Spread Risk

⚡ ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Spread Risk
Reviewed by: Ryan Cockerham, CISI Capital Markets and Corporate Finance
Copyright 2021 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved.
If you're investing in bonds or making someone a loan, you might be concerned with default risk and credit spread risk. Default risk is the danger that a company that's issued a bond or taken out a loan won't pay it back according to its terms, costing you money. Spread risk refers to the danger that the interest rate on a loan or bond turns out to be too low relative to an investment with a lower default risk for it to be a good use of funds.
Both default risk and spread risk are tools used to measure the potential validity of an investment with respect to the possibility that it will result in a loss of principal. Whereas default risk evaluates the likelihood that an individual or organization will not be able to pay back the principal, a spread risk is used to measure the likelihood that the value of an investment instrument will be negatively impacted by the counterparty in question.
If you invest in bonds, make individual loans or otherwise get involved in the credit markets, you're generally doing so in the expectation that you'll get paid back over time according to certain spelled-out terms. If a company borrows money and doesn't pay back the principal and interest as it's promised to, it's said to be in default.
Credit ratings help to measure a company or individual's risk of default, but there's still always a risk that some unforeseen event can force someone to stop paying a loan or bond as promised. Not every default means that investors or lenders will never be paid back, since people and organizations can recover from temporary financial problems, but defaults are almost always unpleasant for anyone relying on steady income from an investment.
Companies more likely to default on loans generally must pay higher interest rates, which if they do continue to make payments, can be rewarding for investors willing to stomach the default risk.
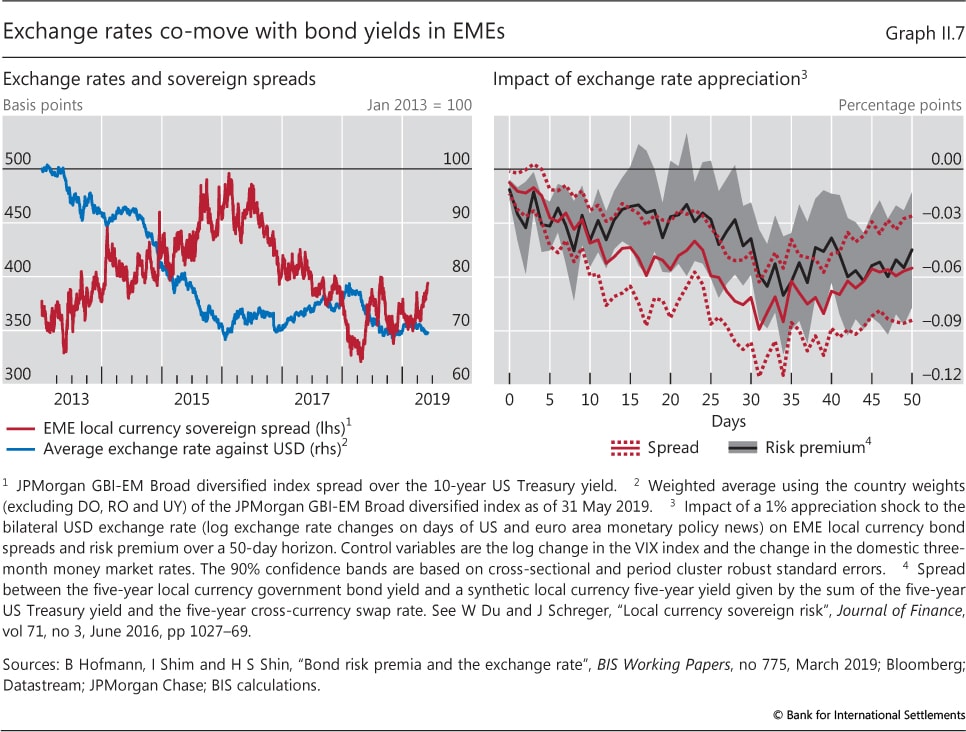
One way to evaluate the interest rate on a bond or loan is to compute what's called a credit spread. That's the difference in interest rates between two loans or bonds that mature at the same time. Often credit spreads are computed between corporate or municipal bonds and U.S. Treasury bonds, considered to be among the safest securities to invest in. Computing spreads against Treasury bonds rather than looking at raw interest rate numbers is useful as a way to evaluate potential investments, regardless of whether interest rates in general are historically high or low.
