Public And Private Companies

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Christina Majaski writes and edits finance, credit cards, and travel content. She has 14+ years of experience with print and digital publications.
Eric Estevez is financial professional for a large multinational corporation. His experience is relevant to both business and personal financial topics.
Privately held companies are—no surprise here—privately held. This means that, in most cases, the company is owned by its founders, management, or a group of private investors. A public company, on the other hand, is a company that has sold all or a portion of itself to the public via an initial public offering (IPO), meaning shareholders have a claim to part of the company's assets and profits.1
The popular misconception is that privately held companies are small and of little interest. In fact, there are many big-name companies that are also privately held—check out the Forbes list of America's largest private companies, which includes big-name brands like Mars, Cargill, Fidelity Investments, Koch Industries, and Bloomberg.2
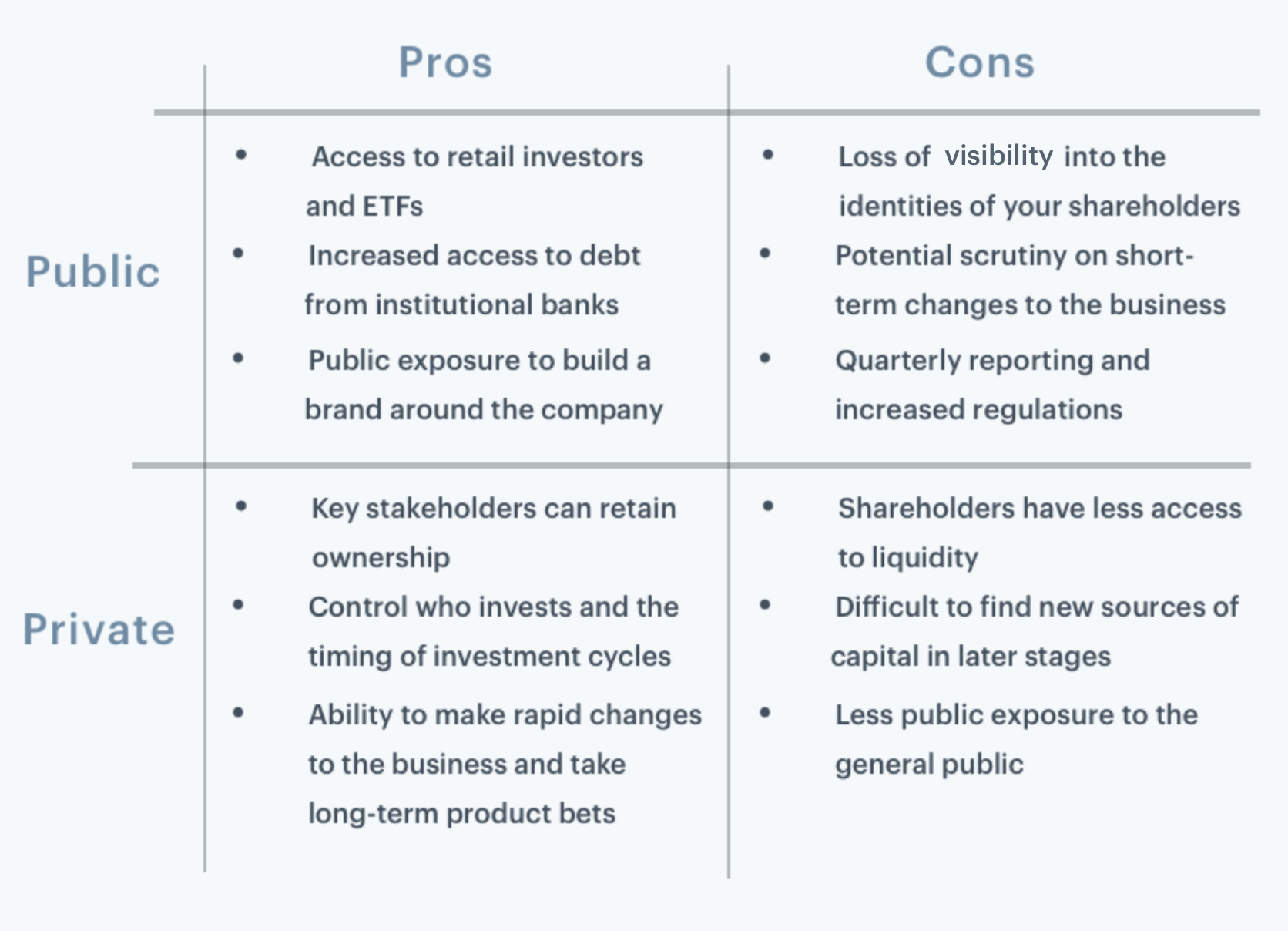
A private company can't dip into the public capital markets and must rely on private funding.
