Public Private Protected C

⚡ ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Public Private Protected C
Join our newsletter for the latest updates.
Join our newsletter for the latest updates.
Examples
Python Examples
JavaScript Examples
C
Examples
Java Examples
Kotlin Examples
C++ Examples
Company
Change Ad Consent
Do not sell my data
About
Advertising
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
Contact
Blog
Youtube
Apps
Learn Python
Learn C Programming
In this tutorial, we will learn to use public, protected and private inheritance in C++ with the help of examples.
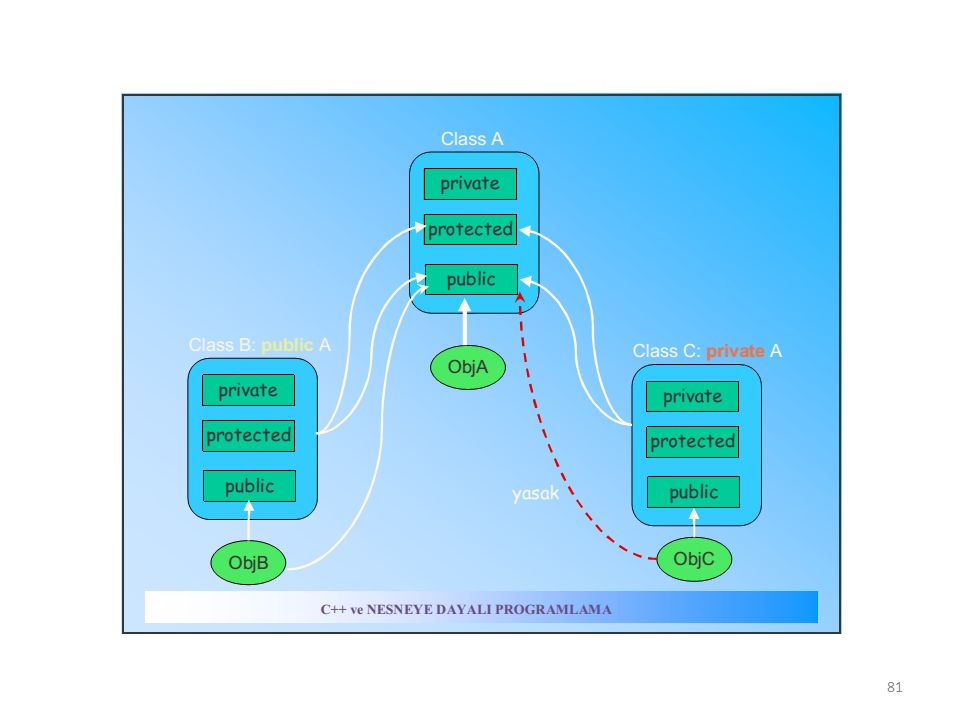
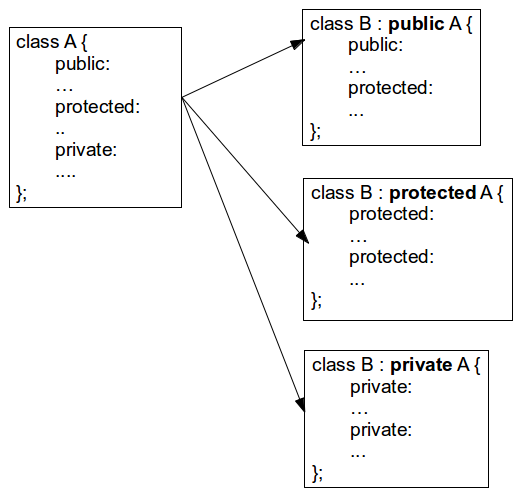
In C++ inheritance , we can derive a child class from the base class in different access modes. For example,
Notice the keyword public in the code
This means that we have created a derived class from the base class in public mode . Alternatively, we can also derive classes in protected or private modes.
