Prolapse Women

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
РекламаMauboussin For Women - Производство Франция - Бесплатная доставка от 2 000р.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17597-vaginal-prolapse
Functions
Example
Risks
Benefits
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Clinical significance
Use
Treatment
Prevention
Many women do not have any symptoms. Those that have symptoms may note a fullness or discomfort in the vagina, a sensation of heaviness or pulling in the pelvis and/or low backache that is relieved when lying down. Other symptoms may be urinary frequency and/or stress incontinence passing urin…
https://www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/vaginal-prolapse
Перевести · 02.01.2018 · Vaginal prolapse happens when the muscles that support the organs in a woman’s pelvis weaken. This weakening allows the uterus, urethra, bladder, or rectum to droop down into the vagina. If the...
Prolapse in Women - Expert Physiotherapy Management Tips
Kegels that STOP Prolapse Worsening - Beginners Guide to Prolapse Repair Exercises
Prolapse Exercises - 5 Safe Strength Exercises for Women
Unsafe Core Abdominal Exercises for Women With Prolapse
Exercising with Prolapse: 6 Core Exercises to Avoid if You Have Prolapse
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-prolapse/symptoms-causes/syc...
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention
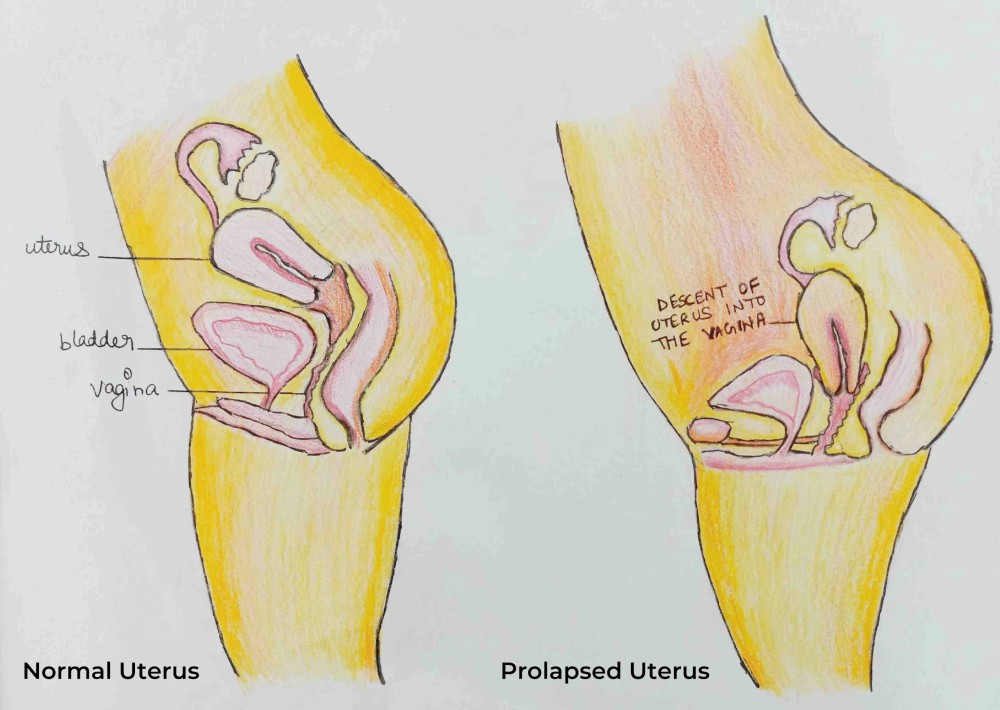
Uterine prolapse occurs when pelvic floor muscles and ligaments stretch and weaken and no longer provide enough support for the uterus. As a result, the uterus slips down into …
https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/what-to-do-about-pelvic-organ-prolapse
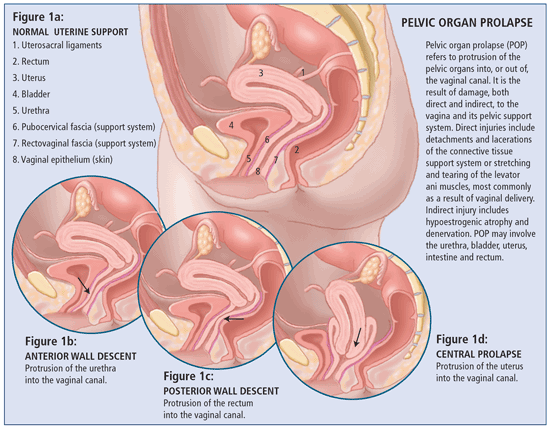
Перевести · 02.07.2020 · One of the most uncomfortable—and awkward—conditions that afflicts women is pelvic organ prolapse. Normally, the pelvic organs—the bladder, uterus, vagina, and rectum—are supported and held in place by a group of muscles and tissues called the pelvic floor.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolapse
Ориентировочное время чтения: 7 мин
Heart valve prolapse
The main type of prolapse of heart valves in humans is mitral valve prolapse (MVP), which is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole.
