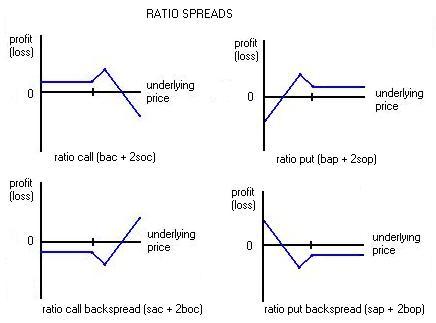
Ratio Spread

🔞 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Ratio Spread
Toggle navigation
The Options Guide
Outlook on Underlying:
Arbitrage
Bearish
Bullish
Neutral - Bearish on Volatility
Neutral - Bullish on Volatility
Profit Potential:
Limited
Unlimited
Loss Potential:
Limited
Unlimited
Credit/Debit:
Credit
Debit
No. Legs:
1
2
3
4
The ratio spread is a neutral strategy in options trading that involves buying a number of options
and selling more options
of the same underlying stock and expiration date
at a different strike price . It is a limited profit, unlimited risk options trading strategy that is taken when
the options trader thinks that the underlying stock will experience little
volatility in the near term.
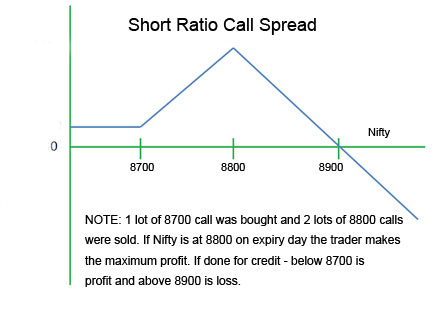
Using calls , a 2:1 call ratio spread can be implemented by buying a number of calls
at a lower strike and selling twice the number of calls at a higher strike.
Maximum gain for the call ratio spread is limited and is made when the underlying stock price at expiration
is at the strike price of the options sold. At this price, both the written calls
expire worthless while the long call expires in the money.
The formula for calculating maximum profit is given below:
Loss occurs when the stock price makes a strong move to the upside beyond the upper beakeven point . There
is no limit to the maximum possible loss when implementing the call ratio spread strategy.
The formula for calculating loss is given below:
Any risk to the downside for the call ratio spread is limited to the debit taken to put on the spread (if
any). There may even be a profit if a credit is received when putting on the spread.
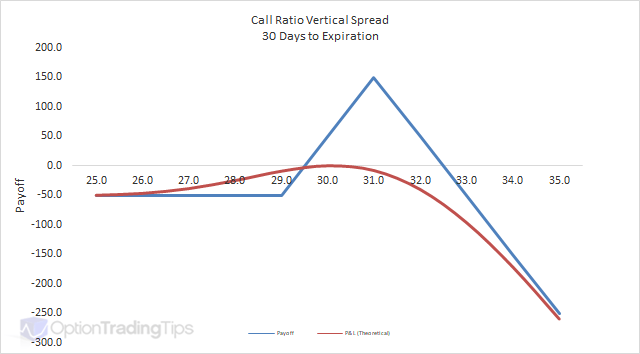
There are 2 break-even points for the ratio spread position. The breakeven points can be calculated using the following formulae.
Using the graph shown earlier, since the maximum profit is $500, points of maximum
profit is therefore equals to 5. Adding this to the higher strike of $45, we can
calculate the breakeven point to be $50. (See example below)
Suppose XYZ stock is trading at $43 in June. An options trader executes a 2:1 ratio
call spread strategy by buying a JUL 40 call for $400 and selling two JUL 45 calls for $200 each. The net debit/credit taken to enter the trade is zero.
On expiration in July, if XYZ stock is trading at $45, both the JUL 45 calls expire
worthless while the long JUL 40 call expires in the money with $500 in intrinsic
value. Selling or exercising this long call will give the options trader his maximum
profit of $500.
If XYZ stock rallies and is trading at $50 on expiration in July, all the options
will expire in the money but because the trader has written more calls than he has
bought, he will need to buy back the written calls which have increased in value.
Each JUL 45 call written is now worth $500. However, his long JUL 40 call is worth
$1000 and is just enough to offset the losses from the written calls. Therefore,
he achieves breakeven at $50.
Beyond $50 though, there will be no limit to the loss possible. For example, at
$60, each written JUL 45 call will be worth $1500 while his single long JUL 40 call
is only worth $2000, resulting in a loss of $1000.
However, there is no downside risk to this trade. If the stock price had dropped
to $40 or below at expiration, all the options involved will expire worthless. Since
the net debit to put on this trade is zero, there is no resulting loss.