While a privately held company can’t rely on selling stocks or bonds on the public market in order to raise cash to fund its growth, it may still be able to sell a limited number of shares without registering with the SEC, under Regulation D.3 This way, privately held companies can use shares of equity to attract investors. Of course, privately held companies can also borrow money, either from banks or venture capitalists, or rely on profits to fund growth.
The main advantage of private companies is that management doesn't have to answer to stockholders and isn't required to file disclosure statements with the SEC.1 However, a private company can't dip into the public capital markets and must, therefore, turn to private funding. It has been said often that private companies seek to minimize the tax bite, while public companies seek to increase profits for shareholders.
The main advantage public companies have is their ability to tap the financial markets by selling stock (equity) or bonds (debt) to raise capital (i.e., cash) for expansion and other projects. Bonds are a form of a loan that a publicly held company can take from an investor. It will have to repay this loan with interest, but it won’t have to surrender any shares of ownership in the company to the investor. Bonds are a good option for public companies seeking to raise money in a depressed stock market. Stocks, however, allow company founders and owners to liquidate some of their equity in the company, and relieve growing companies of the burden of repaying bonds.
One of the biggest differences between the two types of companies is how they deal with public disclosure. If it's a public U.S. company, which means it is trading on a U.S. stock exchange, it is typically required to file quarterly earnings reports (among other things) with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This information is made available to shareholders and the public. Private companies, however, are not required to disclose their financial information to anyone, since they do not trade stock on a stock exchange.1
In most cases, a private company is owned by the company's founders, management, or a group of private investors.
A public company is a company that has sold all or a portion of itself to the public via an initial public offering.
The main advantage public companies have is their ability to tap the financial markets by selling stock (equity) or bonds (debt) to raise capital (i.e., cash) for expansion and other projects.
Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. "Public Companies." Accessed Aug. 8, 2020.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. "Investor Bulletin: Private Placements Under Regulation D." Accessed Aug. 8, 2020.
The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. This compensation may impact how and where listings appear. Investopedia does not include all offers available in the marketplace.
A public company is a corporation whose ownership is distributed amongst general public shareholders through publicly-traded stock shares.
The equity capital market, where financial institutions help companies raise equity capital, comprises the primary market and secondary market.
Equity typically refers to shareholders' equity, which represents the residual value to shareholders after debts and liabilities have been settled.
Companies seek equity financing from investors to finance short or long-term needs by selling an ownership stake in the form of shares.
A stock is a form of security that indicates the holder has proportionate ownership in the issuing corporation.
An initial public offering (IPO) refers to the process of offering shares of a private corporation to the public in a new stock issuance.
Investopedia is part of the Dotdash publishing family.
Home » Finance » Blog » Accounting Fundamentals » Public Company vs Private Company
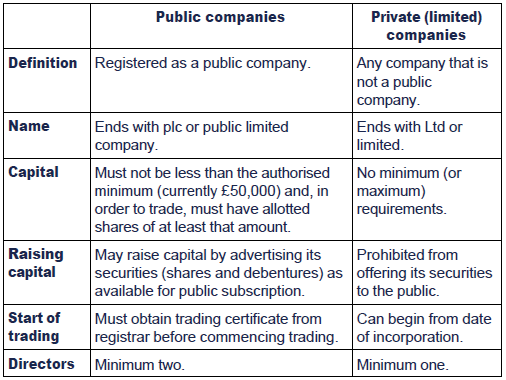
The company is an association of people who want to do certain business activities with having a legal existence. There are multiple types under which a company can be formed under company laws like Statutory Companies, Single Person Company, Companies Limited by shares, a company limited by guarantee, Public Limited Company, Private Limited Company. Company formation type is completely based on the liability of members, the number of members, incorporation mode. Among these types, Private companies and Public companies are the most popular.
