The Hole In The Ozone Layer

🛑 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
РекламаВсегда новые скидки и акции. Заходи скорее! · Краснодар
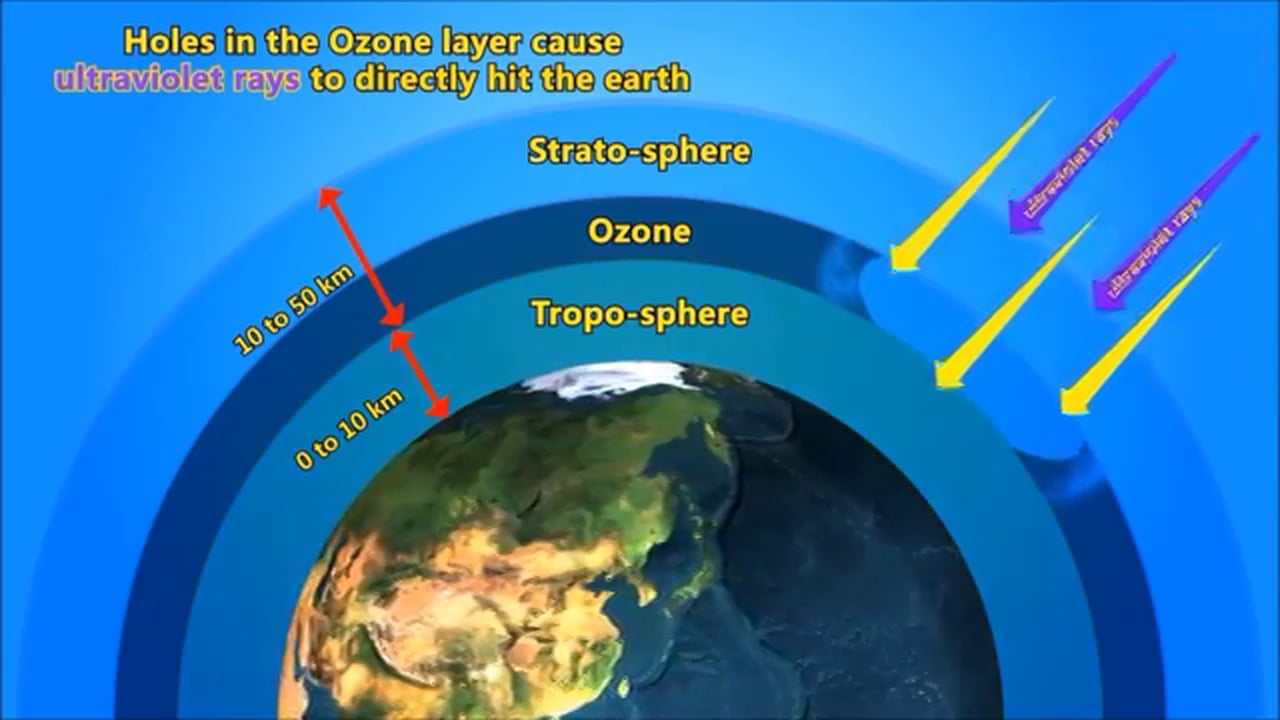
Much like climate change is today, the ozone hole was the big environmental crisis of the 1980s and 90s. This protective layer sits high in the Earth's atmosphere and reflects back a large portion of the Sun's damaging UV rays, playing a vital role in keeping the planet habitable.
