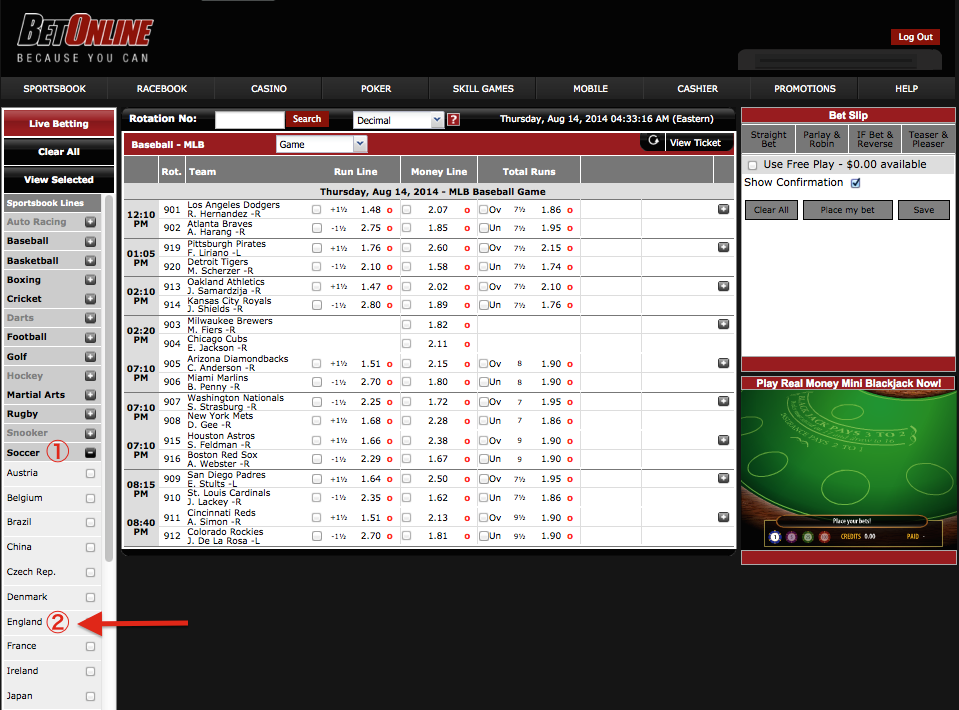
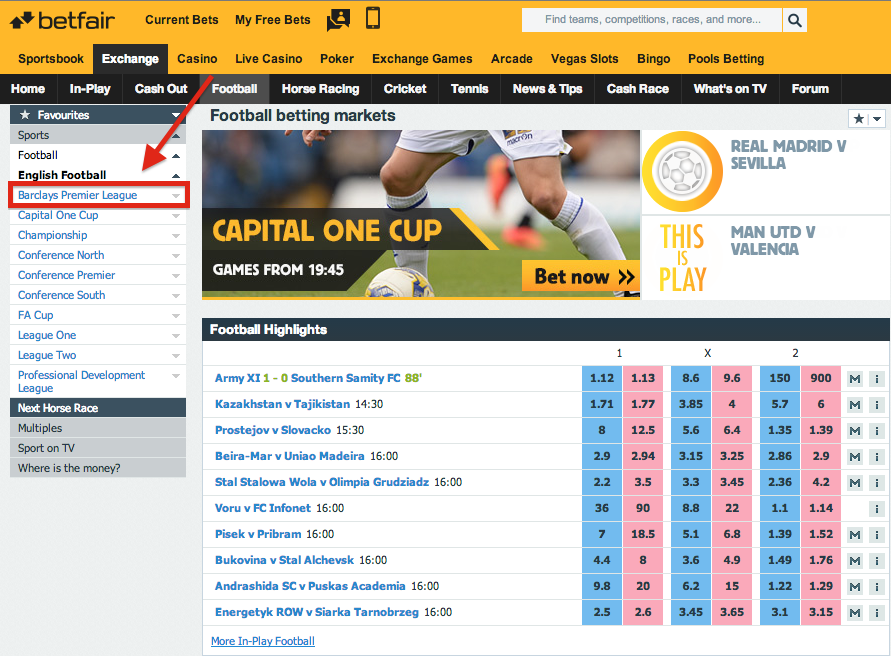
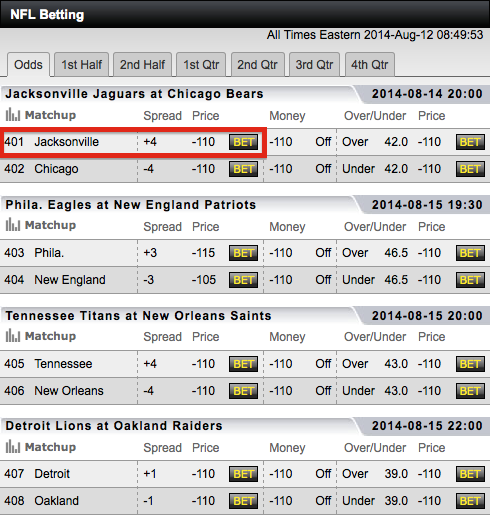
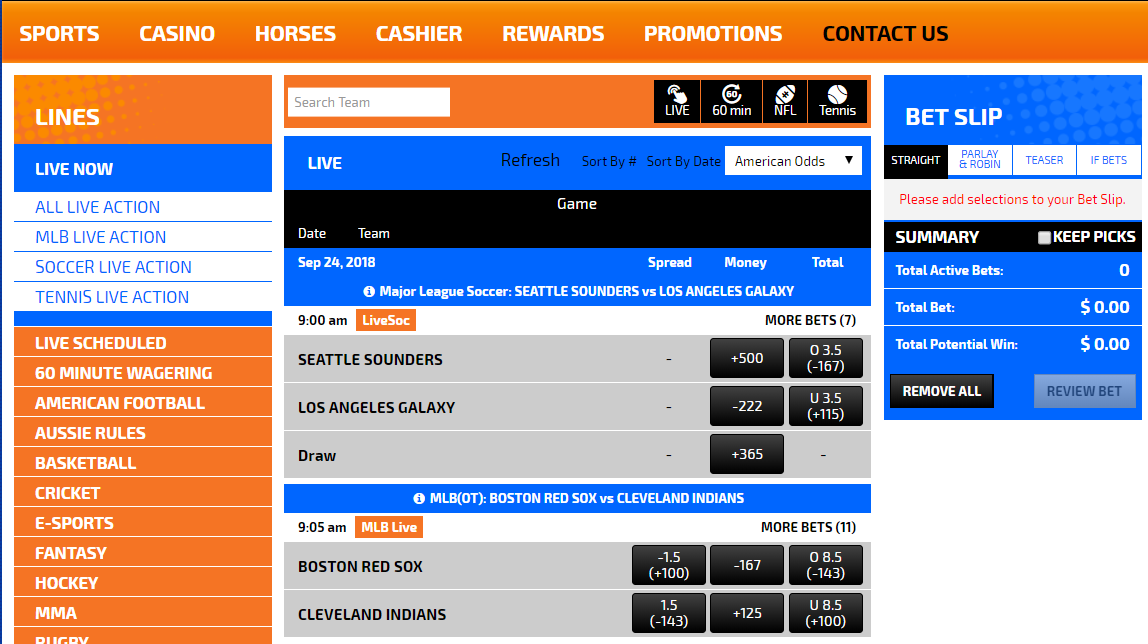
Spread On A Bet

🛑 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Spread On A Bet
Spread bets and CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 75% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading spread bets and CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how spread bets and CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. High volatility increases the risk of sudden, large or rapid losses.
To prioritise the service we give our existing clients, IG is not currently allowing any new positions on GameStop and AMC Entertainment.
Spread bets and CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. High volatility increases the risk of sudden, large or rapid losses.