A private company cannot offer its share to the general public as it is restricted, in a private company the shares are privately held by the members or investors. The private company the suffix after its name Private Limited (PVT LTD), the main advantage of a private company is they don’t need to disclose their financials to the general public. The public company is only answerable to its members/investors only.
Download Corporate Valuation, Investment Banking, Accounting, CFA Calculator & others
A public company under the companies act 2013 means a company that is listed on a stock exchange and can sell its securities to the general public. To become a public company; the company needs to offer an IPO to the public. A publicly listed company means their shareholders can sell securities freely on a stock exchange. A public company needs to disclose its annual report to all the stakeholders. A public company can expand its business by issuing more shares to the general public.
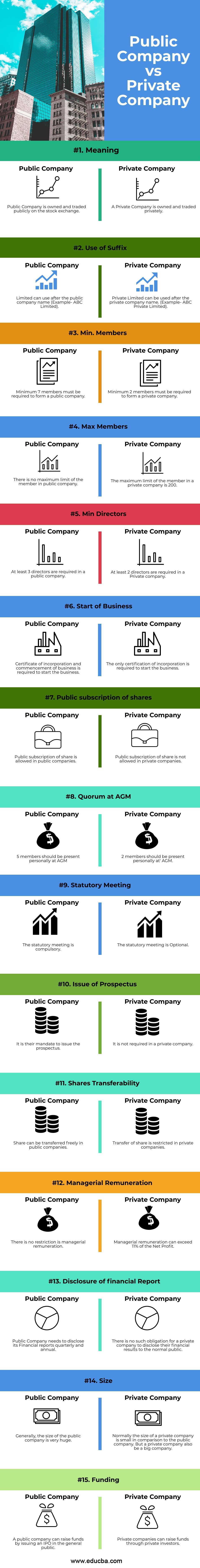
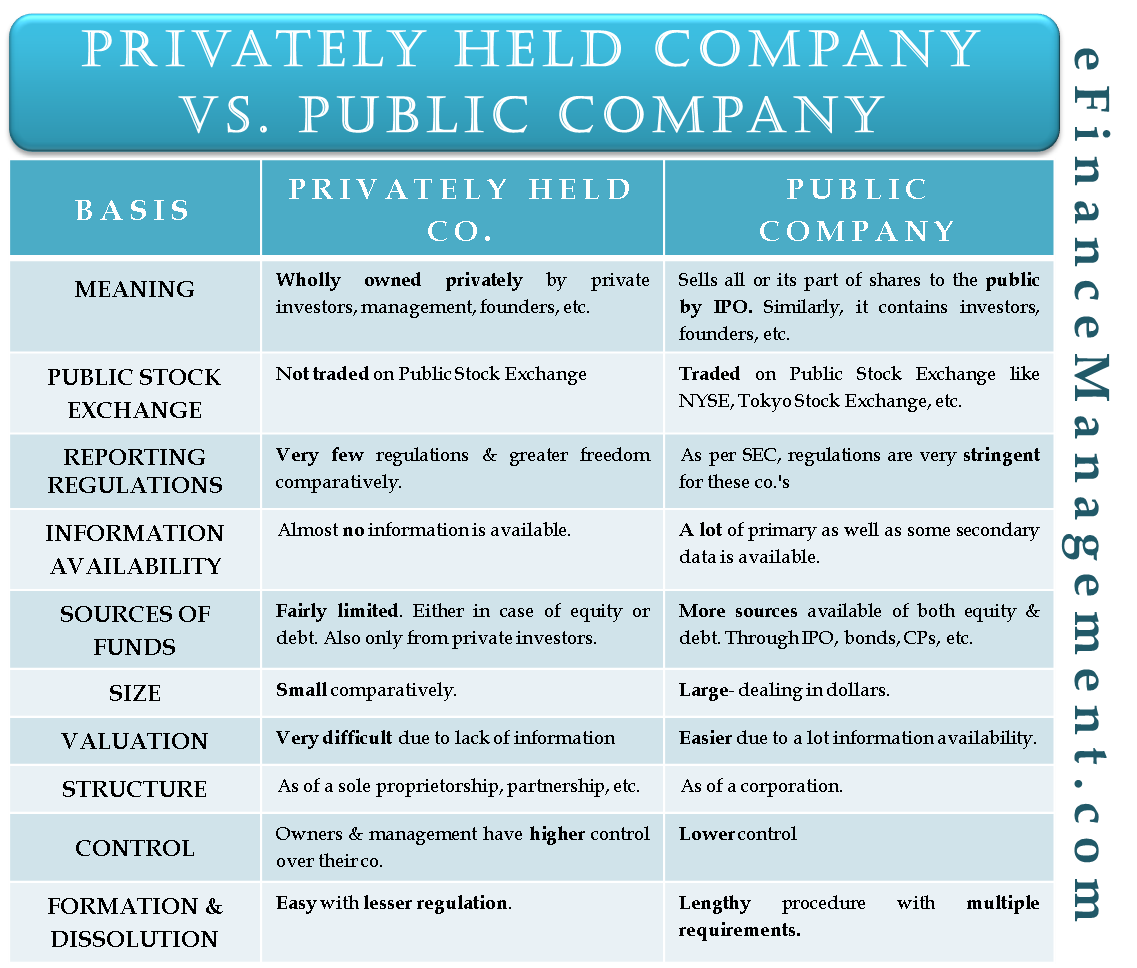
Below are the top 15 differences between Public Company vs Private Company:
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between Public Company vs Private Company
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Public Company vs Private Company:
Finance for Non Finance Managers Course (7 Courses)7 Online Courses | 25+ Hours | Verifiable Certificate of Completion | Lifetime Access
4.5 (6,711 ratings)
A Public Company is owned and traded publicly on the stock exchange.
A Private Company is owned and traded privately.
Limited can use after the public company name (Example- ABC Limited).