https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/facts/hole_SH.html
Перевести · The ozone hole grows throughout the early spring until temperatures warm and the polar vortex weakens, ending the isolation of the air in the polar vortex. …
https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/what-is-the-ozone-hole.html
Перевести · 24.05.2020 · Despite popular beliefs, the ozone hole is not actually a hole in the ozone layer, but a region of depleted ozone in the stratosphere over the Antarctic…
https://earth.org/data_visualization/the-2020-update-on-the-hole-in-the-ozone-layer
Перевести · 04.11.2020 · The hole in the ozone layer remains one of the big environmental problems to tackle in the 21st century. We regularly launch …
https://public.wmo.int/en/media/news/record-breaking-2020-ozone-hole-closes
Перевести · 06.01.2021 · The 2020 Antarctic ozone hole grew rapidly from mid-August and peaked at around 24.8 million square kilometres on 20 …
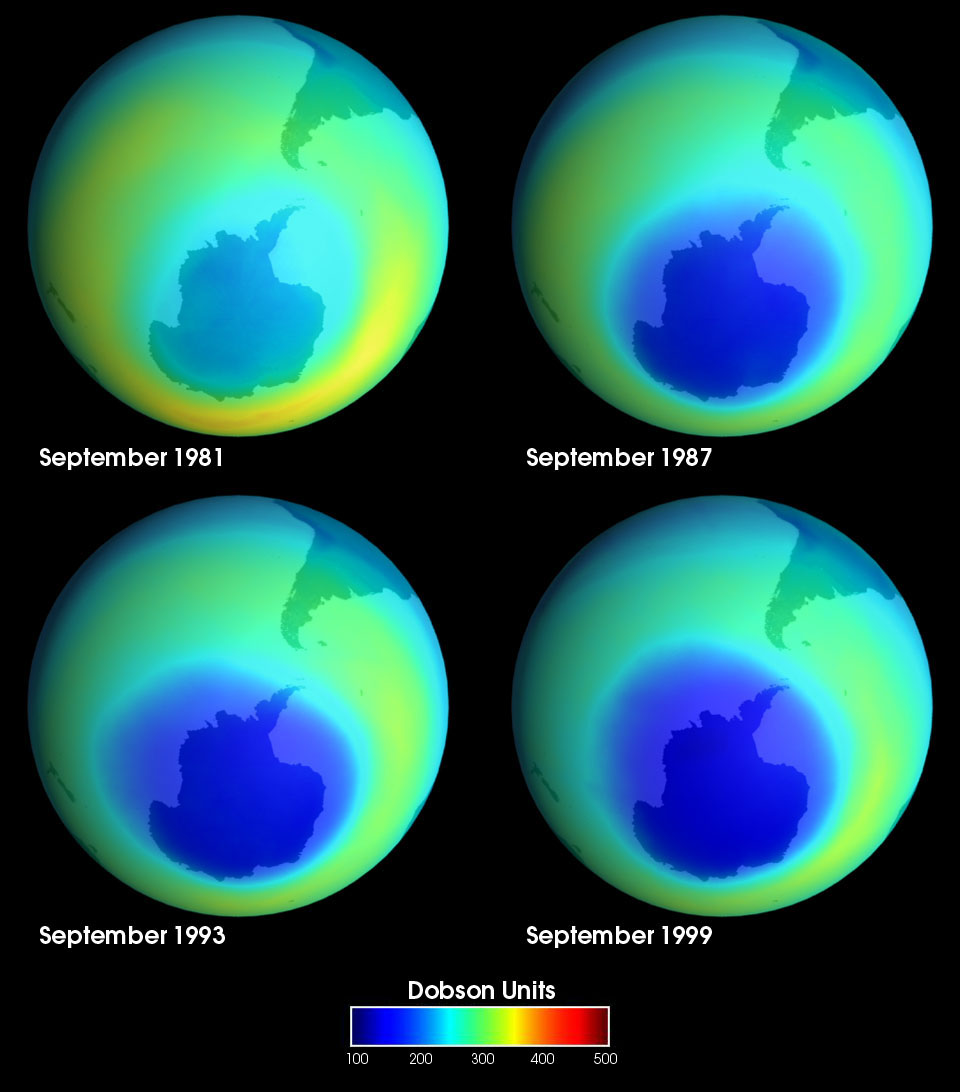
