Spread Order

🛑 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Spread Order
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
^ "Spreads – definition" . Riskglossary.com. Archived from the original on 2012-08-15 . Retrieved 2019-04-24 .
^ Demsetz, H. 1968. "The Cost of Transacting." Quarterly Journal of Economics 82: 33–53 [1] doi : 10.2307/1882244 JSTOR 1882244
^ Lee, Charles M. C. (July 1993). "Market Integration and Price Execution for NYSE-Listed Securities". The Journal of Finance . 48 (3): 1009–1038. doi : 10.2307/2329024 . ISSN 0022-1082 . JSTOR 2329024 .
^ Lee, Charles M. C.; Ready, Mark J. (June 1991). "Inferring Trade Direction from Intraday Data" . The Journal of Finance . 46 (2): 733. doi : 10.2307/2328845 . ISSN 0022-1082 . JSTOR 2328845 .
^ Huang, Roger D.; Stoll, Hans R. (July 1996). "Dealer versus auction markets: A paired comparison of execution costs on NASDAQ and the NYSE". Journal of Financial Economics . 41 (3): 313–357. doi : 10.1016/0304-405x(95)00867-e . ISSN 0304-405X .
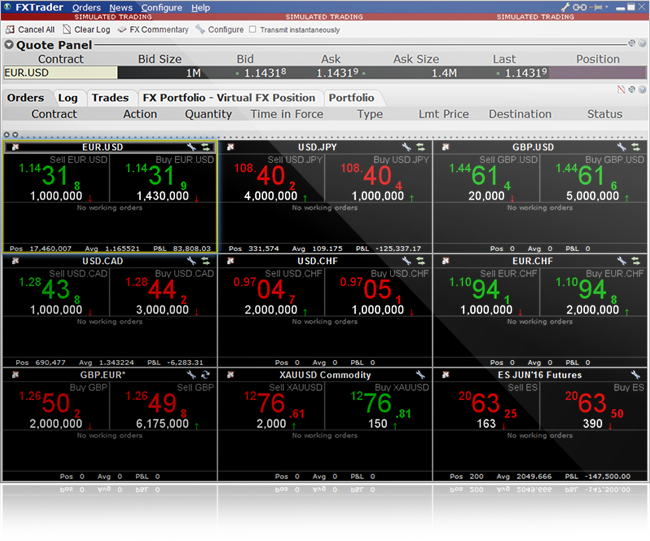
The bid–ask spread (also bid–offer or bid/ask and buy/sell in the case of a market maker ) is the difference between the prices quoted (either by a single market maker or in a limit order book ) for an immediate sale ( offer ) and an immediate purchase ( bid ) for stocks , futures contracts , options , or currency pairs . The size of the bid–ask spread in a security is one measure of the liquidity of the market and of the size of the transaction cost . [1] If the spread is 0 then it is a frictionless asset .
The trader initiating the transaction is said to demand liquidity , and the other party ( counterparty ) to the transaction supplies liquidity. Liquidity demanders place market orders and liquidity suppliers place limit orders . For a round trip (a purchase and sale together) the liquidity demander pays the spread and the liquidity supplier earns the spread. All limit orders outstanding at a given time (i.e. limit orders that have not been executed) are together called the Limit Order Book. In some markets such as NASDAQ , dealers supply liquidity. However, on most exchanges, such as the Australian Securities Exchange , there are no designated liquidity suppliers, and liquidity is supplied by other traders. On these exchanges, and even on NASDAQ, institutions and individuals can supply liquidity by placing limit orders.
