Prussia
Made with Beautifier
Original link from en.wikipedia.org
Not to be confused with Russia.
Prussia was a historically prominent German state that originated in 1525 with a duchy centered on the region of Prussia on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German ChancellorFranz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia, with its capital first in Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, in Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.
In 1871, owing to the efforts of Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck, most German principalities were united into the German Empire under Prussian leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the German Revolution of 1918–19. The Kingdom of Prussia was thus abolished in favour of a republic—the Free State of Prussia, a state of Germany from 1918 until 1933. From 1932, Prussia lost its independence as a result of the Prussian coup, which was taken further in the next few years when the Nazi regime successfully established its Gleichschaltung laws in pursuit of a unitary state. The remaining legal status finally ended in 1947.
The name Prussia derives from the Old Prussians; in the 13th century, the Teutonic Knights—an organized Catholic medieval military order of German crusaders—conquered the lands inhabited by them. In 1308, the Teutonic Knights conquered the region of Pomerelia with Danzig (modern-day Gdańsk). Their monastic state was mostly Germanised through immigration from central and western Germany, and, in the south, it was Polonised by settlers from Masovia. The imposed Second Peace of Thorn (1466) split Prussia into the western Royal Prussia, becoming a province of Poland, and the eastern part, from 1525 called the Duchy of Prussia, a feudal fief of the Crown of Poland up to 1657. The union of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 led to the proclamation of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701.
Prussia entered the ranks of the great powers shortly after becoming a kingdom. It became increasingly large and powerful in the 18th and 19th centuries. It had a major voice in European affairs under the reign of Frederick the Great (1740–1786). At the Congress of Vienna (1814–15), which redrew the map of Europe following Napoleon's defeat, Prussia acquired rich new territories, including the coal-rich Ruhr. The country then grew rapidly in influence economically and politically, and became the core of the North German Confederation in 1867, and then of the German Empire in 1871. The Kingdom of Prussia was now so large and so dominant in the new Germany that Junkers and other Prussian élites identified more and more as Germans and less as Prussians.
The Kingdom ended in 1918 along with other German monarchies that were terminated by the German Revolution. In the Weimar Republic, the Free State of Prussia lost nearly all of its legal and political importance following the 1932 coup led by Franz von Papen. Subsequently, it was effectively dismantled into Nazi German Gaue in 1935. Nevertheless, some Prussian ministries were kept and Hermann Göring remained in his role as Minister President of Prussia until the end of World War II. Former eastern territories of Germany that made up a significant part of Prussia lost the majority of their German population after 1945 as the Polish People's Republic and the Soviet Union both absorbed these territories and had most of its German inhabitants expelled by 1950. Prussia, deemed a bearer of militarism and reaction by the Allies, was officially abolished by an Allied declaration in 1947. The international status of the former eastern territories of the Kingdom of Prussia was disputed until the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany in 1990, but its return to Germany remains a topic among far right politicians, the Federation of Expellees and various political revisionists.
The term Prussian has often been used, especially outside Germany, to emphasise professionalism, aggressiveness, militarism and conservatism of the Junker class of landed aristocrats in the East who dominated first Prussia and then the German Empire.
The main coat of arms of Prussia, as well as the flag of Prussia, depicted a black eagle on a white background.
The black and white national colours were already used by the Teutonic Knights and by the Hohenzollern dynasty. The Teutonic Order wore a white coat embroidered with a black cross with gold insert and black imperial eagle. The combination of the black and white colours with the white and red Hanseatic colours of the free cities Bremen, Hamburg and Lübeck, as well as of Brandenburg, resulted in the black-white-red commercial flag of the North German Confederation, which became the flag of the German Empire in 1871.
Suum cuique ("to each, his own"), the motto of the Order of the Black Eagle created by King Frederick I in 1701, was often associated with the whole of Prussia. The Iron Cross, a military decoration created by King Frederick William III in 1813, was also commonly associated with the country. The region, originally populated by Baltic Old Prussians who were Christianised, became a favoured location for immigration by (later mainly Protestant) Germans (see Ostsiedlung), as well as Poles and Lithuanians along the border regions.