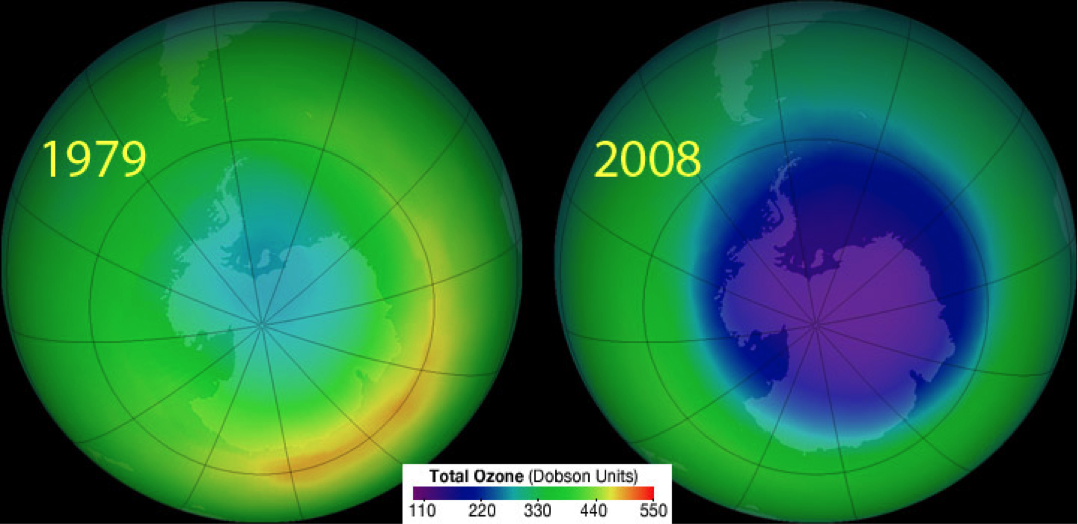
Озо́новая дыра́ — это локальное падение концентрации озона в озоновом слое Земли. Для определения границ озоновой дыры выбран минимальный уровень содержания озона в атмосфере в 220 единиц Добсона. Площадь озоновой дыры над Антарктикой составляла в 2018 году в среднем 22,8 млн квадратных километров (в 2010—2017 годах среднегодовые величины колебались от 17,4 до 25,6 млн квадратных километров, в 2000—2009 годах — от 12,0 до 26,6 млн квадратных километров, в 1990—1999 годах — от 18,8 до 25,9 млн квадратных километров).
What Is The Hole In The Ozone - Part 2 | Environmental Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
YouTube › FuseSchool - Global Education
What's up with the hole in the ozone layer?
What Ever Happened To The Hole In The Ozone Layer?
Here’s Why Repairing the Hole in the Ozone Layer Is Delayed by a Decade
So, what happened to the 'hole' in the Ozone layer?
Whatever happened to the hole in the ozone layer? | Global 3000