To prioritise the service we give our existing clients, IG is not currently allowing any new positions on GameStop and AMC Entertainment.
We use a range of cookies to give you the best possible browsing experience. By continuing to use this website, you agree to our use of cookies. You can view our cookie policy and edit your settings here , or by following the link at the bottom of any page on our site.
Speculate on whether an asset’s price will rise or fall with spread bets. Discover everything you need to know about what spread betting is and how it works.
Start trading today. Call 0800 195 3100 or email newaccounts.uk@ig.com . We’re here 24 hours a day, from 8am Saturday to 10pm Friday.
Spread betting is a popular derivative product you can use to speculate on financial markets – such as forex, indices, commodities or shares – without taking ownership of the underlying asset. Instead, you’d be placing a bet on whether you think the price will rise or fall.
We invented financial spread betting in 1974, and today we enable you to take advantage of over 17,000+ markets, whether they are rising or falling in price. This gives you a much wider range of opportunities than traditional buy-and-hold investing . Plus, as you won’t be taking ownership of the asset, spread betting is tax-free.*
Ready to start spread betting? Open an account
Spread betting works by tracking the value of an asset, so that you can take a position on the underlying market price – without taking ownership of the asset. There are a few key concepts about spread betting you need to know, including:
Going long is the term used to describe placing a bet that the market price will increase over a certain timeframe. Going short or ‘shorting’ a market is the reverse – placing a bet that the market will decline.
So spread betting enables you to speculate on both rising and falling markets. You would buy the market to go long, or sell the market to go short.
Let’s say you thought the price of gold was going to decline. You could open a spread bet to ‘sell’ the underlying market. The loss or gain to your position would depend on the extent to which your prediction was correct. If the market did decline, your spread bet would profit. But if the price of gold increased instead, your position would make a loss.
Leverage enables you to gain full market exposure for a fraction of the underlying market cost.
Say you wanted to open a position on Facebook shares. As an investor that would mean paying the full cost of the shares upfront. But by spread betting on Facebook shares instead, you might only have to put down a deposit worth 20% of the cost.
It’s important to note that leverage magnifies both profits and losses as these are calculated based on the full value of the position, not just the initial deposit. To manage your exposure, you should create a suitable risk management strategy and to consider how much capital you can afford to put at risk.
When you spread bet, you put down a small initial deposit – known as the margin – to open a position. This is why leveraged trading is sometimes referred to as ‘trading on margin’.
There are two types of margin to consider when spread betting:
Spread betting has three main features: the spread, bet size and bet duration. The spread is the charge you’ll pay for a position, the bet size is the amount of money you want to put up per point of market movement, and the bet duration is how long your position will remain open before it expires.
The spread is the difference between the buy and sell prices, which are wrapped around the underlying market price. They’re also known as the offer and bid. The costs of any given trade are factored into these two prices, so you’ll always buy slightly higher than the market price and sell slightly below it.
For example, if the FTSE 100 is trading at 5885.5 and has a one-point spread, it would have an offer price of 5886 and a bid price of 5885.
The bet size is the amount you want to bet per unit of movement of the underlying market. You can choose your bet size, as long as it meets the minimum we accept for that market. Your profit or loss is calculated as the difference between the opening price and the closing price of the market, multiplied by the value of your bet.
We measure the price movements of the underlying market in points. Depending on the liquidity and volatility of your chosen market, a point of movement can represent a pound, a penny, or even a one hundredth of a penny. You can find out what a point means for your chosen market on the deal ticket.
If you open a £2 per point bet on the FTSE 100 and it moves 60 points in your favour, your profit would be £120 (£2 x 60). If it moved 60 points against you, your loss would be £120.
The bet duration is the length of time before your position expires. All spread bets have a fixed timescale that can range from a day to several months away. You’re free to close them at any point before the designated expiry time, assuming the spread bet is open for trading.
