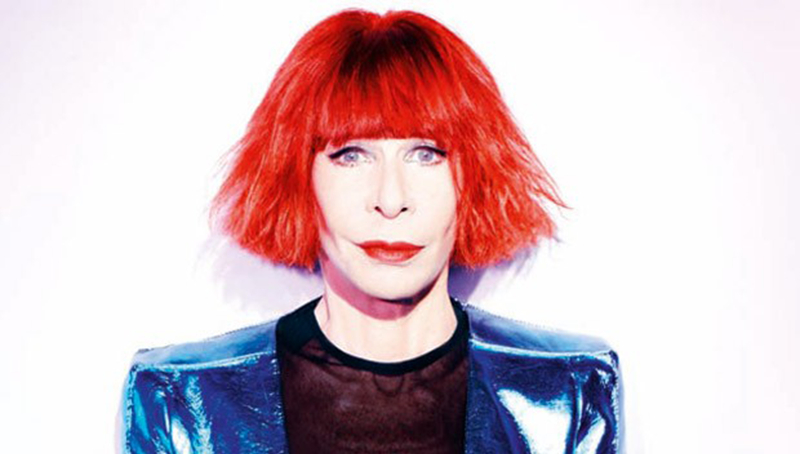
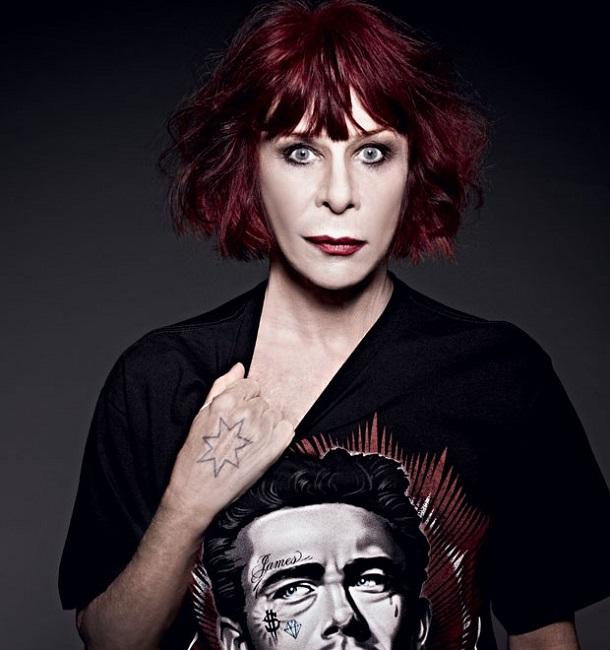
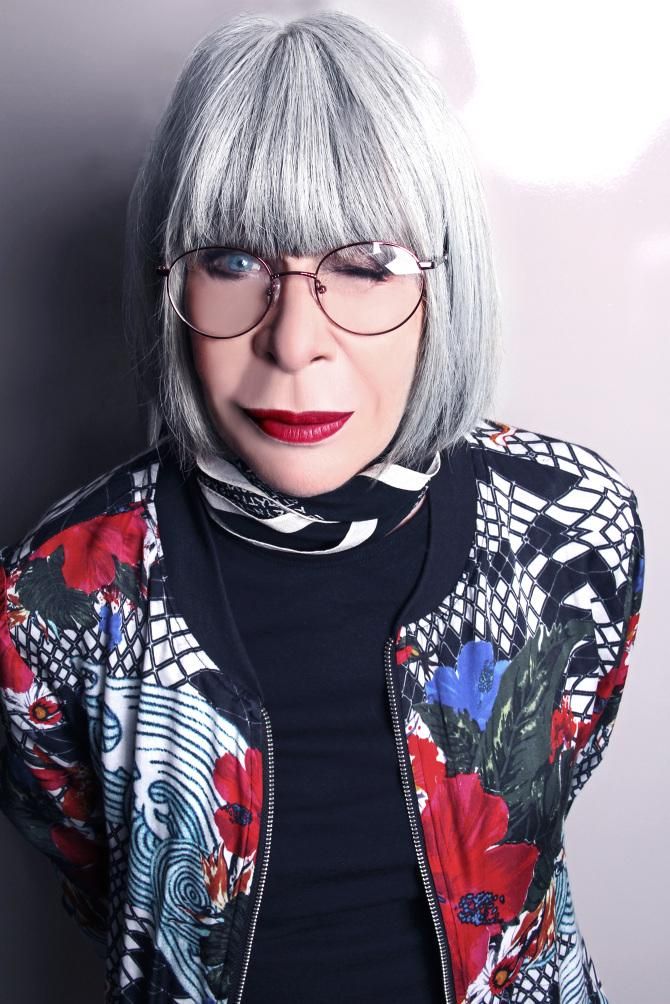
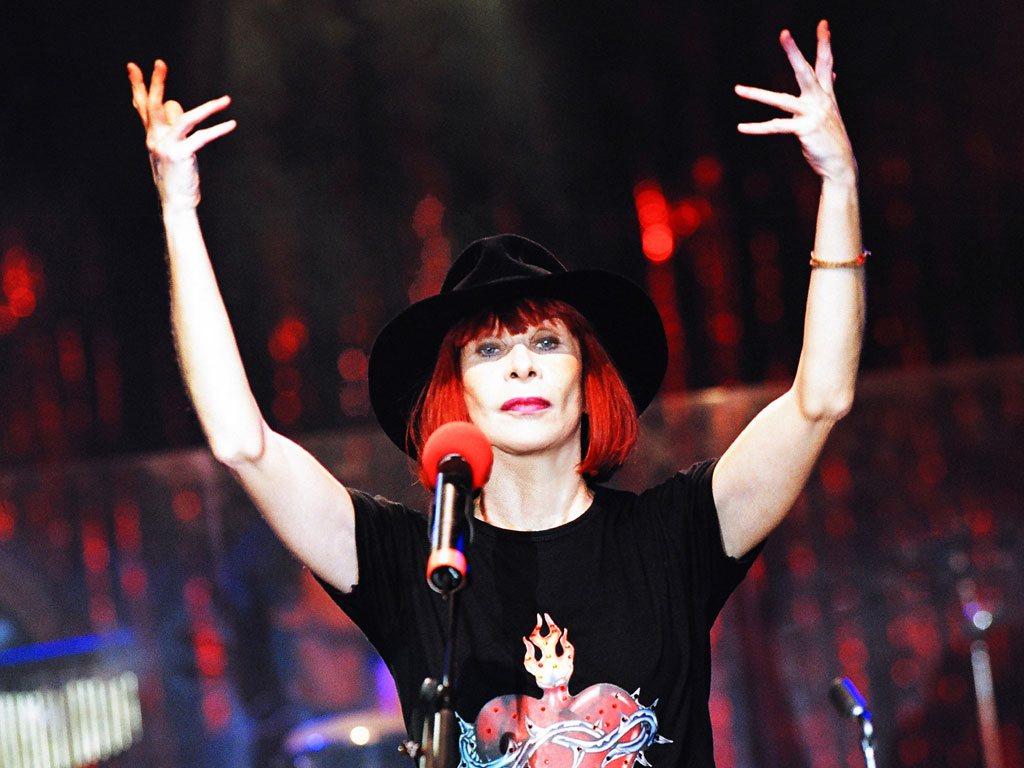
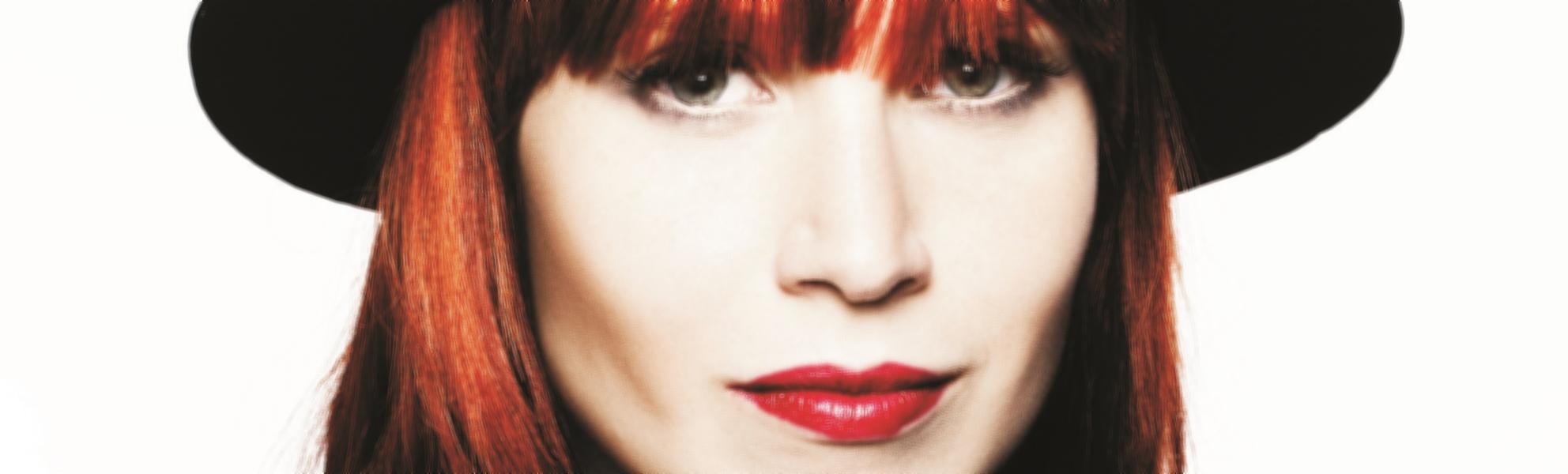