The bid–ask spread is an accepted measure of liquidity costs in exchange traded securities and commodities. On any standardized exchange, two elements comprise almost all of the transaction cost —brokerage fees and bid–ask spreads. Under competitive conditions, the bid–ask spread measures the cost of making transactions without delay. The difference in price paid by an urgent buyer and received by an urgent seller is the liquidity cost. Since brokerage commissions do not vary with the time taken to complete a transaction, differences in bid–ask spread indicate differences in the liquidity cost. [2]
The simplest type of bid-ask spread is the quoted spread. This spread is taken directly from quotes, that is, posted prices. Using quotes, this spread is the difference between the lowest asking price (the lowest price at which someone will sell) and the highest bid price (the highest price at which someone will buy). This spread is often expressed as a percent of the midpoint, that is, the average between the lowest ask and highest bid:
Quoted Spread
=
ask
−
bid
midpoint
×
100
{\displaystyle {\text{Quoted Spread}}={\frac {{\hbox{ask}}-{\hbox{bid}}}{\hbox{midpoint}}}\times 100}
.
Quoted spreads often over-state the spreads finally paid by traders, due to "price improvement", that is, a dealer offering a better price than the quotes, also known as "trading inside the spread". [3] Effective spreads account for this issue by using trade prices, and are typically defined as:
Effective Spread
=
2
×
|
Trade Price
−
Midpoint
|
Midpoint
×
100
{\displaystyle {\text{Effective Spread}}=2\times {\frac {|{\hbox{Trade Price}}-{\hbox{Midpoint}}|}{\hbox{Midpoint}}}\times 100}
. The effective spread is more difficult to measure than the quoted spread, since one needs to match trades with quotes and account for reporting delays (at least pre-electronic trading). Moreover, this definition embeds the assumption that trades above the midpoint are buys and trades below the midpoint are sales. [4]
Quoted and effective spreads represent costs incurred by traders. This cost includes both a cost of asymmetric information, that is, a loss to traders that are more informed, as well as a cost of immediacy, that is, a cost for having a trade being executed by an intermediary. The realized spread isolates the cost of immediacy, also known as the "real cost". [5] This spread is defined as:
Realized Spread
k
=
2
×
|
Midpoint
k
+
1
−
Traded Price
k
|
Midpoint
k
×
100
{\displaystyle {\text{Realized Spread}}_{k}=2\times {\frac {|{\hbox{Midpoint}}_{k+1}-{\hbox{Traded Price}}_{k}|}{{\hbox{Midpoint}}_{k}}}\times 100}
where the subscript k represents the kth trade. The intuition for why this spread measures the cost of immediacy is that, after each trade, the dealer adjusts quotes to reflect the information in the trade (and inventory effects).
Inner price moves are moves of the bid-ask price where the spread has been deducted.
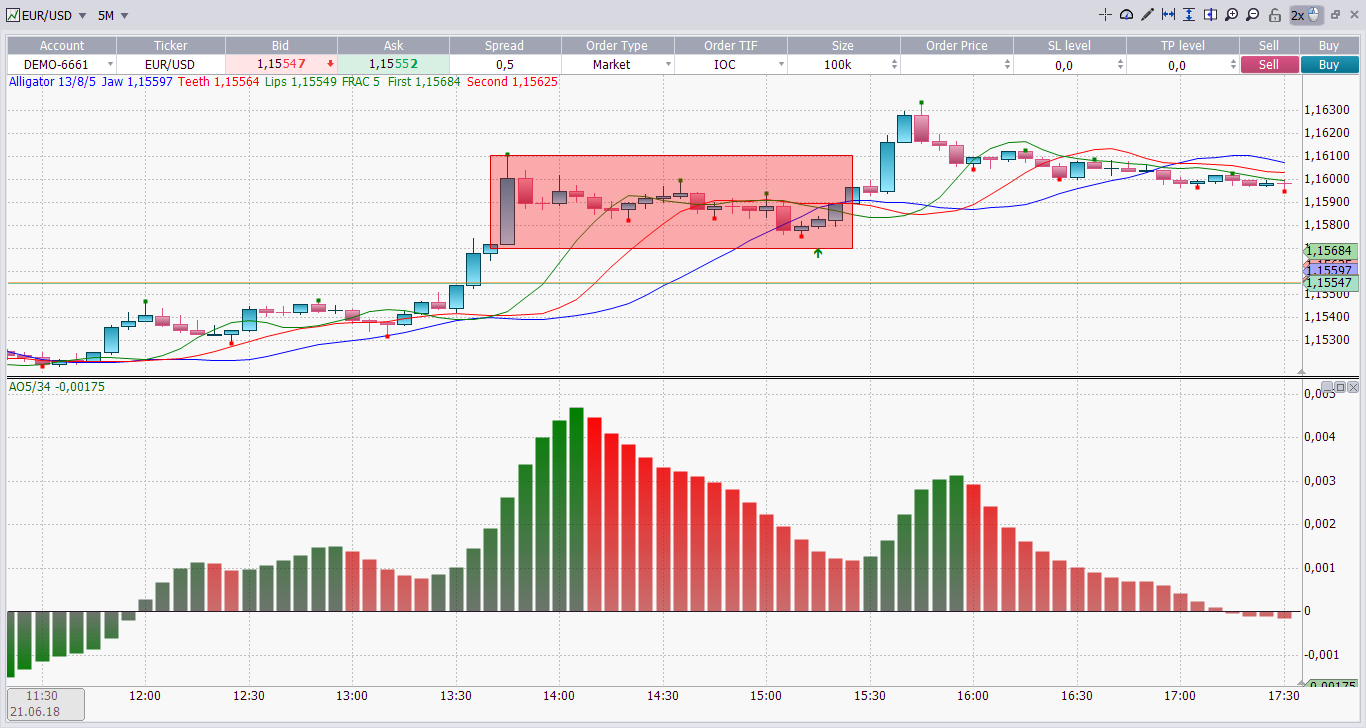
If the current bid price for the EUR/USD currency pair is 1.5760 and the current offer price is 1.5763, this means that currently you can sell the EUR/USD at 1.5760 and buy at 1.5763. The difference between those prices (3 pips ) is the spread.
If the USD/JPY currency pair is currently trading at 101.89/101.92, that is another way of saying that the bid for the USD/JPY is 101.89 and the offer is 101.92. This means that currently, holders of USD can sell 1 USD for 101.89 JPY and investors who wish to buy dollars can do so at a cost of 101.92 JPY per 1 USD.
spread order - это... Что такое spread order ?
Bid–ask spread - Wikipedia
Spread Order | Tradejini
spread order - определение - английский
Spread Definition
: help@tradejini.com
: +91-80-40204020 Call-n-Trade : +91-80-26086600
Sign in
IPO
Trade
Back Office
Partner
Career
FAQ
Downloads
Sidhanth
on January 18, 2019 at 3:12 am
Banu
on September 23, 2019 at 11:17 am
Prateek Gupta
on September 24, 2019 at 2:19 pm
RAVINDRAN
on February 10, 2020 at 11:56 am
Company
About us
Why Tradejini
Product & Services
Pricing
Support
Funds Transfer
FAQ
Trading Platform
Partner
Downloads
Forms
Software
Charges
Holidays
A spread order is an advanced order that has multiple legs/orders within a single order. There are 2 types of spread orders
SP orders are used primarily for two reasons
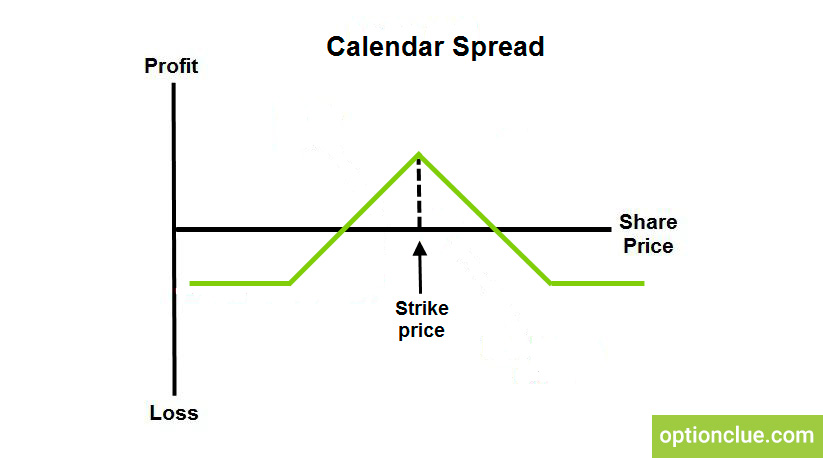
At its core, a calendar spread order performs two actions simultaneously
Here, the desired scrip/contract is of the same underlying.