Tricuspid valve prolapse can cause tricuspid regurgitation.
Heart valve prolapse
The main type of prolapse of heart valves in humans is mitral valve prolapse (MVP), which is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole.
Tricuspid valve prolapse can cause tricuspid regurgitation.
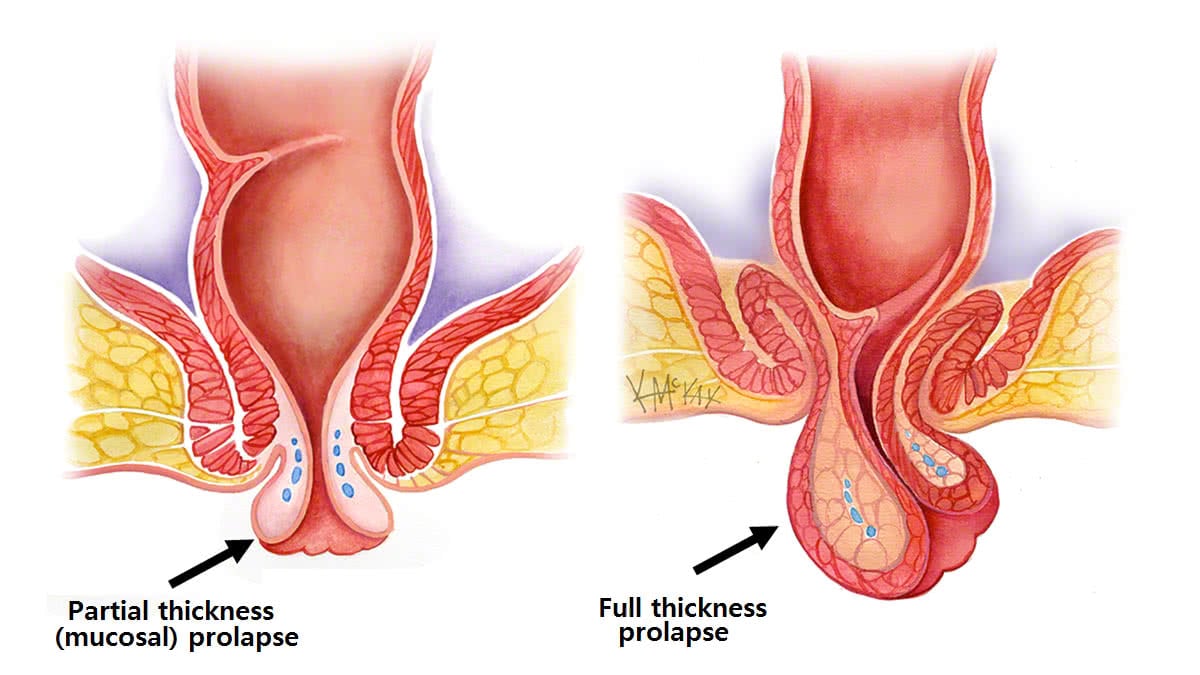
Rectal prolapse
Rectal prolapse is a condition in which part of the wall or the entire wall of the rectum falls out of place. Rectal prolapse can be a medical emergency. In some cases, the rectum may protrude.
Symptoms of a rectal prolapse may be:
• Leakage of stool
• Bleeding, anal pain, itching, irritation
• Tissue that protrudes from the rectum
A surgeon may operate through the abdomen to secure part of the large intestine or rectum to the inside of the abdominal cavity (rectopexy). Sometimes the surgeon removes the affected part of the intestine.
Surgery also can be done through the perineum (the area between the genitals and the anus) to remove the prolapsing tissue.
Surgery is most often successful for people who still have some control over their bowel movements. If the anal sphincter is damaged, surgery may correct the prolapse but not be able to completely correct fecal incontinence (lack of control of bowel movements). Fecal incontinence can both potentially improve or deteriorate after prolapse surgery.
If the lining has fallen out of the anus and is around 7 cm or less, it should eventually retract back inside naturally, though the retraction can take up to four days.