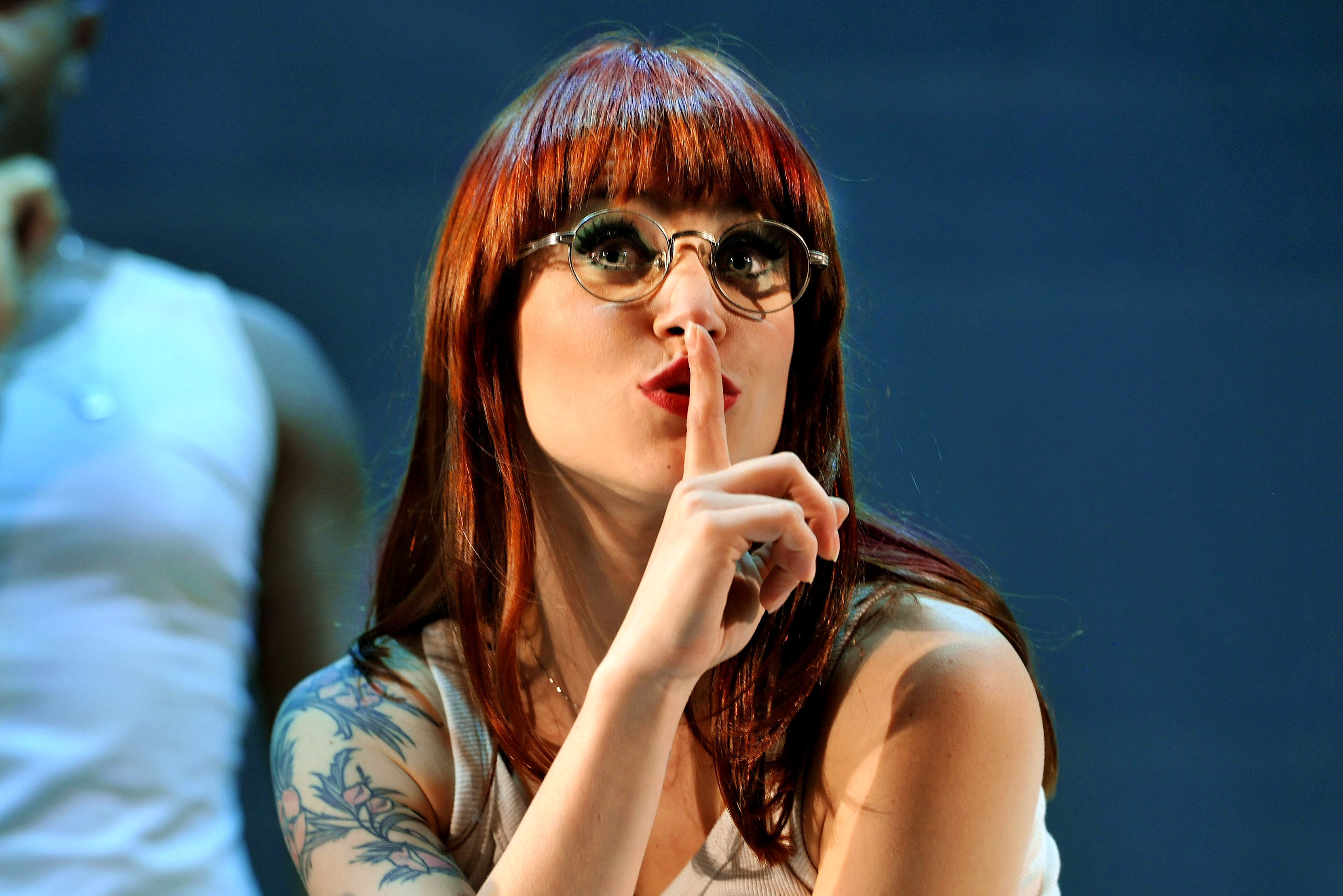
Rita Lee

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In this Portuguese name , the first or maternal family name is Lee and the second or paternal family name is Jones .
