Python Private Variables

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Difficulty Level :
Hard Last Updated :
19 Aug, 2021
# Python code to illustrate how mangling works
def __init__( self , iterate):
self . list .append(item)
# private copy of original geek() method
# provides new signature for geek() but
def geek( self , key, value):
for i in zip (keys, value):
self . list .append(i)
# Python code to illustrate how double
# underscore at the beginning works
def __double_method( self ): # for mangling
def __double_method( self ): # for mangling
# Python code to illustrate double leading and
# '__init__' for initializing, this is a
# custom special method. try not to use it
Python program to determine if the given IP Address is Public or Private using ipaddress module
Access Modifiers in Python : Public, Private and Protected
Global and Local Variables in Python
Python | Extract key-value of dictionary in variables
Python - Breaking Up String Variables
Python | Difference between Pandas.copy() and copying through variables
Python | Assign multiple variables with list values
Python program to find number of local variables in a function
How are variables stored in Python - Stack or Heap?
Python | Unpack whole list into variables
Tracing Tkinter variables in Python
How to Create Dummy Variables in Python with Pandas?
Python - Construct variables of list elements
Python - Pearson Correlation Test Between Two Variables
Assigning multiple variables in one line in Python
Viewing all defined variables in Python
Python program to create dynamically named variables from user input
How to check multiple variables against a value in Python?
Competitive Programming Live Classes for Students
DSA Live Classes for Working Professionals
5th Floor, A-118, Sector-136, Noida, Uttar Pradesh - 201305
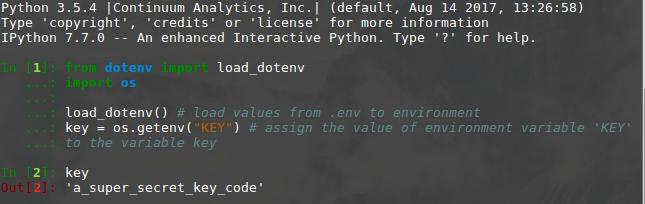
Prerequisite: Underscore in Python In Python, there is no existence of “Private” instance variables that cannot be accessed except inside an object. However, a convention is being followed by most Python code and coders i.e., a name prefixed with an underscore, For e.g. _geek should be treated as a non-public part of the API or any Python code, whether it is a function, a method, or a data member. While going through this we would also try to understand the concept of various forms of trailing underscores , for e.g., for _ in range(10), __init__(self).
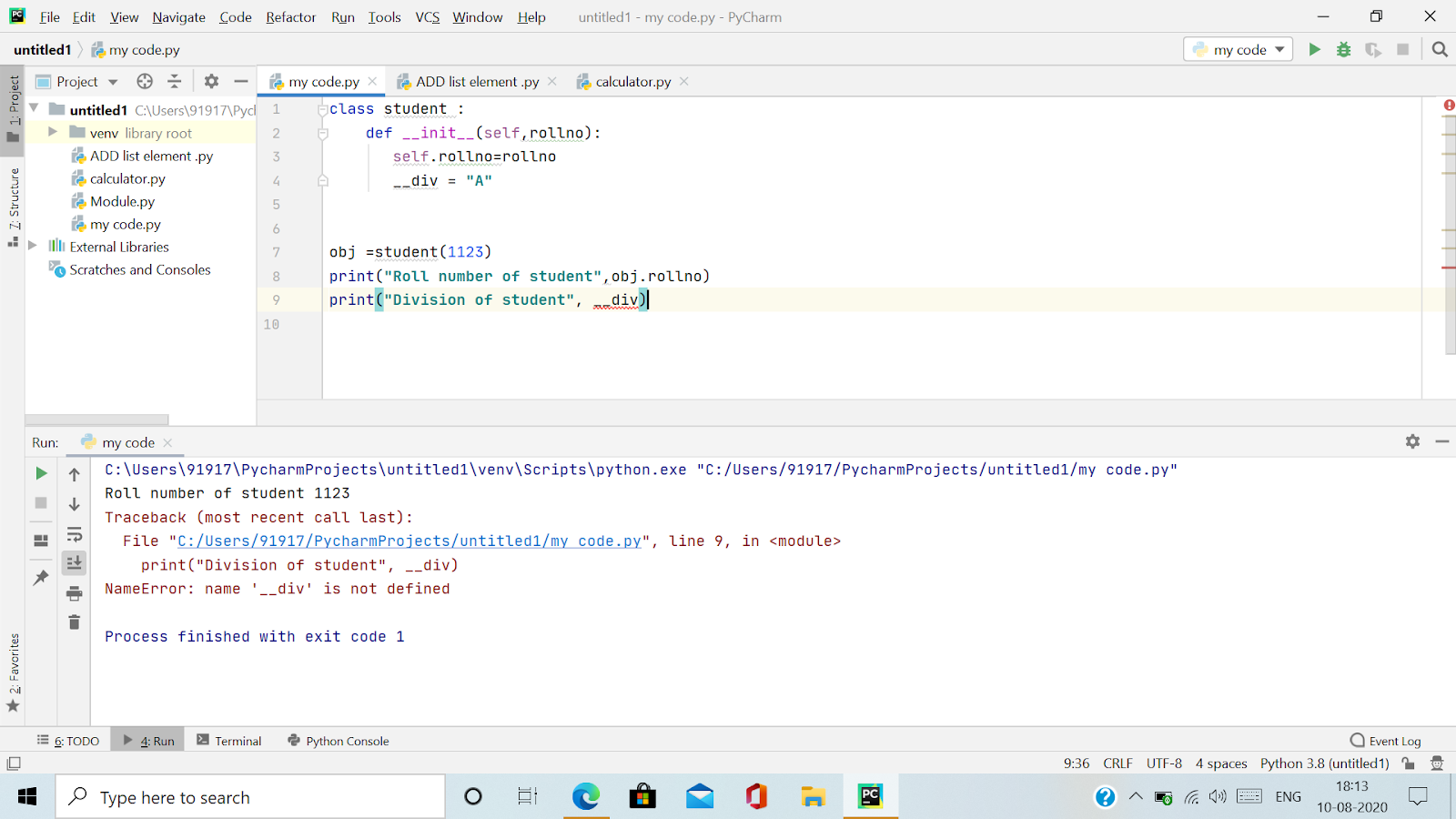