https://www.discovermagazine.com/.../whatever-happened-to-the-hole-in-the-ozone-layer
Перевести · 10.11.2020 · Certain human-made substances had reached the stratosphere and disrupted the ozone layer to the point of depletion, creating an extremely thin section commonly known as the ozone hole…
https://www.eartheclipse.com/environment/causes-and-effects-ozone-depletion.html
Перевести · What is the Ozone Hole? Ozone hole is the area of the Earth’s atmosphere where abnormal reductions of ozone occur…
РекламаВсегда новые скидки и акции. Заходи скорее! · Краснодар
Озо́н — состоящая из трёхатомных молекул O₃ ал…
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Images, data, and information for atmospheric ozone
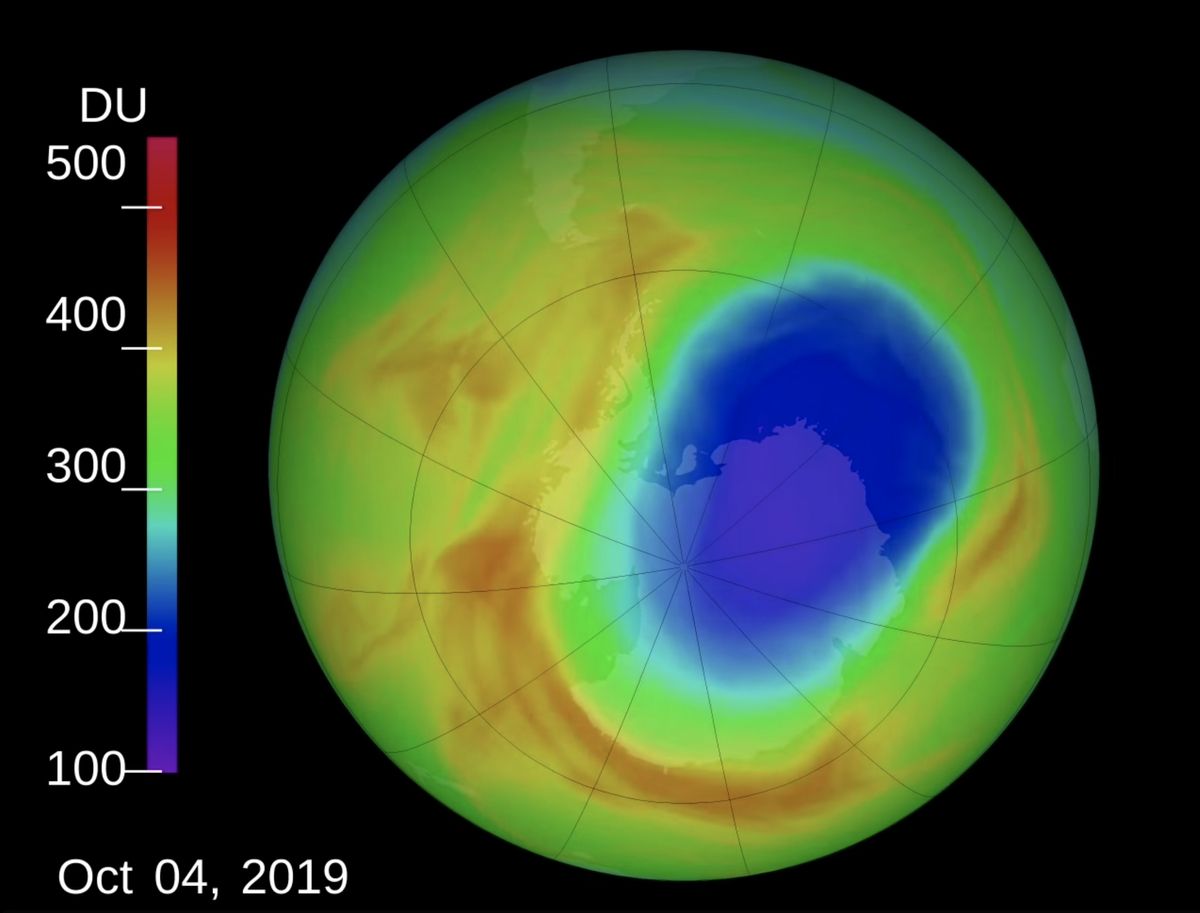
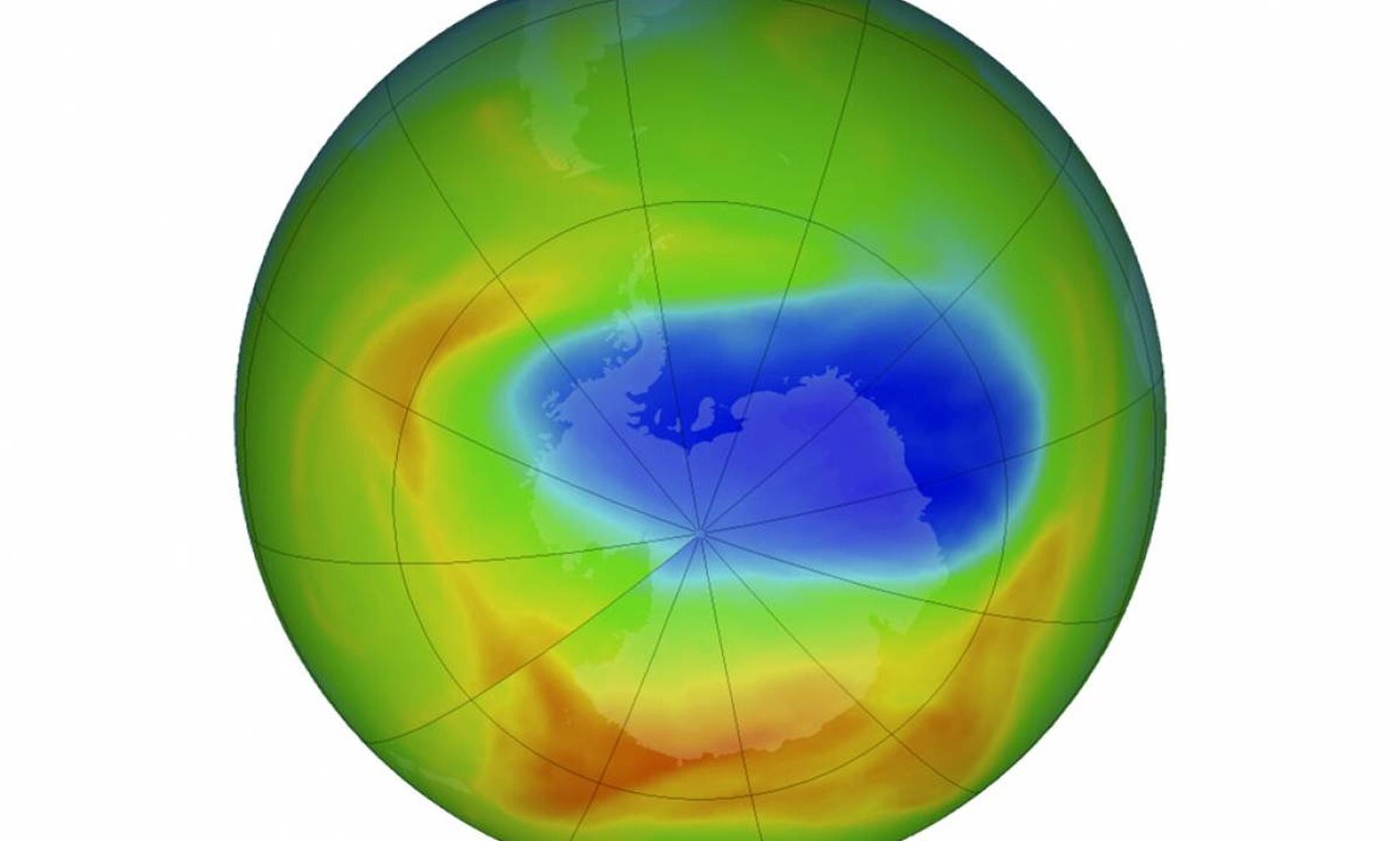
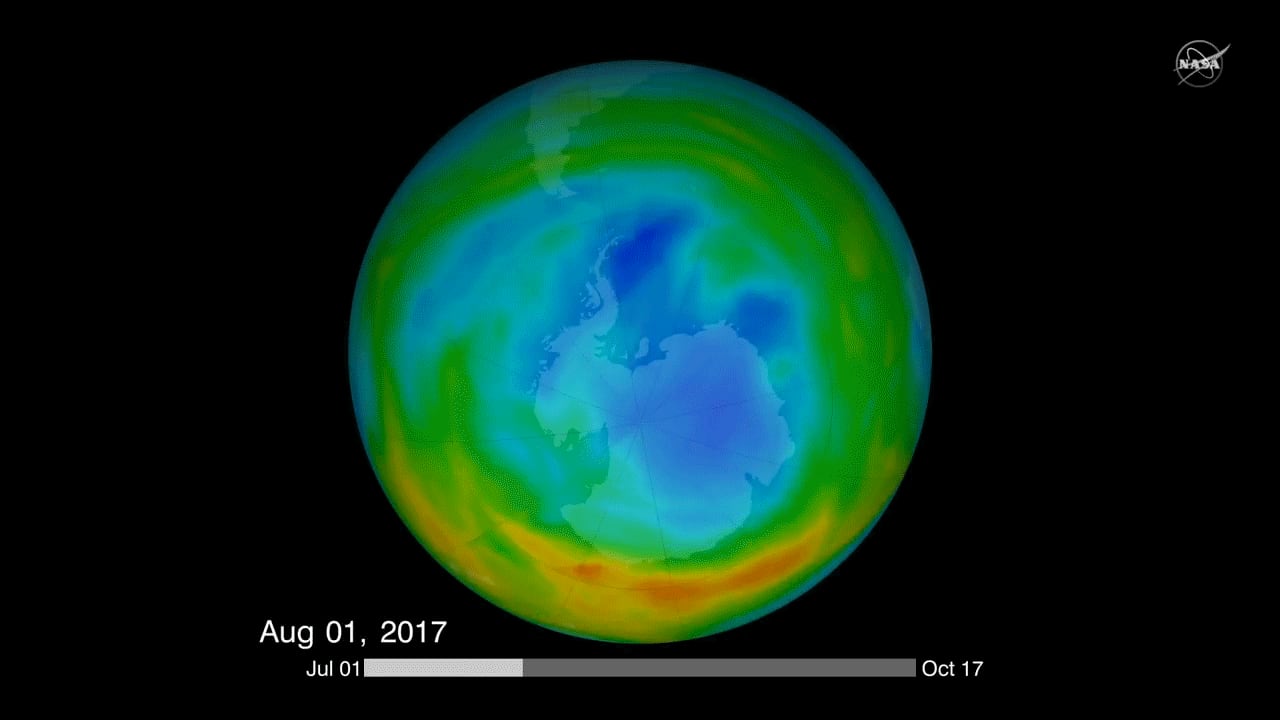
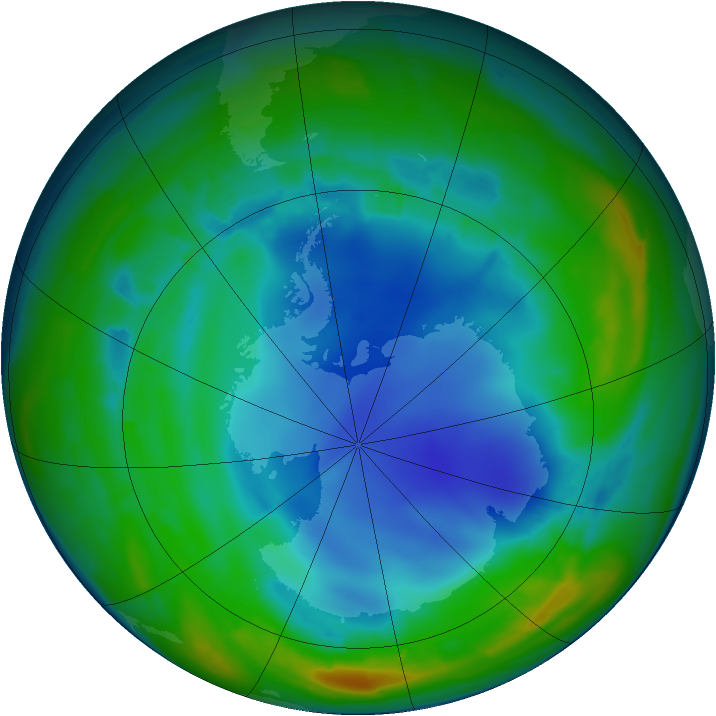