Scrips of the same underlying with different expiry dates are available at different prices. This price difference is known as the Spread. Traders initiate a calendar spread order with the intention of profiting on the movement of this Spread.
Say Nifty Sept is trading at Rs.9800 and Nifty Oct is trading at Rs.9900, the price difference between these contracts, ie Rs.100 is known as the spread. And this is indicated as a different order called “calendar spread order of Nift Sep-Oct futures”
For example, If our trader wants to profit from the increase in spread, he/she will assume a long calendar spread position, where a sell position on Nifty Sept futures and a buy position on Nifty Oct Futures will be opened.
On the other hand, if our trader is looking to profit from the decline in the spread, he/she will assume a short calendar spread position, where a buy position on Nifty Sept Futures and a sell position on Nifty oct Futures will be opened.
Clear so far? No?... Read that again because we are just getting started.
From the example above, our budding trader performs his analysis and concludes that the spread between these two scripts is going to increase from Rs 100 to Rs 127. If his analysis proves right, he stands to make a profit of Rs.27. So naturally, in order to execute this trade, he is looking to start a long spread position, where he will have to sell Nifty Sept Futures and buy Nifty October Futures.
Now, there are two ways our trader can do this, and the implications of these ways can vary significantly. So pay special attention, we know you got the attention span...
The above two methods clearly illustrate the significant difference a Spread Order can bring to your own trading methods.
Important Note - When our trader initiates a long calendar spread position on Nifty Sep-Oct Futures, he/she will hold two open positions, i.e., a sell position on Nifty September futures and a buy position on Nifty October Futures. At this point, he is immune to vigorous market movements, since he’s holding two opposing positions on the same underlying. Now, when the Nifty Sept Futures contract expires on the last Thursday of September, the calendar spread order will turn into a naked buy position on Nifty October Futures, and this point our trader will now be prone to vigorous market movements.
A Roll Over is performed when a trader intends to carry his current month’s position to the next month. Similar to calendar spread order, rollover is performed on scrips/contracts of the same underlying.
The main difference between Calendar spread and Roll Over is that a Calendar Spread Order is a fresh order initiated by the trader to profit on the spread between two scrips/contracts. Whereas, a Roll Over is performed on an existing open position with the intention to prolong or carry the open position to the next available contracts.
A Roll Over performs two actions simultaneously,
For example, If our trader currently holds a long position on Nifty Sept Futures, in order to carry that position, he/she will have to close the long position on Nifty Sept Futures and initiate a long position on Nifty Oct Futures.
On the other hand, If our trader currently holds a short position on Nifty Sept Futures, in order to carry that position, he/she will have to close the short position on Nifty Sept Futures and initiate a short position on Nifty Oct Futures.
Our trader can either perform the above actions either manually or automate the process.
Pretty simple right?... No?... Alright, time for a scenario...
Our budding trader currently holds a long position on Nifty Sept Futures at Rs. 9100. Three days before expiry, he anticipates that the price can potentially move up further to Rs. 9500 in the coming month. If our trader can somehow hold this position, he could make potentially make a profit of Rs. 400. In order to execute this idea successfully, he is looking to close his existing position on Nifty Sept Futures and initiate a long position on Nifty Oct Futures.
There are two ways our budding trader can do this, and yet again, the implications of these methods can vary significantly.
