Success Rates of Surrogate Mother
Understanding SurrogacyAs you consider the intricate steps of the IVF fertilization process, envision the precision involved in selecting the best sperm and eggs for successful fertilization in a controlled laboratory setting. The journey from initial fertilization to the development of viable embryos is a fascinating one, with each stage carefully monitored for quality and potential. Understanding this process sheds light on the complexities of fertility treatments and the delicate balance required for achieving positive outcomes.
Egg Retrieval and Sperm Collection
During the IVF fertilization process, the important step of egg retrieval and sperm collection is conducted to gather the necessary reproductive materials for the procedure. Ovulation induction is initiated to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization. Sperm analysis is vital to assess the quality and quantity of sperm available for fertilization. This analysis helps determine the best course of action to optimize the chances of successful fertilization.
Throughout the process, monitoring follicle growth is essential. Follicles are fluid-filled sacs within the ovaries that contain developing eggs. The growth and development of these follicles are closely monitored through ultrasound scans and hormone level assessments. This monitoring ensures that the eggs are retrieved at the best time for fertilization.
Egg quality is a critical factor in the IVF process. The quality of the eggs retrieved directly impacts the chances of successful fertilization and embryo development. Specialized techniques are used to assess the maturity and quality of the eggs before fertilization occurs.
Simultaneously, semen preparation is carried out to make sure that the sperm is in the best possible condition for fertilization. The sperm sample is processed to separate healthy, motile sperm from seminal fluid and debris, enhancing the chances of successful fertilization when combined with the retrieved eggs.
Fertilizations in the Laboratory
In the laboratory setting, the process of fertilization involves the careful and controlled introduction of sperm to the retrieved eggs for potential embryo development. Sperm selection is a vital step where the healthiest and most motile sperm are chosen to increase the chances of successful fertilization. On the other hand, egg preparation ensures that the eggs are in excellent condition for fertilization, often involving removing surrounding cells to allow better access for sperm.
Fertilization techniques such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used if there are concerns about the sperm's ability to fertilize the egg naturally. Genetic testing can also be performed at this stage to screen for any genetic abnormalities before fertilization. The culture conditions in the laboratory play a critical role in supporting embryo development, providing the necessary nutrients and environment for optimal growth. Embryo quality is closely monitored to select the most viable embryos for transfer.