Before its abolition, the territory of the Kingdom of Prussia included the provinces of West Prussia; East Prussia; Brandenburg; Saxony (including much of the present-day state of Saxony-Anhalt and parts of the state of Thuringia in Germany); Pomerania; Rhineland; Westphalia; Silesia (without Austrian Silesia); Schleswig-Holstein; Hanover; Hesse-Nassau; and a small detached area in the south called Hohenzollern, the ancestral home of the Prussian ruling family. The land that the Teutonic Knights occupied was flat and covered with fertile soil. The area was perfectly suited to the large-scale raising of wheat. The rise of early Prussia was based on the raising and selling of wheat. Teutonic Prussia became known as the "bread basket of Western Europe" (in German, Kornkammer, or granary). The port cities of Stettin (Szczecin) in Pomerania, Danzig (Gdańsk) in Prussia, Riga in Livonia, Königsberg (Kaliningrad), and Memel (Klaipėda) rose on the back of this wheat production. Wheat production and trade brought Prussia into a close relationship with the Hanseatic League during the period of time from 1356 (official founding of the Hanseatic League) until the decline of the League in about 1500.
The expansion of Prussia based on its connection with the Hanseatic League cut both Poland and Lithuania off from the coast of the Baltic Sea and trade abroad. This meant that Poland and Lithuania would be traditional enemies of Prussia, which was still called the Teutonic Knights.
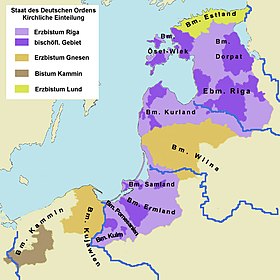
History[edit]Teutonic Order[edit]
Situation after the conquest in the late 13th century. Areas in purple under control of the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights
In 1211 King Andrew II of Hungary granted Burzenland in Transylvania as a fiefdom to the Teutonic Knights, a German military order of crusading knights, headquartered in the Kingdom of Jerusalem at Acre. In 1225 he expelled them, and they transferred their operations to the Baltic Sea area. Konrad I, the Polish duke of Masovia, had unsuccessfully attempted to conquer pagan Prussia in crusades in 1219 and 1222. In 1226 Duke Konrad invited the Teutonic Knights to conquer the Baltic Prussian tribes on his borders.
During 60 years of struggles against the Old Prussians, the Order established an independent state that came to control Prūsa. After the Livonian Brothers of the Sword joined the Teutonic Order in 1237, the Order also controlled Livonia (now Latvia and Estonia). Around 1252 they finished the conquest of the northernmost Prussian tribe of the Skalvians as well as of the western Baltic Curonians, and erected Memel Castle, which developed into the major port city of Memel (Klaipėda). The Treaty of Melno defined the final border between Prussia and the adjoining Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1422.
The Hanseatic League officially formed in northern Europe in 1356 as a group of trading cities. This League came to hold a monopoly on all trade leaving the interior of Europe and Scandinavia and on all sailing trade in the Baltic Sea for foreign countries. The merchants of the interiors of Sweden, Denmark, and Poland came to feel oppressed by the Hanseatic League.
In the course of the Ostsiedlung (German eastward expansion) process, settlers were invited, bringing changes in the ethnic composition as well as in language, culture, and law of the eastern borders of the German lands. As a majority of these settlers were Germans, Low German became the dominant language.
The Knights of the Teutonic Order were subordinate to the papacy and to the emperor. Their initially close relationship with the Polish Crown deteriorated after they conquered Polish-controlled Pomerelia and Danzig (Gdańsk) in 1308. Eventually, Poland and Lithuania, allied through the Union of Krewo (1385), defeated the Knights in the Battle of Grunwald (Tannenberg) in 1410.
The Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) began when the Prussian Confederation, a coalition of Hanseatic cities of western Prussia, rebelled against the Order and requested help from the Polish king, Casimir IV Jagiellon. The Teutonic Knights were forced to acknowledge the sovereignty of, and to pay tribute to Casimir IV in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), losing western Prussia (Royal Prussia) to Poland in the process. Pursuant to the Second Peace of Thorn, two Prussian states were established.
During the period of the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights, mercenaries from the Holy Roman Empire were granted lands by the Order and gradually formed a new landed Prussian nobility, from which the Junkers would evolve to take a major role in the militarization of Prussia and, later, Germany.
Duchy of Prussia[edit]
On 10 April 1525, after signing of the Treaty of Kraków, which officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War (1519–21), in the main square of the Polish capital Kraków, Albert I resigned his position as Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights and received the title "Duke of Prussia" from King Zygmunt I the Old of Poland. As a symbol of vassalage, Albert received a standard with the Prussian coat of arms from the Polish king. The black Prussian eagle on the flag was augmented with a letter "S" (for Sigismundus) and had a crown placed around its neck as a symbol of submission to Poland. Albert I, a member of a cadet branch of the House of Hohenzollern became a Lutheran Protestant and secularized the Order's Prussian territories. This was the area east of the mouth of the Vistula River, later sometimes called "Prussia proper". For the first time, these lands came into the hands of a branch of the Hohenzollern family, who already ruled the Margraviate of Brandenburg, since the 15th century. Furthermore, with his renunciation of the Order, Albert could now marry and produce legitimate heirs.
Brandenburg-Prussia[edit]
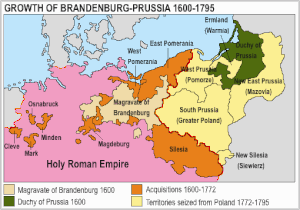
Brandenburg and Prussia united two generations later. In 1594 Anna, granddaughter of Albert I and daughter of Duke Albert Frederick (reigned 1568–1618), married her cousin ElectorJohn Sigismund of Brandenburg. When Albert Frederick died in 1618 without male heirs, John Sigismund was granted the right of succession to the Duchy of Prussia, then still a Polish fief. From this time the Duchy of Prussia was in personal union with the Margraviate of Brandenburg. The resulting state, known as Brandenburg-Prussia, consisted of geographically disconnected territories in Prussia, Brandenburg, and the Rhineland lands of Cleves and Mark.
During the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), various armies repeatedly marched across the disconnected Hohenzollern lands, especially the occupying Swedes. The ineffective and militarily weak Margrave George William (1619–1640) fled from Berlin to Königsberg, the historic capital of the Duchy of Prussia, in 1637. His successor, Frederick William I (1640–1688), reformed the army to defend the lands.
Frederick William I went to Warsaw in 1641 to render homage to King Władysław IV Vasa of Poland for the Duchy of Prussia, which was still held in fief from the Polish crown. In January 1656, during the first phase of the Second Northern War (1654–1660), he received the duchy as a fief from the Swedish king who later granted him full sovereignty in the Treaty of Labiau (November 1656). In 1657 the Polish king renewed this grant in the treaties of Wehlau and Bromberg. With Prussia, the Brandenburg Hohenzollern dynasty now held a territory free of any feudal obligations, which constituted the basis for their later elevation to kings.
Frederick William I succeeded in organizing the electorate by establishing an absolute monarchy in Brandenburg-Prussia, an achievement for which he became known as the "Great Elector". Above all, he emphasised the importance of a powerful military to protect the state's disconnected territories, while the Edict of Potsdam (1685) opened Brandenburg-Prussia for the immigration of Protestant refugees (especially Huguenots), and he established a bureaucracy to carry out state administration efficiently.
Kingdom of Prussia[edit]
On 18 January 1701, Frederick William's son, Elector Frederick III, elevated Prussia from a duchy to a kingdom and crowned himself King Frederick I. In the Crown Treaty of 16 November 1700, Leopold I, emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, allowed Frederick only to title himself "King in Prussia", not "King of Prussia". The state of Brandenburg-Prussia became commonly known as "Prussia", although most of its territory, in Brandenburg, Pomerania, and western Germany, lay outside Prussia proper. The Prussian state grew in splendour during the reign of Frederick I, who sponsored the arts at the expense of the treasury.