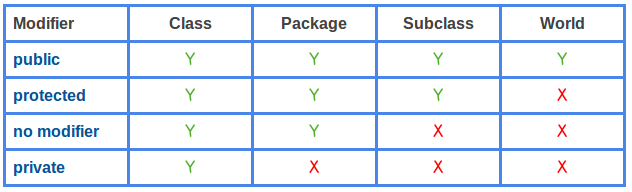
These 3 keywords ( public , protected , and private ) are known as access specifiers in C++ inheritance.
public , protected, and private inheritance have the following features:
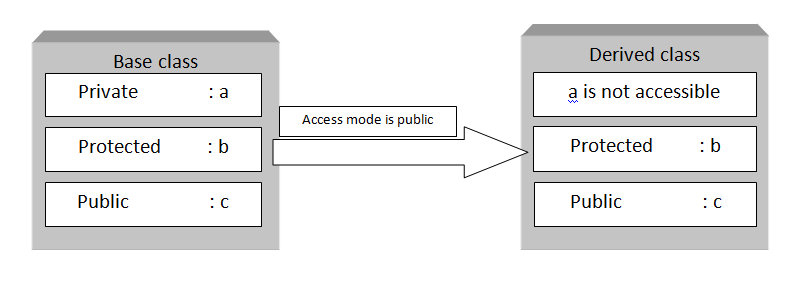
Note: private members of the base class are inaccessible to the derived class.
Here, we have derived PublicDerived from Base in public mode .
Since private and protected members are not accessible, we need to create public functions getPVT() and getProt() to access them:
Here, we have derived ProtectedDerived from Base in protected mode .
As we know, protected members cannot be accessed directly.
As a result, we cannot use getPVT() from ProtectedDerived . That is also why we need to create the getPub() function in ProtectedDerived in order to access the pub variable.
Here, we have derived PrivateDerived from Base in private mode .
As we know, private members cannot be accessed directly.