Ready to start spread betting? Open an account
Say Apple is trading with a sell price of 11550 ($115.50) and a buy price of 11560 ($115.60). You anticipate that Apple shares are going to rise in the next few days, so decide to go long on (buy) Apple shares for £10 per point of movement at 11560.
If Apple shares did rise in price, you might decide to close your trade when the sell price hits 11590. As the market has increased by 30 points (11590 – 11560), you’d be coming out with a profit of £300 (30 x £10), excluding any additional costs.
If the market had fallen in value instead – down to a sell price of 11,510 – you would have ended up with a loss. As the market had moved by 50 points (11,560 – 11,510), you would have made a loss of £500 (50 x £10). Again, not including any additional charges.
Yes, if your prediction of whether the market will rise or fall is correct, you’ll profit and if it’s incorrect, you’ll lose.
It is important to remember that all forms of trading carry risk. So, although spread betting provides opportunities for profit, you should never risk more than you can afford to lose.
When you hedge using a spread bet, you open a position that will offset negative price movement in an existing position. This could be trading the same asset in the opposite direction, or on an asset that moves in a different direction to your existing trade.
For example, if you were worried that inflation might impact the value of your share portfolio, you might decide to take a long position on gold – an asset that typically has an inverse correlation with the dollar and can protect portfolios from inflation. If your shareholdings did decline, the profits from your spread bet on gold could offset any losses. But if your shareholdings rose in value instead, this profit could offset any potential loss to your gold spread bet.
Spread bets are not taxed.* Traditionally, when you buy and sell shares you have to pay stamp duty and capital gains tax on any profits that you make, but spread bets are tax-free. And because you don’t take ownership of the underlying asset, you won’t have to pay stamp duty either.
Spread betting is a bet on the future direction of a market, while a CFD is an agreement to exchange the difference in the price of an asset from when the contract is opened to when it is closed. There are a range of similarities and differences between these two derivative products.
Leverage is an inherent part of spread betting, so you can’t open a position without it. Before you start trading on leverage, it’s a good idea to build up your knowledge on the subject and create a risk management strategy.
Dividend payments have no impact on your spread betting position. If you hold a spread bet open on an equity or index when a dividend payment takes place, we’ll make an adjustment to your position. This means that capital will either be credited or debited to your account if a dividend is paid, depending on whether you have incurred additional running loss/profit.
Find out more about spread betting and test yourself with IG Academy’s range of online courses.
Discover the differences between spread betting and CFD trading
Learn about risk management tools including stops and limits
Browser-based desktop trading and native apps for all devices
* Tax laws are subject to change and depend on individual circumstances. Tax law may differ in a jurisdiction other than the UK.
Spread bets and CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 75% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading spread bets and CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how spread bets and CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. Professional clients can lose more than they deposit. All trading involves risk.
The value of shares, ETFs and ETCs bought through a share dealing account, a stocks and shares ISA or a SIPP can fall as well as rise, which could mean getting back less than you originally put in. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
CFD, share dealing and stocks and shares ISA accounts provided by IG Markets Ltd, spread betting provided by IG Index Ltd. IG is a trading name of IG Markets Ltd (a company registered in England and Wales under number 04008957) and IG Index Ltd (a company registered in England and Wales under number 01190902). Registered address at Cannon Bridge House, 25 Dowgate Hill, London EC4R 2YA. Both IG Markets Ltd (Register number 195355) and IG Index Ltd (Register number 114059) are authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority.
The information on this site is not directed at residents of the United States, Belgium or any particular country outside the UK and is not intended for distribution to, or use by, any person in any country or jurisdiction where such distribution or use would be contrary to local law or regulation.
What Is Spread Betting ?
What is Spread Betting and How Does it Work? | IG UK
Spread Betting Learn How To Spread Bet With CITY-INDEX
What is Spread Betting and How Does it Work? | CMC Markets
How to spread bet | Capital.com
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 73% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Start Spread Betting and pay no UK stamp duty or UK Capital Gains Tax*
Create Account
About Us
StoneX
Partnerships
Affiliates
Press Releases
Careers
Sitemap
Terms and policies
Incisive market analysis into the year ahead - Your Outlook 2021 is now online. Get started by reading: End of the Brexit transition period and Market implications of C19 vaccines .
