Science Digest July 10 / 2023
science.t.meWelcome to @Science telegram channel Digest, your go-to source for concise and captivating summaries of the latest scientific breakthroughs and discoveries across various disciplines, keeping you informed and inspired. Stay updated with cutting-edge research and expand your scientific knowledge with our bite-sized articles.
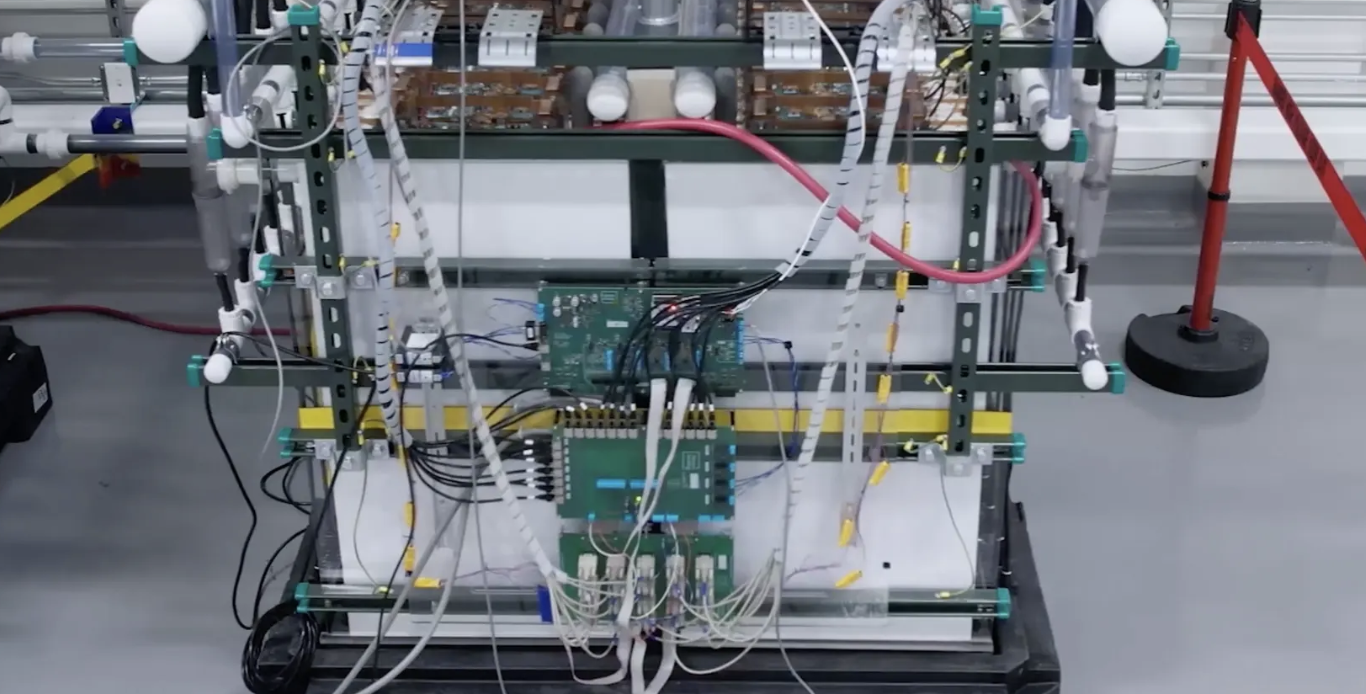
Super-cheap gigawatt-scale rust battery greenlit for Minnesota
Gates- and Bezos-backed startup Form Energy is one of the most exciting companies in the grid-level renewable energy storage space, with a multi-day iron-air battery system just 10% the cost of lithium. A 10-MW/1-GWh demo system has now been approved.