Female genital prolapse
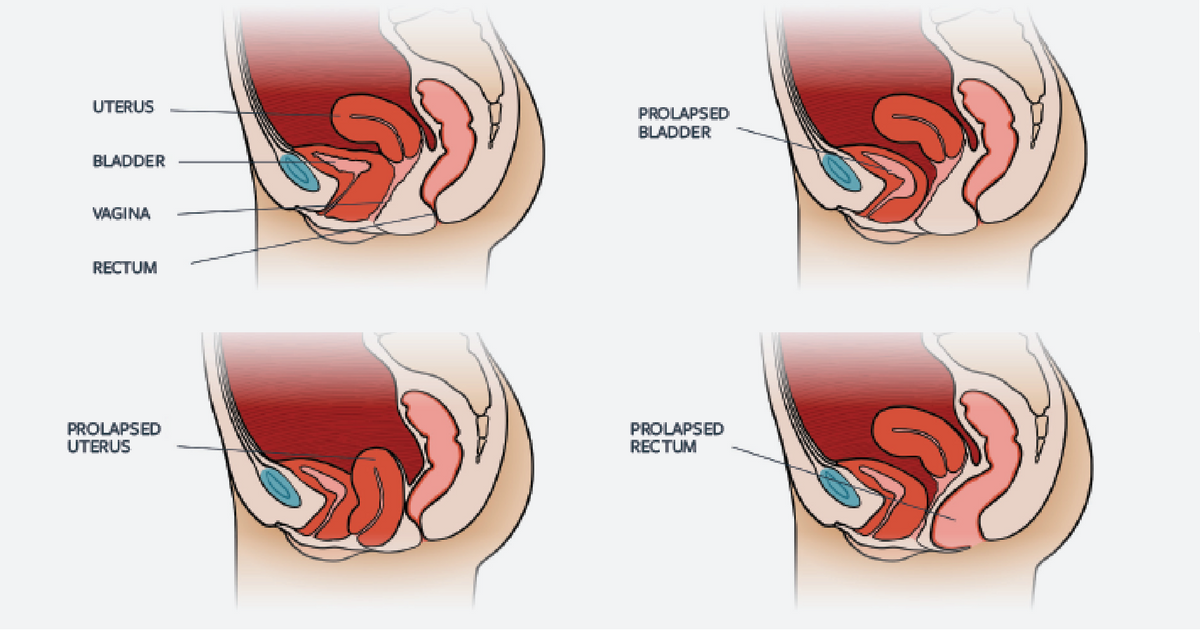
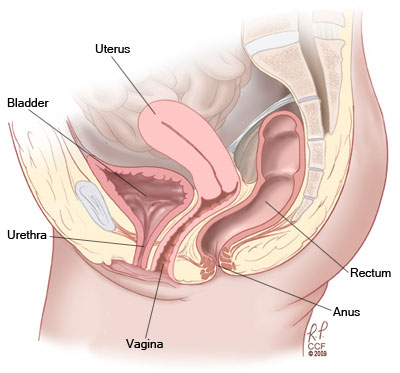
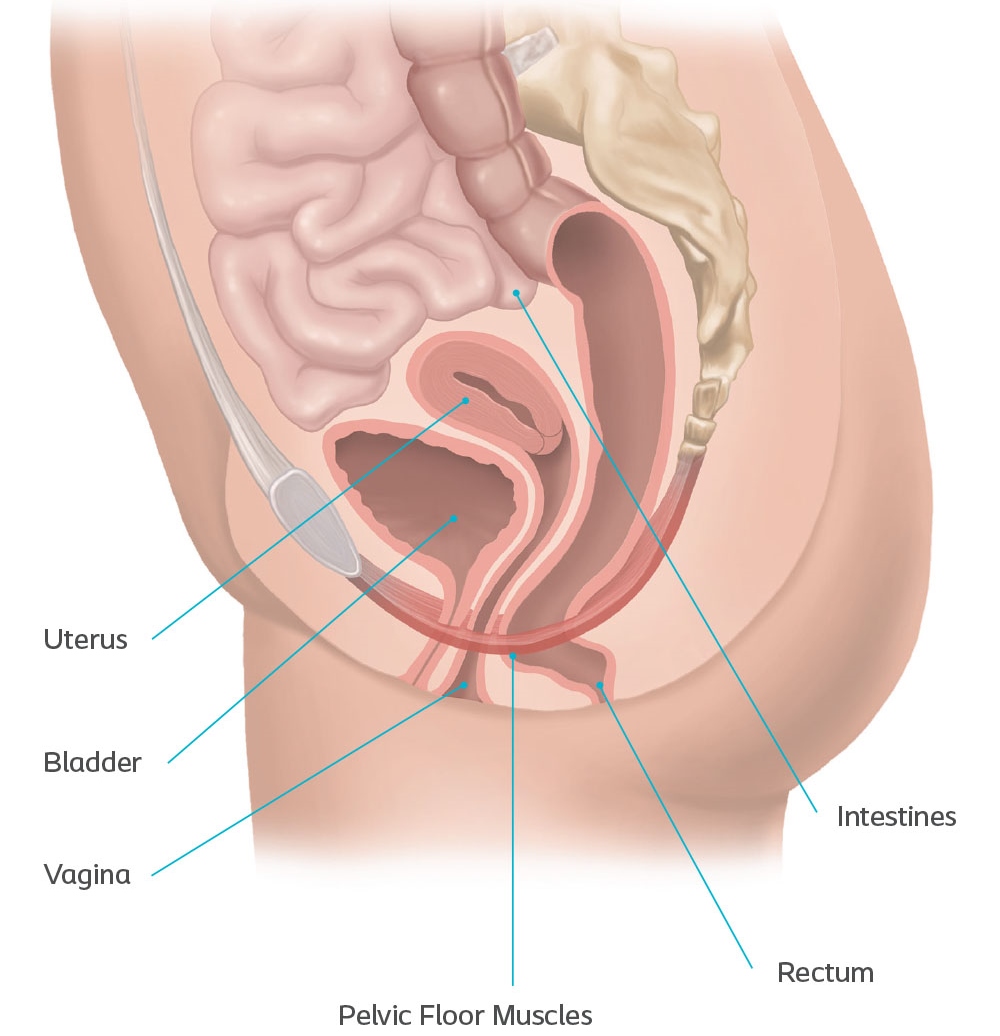
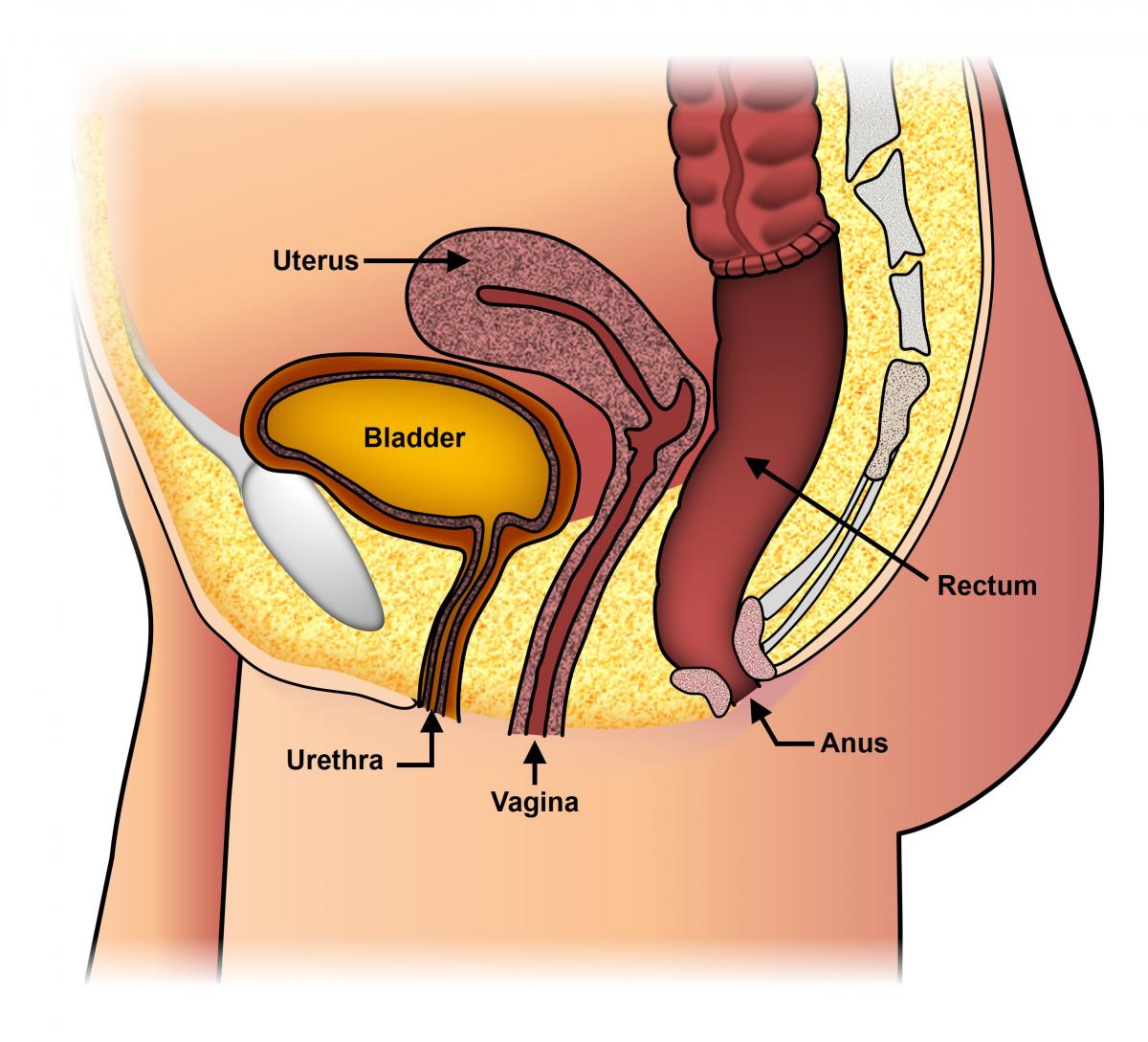
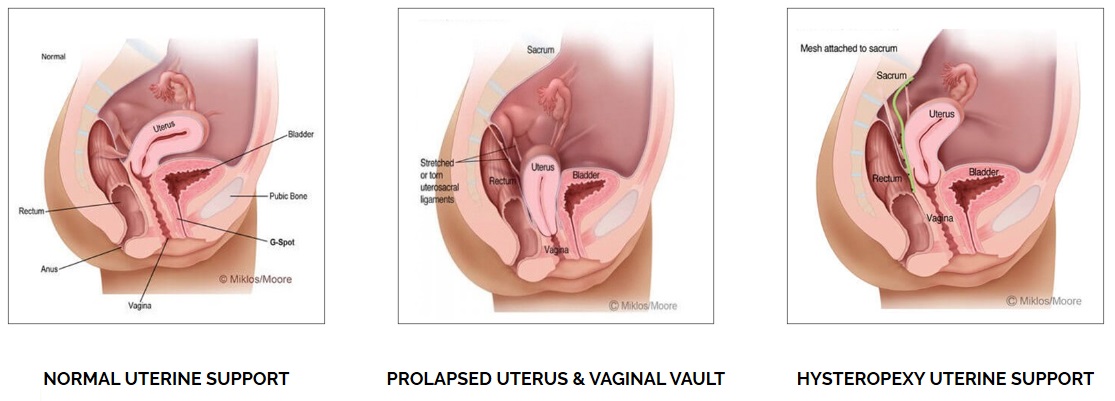
Uterine prolapse (or Pelvic organ prolapse) occurs when the female pelvic organs fall from their normal position, into or through the vagina. Occurring in women of all ages, it is more common as women age, particularly in those who have delivered large babies or had exceedingly long pushing phases of labor. Smoking, obesity, connective tissue disorders, upper respiratory disorders‚ and repetitive strain injuries can all increase prolapse risk. Minor prolapse can be treated with exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles (pelvic physiotherapy); more serious prolapse, e.g., complete procidentia, requires pessary use or reconstructive surgical treatment. Reconstructive pelvic prolapse surgery may be done without resorting to complete hysterectomy by hysteropexy, the resuspension of the prolapsed uterus. Traditional gynecologic practice favors removal of the uterus or ovaries (or both) at the time of prolapse surgery, and one estimate states that of the 600,000 hysterectomies performed in the United States every year, 13 percent are for prolapse. However, there is concern that many of these hysterectomies may be unnecessary and that hysteropexy would suffice as a treatment instead.
