Spread Indicator Sports Bet

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Benzinga Money is a reader-supported publication. We may earn a commission when you click on links in this article.
Learn more.
To start the 2007 NCAA college football season, perennial powerhouse Michigan squared off against Appalachian State, who played in the FCS division ― a step below the division where blue bloods like Michigan, Ohio State and Penn State play.
Michigan was at home in The Big House, its massive 100,000-person stadium where losses occurred less frequently than presidential elections. Appalachian State was a 33-point underdog in the game.
In a stunning upset, Appalachian State took a 34-32 lead late in the 4th quarter and blocked the potential game-winning Michigan field goal on the last play of the day. At the time, Appalachian State was one of the longest underdogs to ever win a game outright ,and you can still annoy Michigan fans to this day by bringing it up.
So how did Appalachian State come to be a 33-point underdog? Because across the country, sports books set point spreads based on a variety of environmental and team-specific factors. In this particular game, the oddsmakers thought Michigan was 33 points better than Appalachian State. Needless to say, they don’t always get it right.
In investing, a spread is the difference between the price a seller is willing to accept for an asset and the price the buyer is willing to pay for that asset. The spread is collected by the market maker for facilitating the deal.
But in investing, individual shares of a specific company are pretty much all equal, except in certain circumstances. When it comes to sports betting, the 2 teams competing are almost never equal, so a spread is required to entice betting action on both sides.
The spread is simply the amount of points oddsmakers favor one team over another in a particular game. When crafting a spread, the oddsmakers will look at factors like skill of the individual teams, location of the game being played and weather forecasts for outdoor sports like football.
A point spread also varies depending on the sport being played. For example, football spreads are usually much wider than baseball spreads since you get 6 points for a touchdown in football but only 1 point for a run in baseball.
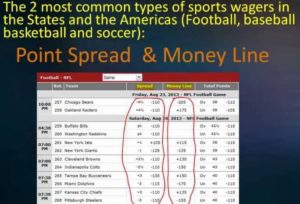
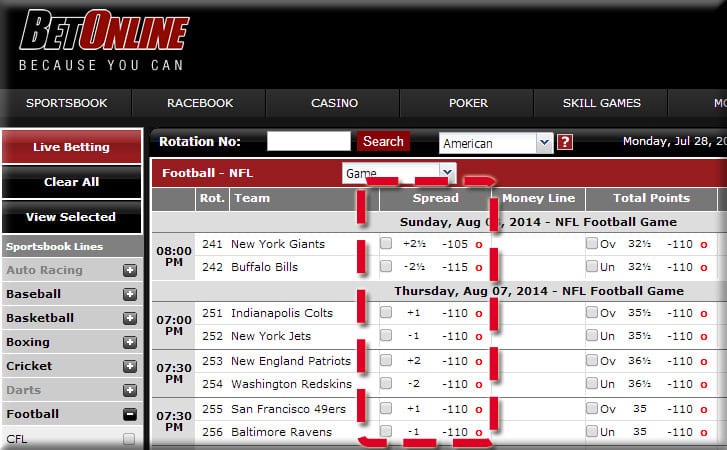
If you aren’t familiar with point spreads, you might be confused at first glance. A point spread will involve 3 figures: the favorite, the underdog and the juice or vig.
Unless the 2 teams are evenly matched, every sporting event will have a favorite and an underdog. The team that’s expected to win the game is the favorite. One of the reasons the spread exists is because teams aren’t evenly matched and just picking winners and losers is easy.
Imagine how much money a sportsbook would lose if the 15-1 Kansas City Chiefs played the 2-14 New York Jets without a spread and payouts were equal on both sides. Everyone would bet the far superior Chiefs, right?
So instead, oddsmakers set a spread of 14.5 points in an attempt to entice equal betting action on both sides. This is the crucial job of an oddsmaker: listing a spread that will garner as close to 50% of the bets on each side as possible.
The odds would read as follows: Chiefs -14.5 (-110) vs Jets +14.5 (-110). More on the numbers in parenthesis in Step 3.
The underdog is the team NOT expected to win the game. But betting on underdogs can still be a profitable venture if they lose the game by fewer points than the listed spread.
In the example above, the Chiefs were a 14.5 point favorite over the Jets. If the Chiefs win the game 28-14, the Jets will have ‘covered the spread’. They lost by fewer points than the oddsmakers projected and a bet on the Jets +14.5 is a winner.