For the Playboy Playmate of the Month, see Rita Lee (model) .
This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification . Please help by adding reliable sources . Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately , especially if potentially libelous or harmful. Find sources: "Rita Lee" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR ( July 2013 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message )
^ "Rita Lee é a brasileira que mais vendeu livros de não-ficção em 2017" . Forbes Brasil. 1 February 2018 . Retrieved 22 January 2020 .
^ Eugene C. Harter. "The Lost Colony of the Confederacy". Texas A&M University Press, 1985, p. 74.
^ "Biography" . ritalee.com.br . Rita Lee. Archived from the original on 19 December 2005.
^ "Rita Lee critica a volta dos Muntantes « House of Progressive" . Archived from the original on 13 February 2007 . Retrieved 12 February 2019 .
^ Victoria Langland, "Il est Interdit d'Interdire: The Transnational Experience of 1968 in Brazil", Estudios Interdisciplinarios de América Latina y el Caribe, Vol. 17, No. 1 (2006)
^ "Mutantes – depois de 30 anos, as mutações voltaram" . Retrieved 7 October 2018 .
^ "Rita Lee – Biography & History" . AllMusic . Retrieved 7 October 2018 .
^ Jump up to: a b "Albuns – Rita Lee & Tutti Frutti – the band" . Archived from the original on 2 December 2013 . Retrieved 19 September 2013 .
^ Jump up to: a b Nascimento, Roberto. "Esse tal de Rock... ACERTOU" (in Portuguese). Estado de São Paulo. Archived from the original on 1 January 2013.
^ "Lista dos 100 maiores discos da música brasileira pela Rolling Stone Brasil" (in Portuguese). Rateyourmusic.com . Retrieved 4 July 2013 .
^ "Cliquemusic : Artista : Rita Lee" (in Portuguese). Cliquemusic.uol.com.br. Archived from the original on 8 March 2017 . Retrieved 12 February 2019 .