Spread betting provides a popular way to go long or short on thousands of financial markets, including indices, shares, currencies, commodities and more. Find out what spread betting is – and how it works – with our handy guide.
In this guide, we’re going to cover all the essentials you need to know about financial spread betting. Scroll down to get started at the beginning, or follow these links to skip to a specific section:
Spread betting is a financial derivative that enables you to trade on the price movements of a wide range of markets. Unlike traditional investing, you don’t take ownership of any assets when spread betting – which means you can go short as well as long, take advantage of leverage and more.
Traders use spread betting to get a range of different benefits. Some, for example, will utilise spread bets to trade when markets are falling as well as rising. Others use them to diversify their exposure by trading FX, shares, indices and commodities 24 hours a day from a single account.
Spread betting works using bets instead of the physical buying and selling of assets. In a traditional Apple trade, for example, you’d buy Apple stock, hold it then sell it. When spread betting, you’d achieve the same result by making a bet that Apple shares will increase in price.
The further that Apple moves in your chosen direction, the more profit you make. The further it moves against you, the greater your loss.
When you open a spread bet, you’ll see two prices listed: the buy price and the sell price. Using this, you can choose whether you want to go long or short. If you think the value of your chosen market will go up, you click buy. If you think it will fall, you click sell.
Then, to close a spread bet, you trade in the opposite direction to when you opened it. So if you bought at the outset, you’d sell to exit – and vice versa.
The spread is the difference between the buy and sell prices listed on a market, and it is how you’ll pay to open a spread betting position. Instead of paying a commission, all the costs to trade are covered in the difference between the buy and sell prices.
The FTSE 100, for instance, might have a spread of 1 point. This means that its buy price will be 0.5 points above its current market price, while its sell price will be 0.5 points lower. Your broker’s fees to open and close your position are all contained within that 1-point spread.
Another key aspect to spread betting is your stake, which is also known as your bet size . Selecting a bet size lets you decide how many pounds per point to allocate to each trade, which dictates how much you’ll make or lose for every point that the market moves.
In UK spread betting, you’ll decide you stake using pounds per point. Say you bet £5 per point that Apple stock will go up. For every point of upward movement, your position will earn you £5. If it drops, then the opposite is true.
If you think that the price of oil is going to go up, then you could place a buy trade with a stake of £2 a point.
This will earn you £2 for every point the price of oil rises. However, should the price of oil fall, you would lose £2 for every point of downward movement.
You realise your profit or loss when you close your position. If oil had moved up 50 points from when you bought it, you would make (50 points x £2) £100. If it had moved down 50 points, you would lose £100.
Leverage is another important aspect of spread betting. It means you can put up a small amount of money to control a much larger amount. When spread betting on stocks, for example, you might only have to put up 20% of the total value of your position. This would mean that the market has a leverage factor of 5:1. Other markets, such as forex, may have leverage of 20:1 or higher.
Bear in mind, though, that leverage will amplify your profits and your losses – so it requires careful risk management.
The deposit that you have to maintain in your account to keep a leveraged trade open is called your margin . When you’re trading with leverage, you’ll need to ensure that you always have sufficient margin in your account.
Say that you want to bet £10 per point on the FTSE 100 when it is trading at 6000, with a leverage factor of 20:1. The total size of your position is (10 x 6000) £60,000, so you’d need to put up (5% of 60,000) £3000 as margin.
Learn more about margin and leverage .
Unlike traditional share dealing, with spread betting you can sell a market if you think it’s going to fall in value. In doing so, you can profit from the falling price. This is known as 'going short'. To short a market, you trade at the sell price instead of the buy.
Tesco is trading at 229. You believe that the company’s share price will fall and decide to go short £5 per point at 229.