In Python, there is something called name mangling, which means that there is limited support for a valid use-case for class-private members basically to avoid name clashes of names with names defined by subclasses. Any identifier of the form __geek (at least two leading underscores or at most one trailing underscore) is replaced with _classname__geek, where classname is the current class name with a leading underscore(s) stripped. As long as it occurs within the definition of the class, this mangling is done. This is helpful for letting subclasses override methods without breaking intraclass method calls. Let’s look at this example and try to find out how this underscore works:
The mangling rules are designed mostly to avoid accidents but it is still possible to access or modify a variable that is considered private. This can even be useful in special circumstances, such as in the debugger.
So basically one underline at the beginning of a method, function, or data member means you shouldn’t access this method because it’s not part of the API. Let’s look at this snippet of code:
The snippet is taken from the Django source code (django/forms/forms.py). This suggests that errors are property, and it’s also a part of the API, but the method, _get_errors, is “private”, so one shouldn’t access it.
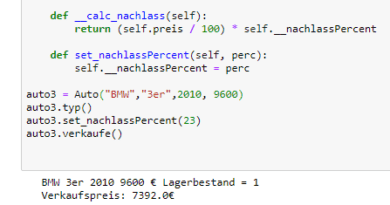
Two underlines, in the beginning, cause a lot of confusion. This is about syntax rather than a convention. double underscore will mangle the attribute names of a class to avoid conflicts of attribute names between classes. For example:
__Double leading and Double trailing underscores__
There’s another case of double leading and trailing underscores. We follow this while using special variables or methods (called “magic method”) such as__len__, __init__. These methods provide special syntactic features to the names. For example, __file__ indicates the location of the Python file, __eq__ is executed when a == b expression is executed.
This article is contributed by Chinmoy Lenka . If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks. I have referred Python Docs, hackernoon.com and igorsobreira.com Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course. And to begin with your Machine Learning Journey, join the Machine Learning – Basic Level Course
Writing code in comment?
Please use ide.geeksforgeeks.org ,
generate link and share the link here.
© Copyright 2021. All Rights Reserved.
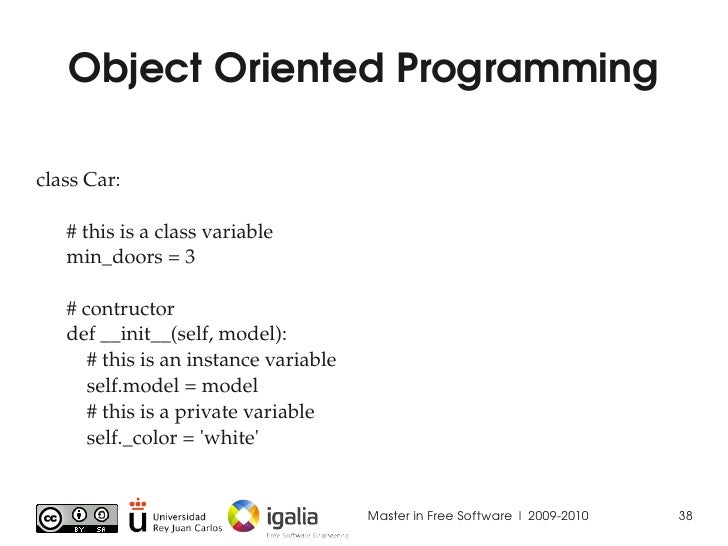