The above two methods clearly show you how efficient it would be to use a spread order to perform a positioning roll over. It cuts out the risk of change in prices of the contract and allows for a Roll Over at a fixed price.
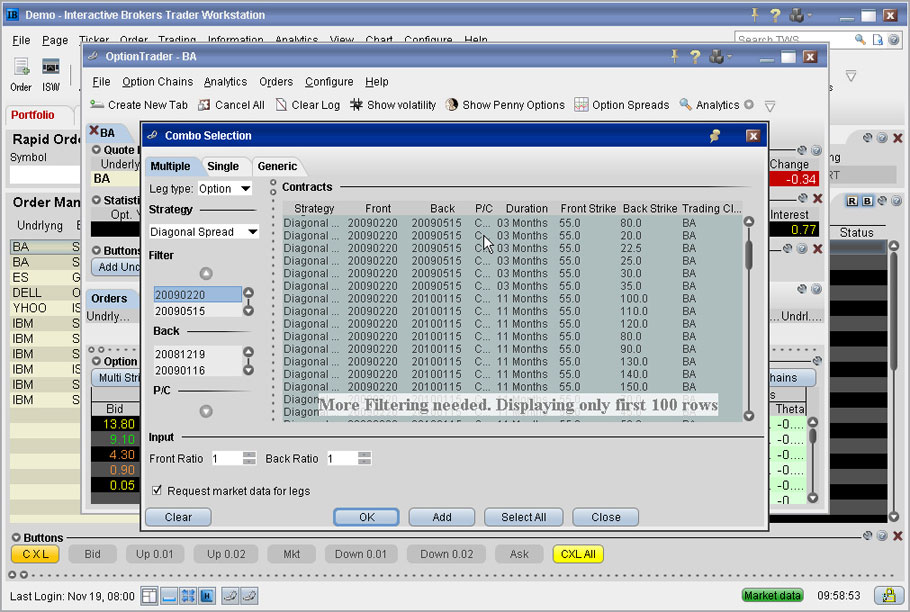
2L, 3L and 4L orders are multiple leg orders that comprise of two, three or four legs respectively, within the same order. These orders are mostly used for options trading, where traders can build strategies using multiple legs/ orders.
Note - Calendar spread and Roll over perform two actions simultaneously and are also considered as 2L orders. The main difference between SP type orders and 2L orders is that SP type orders must be based on the same underlying, whereas 2L orders need not be based on the same underlying.
In essence, 2L, 3L and 4L orders are IOC (Immediate or cancel) orders. This means that all the legs must execute for the order to be successfully executed. If anyone of the legs in the order fails to execute, then all the remaining orders automatically get canceled.
Let’s look at some examples. We shall choose Bank Nifty to illustrate this example.
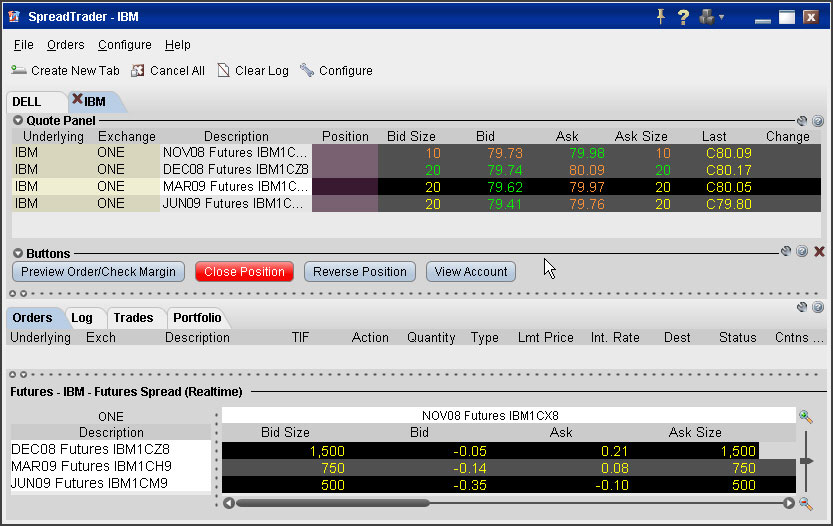
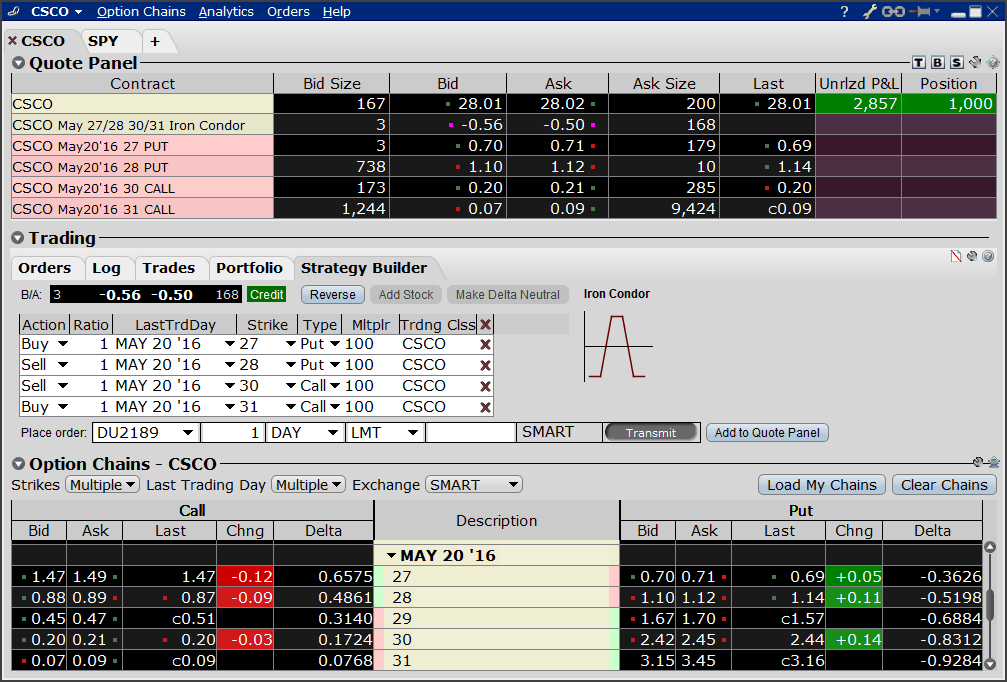
2L Order - A Long straddle is an option strategy that involves two legs and is displayed in the screenshot below. Here,