How does the sportsbook make money if they want to entice equal betting action on both sides? The same way a casino does — they employ a rake. In sports betting, this is referred to as vig or juice and it actually functions similar to a spread in a stock trade.
Let’s use our Chiefs vs Jets example from the previous paragraph. Remember the (-110) figure after the spread? This is the vig, and it’s how much you’ll need to bet in order to win $100.
Most books will set the vig at -110 or -115, which means you must bet $110 or $115 in order to win $100. In order to be a profitable sports betting, you must hit over 52% of your bets in order to beat the vig. A common misperception is that a bettor who hits at a 50% clip breaks even. Due to the vig, hitting 50% of your bets would produce a negative ROI and the only one profiting is the book.
Here’s how a point spread will look at most American sportsbooks:
If you want to bet the Chiefs point spread, they will need to win by 15 points or more, and you’ll win $100 on a $110 bet. If the Chiefs only win by 14 points, you lose the full $110.
The point spread enables bettors to place a near-even money bet on a game, but it’s not the only way to wager on a sporting event. If you want to just pick winners and losers, you can bet what’s called the moneyline. A moneyline bet is a straight win or loss wager. If you bet the favorite and they win, you collect regardless of the score.
Of course, betting on favorites is expensive. Oddsmakers create moneyline odds based on the likelihood of the favorite winning the game. You’ll often see odds listed as fractions (ie. 5/2), but American sports books tend to list them in the same format as the point spread vig.
The Chiefs were a 14.5 point favorite in our previous example, which means oddsmakers give them about a 95% chance of winning (or 1/20). If you wanted to bet on a Chiefs win by any margin, you’d have to bet the moneyline at 1/20 odds. That means wagering $20 for every $1 of potential profit. In order to win $100, you’d have to wager $2,000.
Yes, the Chiefs likely win, but betting $2,000 to win $100 is awfully risky for a single sporting event, especially when you consider player injury risk.
Betting on a point spreads has 3 potential outcomes:
The spread is the spread regardless of sport. If an NBA team is favored by 14.5, they must win by 15 or more to cover the spread. NBA and NFL are 2 of the most popular sports to bet because scoring is frequent and less random than the NHL or MLB.
The difference comes from how these spreads are calculated. In the NFL, 3 factors go into the spread: talent level of the teams, location of venue, and weather forecast for the game. For the NBA, the schedule is unbalanced and games are played indoors.
NBA point spreads use the following factors: talent level of teams, location of venue, and schedule discrepancies between teams. For example, a team with a day of rest will get a more favorable points spread if they play a team who competed the night before. Since NFL games are usually played a week apart, schedule doesn’t play as large a role in determining the spread.
Sports betting is opening up across the country, but legality is on a state-by-state basis and not all sportsbooks are available in each state.
Here’s a list of our favorite sportsbooks. Be sure the one you choose is available in your state:
get started securely through FanDuel’s website
get started securely through DraftKings’s website
Sports betting is a simple endeavor to participate in, but impossible to master. A point spread is a simple concept that enables bettors to get close to even money action on whichever side they choose. It also gives the sportsbook the ability to smooth their liability out to close to a 50/50 proposition.
If 50% of bettors choose 1 team and 50% choose the opponent, the book is guaranteed to profit thanks to the vig. Understanding these concepts can help gamblers minimize losses and increase profits.
Why are point spreads in the NFL so much lower than in college?
In the NFL, there are 32 teams. In college football, there are well over 100 in the top division alone. Since more teams are present, the talent level between the top and bottom teams is greater so point spreads in college are often higher.
In the NFL, team talent levels are more closely aligned, even when the best team plays the worst team.
A +7 spread means that the team in question is expected to lose by 7 points. If you bet a team with a +7 spread, they must win or lose by 6 or fewer in order for the bet to cash. Likewise, a team with a -7 spread must win by 8 or more to make a profit.
What does ‘pick em’ or ‘pick’ mean in NFL betting?
Sometimes, the 2 teams playing are evenly matched after factoring in talent level, venue, and weather forecast. When this happens, the game will be listed as a ‘pick’, which is essentially the oddsmakers saying, “We don’t know”.
A pick ‘em or pick is a toss-up or coinflip. If you bet $100 on either side, you’ll win $100 if they win minus the vig.
get started securely through FanDuel's website
get started securely through DraftKings's website
Get the best games and picks of the week delivered directly to your inbox!