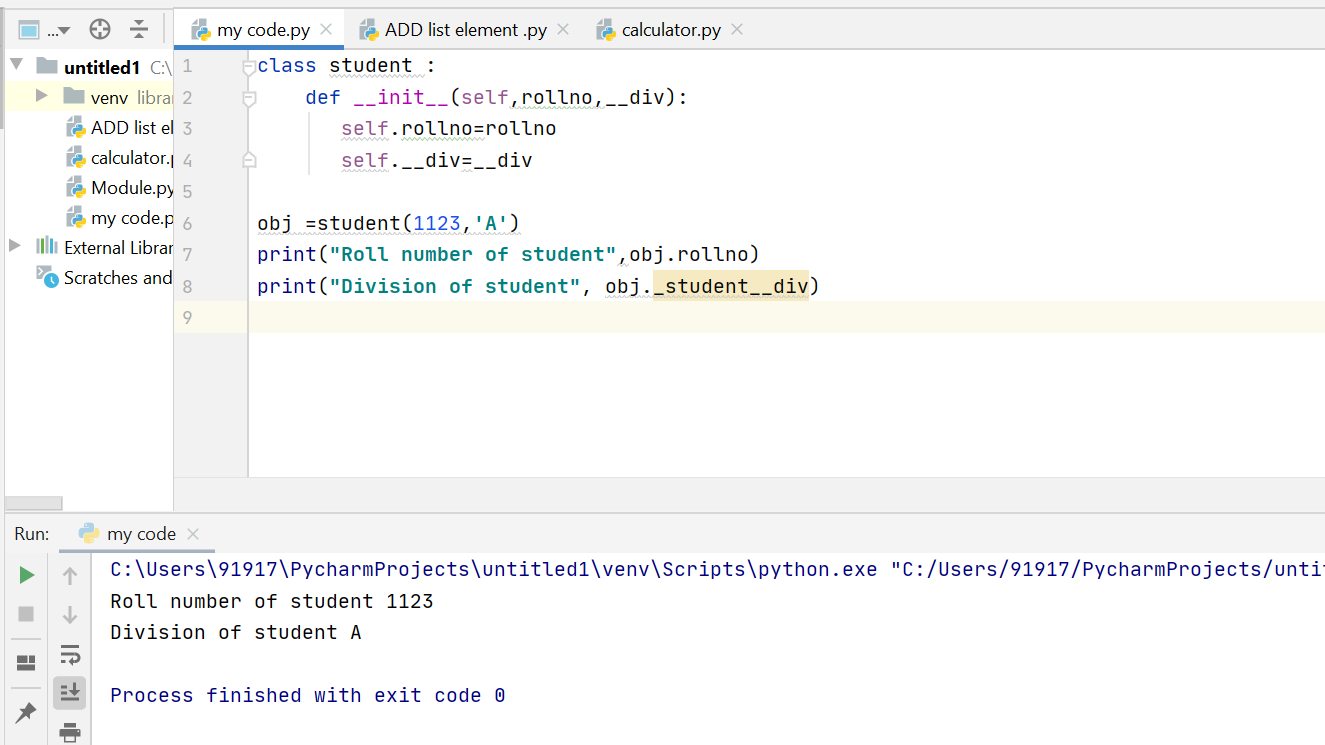
In actual terms (practically), python doesn’t have anything called private member variable in Python. However, adding two underlines(__) at the beginning makes a variable or a method private is the convention used by most python code.
Let’s understand this concept through an example −
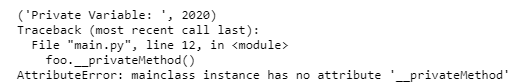
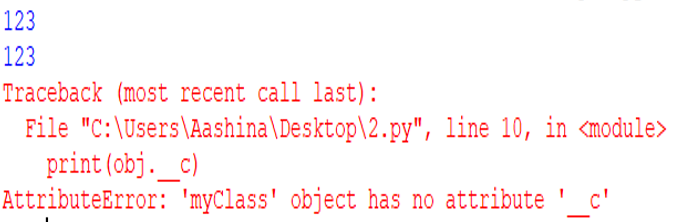
In the above program, __privMeth is a private method and __privateVar is a private variable. Let’s see its output now −
From the above output, we can see that outside the class “myClass”, you cannot access the private method as well as the private variable. However, inside the class (myClass) we can access the private variables. In the hello() method, the __privateVar variable can be accessed (as shown above: “Private Variable value: 27”).
So from the above example, we can understand that all the variables and the methods inside the class are public by the method. When we declare data member as private it means they are accessible only side the class and are inaccessible outside the class. The technique of making a variable or method private is called data mangling. Any identifier of the form __spam (at least two leading underscores, at most one trailing underscore) is textually replaced with _classname__spam , where classname is the current class name with a leading underscore(s) stripped. This mangling is done without regard to the syntactic position of the identifier, as long as it occurs within the definition of a class.
Double underscore names are meant to avoid accidental overriding by a subclass instead.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/private-variables-python/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/private-variables-in-python
Russian Hairy Ass Porn
Extra Small Teenage Porn Pics
Ass Toy Anal Girl
Private Variables in Python - GeeksforGeeks
Private Variables in Python - Tutorialspoint
Python Private Variables | How does Private Variables Work ...
Private Variables in Python Program - Tutorialspoint
Private Variables in Python – pythoncontent
Private variables in Python. Learn Python programming with ...
9. Classes — Python 3.9.7 documentation
Private Methods in Python - GeeksforGeeks
How to Create Private Variables and Methods in Python ?
Python Private Variables






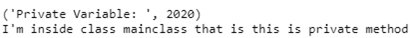
























































-p-500.png)