Private Limited can be used after the private company name. (Example- ABC Private Limited).
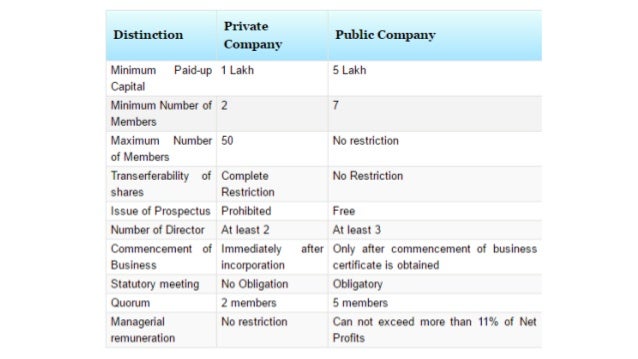
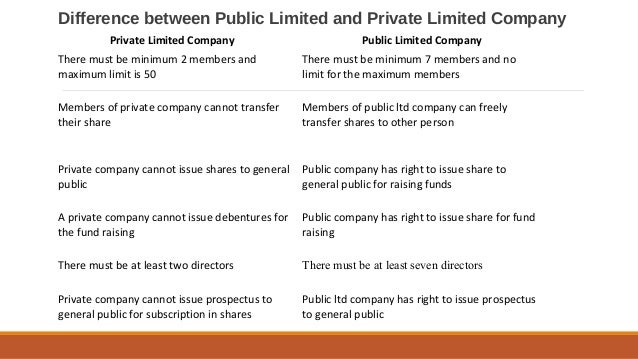
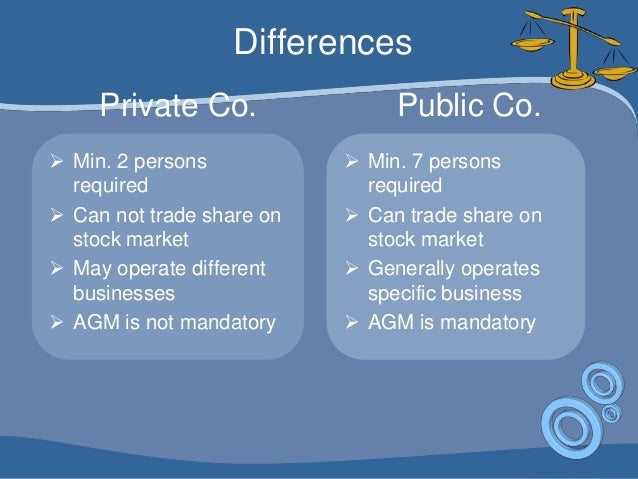
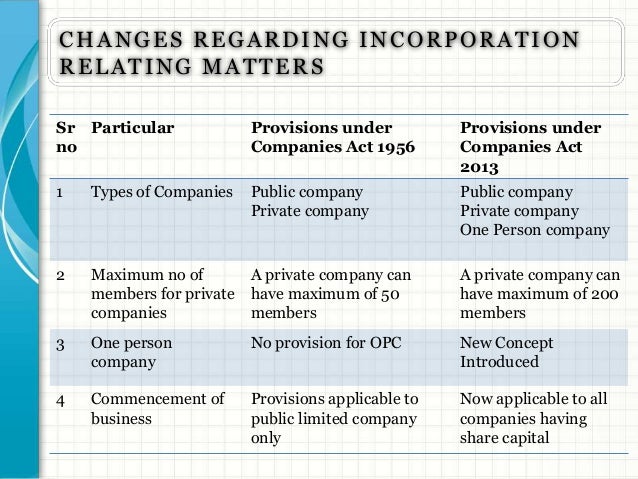
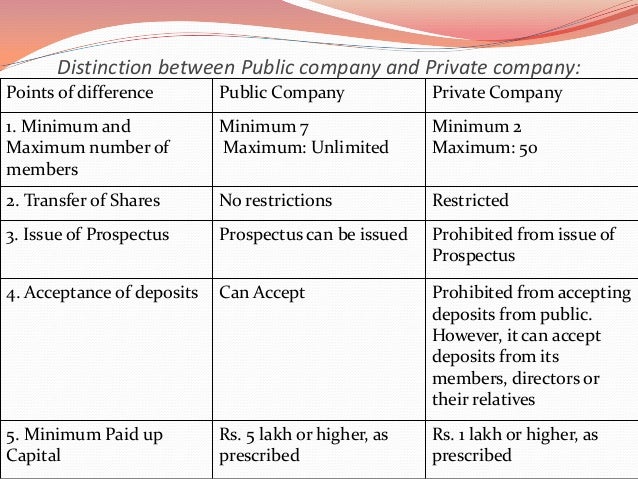
Minimum 7 members must be required to form a public company.
Minimum 2 members must be required to form a private company.
There is no maximum limit of the member in a public company
The maximum limit of the member in a private company is 200.
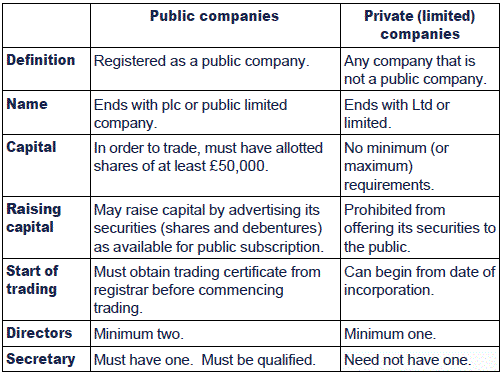
At least 3 directors are required in a public company.
At least 2 directors are required in a Private company.
Certificate of incorporation and commencement of business is required to start the business.
The only certification of incorporation is required to start the business.
