Public Private Static

🛑 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Public Private Static
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
Cardiologist reveals only meat that is healthier than vegetables.
World renowned cardiologist reveals the only protein your body needs to burn calories.
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
Originally Answered: What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private", "protected" mean in Java?
What is private, public and protected in Java?
What is difference between static and public keyword in Java?
What is difference between private, public and protected static specifiers in Java?
What does public static void mean in Java?
In Java, what does "String args []" at 'public static void main (String args[])' mean?
Answered 4 years ago · Author has 309 answers and 568.2K answer views
Why can’t inner class methods be static in Java?
Originally Answered: why inner class methods can't be static in java?
Answered 3 years ago · Author has 443 answers and 1.1M answer views
What is private, public and protected in Java?
Answered 4 years ago · Author has 68 answers and 160.8K answer views
What is difference between static and public keyword in Java?
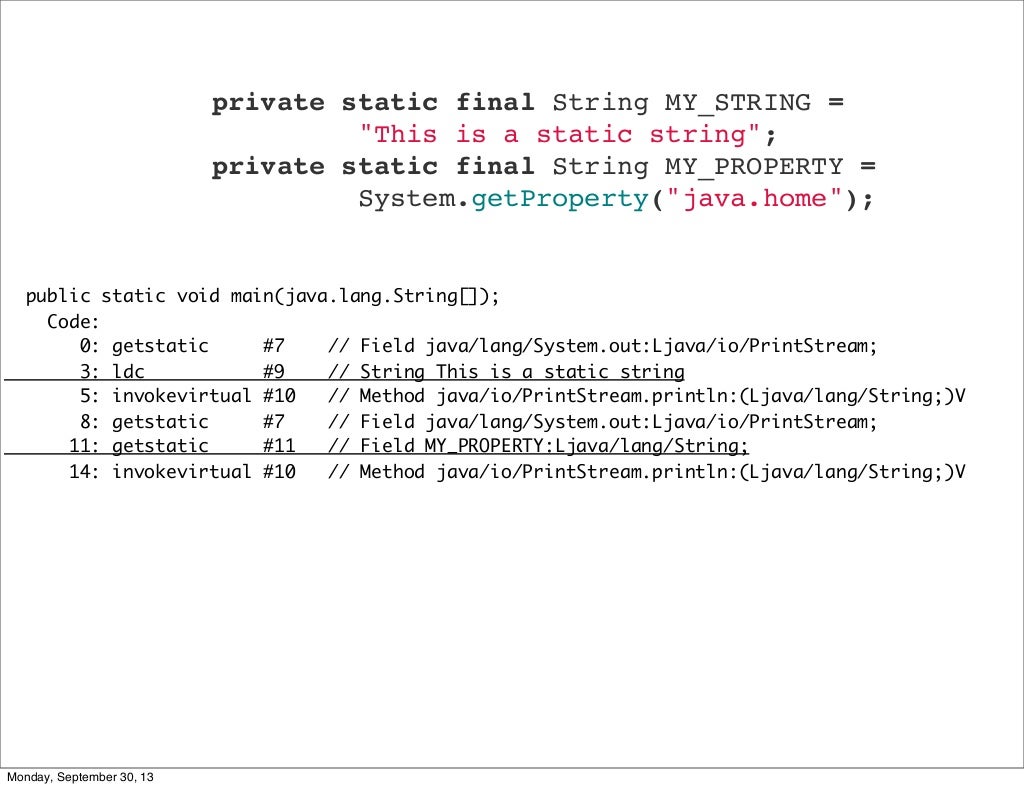
public static void main(String[] arguments) {
What does “static” in the fourth line mean in this Java code: public abstract class Hello { protected static Name name; static { // name = null; } }?
What is the difference between private, public, package and protected in Java?
What are the differences between protected, private, and public in Java?
What's the real difference when you define a variable as private and private static in Java?
What if I write static public void instead of public static void in Java? Will that make any difference?
What does public static void mean in Java?
Answered 5 years ago · Author has 74 answers and 218.4K answer views
In Java, what does "String args []" at 'public static void main (String args[])' mean?
Answered 6 years ago · Author has 192 answers and 492.4K answer views
What does “static” in the fourth line mean in this Java code: public abstract class Hello { protected static Name name; static { // name = null; } }?
