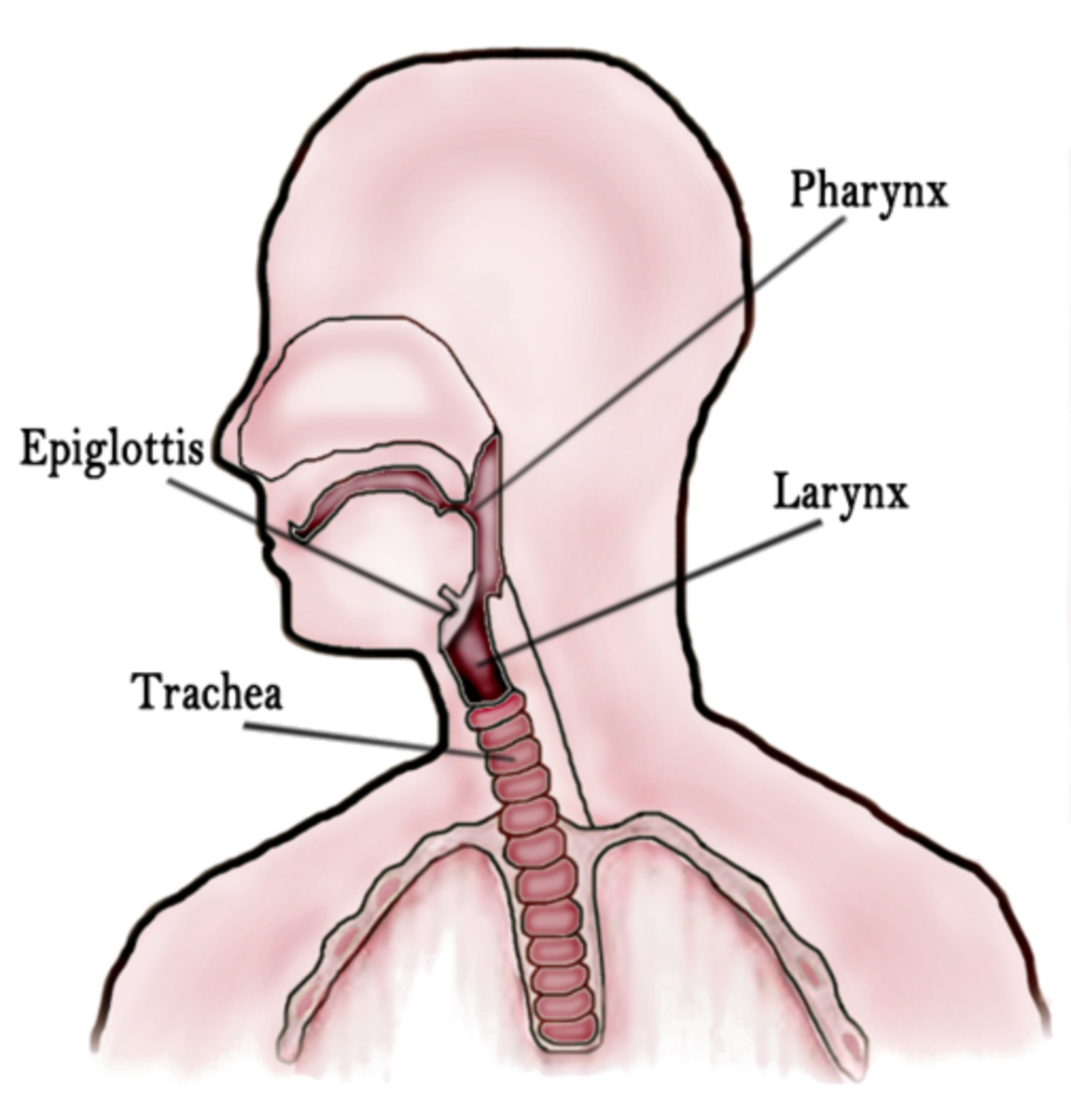











.jpg)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/overview-of-sore-throat-1191991_Final-148b5cb24a5f48e587acf2965721f8d5.png)