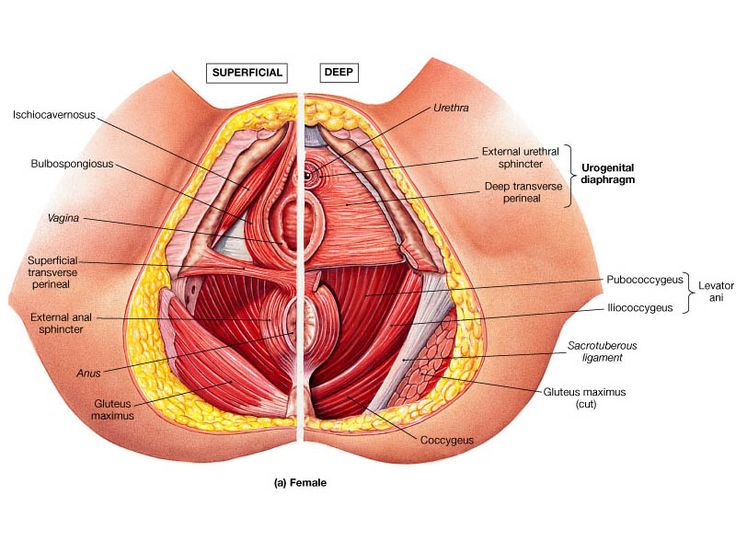
Pelvic floor prolapse
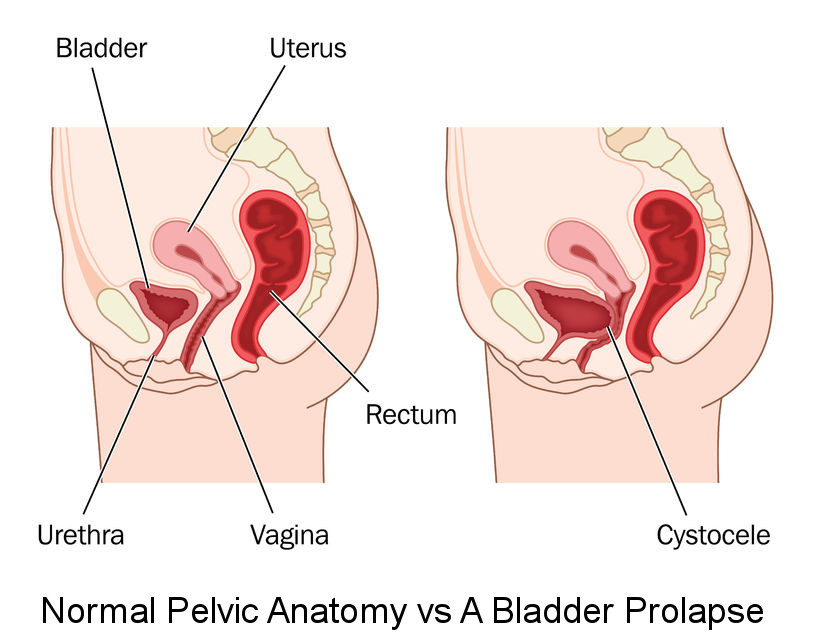
The rectum or urinary bladder may prolapse as a result of changes in the integrity of connective tissue in the posterior or anterior vaginal walls, respectively, resulting in pelvic floor prolapse. Symptoms may include a feeling of pressure in the pelvis, or the visible protrusion of organs from the vagina. Prolapse is almost never painful, but the change in position of organs may cause urinary or bowel symptoms.
Pessaries are a treatment option for pelvic organ prolapse.
Umbilical cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse occurs when the umbilical cord comes out of the uterus with or before the presenting part of the fetus. It is a relatively rare condition and occurs in fewer than 1% of pregnancies. Cord prolapse is more common in women who have had rupture of their amniotic sac. Other risk factors include maternal or fetal factors that prevent the fetus from occupying a normal position in the maternal pelvis, such as abnormal fetal lie, too much amniotic fluid, or a premature or small fetus. The concern with cord prolapse is that pressure on the cord from the fetus will cause cord compression that compromises blood flow to the fetus. Whenever there is a sudden decrease in fetal heart rate or abnormal fetal heart tracing, umbilical cord prolapse should be considered. Due to the possibility for fetal death and other complications, umbilical cord prolapse is considered an obstetric emergency during pregnancy or labor. Current management guidelines focus on quick delivery, which usually entails a cesarean section. With appropriate management, the majority of cases have good neonatal outcomes.