^ "All Brazilian Music: Artista: Rita Lee" . Archived from the original on 5 August 2011.
Wiki Loves Monuments: your chance to support Russian cultural heritage!
Photograph a monument and win!
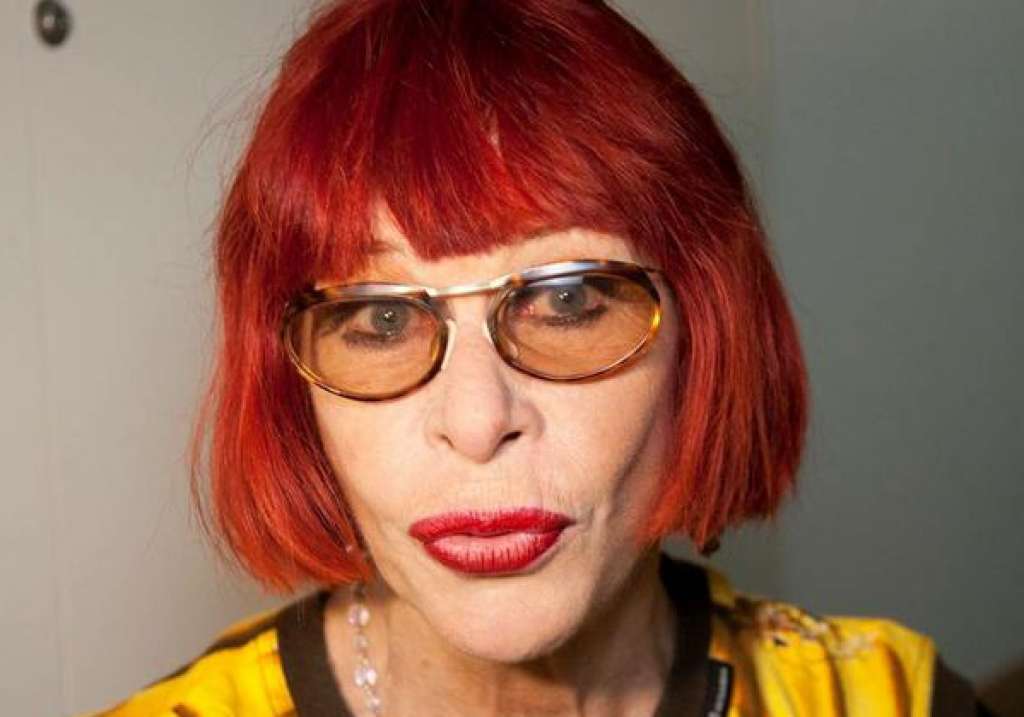
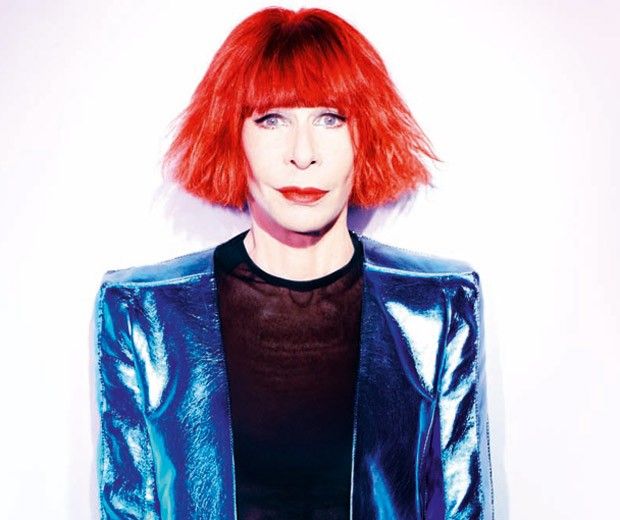
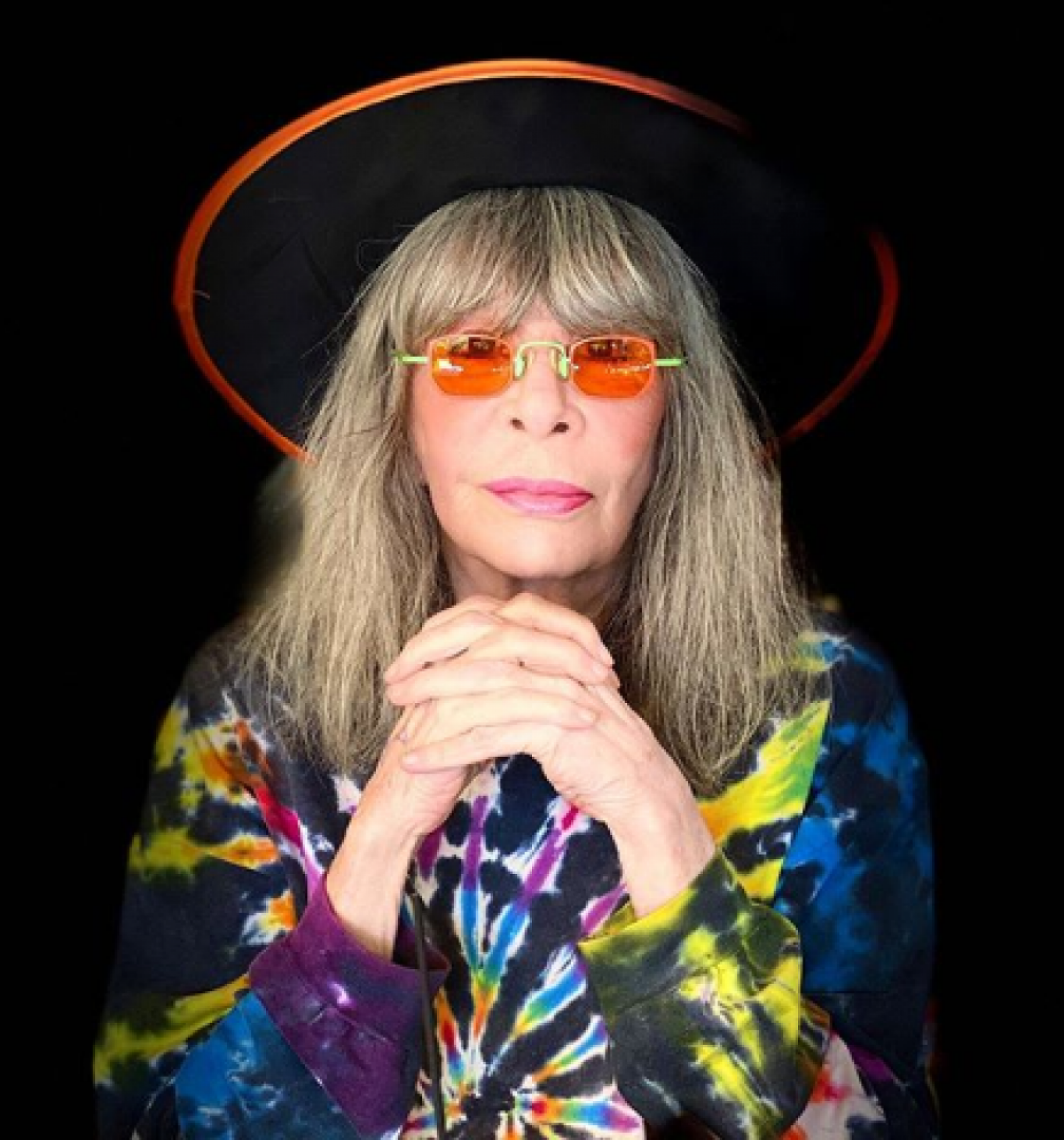
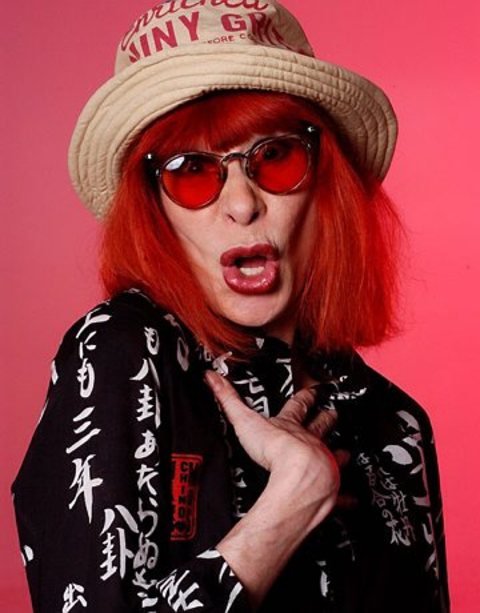
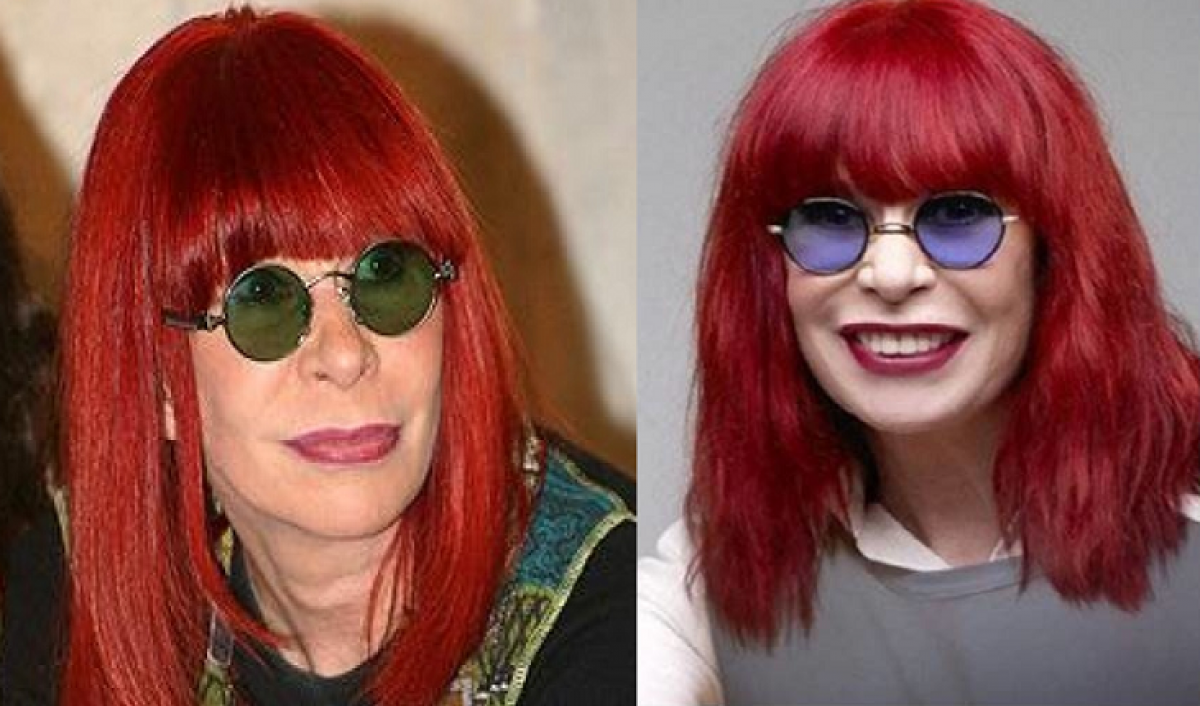
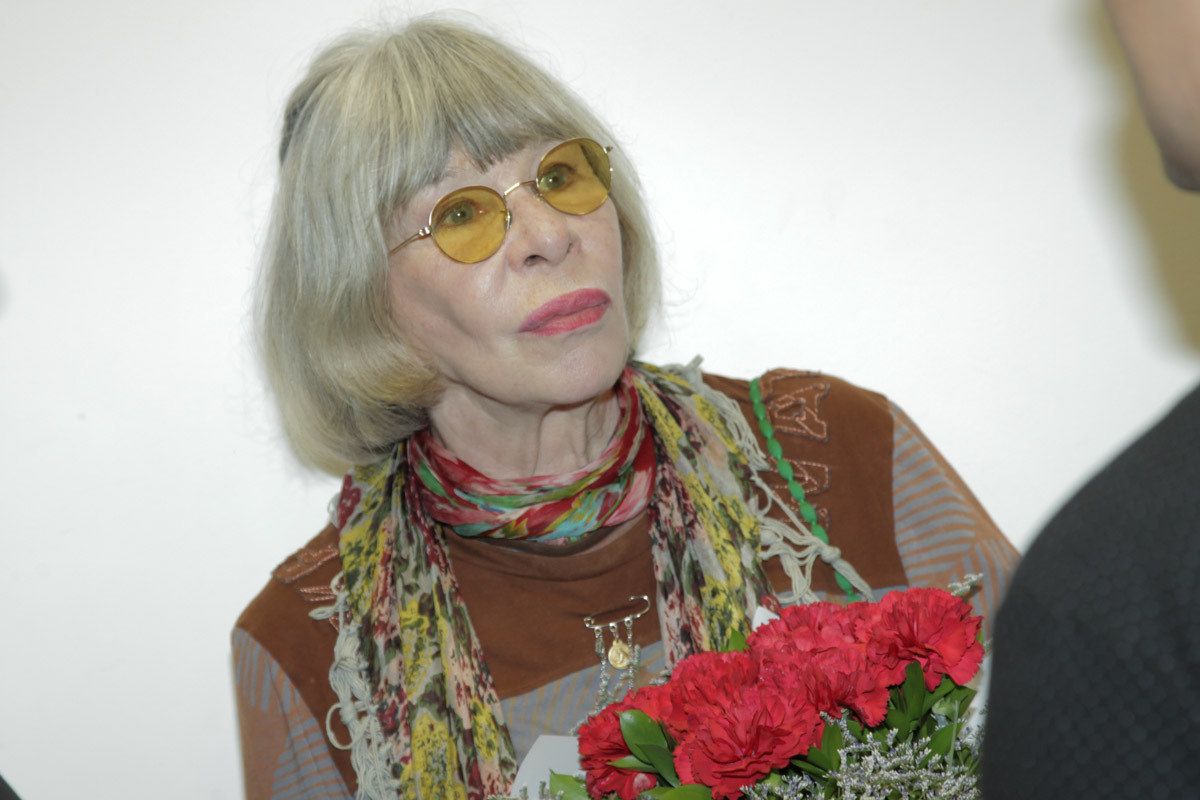
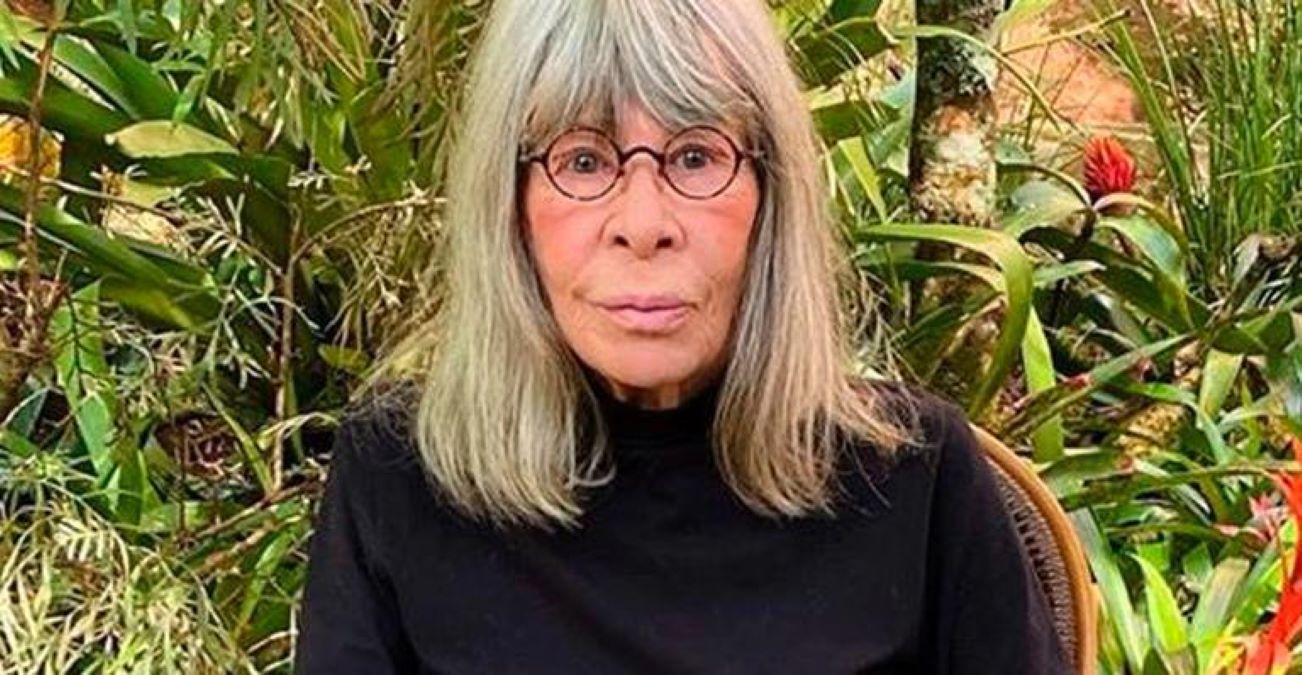
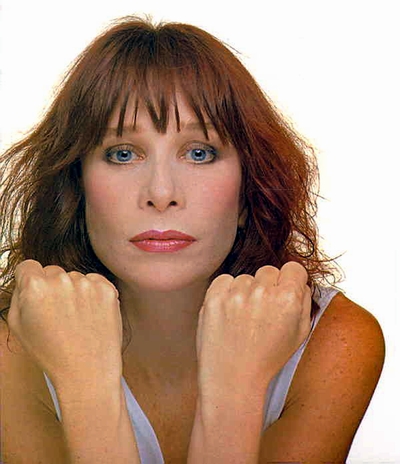
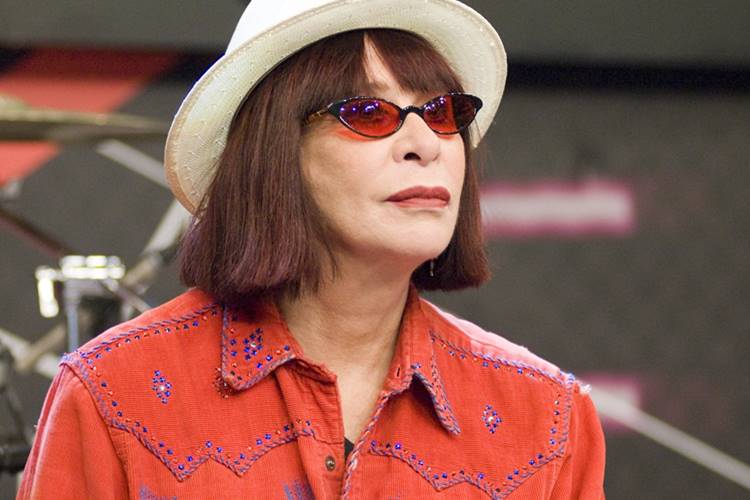
Rita Lee Jones ( Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈʁitɐ li] , born 31 December 1947) is a Brazilian rock singer, composer and writer. She is a former member of the Brazilian band Os Mutantes and is a popular figure in Brazilian entertainment, where she is also known for being an animal rights activist and a vegan . She has sold more than 60 million albums worldwide [ citation needed ] . Her autobiography Rita Lee: Uma Autobiografia was the best-selling non-fiction book of 2017 in Brazil. [1]
Rita Lee was born in São Paulo , Brazil, to an American father, Charles Fenley Jones, [2] a dentist descended from the Confederates , and Romilda Padula, a Brazilian mother of Italian ancestry and a pianist. Rita studied classical piano with the renowned pianist Magdalena Tagliaferro . In place of the traditional adolescent debut ball, she asked to receive a drum set.
She was educated in a French-language school and became fluent in Spanish, French, and Italian, as well as her native Portuguese and the English that her parents spoke at home. [3] She went to college, with the popular actress Regina Duarte as one of her classmates, but she soon left to pursue her musical career.