Riskier loans pay higher interest rates and thus carry higher spreads. When people are more concerned about defaults in general, such as when the economy is entering a recession, credit spreads tend to be higher since people are less willing to take on riskier investments, and organizations looking to borrow money have to pay relatively higher interest rates to get investors to take that risk.
Spread risk refers to the risk that the credit spread for a particular investment turns out not to be high enough to justify investing in that particular loan or bond versus other, lower default risk investments, causing the investment to be less worthwhile. For example, if an investor buys a corporate bond with a 3 percentage point credit spread above the comparable Treasury bond, and that premium later drops to 1 percentage point, the value of the bond will drop since investors will be less inclined to take on the added default risk for that smaller spread.
spread risk - английский определение, грамматика, произношение... | Glosbe
Default Risk Vs. Spread Risk
In what types of financial situations would credit spread risk be...
spread risk 🎓 перевод с английского на русский
spread risk - Russian translation – Linguee
Sponsored
Compete Risk Free with $100,000 in Virtual Cash
Put your trading skills to the test with our
FREE Stock Simulator.
Compete with thousands of Investopedia traders and trade your way to the top! Submit trades in a virtual environment before you start risking your own money.
Practice trading strategies
so that when you're ready to enter the real market, you've had the practice you need.
Try our Stock Simulator today >>
A credit rating is an assessment of the creditworthiness of a borrower—in general terms or with respect to a particular debt or financial obligation.
A credit default swap (CDS) is a particular type of swap designed to transfer the credit exposure of fixed income products between two or more parties.
Junk bonds are debt securities rated poorly by credit agencies, making them higher risk (and higher yielding) than investment grade debt.
Risk takes on many forms but is broadly categorized as the chance an outcome or investment's actual return will differ from the expected outcome or return.
Delivery risk refers to the chance that one side may not fulfill its end of the agreement by not delivering an asset or cash value of the contract.
Counterparty risk is the likelihood or probability that one of those involved in a transaction might default on its contractual obligation.
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Investopedia is part of the Dotdash publishing family.
Default risk and spread risk are the two components of credit risk , which is a type of counterparty risk. Think of default risk as more closely associated with the general conception of counterparty risk: noncompliance with the specifications and terms of a contract. Spread risk can be related to investment risk, such as when a price or yield changes as a result of a change in credit rating.
Credit spread risk is not the same thing as the risks associated with a credit spread option , although there are credit spread risks in a credit spread option. Credit spread options are a type of derivative where one party transfers credit risk to another party, usually in exchange for a promise to make cash payments if the credit spread changes. This type of contract is most common among debt securities that have low credit ratings.
Nearly every single loan or credit extension comes with a form of default risk. Default risk is measured by the likelihood an individual or company will not make contractual payments on a debt obligation. Default risk does not exist with financial transactions, for example, stock purchases, that have no guarantee of payment.
For a simple example of default risk, consider a borrower who takes out a $300,000 home loan. The bank that made the loan does not know with certainty whether the borrower will repay the loan on time, so it assumes default risk in the transaction. To compensate for default risk, an interest rate is applied to the loan and the bank may also require a sizable down payment.
Subject to a dispute in utmost good faith by the issuer, payment default represents a failure to pay any amount due of the reference asset or any other future indebtedness of the issuer for funds borrowed, raised or guaranteed. Bonds, loans, credit lines and even cash-on-delivery (COD) purchases all assume a kind of default risk.
Spread risks are not associated with contractual guarantees but rather originate from the intersection of interest rates, credit ratings and opportunity cost . There are really two types of spread risk, although they are not mutually exclusive.
The first kind, true spread risk, represents the likelihood the market value of a contract or a specific instrument is reduced based on the actions of the counterparty. If the issuer of a bond does not default on its bond obligations, but makes other financial mistakes that lower the issuer's credit rating, the value of the bonds likely drops. This risk is assumed by the investor.
The second type of spread risk comes from credit spreads . Credit spreads are the difference between yields of various debt instruments. The lower the default risk, the lower the required interest rate; higher default risks come with higher interest rates. The opportunity cost of accepting lower default risk, therefore, is higher interest income. Credit spread risk is an important but often ignored component of income investing.
Japan Moms Sleep Porn
Private Shooting
Girls Have Fuck Sperm Blowjob Himself Shamel
Outdoor 64
Sex Porno Ass