Frederick I was succeeded by his son, Frederick William I (1713–1740), the austere "Soldier King", who did not care for the arts but was thrifty and practical. He was the main creator of the vaunted Prussian bureaucracy and the professionalised standing army, which he developed into one of the most powerful in Europe. His troops only briefly saw action during the Great Northern War. In view of the size of the army in relation to the total population, Mirabeau said later: "Prussia, is not a state with an army, but an army with a state." Frederick William also settled more than 20,000 Protestant refugees from Salzburg in thinly populated eastern Prussia, which was eventually extended to the west bank of the River Memel, and other regions. In the treaty of Stockholm (1720), he acquired half of Swedish Pomerania.
The king died in 1740 and was succeeded by his son, Frederick II, whose accomplishments led to his reputation as "Frederick the Great". As crown prince, Frederick had focused, primarily, on philosophy and the arts. He was an accomplished flute player. In 1740, Prussian troops crossed over the undefended border of Silesia and occupied Schweidnitz. Silesia was the richest province of Habsburg Austria. It signalled the beginning of three Silesian Wars (1740–1763). The First Silesian War (1740–1742) and the Second Silesian War (1744–1745) have, historically, been grouped together with the general European war called the War of Austrian Succession (1740–1748). Holy Roman EmperorCharles VI had died on 20 October 1740. He was succeeded to the throne by his daughter, Maria Theresa.
By defeating the Austrian Army at the Battle of Mollwitz on 10 April 1741, Frederick succeeded in conquering Lower Silesia (the northwestern half of Silesia). In the next year, 1742, he conquered Upper Silesia (the southeastern half). Furthermore, in the third Silesian War (usually grouped with the Seven Years' War) Frederick won a victory over Austria at the Battle of Lobositz on 1 October 1756. In spite of some impressive victories afterward, his situation became far less comfortable the following years, as he failed in his attempts to knock Austria out of the war and was gradually reduced to a desperate defensive war. However, he never gave up and on 3 November 1760 the Prussian king won another battle, the hard-fought Battle of Torgau. Despite being several times on the verge of defeat Frederick, allied withGreat Britain, Hanover and Hesse-Kassel, was finally able to hold the whole of Silesia against a coalition of Saxony, the Habsburg monarchy, France and Russia.Voltaire, a close friend of the king, once described Frederick the Great's Prussia by saying "...it was Sparta in the morning, Athens in the afternoon."
Silesia, full of rich soils and prosperous manufacturing towns, became a vital region to Prussia, greatly increasing the nation's area, population, and wealth. Success on the battleground against Austria and other powers proved Prussia's status as one of the great powers of Europe. The Silesian Wars began more than a century of rivalry and conflict between Prussia and Austria as the two most powerful states operating within the Holy Roman Empire (although both had extensive territory outside the empire). In 1744, the County of East Frisia fell to Prussia following the extinction of its ruling Cirksena dynasty.
In the last 23 years of his reign until 1786, Frederick II, who understood himself as the "first servant of the state", promoted the development of Prussian areas such as the Oderbruch. At the same time he built up Prussia's military power and participated in the First Partition of Poland with Austria and Russia in 1772, an act that geographically connected the Brandenburg territories with those of Prussia proper. During this period, he also opened Prussia's borders to immigrants fleeing from religious persecution in other parts of Europe, such as the Huguenots. Prussia became a safe haven in much the same way that the United States welcomed immigrants seeking freedom in the 19th century.
Frederick the Great (reigned 1740–1786) practised enlightened absolutism. He built the world's best army, and usually won his many wars. He introduced a general civil code, abolished torture and established the principle that the Crown would not interfere in matters of justice. He also promoted an advanced secondary education, the forerunner of today's German gymnasium (grammar school) system, which prepares the brightest pupils for university studies. The Prussian education system was emulated in various countries, including the United States.
