SPDR S&P500 ETF
Blackmoon Team101 Educational Series

Preface
The ETF assets in US have grown at a 34% annualized since 2000, bringing the current total to $3.4 trillion, according to James Ross, Chairman of the Global SPDR Business in State Street Global Advisors. Without a doubt such numbers indicate high popularity of ETFs among the investors. But what made this type of investments so attractive? And what stands behind the term “ETF”? Let’s start our journey from the beginning of ETF history and consider the SPDR S&P500 ETF, one of the largest ETFs in terms of AuM, in its context.
ETF Begins
The idea of index investing appeared more than 30 years ago. At that time only trusts and closed end funds tried to provide the investors with the opportunity to get exposure to one class of assets. According to “The Exchange-Traded Funds Manual” written by Gary Gastineau, the first kind of ETF was Index Participation Shares for the S&P 500 launched in 1989. However, the Federal Court of Chicago decided that the fund worked like future contracts and so should be traded on the futures exchange.
The date of establishment of the ETF vehicles is considered to be January 22, 1993 when State Street Global Advisors created SPDR S&P 500 ETF. It was the very first ETF, becoming the flagship for the exchange traded products and meaningfully impacted the modern investment landscape.
SPDR S&P500 ETF
The SPDR S&P500 ETF was designed to track the performance of the US large cap market equities included in S&P 500 index. So the purchase of shares of this ETF provides investors with the access to the US large cap space and also with the investment results corresponding to the price and yield of the S&P500 index. Let’s take a closer look at the underlying index.
Standard and Poor’s 500 (S&P 500®) is an American stock market index based on the market capitalization of 500 large companies having common stock listed on NYSE and NASDAQ. Created in 1957 the S&P 500 index was the first US market-cap-weighted stock index. One of the major characteristics which makes each index unique is its proprietary components selection model. The companies included in the S&P 500 are selected by the S&P Index Committee, a team of analysts and economists at Standard & Poor’s.
S&P designed several criteria for including the company in the index:
- Universe. All constituents must be U.S. companies.
- Eligibility Market Cap. Companies with market cap of USD 6.1 bn or greater.
- Public Float. At least 50% of shares outstanding must be available for trading.
- Financial Viability. Companies must have positive as-reported earnings over the most recent quarter, as well as over the most recent four quarters (summed together).
- Adequate Liquidity and Reasonable Price. Consists of highly tradable common stocks, with active and deep markets.
The components of the index are reviewed quarterly in order to remain indicative of the US stock market (well, I even believe when the new company is included in the index, its management celebrates this event).
Thanks to its companies selection methodology, today S&P 500 index covers appr. 80% of available market capitalization and so is considered as one of the best representations of the US stock market.
Let’s return back to the SPDR S&P 500 ETF. This ETF holds the portfolio of common stocks that are included in the S&P 500 index, with the weight of each stock in the portfolio substantially corresponding to the weight of such stock in the S&P 500 index.
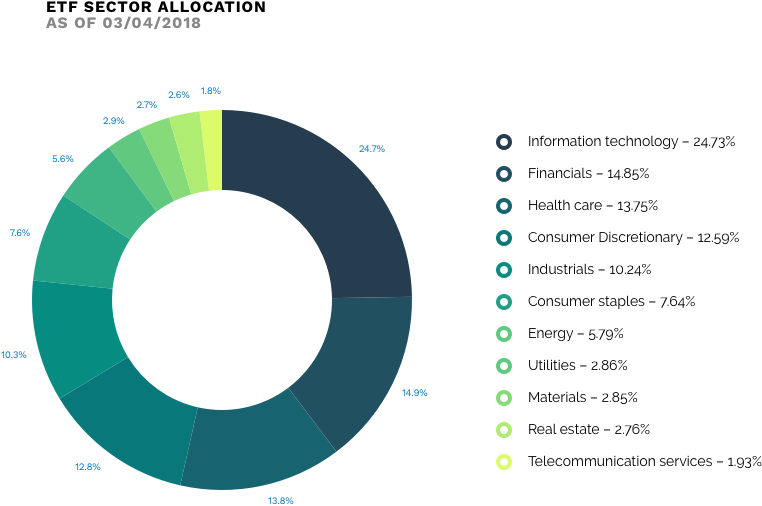
And what about investment returns?
The value of each unit in SPDR S&P500 ETF at any given time reflects the movement of the underlying index. So the objective of this fund is to generate the investment results corresponding to the returns of the index composed of the US 500 large cap market equities. As of March 23, 2018 returns were solid over the 1-Y, 3-Y and 5-Y period, with gains of 17.11%, 11.08% and 14.65%, respectively.
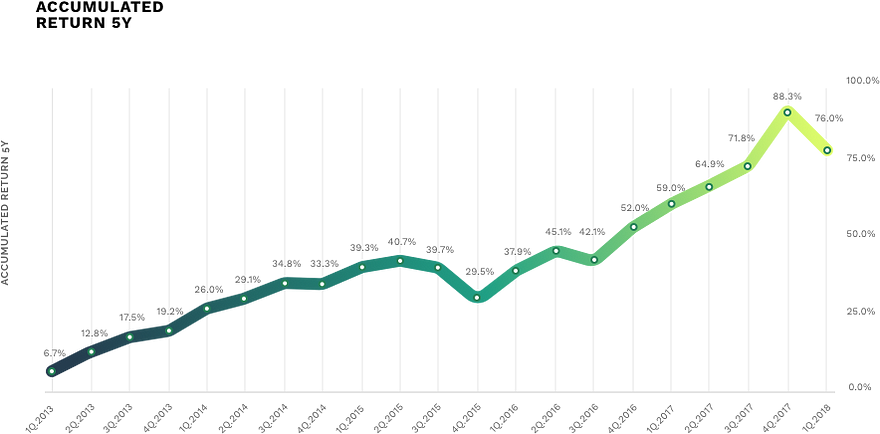
New horizons for the conventional vehicles
SPDR S&P 500 ETF is the best recognised and the oldest ETF which typically tops rankings for the largest asset under management and greatest trading volume. To sum it all up, the key benefits of SPDR S&P 500 ETF are:
- Closely tracks the performance of the S&P 500 index;
- The oldest of the S&P 500 benchmarked fund;
- Ability to get a depth of the market exposure;
- Provides an opportunity to diversify the portfolio;
- Can be used as a hedging instrument;
- Highly liquid.
Thanks to the success of SPDR S&P500 ETF derived from its key advantages, today the number and variety of ETFs allow its investors to get exposure to nearly each market asset class.
How do crypto investors may get exposure to such a popular instrument as ETF among traditional investors? The Blackmoon Platform provides a unique opportunity for a blockchain investor to access the performance of a liquid, conventional and diversified instrument as an ETF, gaining exposure to the US large cap space without leaving the Blockchain ecosystem. You may find more information regarding the SPDR S&P500 ETF and Blackmoon Platform here.
- platform website: blackmoonplatform.com
- telegram chat for the investors in asset tokens https://t.me/blackmoonplatform
- telegram chat for the BMC token holders https://t.me/blackmooncrypto
Disclaimer: This article provides you with educational material only and was prepared by Blackmoon team for information purposes only. Cryptocurrency markets are unregulated and carry a high degree of risk, including risk of loss of entire investment. Only risk capital you can afford to lose. This post is not intended to be investment advice. Before deciding to invest, you should seek independent legal and professional advice.