Tesco announces that it mistakenly overstated its pre-tax profits for the last six months by £250m. After two weeks, Tesco’s share price has plummeted to 168p as shareholders lose confidence in the retailer. You decide to close your trade at 168p.
Tesco stock has fallen 61 points. Your spread bet earns you £5 for every downward point of movement, so your trade would earn you (61 x 5) £305.
However, if Tesco stock had risen 61 points instead, you would lose £305. It’s also worth noting that this illustrative example does not include overnight financing charges .
When spread betting, it is crucial to maintain appropriate risk management. Typically, this involves identifying the risks that you may face when trading, then creating a risk management plan that sets out how to mitigate them for each position.
Stops are an essential tool to control risk. When you place a stop on an open position, you’re instructing your spread betting provider to automatically exit the trade if it moves a certain amount against you. This limits your risk by setting a maximum loss from any given position.
Learn more about spread betting risks .
A popular product for investors, Financial Spread Betting is a way to actively participate in financial markets.
Spread betting may be ideal for investors who want the opportunity to try and make a better return for their money. However, it comes with significant risks to your capital and is not suitable for everyone. We strongly suggest trading on a demo account before you try spread betting on live markets.
Spread betting is ideal for people who want:
City Index offers a choice of over 4000 spread bet markets, including:
You can try out trading on all these markets with a free demo account .
Spread bets are tax free in the UK. That means you don’t need to pay capital gains tax on any profits you make, unlike traditional share dealing. You also won’t have to pay stamp duty.
However, tax laws are subject to change and depend on individual circumstances. Please seek independent advice if necessary.
Spread betting and CFDs are both leveraged products that enable you to speculate on the price movements of financial markets. But they work in different ways.
With spread betting, you bet a certain number of pounds per point on the future direction of a market. With CFDs, you trade a contract in which you agree to exchange the difference in asset’s price from when you opened your position to when you close it.
When you spread bet on shares with City Index, we’ll automatically adjust your open positions to reflect dividends.
If you are long on a company that declares a dividend, we'll credit your account. If you are short, you pay the dividend. This happens before the market opens on the ex-dividend date.
Learn more about corporate actions here .
No, forex and spread betting aren’t the same thing. Forex is an asset class, like shares, indices or commodities. In forex trading, you are speculating on the price movements of currency pairs.
You can use spread betting to trade lots of different asset classes – that includes forex, as well as shares, indices, commodities and more.
It depends on your chosen provider. You should decide exactly how much capital you want to risk before you start trading.
At City Index, we recommend that you deposit a minimum of £100, or however much you need to substantially cover the margin requirement of your first trade. It is prudent to also have enough equity in your account to sustain any significant moves against your position.
No. Day trading is an approach to the markets that involves ensuring that all your positions are closed by the end of the day. Spread betting is a type of leveraged financial derivative.
As day traders only keep their positions open for a short amount of time, they often use leverage to amplify their profits and losses. Spread betting is a popular method of achieving this, but it isn’t the same as day trading.
To hedge with spread betting, you open a spread bet that earns you a profit if an existing open position incurs a loss.
For instance, you might own Barclays shares as part of your investment portfolio. If you're worried about a temporary downturn, then you could sell your shares – but then you'd lose your position on the company.
Or instead of selling your shares, you could open a short spread bet on Barclays. Then, if Barclays’ share price does fall, the loss in your portfolio would be offset by the profit from your spread bet.
Want to learn more about spread betting? Explore these free resources to discover everything you need to know.
Alternatively, open a live trading account now – you can get started in less than five minutes.
View spreads, margins and commissions for City Index products
Take control of your trading with powerful platforms and tools
View upcoming trading opportunities for the weeks ahead
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 73% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
We use cookies, and by continuing to use this site or clicking "Agree" you agree to their use. Full details are in our Cookie Policy .
Sperm Collection
Asian School Girl Nude
Donic Outdoor
Russian Nudist Photo
Ass Sperm Anal