© 2021 Benzinga | All Rights Reserved
Advertiser Disclosure: TD Ameritrade, Inc. and Accretive Capital LLC are separate, unaffiliated companies and are not responsible for each other’s services and products.
Editorial Disclosure: Reviews are as determined by Benzinga Money. Opinions expressed here are solely the author’s and have not been reviewed, approved or otherwise endorsed by reviewers.
September 5, 2013 by Terry posted in • No Comments
This article is intent to demonstrate to you what technical analysis is all about and how best you can deploy it to enhance your spread betting profitability. This objective will be achieved by introducing a couple of famous and well regarded technical indicators.
You could benefit greatly if you decide to integrate the many attributes of the Money Flow Index (MFI) into your spread betting trading strategies especially if you prefer using technical analysis to locate quality trading opportunities. This is because you can exploit the MFI to assist you in quantifying the sums of money flowing out of and into assets of interest.
You will discover that the MFI has many features that exhibit numerous similarities to those of the popular and well-known Relative Strength Index (RSI). However, the RSI was invented to monitor volume whereas the MFI tracks price. Colin Twiggs developed the MFI by basing it on the concepts of an early technical indicator, invented by Marc Chaikin.
Twiggs advised that you should utilize the MFI to help you detect the births and terminations of trends. You will find that the MFI generates better quality statistics when you display it on trading charts using the daily time-frame and higher. You are also recommended to verify all MFI findings by utilizing a second confirmatory technical indicator.
If the MFI is beginning to bounce higher from its oversold level at 20, and starts tracking a rising price action, then this is a good indication that a new bull trend has been created. Similarly, you can identify good quality selling opportunities if the MFI drops below its overbought level at 80 and supports decreasing values in price.
For instance, you can observe in the above diagram that the MFI (blue line) detects a good entry point for a long spread. You must realize that to be able to utilize the MFI well that it signals overbought conditions for the currency pair when it produces readings of 80+, see above chart. Similarly, you must view values of 20- as oversold conditions.
For example, if you detect that the MFI has just climbed above its 20 level after recording oversold values then you should evaluate such a development as a strong buying opportunity for a long spread bet. Under such circumstances, you must continue to adopt caution because price could still plunge by hundreds of points. Consequently, you are recommended to always confirm all MFI readings by using a secondary technical indicator before opening a new spread bet.
The MFI generates its readings by multiplying volume by the average price and then ranging the resultant on a scale between one hundred and zero. If you detect that the MFI is starting to post falling readings but that price is still climbing then you should anticipate that a new market top is in the process of being created.
The On Balance Volume Indicator (OBV)
You can utilize the On Balance Volume indicator to help you to compare the price and volume flows of underlying assets for spread bets over a chosen time-period. Joseph Granville invented the On-Balance-Volume technical indicator in 1962 when he introduced it to the markets together with his OBV strategy in his revered hardback – ‘How to read the Stock Market’. Since then, the OBV indicator has acquired an impressive reputation by becoming one of the most reliable momentum tools available at evaluating the interactions between the price, volume and momentum of stocks, currencies and commodities.
Fundamentally, the OBV considers all of a trading day’s volume as up-volume if the price of an asset registers a closing value exceeding that of the previous day. Similarly, the OBV will classify a day’s volumes as down volume if price posts a closing value that is lower than that of its immediate predecessor. Consequently, the OBV main line represents the collective total of all these negative and positive volume flows.
You can observe all these features in the following diagram. Very importantly, the OBV may be predicting an imminent price retracement when its values begin to change course. In fact, Granville first identified this important attribute of his invention after performing extensive research. You can observe this aspect of the OBV in the next diagram when the OBV starts to fall announcing the end of the present bull trend.
If you notice that the OBV values are climbing then you should also be able to verify that price has commenced climbing as well. In addition, you can utilize the OBV to assist you in detecting new price trends. For example, if the OBV starts to produce a sequence of higher highs and lows, then you should view such a development as a good quality buy signal for a long spread bet. Alternatively, if the OBV begins posting a series of lower lows and highs, then you should regard this pattern as a very serious sign to open a short spread bet.
You can also identify new quality trading opportunities developing if the OBV commences to generate values that diverge from price. This is because the design of the OBV focuses on the trends of assets. Granville advised that when volume starts to decrease during a bull trend, then a market top may be forming as buying pressure has begun to fade.