As a result, we cannot use getPVT() from PrivateDerived . That is also why we need to create the getPub() function in PrivateDerived in order to access the pub variable.
C++ friend Function and friend Classes
© Parewa Labs Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Yes (inherited as protected variables)
Yes (inherited as private variables)
Yes (inherited as private variables)
Access Modifiers - C # Programming Guide | Microsoft Docs
Public , Protected and Private Inheritance in C ++ Programming
Difference between private , public , and protected modifiers in C ++
C # Access Modifiers ( Public , Private , Protected , Internal) - Tutlane
C ++ для начинающих private , public , protected – С++ для начинающих
© Copyright 2021. All Rights Reserved.
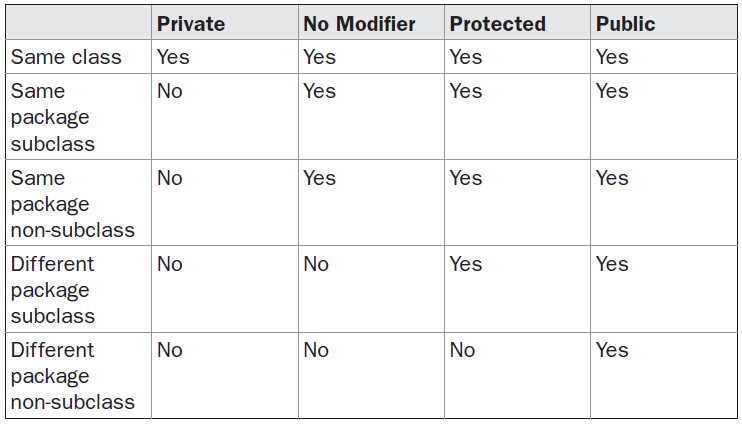
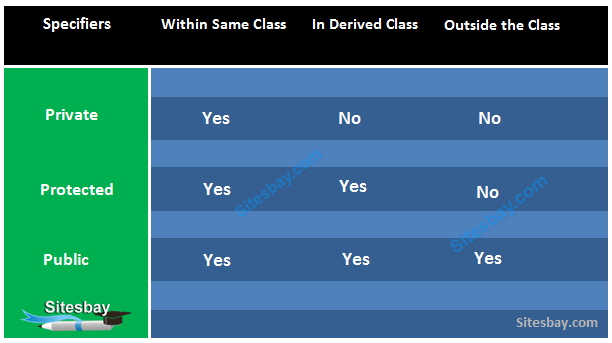
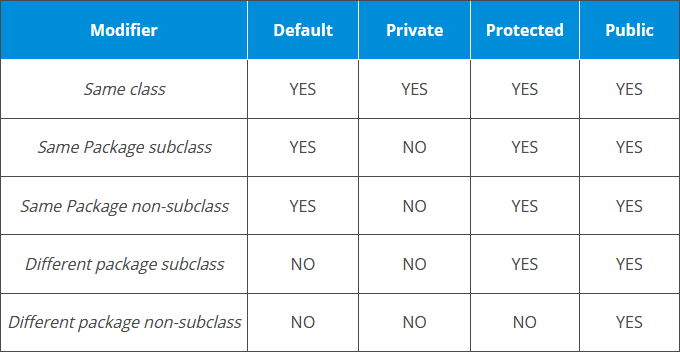
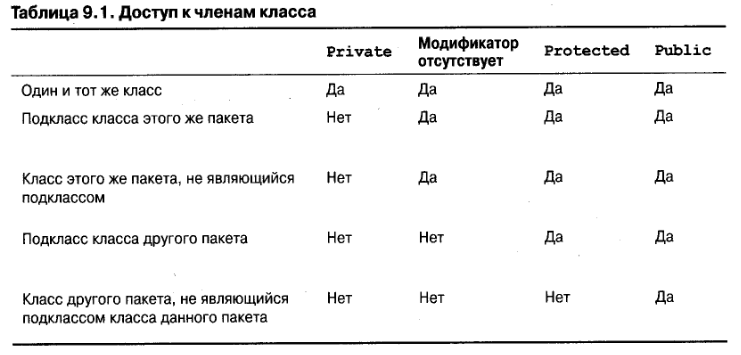
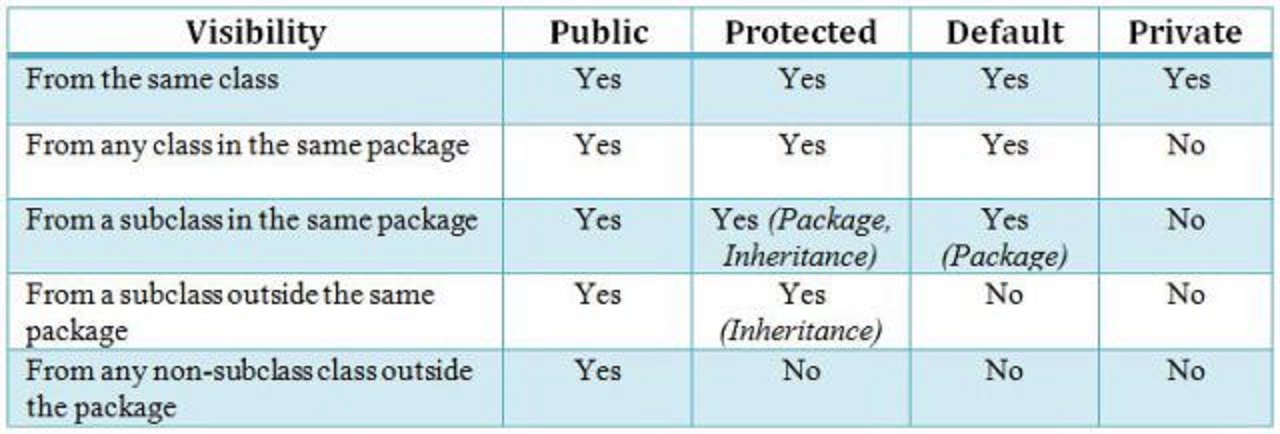
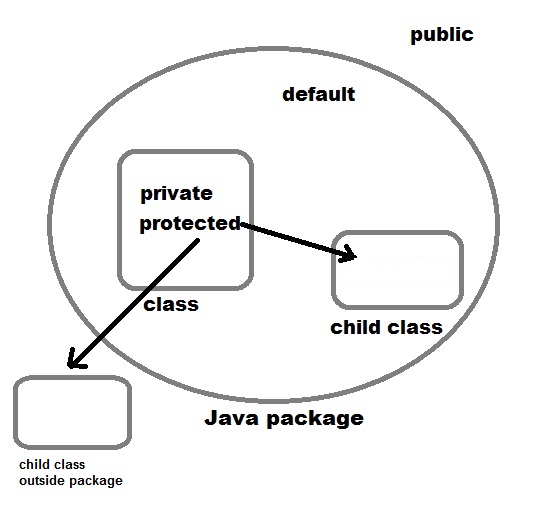
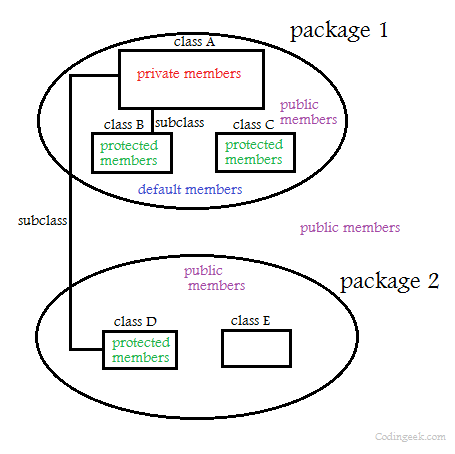
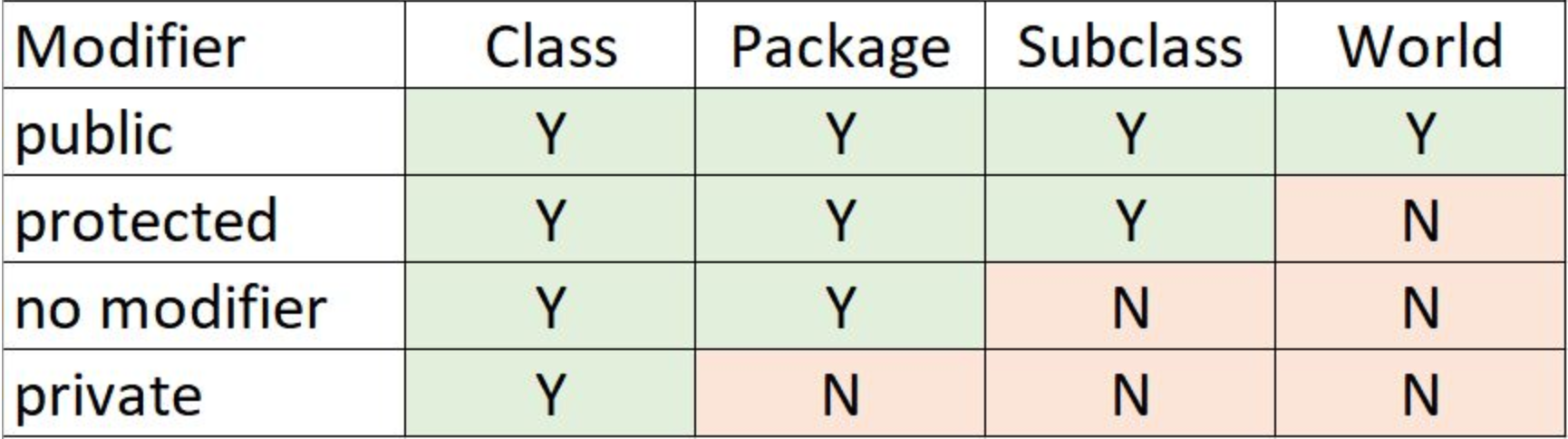