Note: While we have covered the use of this strategy with reference to stock options, the ratio spread is equally applicable using ETF options, index options as well as options on futures .
For ease of understanding, the calculations depicted in the above examples did not take into account commission charges as they are relatively small amounts (typically around $10 to $20) and varies across option brokerages .
However, for active traders, commissions can eat up a sizable portion of their profits in the long run. If you trade options actively, it is wise to look for a low commissions broker. Traders who trade large number of contracts in each trade should check out OptionsHouse.com as they offer a low fee of only $0.15 per contract (+$4.95 per trade).
The following strategies are similar to the ratio spread in that they are also low volatility strategies that have limited profit potential and unlimited risk.
The call ratio spread can also be used to repair a long stock position that has been hit with an unrealized loss. This stock repair
strategy can reduce the price needed to breakeven on the long stock with
virtually no cost.
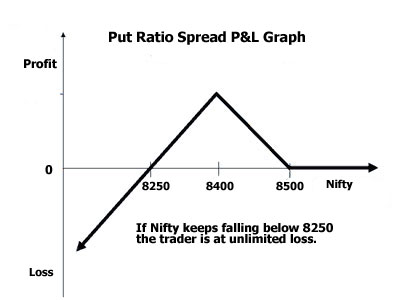
The ratio spread can also be constructed using puts. The put ratio spread is similar
to the call ratio spread strategy but has a slightly more bullish and less bearish
risk profile.
The converse strategy to the ratio spread is the backspread.
Backspreads
are used when large movements is expected of
the underlying stock price.
Buying straddles is a great way to play earnings.
Many a times, stock price gap up or down following the quarterly earnings report
but often, the direction of the movement can be unpredictable. For instance, a sell
off can occur even though the earnings report is good if investors had expected
great results.... [Read on...]
If you are very bullish on a particular stock for the long term and is looking to
purchase the stock but feels that it is slightly overvalued at the moment, then
you may want to consider writing put options on the
stock as a means to acquire it at a discount.... [Read on...]
Also known as digital options, binary options belong to a special class of exotic options in which the option trader speculate purely on the direction of the underlying within a relatively short period of time..... [Read on...]
If you are investing the Peter Lynch style, trying to predict the next multi-bagger,
then you would want to find out more about LEAPS® and why I consider them to be a great option for investing in the next Microsoft®....
[Read on...]
Cash dividends issued by stocks have big impact on their option prices. This is
because the underlying stock price is expected to drop by the dividend amount on the ex-dividend date.... [Read on...]
As an alternative to writing covered calls, one can enter a bull call spread for
a similar profit potential but with significantly less capital requirement. In
place of holding the underlying stock in the covered call strategy, the alternative.... [Read on...]