Fertilization rates are calculated by checking the number of successfully fertilized eggs, indicating the efficiency of the process. Regular fertilization checks are conducted to assess the progress and adjust techniques if needed. Timing is crucial in fertilization to ensure that the sperm and egg are at their peak fertility, increasing the chances of fertilization success. By meticulously managing these aspects, the laboratory can optimize the fertilization process and improve the chances of successful embryo development.
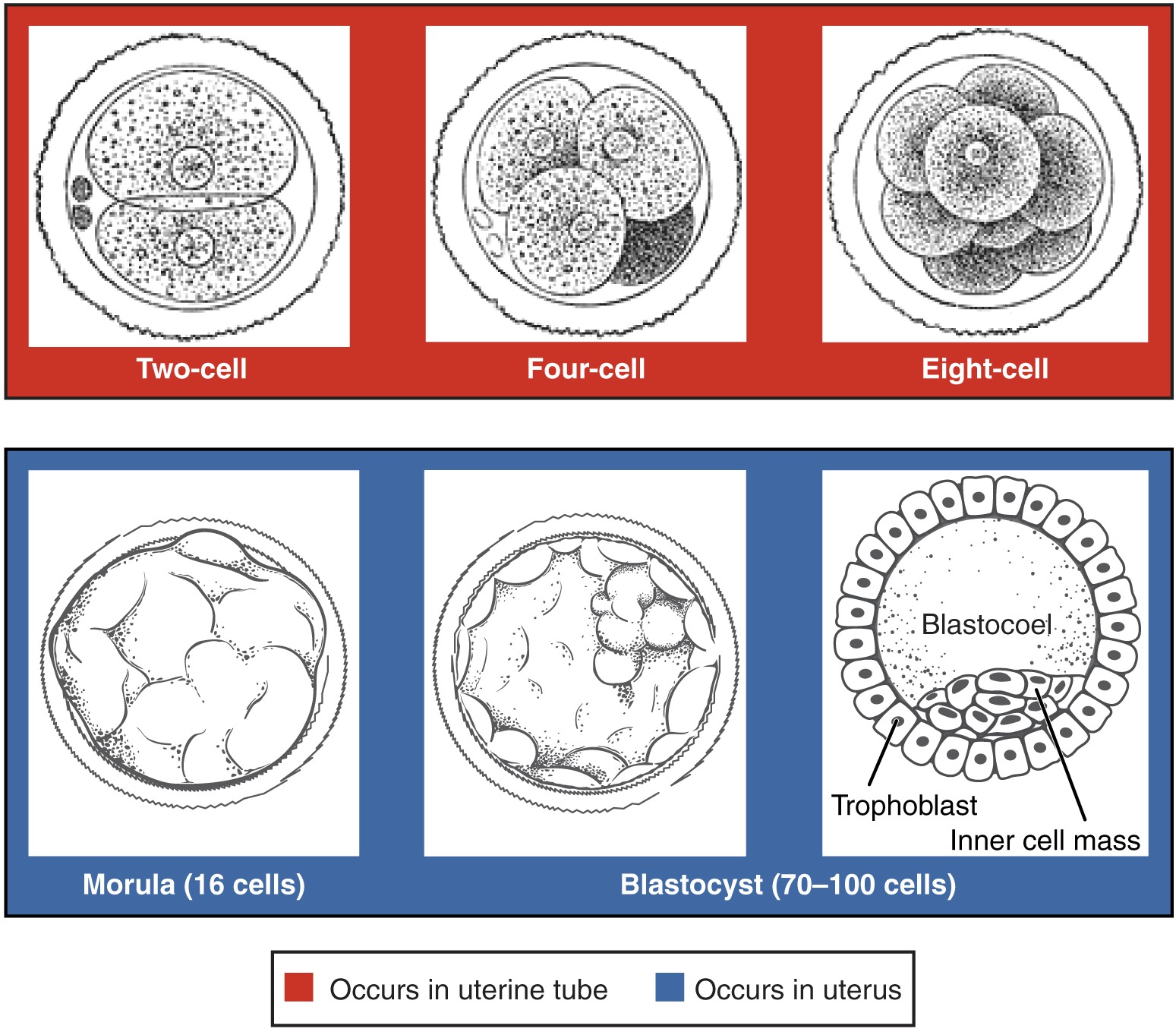
Embryo Development and Monitoring
Embryo development and monitoring require precise observation of growth and quality indicators to guarantee ideal conditions for successful transfer. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes multiple rounds of cell division, progressing from a single cell to a multicellular embryo. This pivotal phase involves meticulous monitoring to assess the rate and pattern of cell division, ensuring proper development. Genetic testing may be conducted at this stage to screen for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic disorders, enhancing the selection of healthy embryos for implantation.
As the embryo matures, it undergoes blastocyst formation, where it develops a fluid-filled cavity and two distinct cell types. This stage marks a significant milestone in embryonic development, indicating the readiness of the embryo for potential implantation. Monitoring the growth and expansion of the blastocyst is crucial to assess its quality and viability for transfer. Additionally, the implantation process is a critical step where the blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall, establishing a pregnancy.
Continuous growth monitoring is essential throughout the development process to track the embryo's progression and ensure it meets the necessary criteria for transfer. By closely observing key indicators like cell division, genetic makeup, blastocyst formation, and implantation potential, healthcare providers can optimize the chances of a successful IVF procedure.
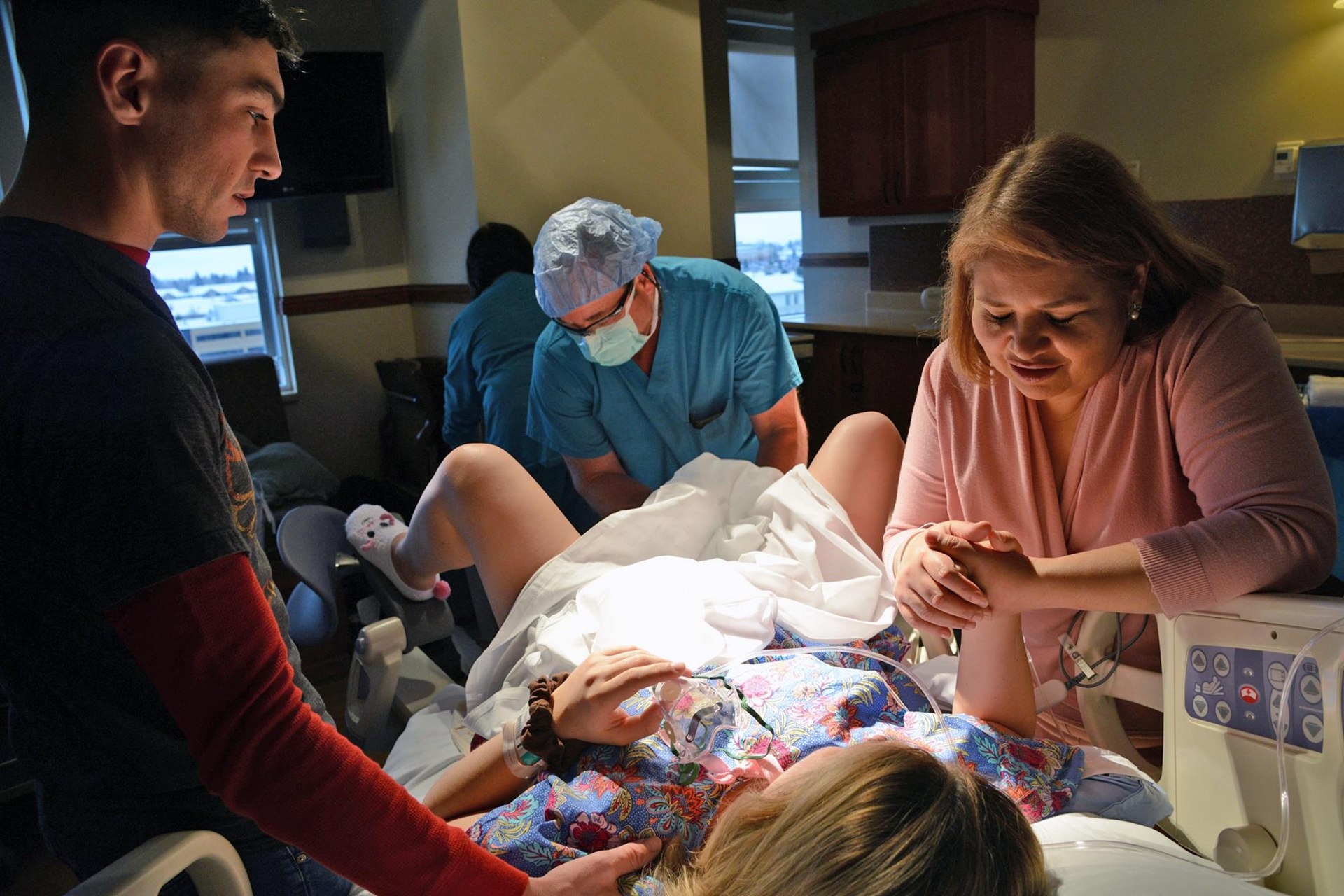

Embryo Transfer Process
Monitoring the progress of the embryo transfer process involves evaluating key parameters to optimize successful implantation and pregnancy establishment. The transfer procedure is a critical step in IVF treatment, where embryos are delicately placed into the uterus to enhance implantation success. This step is meticulously carried out to guarantee the best possible outcomes for the patient.
The uterine environment plays an essential role in determining the success of embryo implantation. Factors such as the thickness of the endometrial lining and the receptivity of the uterus are important in facilitating successful implantation. By carefully evaluating the uterine environment before the transfer, healthcare providers can improve the chances of implantation success.