Originally Answered: What does 'static' in the fourth line mean in this Java code?
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
Answered 2 years ago · Author has 994 answers and 1.7M answer views
What does 'instantiated' mean in Java?
Answered 5 years ago · Author has 640 answers and 2.1M answer views
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
Updated 2 years ago · Author has 1.9K answers and 3.9M answer views
Originally Answered: What does! Mean in Java?
What is anonymous object instantiation?
Originally Answered: What is anonymous object instantiation?
Answered 5 years ago · Author has 1.3K answers and 2.3M answer views
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
What is private, public and protected in Java?
What is difference between static and public keyword in Java?
What is difference between private, public and protected static specifiers in Java?
What does public static void mean in Java?
In Java, what does "String args []" at 'public static void main (String args[])' mean?
What does “static” in the fourth line mean in this Java code: public abstract class Hello { protected static Name name; static { // name = null; } }?
What is the difference between private, public, package and protected in Java?
What are the differences between protected, private, and public in Java?
What's the real difference when you define a variable as private and private static in Java?
What if I write static public void instead of public static void in Java? Will that make any difference?
How do I call a static method and edit it in another class in Java?
What are the advantages of static methods in Java?
What is anonymous object instantiation?
Why can static methods in Java be called without creating objects? How is it useful?
What is private, public and protected in Java?
What is difference between static and public keyword in Java?
What is difference between private, public and protected static specifiers in Java?
What does public static void mean in Java?
In Java, what does "String args []" at 'public static void main (String args[])' mean?
What does “static” in the fourth line mean in this Java code: public abstract class Hello { protected static Name name; static { // name = null; } }?
In Java, Static means shared common global memory for objects.
Instantiated means objects creation.
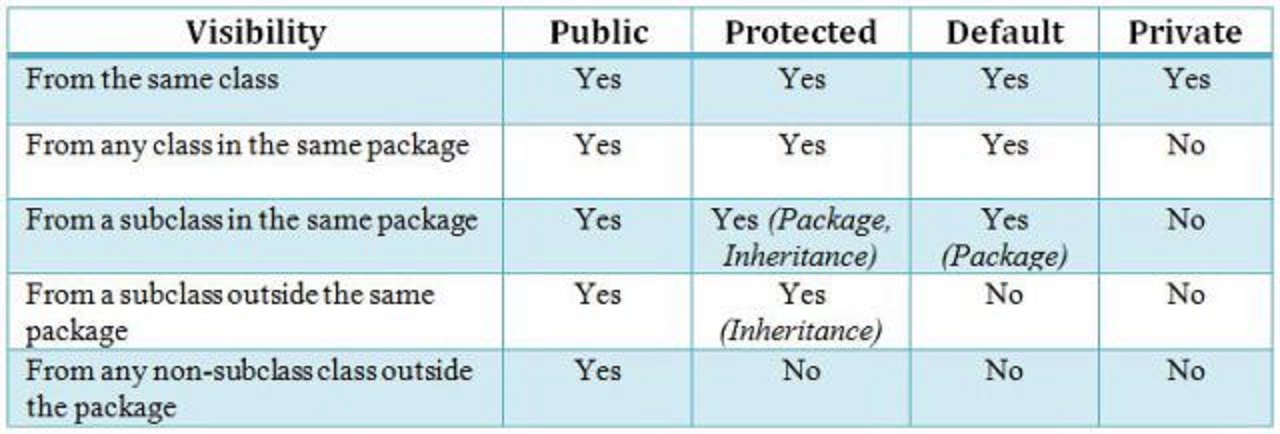
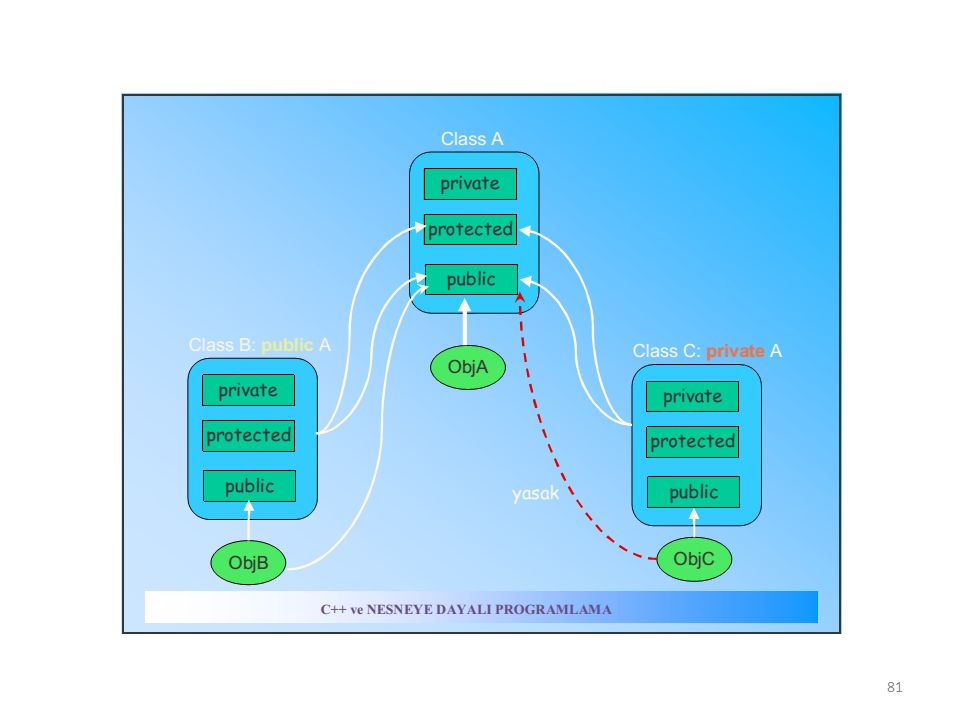
In java we have four Access Specifiers and they are listed below.
1. public 2. private 3. protected 4. default(no specifier)
We look at these Access Specifiers in more detail.
Public Specifiers achieves the highest level of accessibility. Classes, methods, and fields declared as public can be accessed from any class in the Java program, whether these classes are in the same package or in another package.
public class Demo { // public class public x, y, size; // public instance variables }
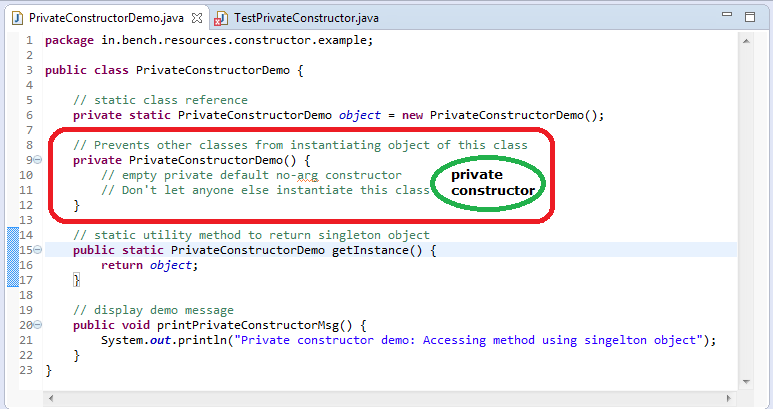
Private Specifiers achieves the lowest level of accessibility.private methods and fields can only be accessed within the same class
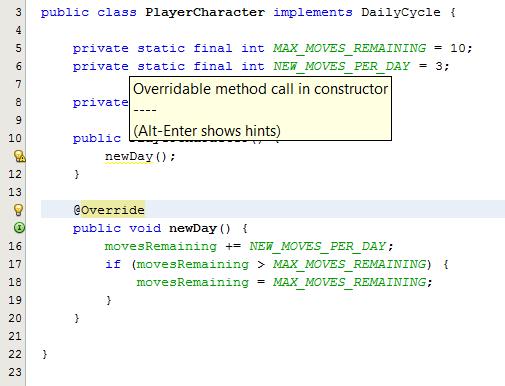
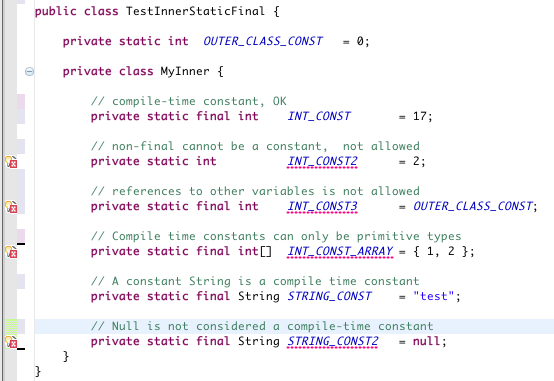
First let's clear something up, STATIC inner classes CAN have static members.