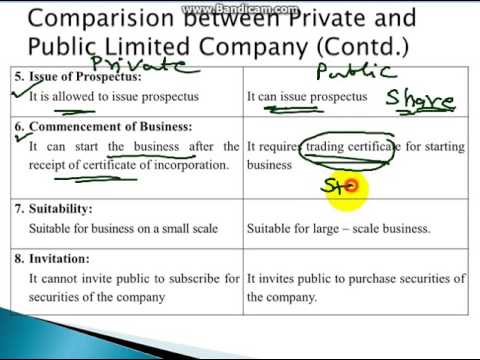
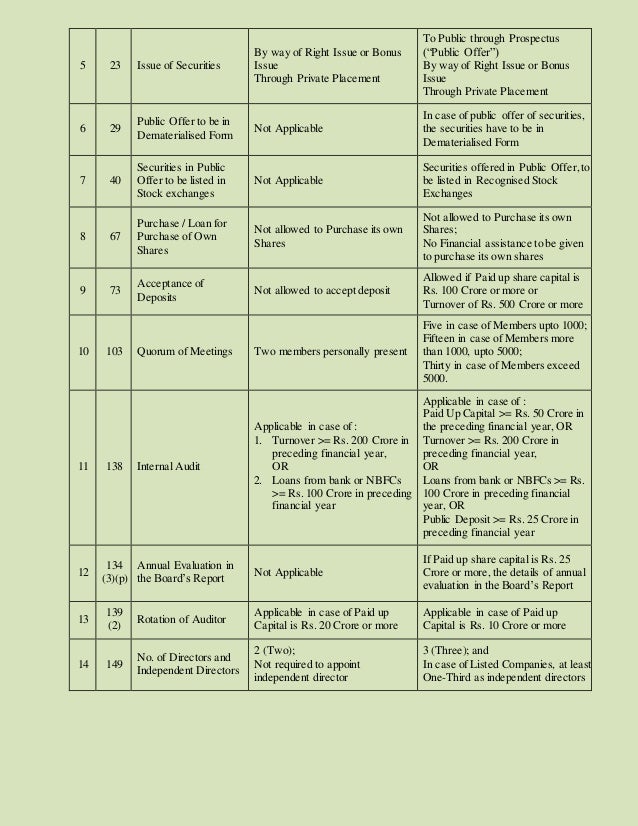
Public subscription of share is allowed in public companies.
Public subscription of share is not allowed in private companies.
5 members should be present personally at AGM.
2 members should be present personally at’ AGM.
The statutory meeting is compulsory.
It is their mandate to issue the prospectus.
It is not required in a private company.
Share can be transferred freely in public companies.
Transfer of share is restricted in private companies.
There is no restriction is managerial remuneration.
Managerial remuneration can exceed 11% of the Net Profit.
A public company needs to disclose its financial reports quarterly and annually.
There is no such obligation for a private company to disclose its financial results to the normal public.
Generally, the size of the public company is very huge.
Normally the size of a private company is small in comparison to a public company. But a private company also be a big company.
A public company can raise funds by issuing an IPO in the general public.
Private companies can raise funds through private investors.
We have seen both the types of companies and both types of companies have their advantages and disadvantages. A private company cannot issue its share and a public company can raise capital from the general public by issuing the securities. Majorly, the size of the public company is relatively higher as compared to private companies. A public can transform into a private company or a private company can also be transformed into a public company by offering an IPO.
This is a guide to Public Company vs Private Company. Here we discuss the Public Company vs Private Company key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more:-
All in One Financial Analyst Bundle (250+ Courses, 40+ Projects)
© 2020 - EDUCBA. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. THE CERTIFICATION NAMES ARE THE TRADEMARKS OF THEIR RESPECTIVE OWNERS.
Corporate Valuation, Investment Banking, Accounting, CFA Calculator & others
*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy
*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Corporate Valuation, Investment Banking, Accounting, CFA Calculator & others
*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Focusrite Scarlett 2i2 Solo
Www Banged Moms Com
Freedom 69 Sex
Young Teen Interracial
Sex Sestra Adn Brat
Private vs. Public Company: What's the Difference?
Public Company vs Private Company | Top 15 Difference w…
A Public Company vs. Private Company
Private vs. Public Companies: 5 Key Differences - 2021 ...
Private vs Public Company - Key Differences Between the Two
Public Company vs Private Company | Top 6 Must Know ...
Public And Private Companies

























/GettyImages-80357560-57a5353c5f9b58974ab7e5b8.jpg)