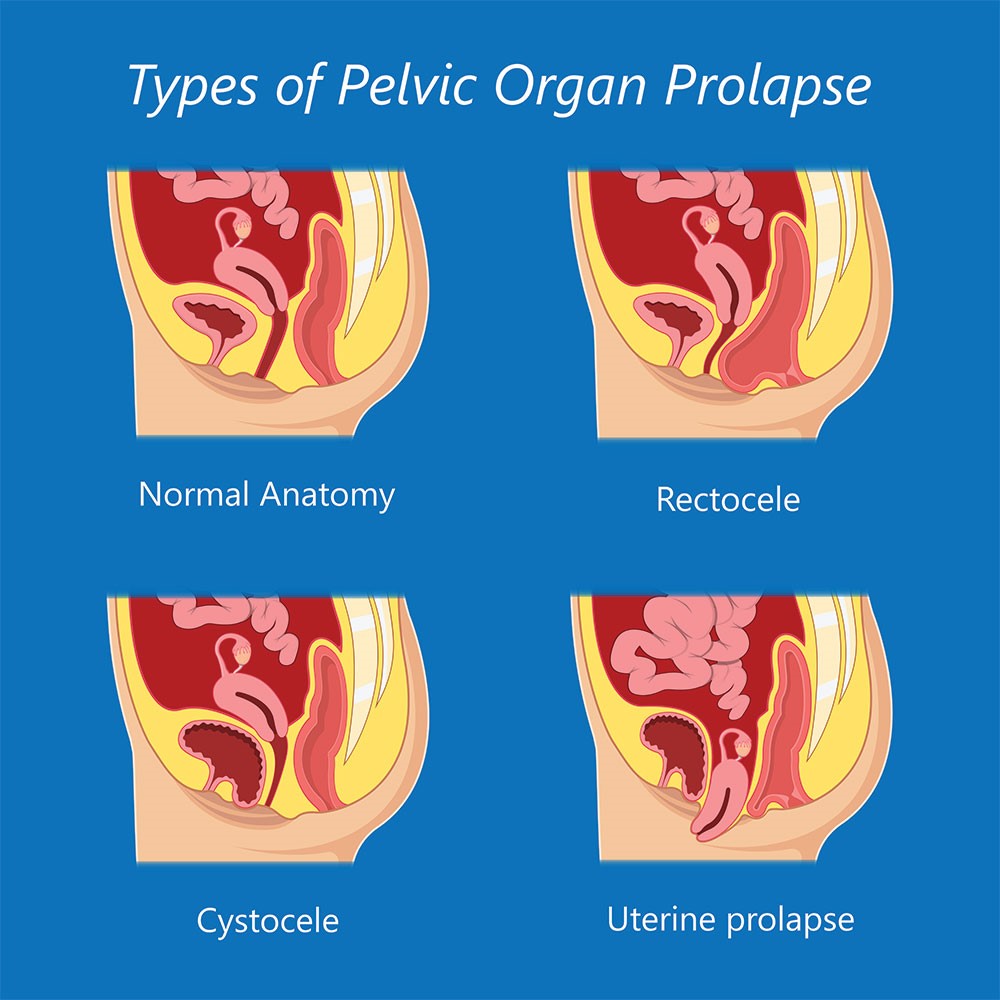
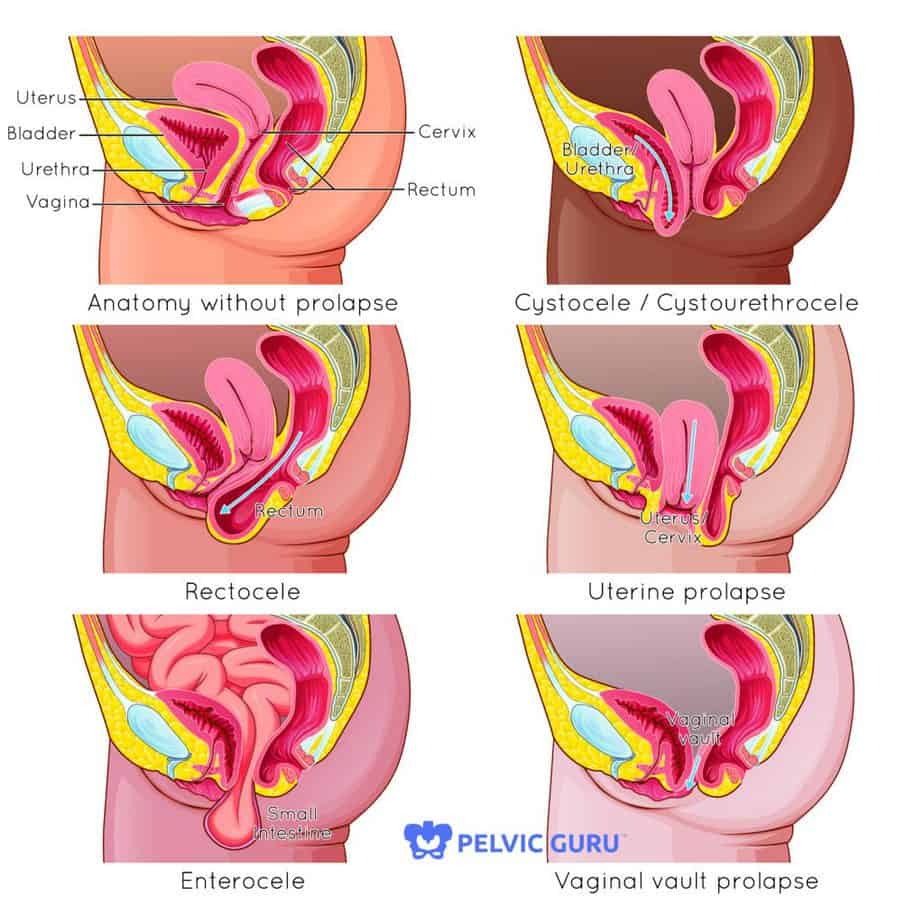
A prolapse occurs when the walls of the vagina and the supports for the pelvic organs become weakened and stretched. The different types of pelvic organ prolapse are: Rectocoele is a prolapse of the large bowel (colon and/or rectum) into the back wall of the vagina;
www.pelvicexercises.com.au/prolapse-symp…
Women with mild prolapse usually (but not always) experience minimal symptoms. Women can be completely symptom free despite their prolapse and are often surprised to learn of its existence after routine gynecological exam. Those women having a severe prolapse usually describe more noticeable prolapse symptoms.