The ozone hole is not technically a “hole” where no ozone is present, but is actually a region of exceptionally depleted ozone in the stratosphere over the Antarctic that happens at the beginning of Southern Hemisphere spring (August–October). Satellite instruments provide us with daily images of ozone over the Antarctic region. The ozone hole image below shows the very low values (blue and purple colored area) centered over Antarctica on 4 October 2004. From the historical record we know that total column ozone values of less than 220 Dobson Units were not observed prior to 1979. From an aircraft field mission over Antarctica we also know that a total column ozone level of less than 220 Dobson Units is a result of catalyzed ozone loss from chlorine and bromine compounds. For these reasons, we use 220 Dobson Units as the boundary of the region representing ozone loss. Using the daily snapshots of total column ozone, we can calculate the area on the Earth that is enclosed by a line with values of 220 Dobson Units (the white line in the figure below).
The ozone hole is the region over Antarctica with total ozone of 220 Dobson Units or lower. This map shows the ozone hole on October 4, 2004. The data were acquired by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument on NASA’s Aura satellite.
Many people have heard that the ozone hole is caused by chemicals called CFCs, short for chlorofluorocarbons. CFCs escape into the atmosphere from refrigeration and propellant devices and processes. In the lower atmosphere, they are so stable that they persist for years, even decades. This long lifetime allows some of the CFCs to eventually reach the stratosphere. In the stratosphere, ultraviolet light breaks the bond holding chlorine atoms (Cl) to the CFC molecule. A free chlorine atom goes on to participate in a series of chemical reactions that both destroy ozone and return the free chlorine atom to the atmosphere unchanged, where it can destroy more and more ozone molecules. For those who know the story of CFCs and ozone, that is the part of the tale that is probably familiar.