3L order - Covered Straddle is an option strategy that involves three legs and is displayed in the screenshot below. Here,
4L Orders - Long Butterfly is a popular options strategy that involves four legs and is displayed in the screenshot below. Here,
The above examples include only a few multiple-leg orders, among the thousands of strategies used in trading options. Additionally, orders placed on the same contract with the same buy/sell position on are not eligible in multiple-leg orders.
To place a Spread Order we must first add a spread scrip. We shall first learn how to add an SP type scrip and then how to place the order.
Open Nest Trader, Right Click on market watch window → Select “Start” and Click on “Add Scrips” tab OR press “Ctrl+S” → On the Scrip Bar, Under segments, Choose “NFO” → Under Order type select “SPREAD” → Select desired month’s script to add → “Enter”
Open Nest Trader, On the Menu Bar, → Click on “Orders and Trades” tab → Select “Spread Order” → Under order type, select “SP” for a calendar spread and position roll over OR select “2L, 3L or 4L” for multiple leg orders → Enter details → Click “Submit”
Open Nest Trader → Select the desired spread “Script” from market watch → Press the shortcut key “CTRL + Shift + F1” to open Spread Order Entry window → Under order type, select “SP” for calendar spread and position roll over OR select “2L, 3L or 4L” for multiple leg orders → Enter details → Click “Submit”.