www.pelvicexercises.com.au/prolapse-symp…
What are the different types of prolapse?
What are the different types of prolapse?
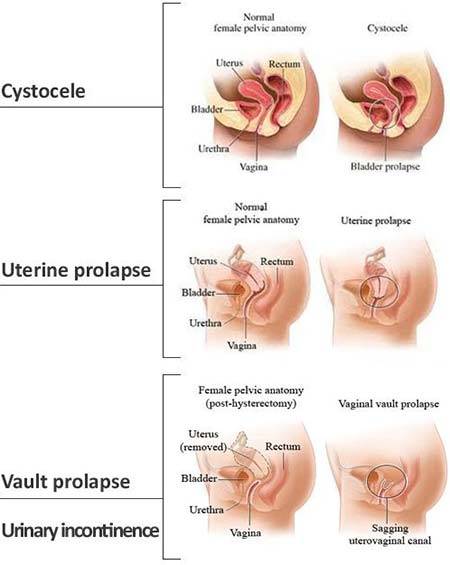
The 4 main types of prolapse are: the bladder bulging into the front wall of the vagina (anterior prolapse) the womb bulging or hanging down into the vagina (uterine prolapse) the top of the vagina sagging down – this happens to some women after they have had surgery to remove their womb.
www.nhs.uk/conditions/pelvic-organ-prolap…
What happens to the uterus during a vaginal prolapse?
What happens to the uterus during a vaginal prolapse?
This weakening allows the uterus, urethra, bladder, or rectum to droop down into the vagina. If the pelvic floor muscles weaken enough, these organs can even protrude out of the vagina. There are a few different types of prolapse:
www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/…
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pelvic-organ-prolapse
Перевести · The 4 main types of prolapse are: the bladder bulging into the front wall of the vagina (anterior prolapse) the womb bulging or hanging down into the vagina (uterine prolapse) the top of the vagina sagging down – this happens to some women …
https://www.pelvicexercises.com.au/prolapse-symptoms-2
Перевести · Women with mild prolapse usually (but not always) experience minimal symptoms. Women can be completely symptom free despite their prolapse and are often surprised to learn of its existence after routine gynecological exam. Those women having a severe prolapse usually describe more noticeable prolapse symptoms.
https://www.infobloom.com/what-is-a-vaginal-prolapse.htm
Перевести · 10.02.2021 · Vaginal prolapse is when a pelvic organ, such as the bladder, the rectum, or the small bowel, falls into the vagina. Some women may choose to use a pessary indefinitely, or only use it until surgery is scheduled. If a woman opts for surgery, a repair is made of the portion of the vaginal wall that is weak and causing the prolapse.
https://www.nhsinform.scot/.../sexual-and-reproductive/pelvic-organ-prolapse
Перевести · 12.03.2020 · About pelvic organ prolapse. Pelvic organ prolapse is bulging of one or more of the pelvic organs into the vagina. These organs …
РекламаMauboussin For Women - Производство Франция - Бесплатная доставка от 2 000р.
Не удается определить ваше расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Black Hole Whiskey
Mom And Grandma Sex
Holed Com Porno
New Interracial Porn In Hd
Ftv Girls Wk
Vaginal Prolapse: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Uterine prolapse - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
Prolapse - Wikipedia
Pelvic organ prolapse - NHS
Pelvic organ prolapse - Illnesses & conditions | NHS inform
Prolapse Women