The part of the story that fewer people know is that while the chlorine atoms freed from CFCs do ultimately destroy ozone, the destruction doesn’t happen immediately. Most of the roaming chlorine that gets separated from CFCs actually becomes part of two chemicals that—under normalatmospheric conditions—are so stable that scientists consider them to be long-term reservoirs for chlorine. So how does the chlorine get out of the reservoir each spring?
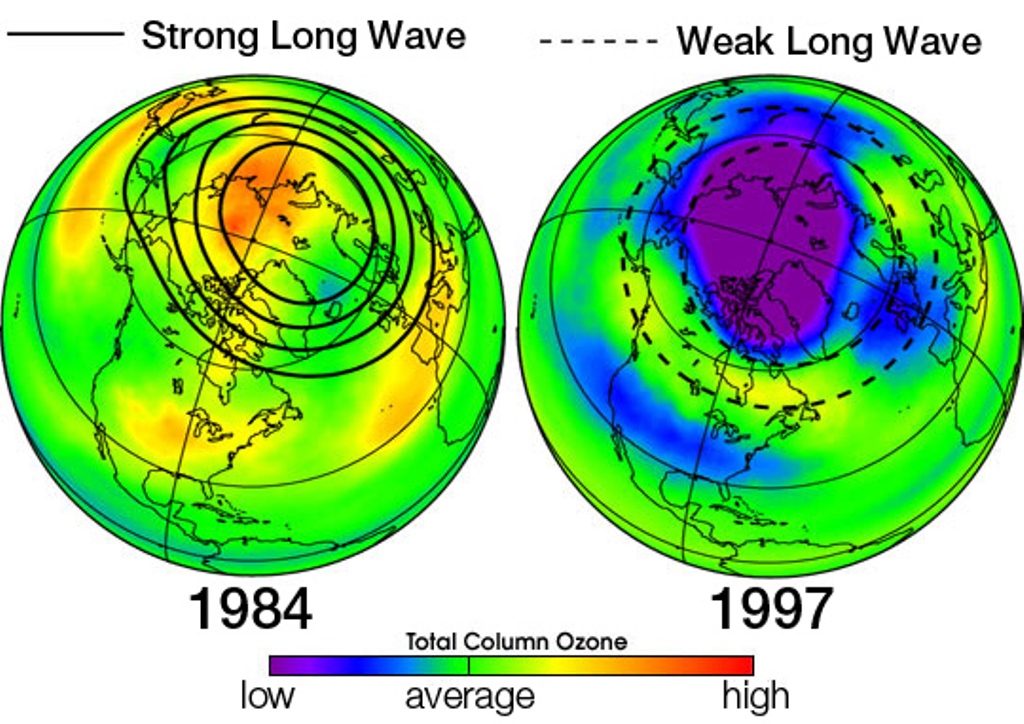
Under normal atmospheric conditions, the two chemicals that store most atmospheric chlorine (hydrochloric acid, and chlorine nitrate) are stable. But in the long months of polar darkness over Antarctica in the winter, atmospheric conditions are unusual. An endlessly circling whirlpool of stratospheric winds called the polar vortex isolates the air in the center. Because it is completely dark, the air in the vortex gets so cold that clouds form, even though the Antarctic air is extremely thin and dry. Chemical reactions take place that could not take place anywhere else in the atmosphere. These unusual reactions can occur only on the surface of polar stratospheric cloud particles, which may be water, ice, or nitric acid, depending on the temperature.
The frozen crytals that make up polar stratospheric clouds provide a surface for the reactions that free chlorine atoms in the Antarctic stratosphere.
