The History of the FIFA Women’s World Cup
 FIFA Women’s World Cup Timeline: 1991‒2019
FIFA Women’s World Cup Timeline: 1991‒2019The ninth edition of the FIFA Women’s World Cup that kicked off this summer in Australia and New Zealand is expected to break records.
For the first time, 32 teams are competing at the premier international event for women’s soccer, up from 24 teams in the two prior editions. And according to FIFA, the tournament is already on pace to become the most attended women’s sports event in history, with over a million tickets already sold.
Eight countries are making their debut in the tournament after qualifying for the first time:
- Philippines
- Ireland
- Zambia
- Haiti
- Vietnam
- Portugal
- Panama
- Morocco
How has the tournament grown?
This graphic created by JVDW Designs explores the timeline of this tournament, from its origins with only 12 teams in 1991 to expansions during the 21st century.
The Origins of Women’s SoccerThough there are reports of women’s soccer matches as early as the 1700s, the sport started to grow in popularity in 1895 thanks to the British Ladies’ Football Club (BLFC), one of the first women’s soccer clubs.
Despite receiving no support from soccer associations in the UK, the club held its inaugural match in London and then went on tour. They received a lot of attention in the press, both due to the sport itself and debates in Victorian England over women’s rights.
After gaining in popularity over the next decades and even drawing bigger crowds than men’s matches, England’s governing soccer association retaliated by banning women’s soccer in 1921. The stated reason was that “the game of football is quite unsuitable for females and ought not to be encouraged.”
Other countries followed suit over time, sidelining women’s soccer from France to Brazil. It wasn’t until the success of the 1966 Men’s World Cup in England, which set records for attendance and was the first to be broadcast to other continents, that England and then other countries in Europe re-established women’s soccer due to increased interest.
The FIFA Women’s World CupAfter multiple international tournaments in the 1970s and 1980s, FIFA finally organized the inaugural FIFA Women’s World Cup in China in 1991.
At the outset, the athletes participating in the Women’s World Cup were not treated as professionals. In her 2019 book, sports journalist Caitlyn Murray details that uniforms were sometimes hand-me-downs from men’s teams, and accommodations during travel were far from luxurious. Notably, the tournament also lacked prize money until 2007.
In total, 35 different national teams have participated in at least one of the eight tournaments held through 2019. Here is the full list, with host countries noted in bold:
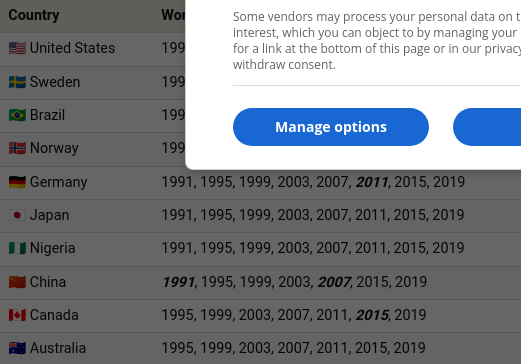
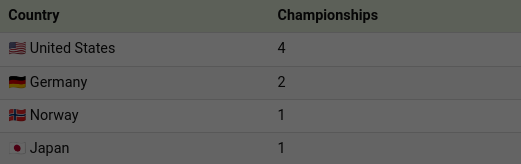
From the onset, the U.S. emerged as dominant forces in the women’s game. They won the inaugural official tournament in 1991 and are one of just seven countries that have qualified for each edition of the Women’s World Cup from 1991 to 2019.
In total, the American side has won four FIFA Women’s World Cups so far. Throughout the tournament’s history, they’ve never finished lower than third place.
The all-time leading World Cup goal scorer, however, comes from Brazil. Marta Vieira da Silva, or “Queen Marta,” etched her name in history by scoring an impressive 17 goals across five World Cups for Brazil, surpassing the men’s World Cup goalscoring record of 16 goals.
As the ninth edition unfolds, the tournament’s growth and global appeal continue to soar. With an even brighter future in the cards for women’s soccer, the question remains: who will come out on top in the 2023 Women’s World Cup?
The post The History of the FIFA Women’s World Cup appeared first on Visual Capitalist.