If you observe such a development then you should deduce that price will not continue to climb for much longer and that you should expect a retraction very soon. Granville also verified that a similar action occurs in bear trends if you notice that volumes are beginning to increase.
In addition, he also recommended utilizing a twenty-period moving average in conjunction with the OBV in order to help detect when trends are about to terminate. You can detect such developments more easily by identifying when the moving average and the OBV line crossover. You should understand that the OBV is evaluated by traders to be one of the simplest and most popular momentum indicators available
Reversals could also be imminent when you observe any price and OBV divergences. If you also discover that the OBV is altering direction after it has been following price for some time, then you should regard this development as a potential opportunity to activate a new spread bet.
J. Welles Wilder designed his Average True Range (ATR) as a volatility indicator and introduced it to the trading markets in 1978. The ATR uses volatility levels and daily price movements to generate readings indicating how bullish traders are at buying assets. The ATR achieves this task by calculating the average true price range over a selected period of time.
The true range is determined by utilizing the difference between the daily high and open; the largest difference between the daily high and low and the difference between the daily low and open. Consequently, the ATR generates values representing the moving average of true range.
As such, when the ATR posts high values that it is warning that a major price reversal could be imminent because of high volume levels. In contrast, low readings imply price flat-lining with low trading volumes. In addition, when the Average True Range posts low readings then it has identified conditions suitable for range trading whilst high ones indicate that price has achieved a top or bottom. You are also recommended to use this indicator with a fourteen period on charting charts displaying the daily time-frame or higher.
You can utilize the ATR to help you detect breakouts which are associated with its high values. You will also find that the higher value are produced as a result of panic buying or selling which results in price achieving tops or bottoms. Alternatively, you will discover that the lower readings strongly indicate that price has entered a consolidation period. However, you should not use the ATR to detect overbought or oversold conditions because Wilder did not include these conditions into the design of the ATR.
You should also not attempt to detect new trading opportunities with the ATR because this is not its primary function. Instead, you must realize the when the ATR is posting its highest readings it is very proficient at identifying market tops and bottoms. This is a very important attribute because you will then have an advance warning that price is about to undergo a major reversal in its current direction. In addition, you can utilize the ATR to help you cope better with volatile trading times because it has been specifically design to deal with these conditions.
This indicator is an oscillator that has many similarities to the Rate of Change Indicator but it focuses on volume instead of price. Consequently, you will find that the V-ROC produces readings that reflect volume changes. Many experts claim that because price reversals are usually partnered by significant rises in trading volumes that this is a useful parameter to track.
You will discover that you can use the V-ROC is assist you in detecting new bull and bear trading trends. The V-ROC creates readings that oscillate about a zero line and generates high values with increasing levels of trading volume and lower ones when volumes drop. The readings produced by the V-ROC are determined by dividing the volume movement over a selected time period by its value recorded when the period started.
As such, if you notice that the V-ROC is generating negative values then you should be able to verify that the trading volume is diminishing. In contrast, positive readings are indicative of rising volumes. Consequently, you can utilize the V-ROC to help you detect market bottoms, market tops, overbought condit
Solo Hot Dripping Aveliporn Com Mp4
Ass Babes Foto
Www Xhxx Com Bondage
Sexy Latina Babe Solo
Wife Fuck Movie
How to Read Spreads in Sports Bets • Benzinga
The Most Common Technical Indicators for Spread Betting
NBA Spread Betting Explained | How To Spread Bet On Basketball
Sports Betting Indicators | Percentages & Line Movement
Spread betting in sport | What is spread betting? | OddsMonkey
What Is Point Spread Betting? | How to Bet on Point Spreads
What is Sports Spread Betting - Sport To Bet
Combining Technical Indicators | Spread Betting
7 Spread Betting markets You can Trade - My Trading Skills
Spread Indicator Sports Bet



















/SportsBetting-58d2b6195f9b584683b46637.jpg)

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/54923867/jalendeondre.0.jpg%3fresize%3d640%252C427%26ssl%3d1)














/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/57678809/625992470.jpg.0.jpg%3fresize%3d640%252C427%26ssl%3d1)




/GettyImages-56294676-58b7233f5f9b5880801e9105.jpg)











































/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/56264997/632829892.0.jpg)