In 1966, Lee formed the band Os Mutantes with Arnaldo Baptista and Sérgio Dias . The band released five albums between 1968 and 1972. In that time, Lee had also released her first two solo works, although these records were produced with fellow members of Os Mutantes. When the band reformed in 2006, she refused to join, calling the reunion an attempt to "earn cash to pay for geriatry ". [4]
Lee formed a band with two other friends, excelling at vocals so much that they backed stars such as Tony Campelo, Jet Blacks, Demetrius, and Prini Lopez, when they met the brothers Arnaldo and Sérgio Dias Baptista. Adopting the name O'Seis (a pun with "the six" and the Brazilian caipira way of saying "you all"), they recorded the single "O Suicida," which was never released. When the rest of the band left for college, only three of them remained. Picking the name Os Mutantes, they backed Nana Caymmi on her then-husband's composition "Bom Dia" ( Gilberto Gil ). When Gil met them, he immediately knew Os Mutantes were on the same track as the Baianos, and the band worked extensively with the members of the Tropicalia collective over the next two years, becoming an integral part of the movement. Gil Invited them to accompany him at TV Record's 1967 III Festival da MPB, where they performed Gil's "Domingo no Parque" with the addition of Rogério Duprat conducting an orchestra with his revolutionary arrangements. Gil's friend Caetano Veloso also performed with a rock group (São Paulo band Beat Boys), and although the novelty of electric instruments and the general irreverence of the mixing of western pop and strange orchestral sounds irritated some in the festival audience, both performances ultimately won approval, with Gil coming second and Veloso taking fourth place. Within a year, however, the nascent Tropicalia movement would face strident opposition from both the military junta that ruled Brazil at the time, and from Brazil's student left, who regarded the Tropicalistas' dalliance with Western pop as a sell-out. Soon after, Os Mutantes recorded their single "O Relógio".