Embryo quality is another crucial aspect to consider during the transfer process. High-quality embryos have a higher likelihood of implanting successfully, leading to increased pregnancy chances. Healthcare providers closely examine the embryos to select the most viable ones for transfer, maximizing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Throughout the transfer process, healthcare providers focus on optimizing the conditions for successful implantation and pregnancy establishment. By paying close attention to the transfer procedure, uterine environment, embryo quality, and overall pregnancy chances, healthcare teams aim to enhance the likelihood of a positive outcome for individuals undergoing IVF treatment.
Achieving a Successful Pregnancy
To optimize the likelihood of a successful pregnancy following the embryo transfer process, careful attention must be given to the conditions supporting implantation and early development. Hormone therapy plays an essential role in preparing the uterine lining for implantation. By carefully timing the administration of hormones such as progesterone, which supports the early stages of pregnancy, the chances of successful implantation can be greatly increased.
Genetic testing of embryos before transfer can also enhance the success of pregnancy. This testing, known as preimplantation genetic testing (PGT), helps identify chromosomal abnormalities or genetic conditions in embryos, allowing for the selection of the healthiest embryos with the highest potential for successful implantation and development.
Additionally, the use of frozen embryos can positively impact implantation success. Frozen embryo transfers have been shown to have comparable success rates to fresh embryo transfers, offering the flexibility to optimize the timing of the transfer based on the recipient's hormonal cycle.
In cases where carrying a pregnancy is not possible, gestational surrogacy can be a viable option. This involves the transfer of embryos created through IVF into the uterus of a surrogate who carries the pregnancy to term. Gestational surrogacy allows individuals or couples struggling with infertility to achieve their dream of parenthood by utilizing the assistance of a surrogate to carry the pregnancy to term.
To sum up, the IVF fertilization process involves meticulous selection of healthy sperm and eggs, followed by laboratory fertilization and embryo monitoring. Techniques like ICSI and genetic testing maximize the best chances for successful embryo development. The goal is to transfer viable embryos for implantation, optimizing conditions for a successful pregnancy. By focusing on the quality and viability of embryos, healthcare providers aim to enhance the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy through IVF.