Napoleonic Wars[edit]
During the reign of King Frederick William II (1786–1797), Prussia annexed additional Polish territory through the Second Partition of Poland in 1793 and the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. His successor, Frederick William III (1797–1840), announced the union of the Prussian Lutheran and Reformed churches into one church.
Prussia took a leading part in the French Revolutionary Wars, but remained quiet for more than a decade because of the Peace of Basel of 1795, only to go once more to war with France in 1806 as negotiations with that country over the allocation of the spheres of influence in Germany failed. Prussia suffered a devastating defeat against Napoleon Bonaparte's troops in the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, leading Frederick William III and his family to flee temporarily to Memel. Under the Treaties of Tilsit in 1807, the state lost about one-third of its area, including the areas gained from the second and third Partitions of Poland, which now fell to the Duchy of Warsaw. Beyond that, the king was obliged to pay a large indemnity, to cap his army at 42,000 men, and to let the French garrison troops throughout Prussia, effectively making the Kingdom a French satellite.
In response to this defeat, reformers such as Stein and Hardenberg set about modernising the Prussian state. Among their reforms were the liberation of peasants from serfdom, the Emancipation of Jews and making full citizens of them. The school system was rearranged, and in 1818 free trade was introduced. The process of army reform ended in 1813 with the introduction of compulsory military service for men. By 1813, Prussia could mobilize almost 300,000 soldiers, more than half of which were conscripts of the Landwehr of variable quality. The rest consisted of regular soldiers that were deemed excellent by most observers, and very determined to repair the humiliation of 1806.
After the defeat of Napoleon in Russia, Prussia quit its alliance with France and took part in the Sixth Coalition during the "Wars of Liberation" (Befreiungskriege) against the French occupation. Prussian troops under Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher contributed crucially (alongside the British and Dutch) to the final victory over Napoleon in the Battle of Waterloo of June 1815. Prussia's reward in 1815 at the Congress of Vienna was the recovery of her lost territories, as well as the whole of the Rhineland, Westphalia, 40% of Saxony and some other territories. These western lands were of vital importance because they included the Ruhr Area, the centre of Germany's fledgling industrialisation, especially in the arms industry. These territorial gains also meant the doubling of Prussia's population. In exchange, Prussia withdrew from areas of central Poland to allow the creation of Congress Poland under Russian sovereignty. In 1815 Prussia became part of the German Confederation.
Wars of liberation[edit]
The first half of the 19th century saw a prolonged struggle in Germany between liberals, who wanted a united, federal Germany under a democratic constitution, and conservatives, who wanted to maintain Germany as a patchwork of independent, monarchical states with Prussia and Austria competing for influence. One small movement that signalled a desire for German unification in this period was the Burschenschaft student movement, by students who encouraged the use of the black-red-gold flag, discussions of a unified German nation, and a progressive, liberal political system. Because of Prussia's size and economic importance, smaller states began to join its free trade area in the 1820s. Prussia benefited greatly from the creation in 1834 of the German Customs Union (Zollverein), which included most German states but excluded Austria.
In 1848 the liberals saw an opportunity when revolutions broke out across Europe. Alarmed, King Frederick William IV agreed to convene a National Assembly and grant a constitution. When the Frankfurt Parliament offered Frederick William the crown of a united Germany, he refused on the grounds that he would not accept a crown from a revolutionary assembly without the sanction of Germany's other monarchs.
The Frankfurt Parliament was forced to dissolve in 1849, and Frederick William issued Prussia's first constitution by his own authority in 1850. This conservative document provided for a two-house parliament. The lower house, or Landtag was elected by all taxpayers, who were divided into three classes whose votes were weighted according to the amount of taxes paid. Women and those who paid no taxes had no vote. This allowed just over one-third of the voters to choose 85% of the legislature, all but assuring dominance by the more well-to-do men of the population. The upper house, which was later renamed the Herrenhaus ("House of Lords"), was appointed by the king. He retained full executive authority and ministers were responsible only to him. As a result, the grip of the landowning classes, the Junkers, remained unbroken, especially in the eastern provinces.