In 1968, Os Mutantes performed on the album/manifesto Tropicália ou Panis et Circensis (Philips), with Nara Leão , Caetano Veloso , Gilberto Gil, Gal Costa , and Tom Zé . This was also when they recorded their first LP, Os Mutantes , and they also backed Gilerto Gil on his second self-titled solo album . In September 1968, Os Mutantes backed Caetano Veloso during his two notorious performances in TV Globo's Third International Song Festival in Rio. The ensemble was met with howls of disapproval from leftist students in the audience at their first-round appearance, due to their challenging psychedelic music, as well as Veloso's lurid costume, and his sexually provocative stage moves. The confrontation climaxed in the second round of the competition on 15 September, when Veloso performed his newly-written psychedelic protest song "É Proibido Proibir" ("It is Forbidden to Forbid"). Left-wing students in the audience (who were strongly opposed to the Tropicalismo experiment) loudly abused, booed and jeered the performers, and pelted the stage with fruit, vegetables and paper balls. A large group in audience showed their disapproval by turning their backs to the stage, prompting Lee and her bandmates to turn their backs on the audience, and Veloso responded angrily to the heckling, haranguing the students at length for their conservatism. [5] The group also performed their "Caminhante Noturno", which won seventh place. In the same year, they participated at the IV FMPB with their "Dom Quixote" and, by Lee and Tom Zé, "2001". At the end of this year, they performed with the Baianos at the Sucata nightclub, Rio, and recorded their second album, also self-titled.