The reason why inner classes cannot have static members is because static members are usually instantiated when the program starts. However, an inner class depends on having an instance of its enclosing class in order to create it and then access it's members. So the decision to not have static members for an inner class makes sense due to this dependency. The static member cannot be accessed until something has been created i.e. the enclosing class instance, so why have it?
I could also see this making sense implementation wise, because if the JVM has a special location for static members, then it won't make much sense to pollute that space with static members of inner class, which are not available in the global
The access to classes, constructors, methods and fields are regulated using access modifiers i.e. a class can control what information or data can be accessible by other classes. To take advantage of encapsulation, you should minimize access whenever possible.
Java provides a number of access modifiers to help you set the level of access you want for classes as well as the fields, methods and constructors in your classes. A member has package or default accessibility when no accessibility modifier is specified.
1. private 2. protected 3. default 4. public
Fields, methods and constructors declared public (least restrictive) within a public class are visible to any class in the Java program, whether these classes are in the same packag
A class, method, constructor, interface, etc. declared using public keyword can be accessed from any other class. Therefore, fields, methods, blocks declared inside a public class can be accessed from any class belonging to the Java Universe.
However, if the public class we are trying to access is in a different package, then the public class still needs to be imported. Because of class inheritance, all public methods and variables of a class are inherited by its subclasses.
The following function uses public access control −
The main() method of an application has to be public. Otherwise, it could not be called by a Java interpreter (such as java) to run the class
If you declare any variable as stati
Each keyword in the long statement is necessary and plays its effective role in making programs run.
I'm answering presuming you are talking about public static void main(String args[])
The public keyword is an access specifier, which allows the programmer to control the visibility of class members. When a class member is preceded by public, then that member can be accessed by code outside the class in which it is declared.In this case, main( ) must be declared as public, since it must be called by code outside of its class when the program is started. The keyword static allows main( ) to be called without having to instantiate a particular instance of the class. This is necessary since main( ) is called by the Java interpreter before any objects are made. The keyword void simply tells the compiler that main( ) does not return a value. As you will see, methods may also return values. As stated, main ( ) is the method called when a Java application begins.
You know how constructors are for setting default state for when a new object is initialized? Ever wonder how that should be done for static variables that need to be separately initialized (for example, if their instantiation involves catching an Exception)? Well I like to think of it as a sort of constructor for static variables.
However, that is not technically true. This is because of the nature of static - static is for variables or methods that are independent of individual objects. They don't rely on object instantiation, but are simply "constant" or "global" within a class.
Having said this, static blocks should be used sparingly, namely because static members are seldom required to be initialized within a static block. Also, there isn't much that y
These are the modifiers associated with the variables within a class.
Static: The variable is common to the entire class, not specific to any object. public: Provides the highest level of visibility to this variable. The scope of the variable (as long as it exists) is not limited to just this class or this package, but any other object even from a different package can use this variable by importing that package/file in it's environment.
private: Least level of visibility provided. Only the objects of this class can see it.
protected: Provides access mid way between public and private in the sense that the children of this class can also see this variable.
Generally, from my experience of teaching Java, people still get confused with static modifier. As a rule of thumb, the static modifier s
It means a new object is created using a class.
Three events occur as part of the creation of a new instance of a class:
•A new object is dynamically allocated in memory, and all instance variables are initialized to standard default values. The default values are null for reference variables and 0 for all base types except boolean variables (which are false nby default).
•The constructor for the new object is called with the parameters specified.The constructor may assign more meaningful values to any of the instance variables, and perform any additional computations that must be done due to the creation of this object.
•After the constructor returns, the new operator returns a reference (that is, a memory address) to the newly created object. If the expression is in the form of an assignment
Before explaining above concept I must tell you this are OOPS concept not only java concepts, OOPS supporting language support all above concept:
1) static: Static is the starting point of the jvm. So only we are using in java public static void main .