For large electrical grids to move toward 100% renewable energy, grid operators need clever, affordable, practical and eco-friendly ways to store up energy that's generated at inconvenient times, and then release it when demand is outstripping supply. This needs to happen on different timescales; some of this grid smoothing needs to happen on a daily basis, and that's an area where lithium "big battery" projects are already doing a great job. But lithium is less suited to longer-duration storage; it doesn't like staying fully charged for days or months at a time, so other, slower, bulk storage options are being developed to buffer energy grids against multi-day bad weather spells and seasonal lulls in renewable generation.
Cancer breakthrough uses CRISPR to target extra chromosomes
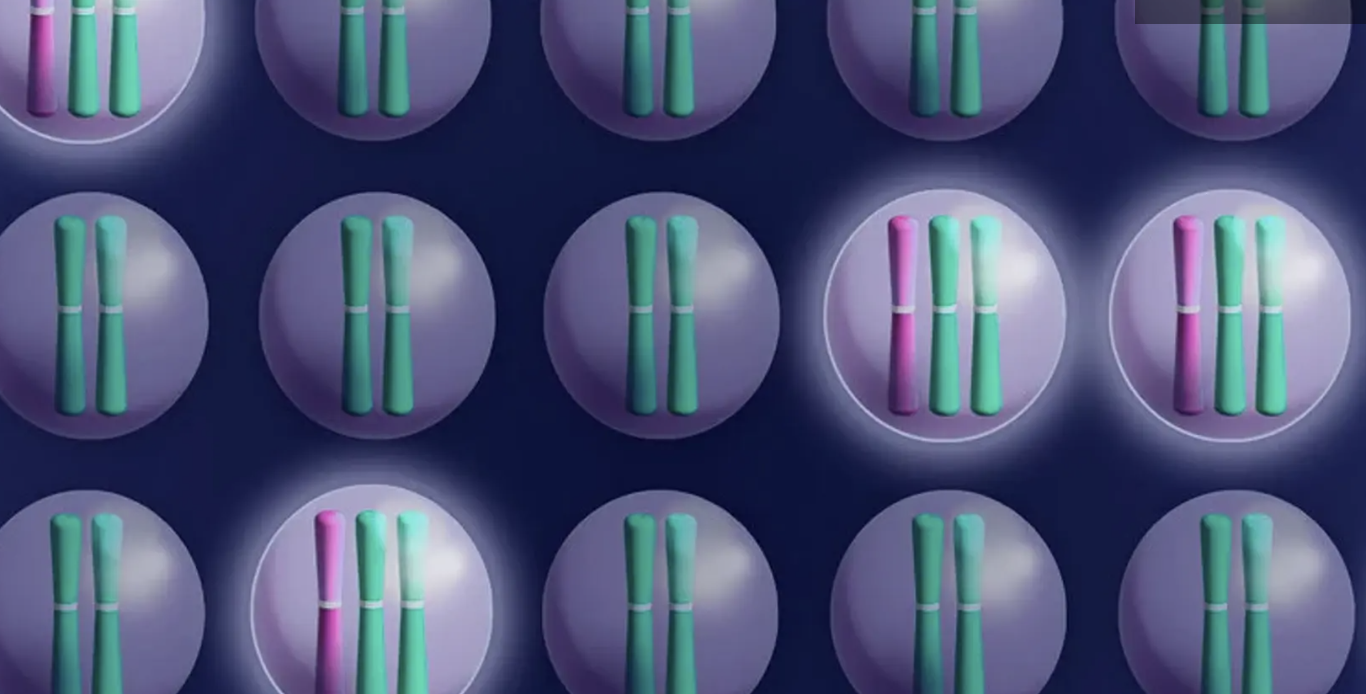
Yale scientists have discovered a new potential treatment avenue to fight cancer. Using CRISPR gene-editing, the team eliminated extra chromosomes from cancer cells and found that they could no longer grow out of control.
Healthy human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes, but it’s been observed for over a century that the majority of cancer cells have extras. This condition is known as aneuploidy, but its exact role in cancer remained a mystery – was it a root cause of cancer or just a symptom of it? In a new study, scientists at Yale investigated that role.