In 1969, following the arrests of Gil and Veloso, Os Mutantes went to Europe, playing at Cannes, France, at the MIDEM, and in Lisbon, Portugal . Then, they returned to Brazil and presented the show O Planeta dos Mutantes, the first multi-media experiment in Brazil. With bassist Liminha and drummer Dinho, they participated in the V FIC with "Ando Meio Desligado" (Arnaldo and Rita).
In 1970, Lee recorded her solo album, Build Up , produced by Arnaldo Baptista. Soon after, they had a stint at the Olympia in Paris. In that period, during their somewhat frequent tours in Europe, they recorded an LP that was never fully released, Tecnicolor , with the exception of some tracks included on 1971's Jardim Elétrico . The LP, A Divina Comédia ou Ando Meio Desligado , is from that year and Jardim Elétrico (Polydor) from the next. In 1972, Lee recorded another solo album backed by Os Mutantes, Hoje É o Primeiro Dia do Resto da Sua Vida (Philips). After releasing the Mutantes e Seus Cometas no País do Baurets , Lee was ejected from the group by Arnaldo. [6] Following a period of depression, during which she became locked up in her home, [ citation needed ] she decided to abandon her career, but, at the same time, she was writing the material that would make her famous as a solo artist. [7]
Following her removal from Os Mutantes in late 1972, Lee started a solo career. She was initially part of a female duo with singer Lúcia Turnbull called Cilibrinas do Éden, and after a short time the duo met Lisergia, a band that would eventually become Lee's backing band with the name of Tutti Frutti .
In 1974, the band recorded their first album Atrás do Porto Tem Uma Cidade ( There is a City Behind the Harbor ) that brought some great songs such as "Mamãe Natureza", "Menino Bonito", and "Pé de Meia". [8] In 1975, she recorded the album Fruto Proibido with the band. The album was praised by critics, sold more than 200,000 copies – a record to Brazilian rock and roll singers at the time [ citation needed ] – and Lee was given the title "Queen of Rock". [9] In 2007, the Brazilian edition of Rolling Stone magazine ranked this album as the 16th-best Brazilian album of all time in its " 100 Best List ". [10] The producer was Andy Mills, producer of Alice Cooper and then Lee's boyfriend. [9]
In the late 1970s, Lee started a partnership with her husband, Roberto de Carvalho, and many subsequent albums were credited to the duo Lee/Carvalho. [11] In the late 1970s, Lee was mentioned in the Caetano Veloso song, "Sampa".
In 1976, pregnant for the first time, she was arrested for possession of marijuana and condemned to one year of house imprisonment, when she composed with Paulo Coelho the single "Arrombou a Festa", which sold 200,000 copies. She continued to perform, under special judge permits. Soon after, she recorded the single "Doce de Pimenta" with singer Elis Regina , and recorded and toured with Gilberto Gil in the show/album Refestança .
In 1978, she released Babilônia , her fourth and last album with the band Tutti Frutti. The last work came after disagreements between members of the band. The guitarist Luis Carlini left the band, taking the name Tutti Frutti with him. Rita and the rest of the band finished the tour under the name Rita Lee & Cães e Gatos. [8] Lee started recording with her husband, Roberto de Carvalho. The couple wrote hits such as "Mania de Você" (1979), "Lança Perfume" (1980), "Saúde" (1981), "Flagra" (1982), and "On the Rocks" (1983). [12]
Lee was married to Mutante Arnaldo Baptista from 1971 to 1972. In 1976, MPB singer Ney Matogrosso introduced her to guitarist Roberto de Carvalho, whom she married, and they had three children: Beto Lee , João Lee, and Antônio. She has been married to Carvalho ever since and refers to him as her "boyfriend". [ citation needed ]
Aside from her musical career, Lee had a humor program called Radio Amador on Brazilian radio for nine months in 1986. That same year, Lee wrote three children's books and appeared in Brazilian movies and TV shows. In 1990, she started her own talk show, called TvLeeZão (a play on "televisão", the Portuguese word for television), on MTV Brasil . From 2002 to 2004, she hosted the Brazilian cable TV talk show Saia Justa . In 2005, her husband and she started a new talk show, called Madame Lee . She also made a brief cameo in the 2002 film Durval Discos . In 2008–09, she performed a new show called Pic Nic Tour . In 2010, she performed another new show called Etc...Tour , revisiting some forgotten songs from her long career. In 2011, she began to produce and record two new albums. The first one has new unreleased songs, and the second one is called Bossa'n Movies where she continues the project started with Bossa'n Roll in 1991 and Bossa'n Beatles ( Aqui, ali, em qualquer lugar ).
In 2011, she contributed the track "Pistis Sophia" to the Red Hot Organization 's most recent charitable album, Red Hot+Rio 2 . The album was a follow-up to the 1996 Red Hot + Rio . Proceeds from the sales were donated to raise awareness and money to fight AIDS and related other health and social issues.
( 1947-12-31 ) 31 December 1947 (age 73)
Singer, songwriter, actress, author, TV host
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
↑ Rita Lee // ČSFD (чеш.) — 2001.
↑ Rita Lee é a brasileira que mais vendeu livros de não-ficção em 2017 (неопр.) . Forbes Brasil (1 февраля 2018). Дата обращения: 22 января 2020.
↑ Eugene C. Harter. «The Lost Colony of the Confederacy». Texas A&M University Press, 1985, p. 74.
↑ Biography (неопр.) . ritalee.com.br . Rita Lee. Архивировано 19 декабря 2005 года.
↑ Rita Lee critica a volta dos Muntantes « House of Progressive (неопр.) . Дата обращения: 12 февраля 2019. Архивировано 13 февраля 2007 года.
↑ Victoria Langland, «Il est Interdit d’Interdire: The Transnational Experience of 1968 in Brazil», Estudios Interdisciplinarios de América Latina y el Caribe, Vol. 17, No. 1 (2006)
↑ Maria Helena Guedes. Os Mutantes! — Clube de Autores. — С. 24. — 62 с.