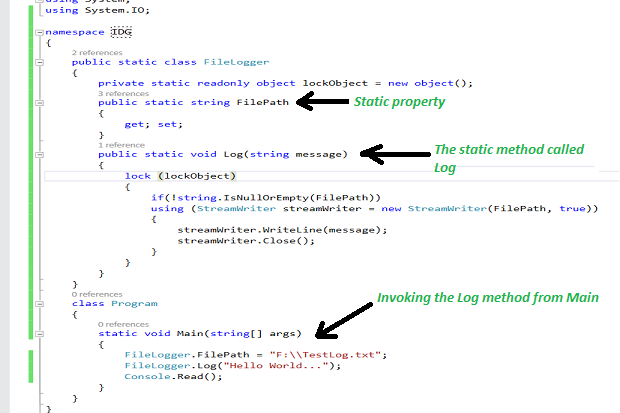
Static mean, one per person, Like this static work in java. That mean Only one static have the class. That mean when you are creating more than one object that time the static is never changed for every object. That is called one per class. Static is Not object property. Static is Class property.
So we can use this without creating instance. We can call static method by classname.methodname. Static method are implicitly final. you can't override a static method with a nonstatic method.
2) instantiated: Instantiation is one of the most important
It is an operator which is found in expressions ; it operates on expressions which produce a boolean result, and negates that result. So for example in the statement
message.setVisible(! formIsComplete);
it evaluates formIsComplete as a boolean then returns the opposite, so message is only visible when the form is NOT complete.
If the part of the expression to the right of the ! doesn't evaluate to a boolean, it's a compiler error. So in my example above, if formIsComplete was an integer variable, that expression wouldn't compile.
Expressions are very often found in if () statements, but I chose the example above to show that expressions can also occur in any other statement.
Simple object instantiation: Sample s = new Sample();
Anonymous object instantiation: new Sample();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader( System.in ));
public , private and protected are all access modifiers in java. For example a public field in a class is accessible to all the classes while private is only accessible from methods of that class. Instantiated means you have to make a reference for the object you want to use. For example MyObject m = new MyObject();
PHP: Область видимости - Manual
What does ' static ', 'instantiated', ' public ', ' private ' and... - Quora
Private class fields - JavaScript | MDN | Private static methods
object oriented - Java - private static vs. public static - Software...
Access Specifiers( Public , Protected, Private ) , Static and... - Forget Code
Select your preferred language English (US) Español Français 日本語 한국어 Polski Русский 中文 (简体) Change language
class ClassWithPrivateField {
#privateField
}
class ClassWithPrivateMethod {
#privateMethod ( ) {
return 'hello world'
}
}
class ClassWithPrivateStaticField {
static # PRIVATE_STATIC_FIELD
}
Class properties are public by default and can be examined or modified outside the
class. There is however a
stage 3 proposal to allow defining private class fields using a hash
# prefix.
Private fields are accessible on the class constructor from inside the class
declaration itself.
The limitation of static variables being called by only static methods still holds.
Private static fields are added to the class constructor at class evaluation time.
There is a provenance restriction on private static fields. Only the class which
defines the private static field can access the field.
This can lead to unexpected behavior when using this .
Private instance fields are declared with # names (pronounced
" hash names "), which are identifiers prefixed with # . The
# is a part of the name itself. It is used for declaration and accessing as
well.
The encapsulation is enforced by the language. It is a syntax error to refer to
# names from out of scope.
Like their public equivalent, private static methods are called on the class itself,
not instances of the class. Like private static fields, they are only accessible from
inside the class declaration.
Private static methods may be generator, async, and async generator functions.
This can lead to unexpected behavior when using this . In
the following example this refers to the Derived class (not
the Base class) when we try to call
Derived.publicStaticMethod2() , and thus exhibits the same "provenance
restriction" as mentioned above:
Private instance methods are methods available on class instances whose access is
restricted in the same manner as private instance fields.
Private instance methods may be generator, async, or async generator functions. Private
getters and setters are also possible:
BCD tables only load in the browser
Last modified: Jan 9, 2021 , by MDN contributors
© 2005- 2021 Mozilla and individual contributors. Content is available under these licenses .
Missionary Sex Creampie
Outdoor Threesome Porn
Lesbian First Time
Nasty House
Anal Piercing Porn