Synthetic lifeform regains lost "fitness" in evolution experiment
How small a canvas can evolution work on? Scientists have experimented with a synthetic lifeform designed to have the simplest possible genome, and found that given the chance it can evolve lost fitness back, showing that indeed, “life finds a way.”
Simple or complex, if you put an organism in an environment evolution will get to work improving it. But is there a lower limit to that? If a lifeform has a genome consisting of just the essential genes, does that leave enough wiggle room for evolution to experiment? Or is it too risky that any minor change could kill the organism? Researchers at Indiana University Bloomington wanted to find out.
Surfactants safely take down mosquitoes without using insecticides
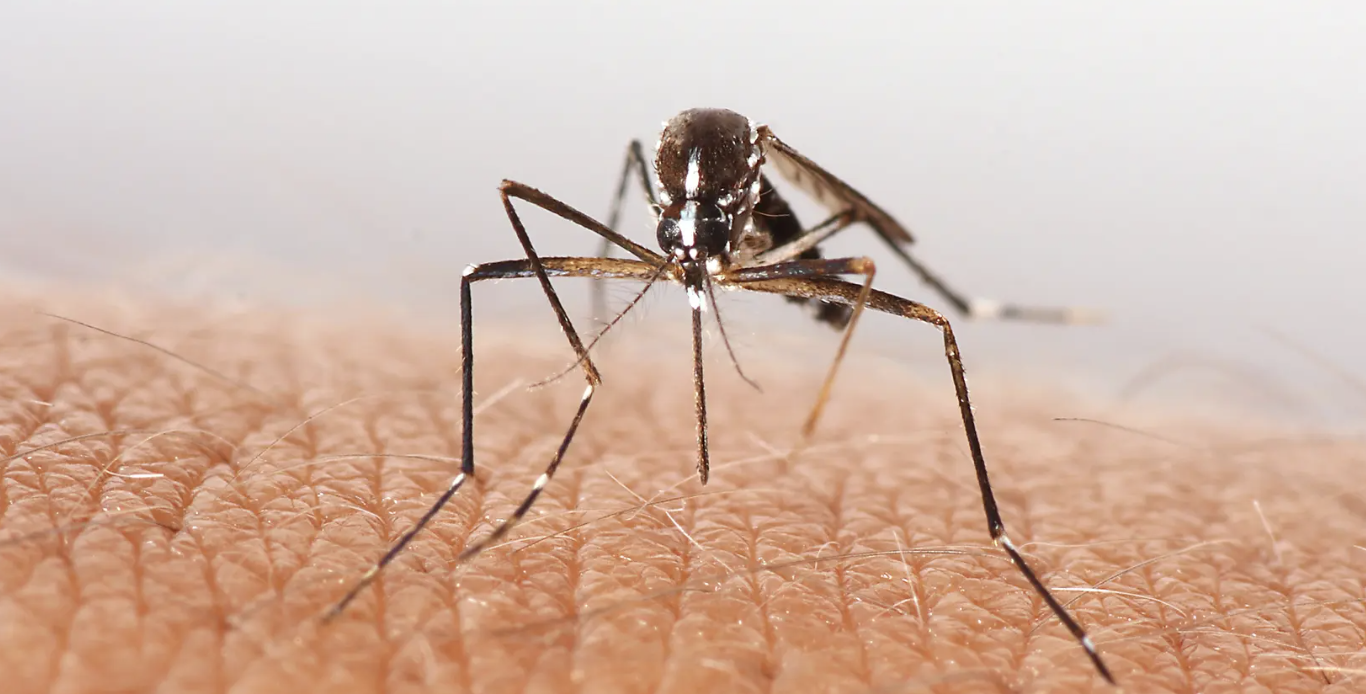

Researchers have developed a surfactant spray that counters the mosquito’s natural water-resisting properties, offering a safe and effective means of taking down mosquitoes without using insecticides. The spray could be used to protect people from the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. Mosquitoes are known to be responsible for spreading potentially deadly diseases such as dengue fever, malaria, Japanese encephalitis and Zika virus, and climate change and urbanization have expanded mosquitoes’ habitat, enabling them to spread disease to more people.