Some stocks pay generous dividends every quarter. You qualify for the dividend if
you are holding on the shares before the ex-dividend date.... [Read on...]
To achieve higher returns in the stock market, besides doing more homework on the
companies you wish to buy, it is often necessary to
take on higher risk. A most common way to do that is to buy stocks on margin.... [Read on...]
Day trading options can be a successful, profitable strategy but there are a couple of things you need to know before you use start using options for day trading.... [Read on...]
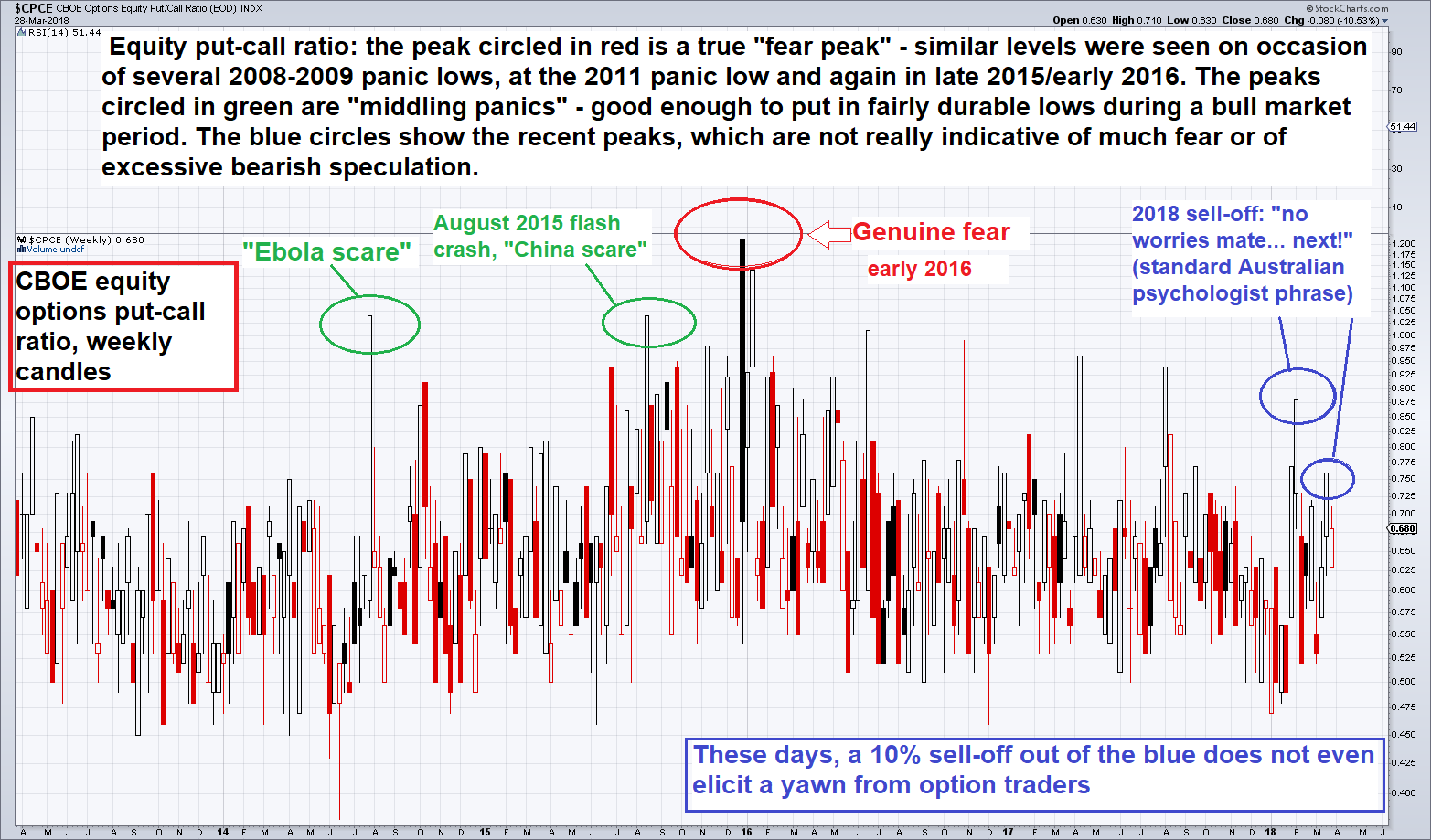
Learn about the put call ratio, the way it is derived and how it can be used as a contrarian indicator.... [Read on...]
Put-call parity is an important principle in options pricing first identified by Hans Stoll in his paper, The Relation Between Put and Call Prices, in 1969. It states that the premium of a call option implies a certain fair price for the corresponding put option having the same strike price and expiration date, and vice versa.... [Read on...]
In options trading, you may notice the use of certain greek alphabets like delta
or gamma when describing risks associated with various positions. They are known as "the greeks".... [Read on...]
Since the value of stock options depends on the price of the underlying stock, it
is useful to calculate the fair value of the stock by using a technique known as
discounted cash flow....
[Read on...]
Risk Warning: Stocks, futures and binary options trading discussed on this website can be considered High-Risk Trading Operations and their execution can be very risky and may result in significant losses or even in a total loss of all funds on your account. You should not risk more than you afford to lose. Before deciding to trade, you need to ensure that you understand the risks involved taking into account your investment objectives and level of experience.
Information on this website is provided strictly for informational and educational purposes only and is not intended as a trading recommendation service. TheOptionsGuide.com shall not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon.
General Risk Warning:
The financial products offered by the company carry a high level of risk and can result in the loss of all your funds. You should never invest money that you cannot afford to lose.
Ratio Spread Definition
Ratio Spread Explained | Online Option Trading Guide
Trade Checklist: Ratio Spread | Options Trading Concepts - YouTube
Ratio Spread - What is a Front Ratio Put & Call? | tastytrade
Ratio Spreads by OptionTradingpedia.com
tastytrade.com - A Real Financial Network
Options Trading Concepts | Mike & His White Board
Russian School Girls Fuck
Outdoor Jeans
Fortnite Overwatch
Incest Mom Homemade
Facial Sperm Cumshot




































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ProfitFromVolatility1-4f68837d0ec244df8eb775a9e65bcf40.png)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/putcall-33278e98152e4610b1dd8e78448eef47.png)