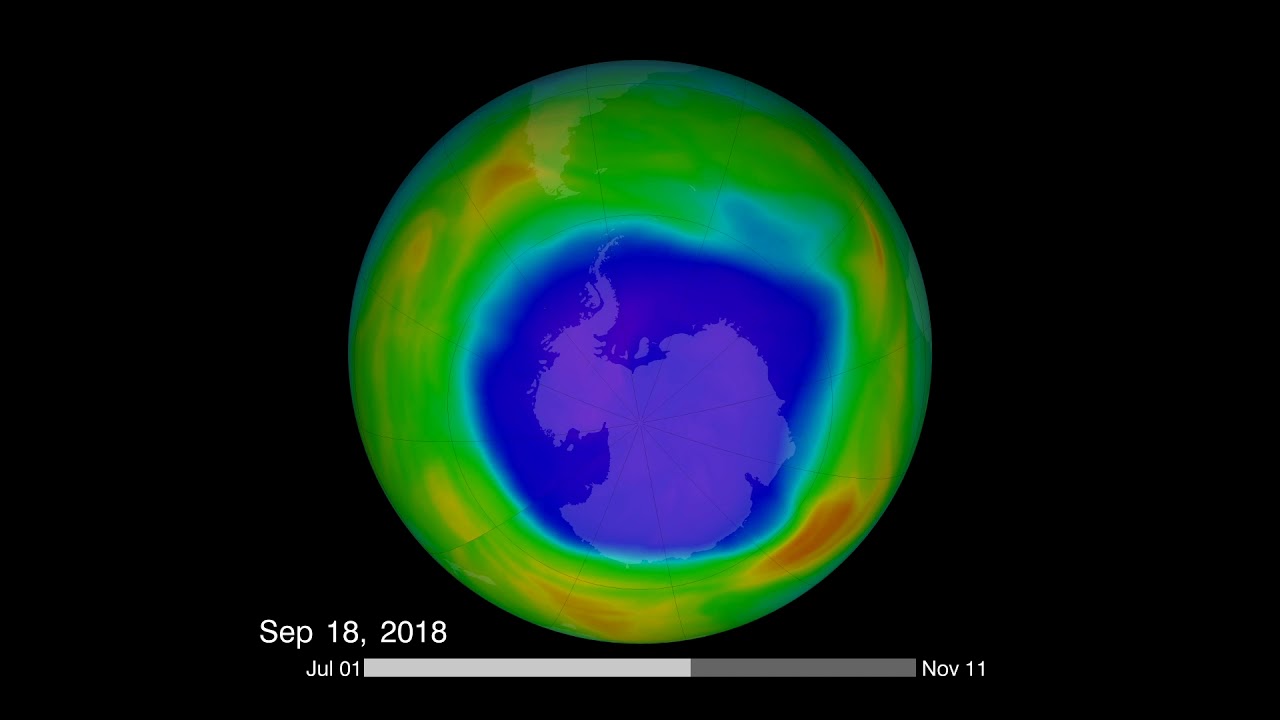
These reactions convert the inactive chlorine reservoir chemicals into more active forms, especially chlorine gas (Cl2). When the sunlight returns to the South Pole in October, UV light rapidly breaks the bond between the two chlorine atoms, releasing free chlorine into the stratosphere, where it takes part in reactions that destroy ozone molecules while regenerating the chlorine (known as a catalytic reaction). A catalytic reaction allows a single chlorine atom to destroy thousands of ozone molecules. Bromine is involved in a second catalytic reaction with chlorine that contributes a large fraction of ozone loss. The ozone hole grows throughout the early spring until temperatures warm and the polar vortex weakens, ending the isolation of the air in the polar vortex. As air from the surrounding latitudes mixes into the polar region, the ozone-destroying forms of chlorine disperse. The ozone layer stabilizes until the following spring.
NASA Official: Paul A. Newman
Curator: Eric R. Nash (SSAI)
Page Last Updated: 2018-10-18
Please credit all material to “NASA Ozone Watch” unless otherwise noted.
Deepthroat Gag Porn
Porno French Hairy Mom Anal
Black Hole Trout Mania
Perfect Grandma Porno
Around Handjob
Nasa Ozone Watch: Ozone hole facts
What Is The Ozone Hole? - WorldAtlas
The 2020 Update on the Hole in the Ozone Layer | Earth.Org ...
Record-breaking 2020 ozone hole closes | World ...
Whatever Happened to the Hole in the Ozone Layer ...
What is an Ozone Hole and Causes and Effects of Ozone ...
The Hole In The Ozone Layer