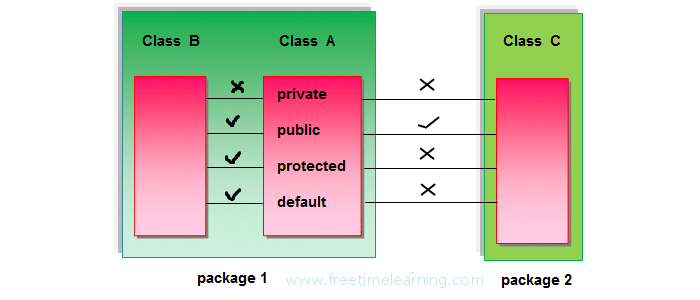
Data hiding is one of the important features of Object Oriented Programming which allows preventing the functions of a program to access directly the internal representation of a class type. The access restriction to the class members is specified by the labeled access modifiers − public, private, and protected sections within the class body.
The default access for members and classes is private.
A public member is accessible from anywhere outside the class but within a program. You can set and get the value of public variables without any member.
A private member variable or function cannot be accessed, or even viewed from outside the class. Only the class and friend functions can access private members.
A protected member variable or function is very similar to a private member but it provided one additional benefit that they can be accessed in child classes which are called derived classes.
Bbw Categories Xhamster
Nasty Nymphos 17
Mature Women Outdoor
Manga Ass
Crying Double Penetration