↑ Mutantes – depois de 30 anos, as mutações voltaram (неопр.) . Дата обращения: 7 октября 2018.
↑ Rita Lee – Biography & History (неопр.) . AllMusic. Дата обращения: 7 октября 2018.
↑ Перейти обратно: 1 2 Albuns – Rita Lee & Tutti Frutti – the band (неопр.) . Дата обращения: 19 сентября 2013. Архивировано 2 декабря 2013 года.
↑ Перейти обратно: 1 2 Nascimento, Roberto Esse tal de Rock... ACERTOU (порт.) (недоступная ссылка) . Estado de São Paulo. Архивировано 1 января 2013 года.
↑ Lista dos 100 maiores discos da música brasileira pela Rolling Stone Brasil (порт.) . Rateyourmusic.com. Дата обращения: 4 июля 2013.
↑ Cliquemusic : Artista : Rita Lee (порт.) . Cliquemusic.uol.com.br. Дата обращения: 12 февраля 2019. Архивировано 8 марта 2017 года.
↑ All Brazilian Music: Artista: Rita Lee (неопр.) . Архивировано 5 августа 2011 года.
Для улучшения этой статьи желательно :
Найти и оформить в виде сносок ссылки на независимые авторитетные источники , подтверждающие написанное . Проверить качество перевода с иностранного языка. Пожалуйста, после исправления проблемы исключите её из списка параметров. После устранения всех недостатков этот шаблон может быть удалён любым участником.
Вики любит памятники: ваш взгляд на культурное наследие России!
Фотографируйте исторические и архитектурные памятники. Авторы лучших снимков получат призы!
Рита Ли ( порт. Rita Lee ; урожд. Рита Ли Джонс , порт. Rita Lee Jones , 31 декабря 1947) — бразильская рок-певица, композитор и писательница. Бывшая участница группы Os Mutantes и популярная в бразильском шоу-бизнесе персона. Также является борцом за права животных и веганом. Её автобиография Rita Lee: Uma Autobiografia в 2017 году стала самой продаваемой не научно-популярной книгой в Бразилии [2] .
Родилась в Сан-Пауло , в Бразилии у американского отца, Чарльза Фенли Джонса [3] , дантиста конфедерадосского происхождения и Ромильды Падулы, бразильской матери итальянского происхождения и пианистки. Изучала классическое фортепиано у известной пианистки Магдалены Тальяферро. Вместо традиционного первого подросткового бала она попросила купить ударную установку.
Получила образование во французской языковой школе и свободно говорила на испанском, французском и итальянском, а также на своем родном португальском и английском, на котором её родители говорили дома [4] . Далее она пошла в колледж, где была коллегой популярной актрисы Регины Дуарте , но вскоре ушла, чтобы продолжить свою музыкальную карьеру.
В 1955 году Ли вместе с Арнальдо Баптистой (англ.) русск. и Серхио Диасом (англ.) русск. основала Os Mutantes .
В период между 1968 и 1972 годами они выпустили пять альбомов. В то же время Ли выпустила пару сольных альбомов, хотя они и были спродюсированы и записаны при участии Os Mutantes. Когда группа реформировалась в 2006 году, она отказалась присоединиться, назвав воссоединение «попыткой заработать деньги, чтобы заплатить за гериатрию » [5] .
Ли сформировала группу также с ещё двумя друзьями и вместе они сопровождали таких исполнителей как, Тони Кампело, Jet Blacks, Demetrius и Прини Лопес, прежде чем повстречали Арнальдо Баптисту и Серхио Диаса. Взяв название O’Seis (игра слов «the six» и «you all» по бразильскому кайпирскому диалекту ) они записали сингл «O Suicida», который никогда не был выпущен. Когда остальные ушли учиться в колледж, группа стала трио. Выбрав название Os Mutantes они приняли участие в сингле тогдашнего мужа Наны Каимми (англ.) русск. «Bom Dia» ( Жил Жилберту ). Когда Жил встретил их, он сразу понял, что Os Mutantes были на том же пути, что и Baianos, и коллектив активно сотрудничал с тропикалия -группами в течение следующих двух лет, став неотъемлемой частью движения. Также Жил пригласил их разогревать его на TV Record’s 1967 III Festival da MPB, где они исполнили его песню «Domingo no Parque» при участии Рожериу Дюпрата. Друг Жила Каэтано Велозо также выступал с рок-группой (группа Beat Boys из Сан-Паулу), и хотя новость об использовании электрических инструментах и общее неуважение к смешиванию западной поп-музыки и странных оркестровых звуков раздражали некоторых зрителей фестиваля, оба выступления в конечном итоге получили одобрение вместе с Жилом, занявшим второе место и Велозу, занявшим четвёртое место. За год, однако, зарождающееся движение Тропикалия столкнётся с резким неприятием как со стороны военной хунты, которая управляла Бразилией в то время, так и со стороны некоторых бразильских студентов, которые расценивали склонность тропикалистов к западной поп-музыке как продажность. Вскоре после этого Os Mutantes записали свой сингл «O Relógio».
В 1968 году Os Mutantes появились на совместном альбоме с Нарой Леан , Каэтану Велозу , Жилбертом Жилом, Галой Коста и Томом Зе — Tropicália ou Panis et Circensis ru en (Philips). Тогда же они записали свой собственный дебютный альбом Os Mutantes и снова сотрудничали с Жилбертом Жилом на его втором одноимённом альбоме. В сентябре 1968 года Os Mutantes играли с Каэтану Велозу на его двух выступлениях на Третьем международном фестивале песни TV Globo в Рио. Во время выступления в первом туре ансамбль освис
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rita_Lee
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rita_Lee
Sex Tube Allison Desire Camera
Behringer Tm300 Tube Amp Modeler
Mom In Stocking Sex
Rita Lee - Wikipedia
Ли, Рита — Википедия
Rita Lee - Bossa'n Beatles - YouTube
Rita Lee - Слушать онлайн все песни и альбомы исполнителя ...
Rita Lee | Multishow Ao Vivo (Show Completo) - YouTube
Rita Lee - Rita Lee (Álbum Completo) [1979] - YouTube
Музыка Rita lee | Last.fm
Ruta Lee - Wikipedia
List of people in Playboy 1970–1979 - Wikipedia
Rita Lee | Rock Archeologia 60 – 70
Rita Lee