Open Nest Trader → Right click on the spread “Script” from market watch → Click on “Buy Order Entry” to open Spread Order Entry window → Under order type, select “SP” for calendar spread and position roll over OR select “2L, 3L or 4L” for multiple leg orders → Enter details → Click “Submit”.
Modifying and Exiting a Spread Order
All pending spread orders can be modified or exited via Order Book. To Modify or Exit a spread order, open Order book either by using the shortcut key (F3) or click on “View Orders and Trades” button on the menu bar → Select “Order Book”.
Since multiple leg orders (2L, 3L, and 4L) are IOC orders, they cannot remain pending. So consequently, these orders cannot be modified once they are executed. To exit a multiple leg order, open Order book either by using the shortcut key (F3) or click on “View Orders and Trades” button on the menu bar → Select “Order Book”.
Watch the video below on how to place Spread Orders
Noteworthy points about Spread Orders
Very illustrative and easy to understand.
What is the premium collected for Long Bull spread of NIFTY options say the spread difference is 100. (11500 and 11600 each at strike of 140 and 100) with the diffrence is 40 at risk for the spread diff of 100 with max profit of 60.
Is it just 40 * lot size or different (excluding brokerage and STT, etc)?
Hi Bhanu, apart from Premium difference Bull call spread will attracts the Margin also. For Buying Nifty 11500 CE and selling 11600 CE required margin is Rs.76000.
Multiple leg orders are IOC (Immediate or cancel) orders, CAN WE PLACE IN DAY ORDER. PLS EXPLAIN.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
For more information about our products and services .
Vasavi Square, 2nd Floor, No.75/757, 10th Main Road, 4th Block, Jayanagar, Bangalore - 560011.
Suvas,No 4, Shankarmutt Road, 3rd Cross, Shankarpuram, Bangalore - 560004.
223, Vijay Enclave, 2nd Floor, TV Swamy Road East, R.S. Puram, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu - 641002.
SEBI REGISTRATION NO.: INZ000160938
(NSE: CM-FO-CD | BSE: CM-FO-CD | MCX: FO | MSEI: CM-FO-CD)
CDSL Depository Participant: IN-DP-470-2020
Please ensure you carefully read the Risk Disclosure Documents as prescribed by SEBI.
For any complaints email at complaints @tradejini.com.
"Prevent Unauthorized Transactions in your trading/demat account Update your Mobile Number/Email IDs with your Stock brokers/Depository Participant.Receive alerts/information of your transactions on your Registered Mobile/Email for all debit and other important transactions in your trading/demat account directly from Exchange/CDSL on the same day."
"KYC is one time exercise while dealing in securities markets - once KYC is done through a SEBI registered intermediary (broker, DP, Mutual Fund etc.),you need not undergo the same process again when you approach another intermediary."
No need to issue cheques by investors while subscribing to IPO.Just write the bank account number and sign in the application form to authorise your bank to make payment in case of allotment.No worry for refund as the money remains in investor's account.
This is to inform you as per Rules, Regulations and Bye-laws of Multi Commodity Exchange of India Ltd (MCX),that we do client based trading and proprietary trading.
Procedure to file a complaint on SCORES (Easy & quick). Register on SCORES portal and have the mandatory details for filing complaints on SCORES (Name, PAN, Address, Mobile Number and E-mail ID). Benefits: Effective Communication and Speedy redressal of the grievances.
Stock Brokers can accept securities as margin from clients only by way of pledge in the depository system w.e.f. September 01, 2020
Update your email id and mobile number with your stock broker / depository participant and receive OTP directly from depository on your email id and/or mobile number to create pledge
Check your securities / MF / bonds in the consolidated account statement issued by NSDL/CDSL every month
@2016 Tradejini | All Rights Reserved. Powered by FluidAgain
Real Double Penetration
Sexy Women Lingerie
Secretary Xazayn Selka Seks
Sex Japanese Xhamster
Public Babe Porn