Four-armed robotic surgical system is controlled by hands and feet
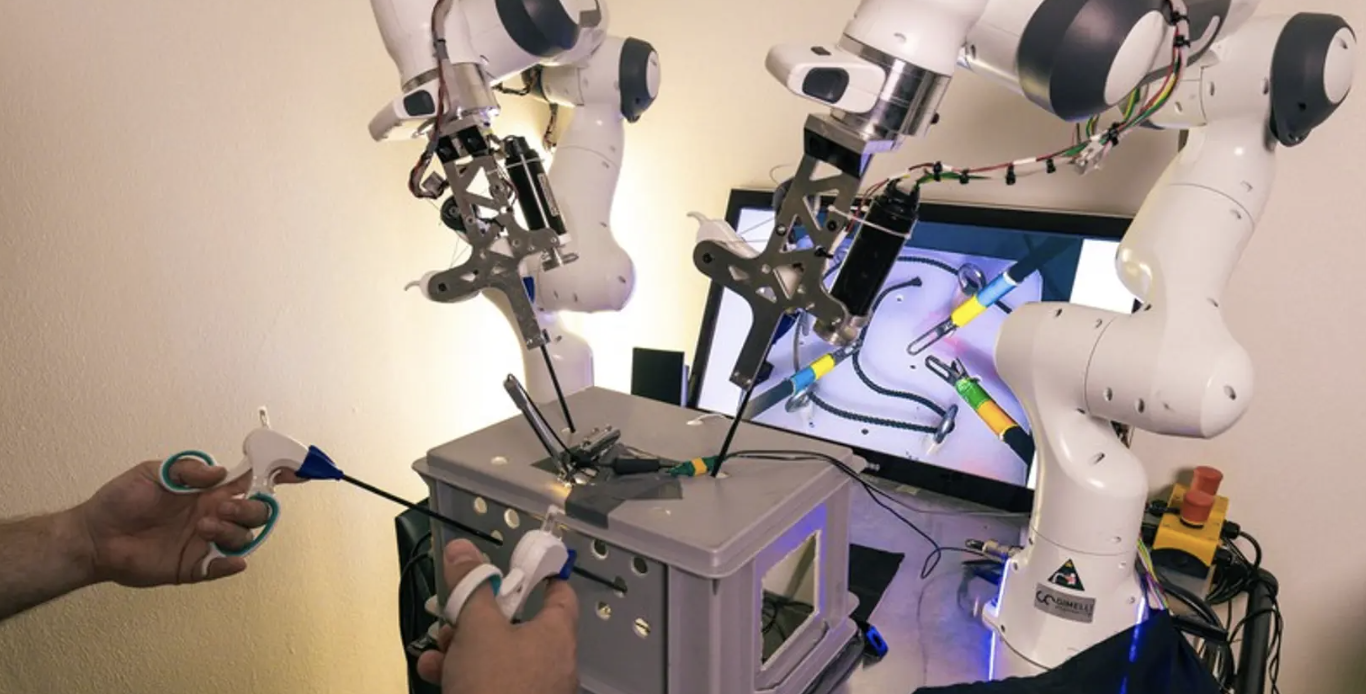
Robotic surgical systems such as the da Vinci X are very impressive, with their two arms that are controlled by the surgeon's two hands. An experimental new system takes things even further, though, by adding two more arms controlled by the user's feet.The four-armed laparoscopic setup is being developed by scientists at Switzerland's EPFL research institute.Each of the user's hands grasps a separate controller that looks kind of like a set of scissor handles. Utilizing these, it's possible to simultaneously manipulate both of the main robotic arms, each of which can be holding a different primary surgical tool (such as a scalpel or retractor).
👉 Subscribe @science
Science Digest 3 July 2023 here
Science Digest 29 June 2023 here
Science Digest for 30 June 2023 here