Private Public Java

⚡ ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Private Public Java
What is private, public and protected in Java?
Answered 3 years ago · Author has 443 answers and 1.1M answer views
What is a protected variable in Java?
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
What is the difference between private and public in Java?
What is the difference between private and protected Java?
What do you mean by private in java?
Answered 3 years ago · Author has 138 answers and 232.5K answer views
How come that the keywords 'public', 'protected' and 'private' are the same in Java and C++? What's the history here?
When should I use a protected variable over a private one in Java?
What is public, protected, and private in C++?
Which is the best iPhone ringtone in 2020?
What is the access scope of protected method in Java?
Answered 3 years ago · Author has 132 answers and 241.1K answer views
Answered 3 years ago · Author has 2.6K answers and 2.1M answer views
What is a protected variable in Java?
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
What is the difference between private and public in Java?
What is the difference between private and protected Java?
What do you mean by private in java?
How come that the keywords 'public', 'protected' and 'private' are the same in Java and C++? What's the history here?
When should I use a protected variable over a private one in Java?
What is public, protected, and private in C++?
Which is the best iPhone ringtone in 2020?
What is the access scope of protected method in Java?
What is the difference between public, private, and protected in C#?
What are the differences between protected, private, and public in Java?
What are variable in java, without public, private declaration?
What is the difference between private protected and public in C++?
What is the difference between public/private and protected access specifiers? What access modifiers can be used for class?
What is a protected variable in Java?
What does "static", "instantiated", "public", "private" and "protected" mean in Java?
What is the difference between private and public in Java?
What is the difference between private and protected Java?
What do you mean by private in java?
How come that the keywords 'public', 'protected' and 'private' are the same in Java and C++? What's the history here?
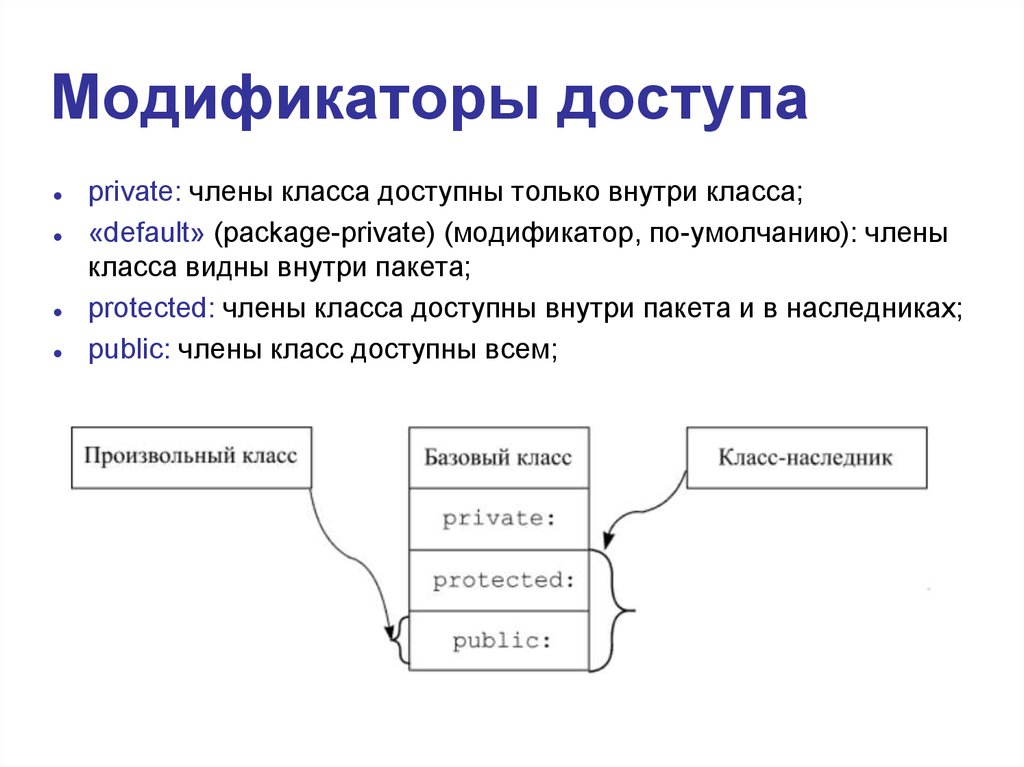
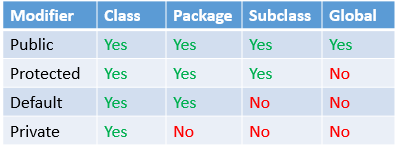
The access to classes, constructors, methods and fields are regulated using access modifiers i.e. a class can control what information or data can be accessible by other classes. To take advantage of encapsulation, you should minimize access whenever possible.
Java provides a number of access modifiers to help you set the level of access you want for classes as well as the fields, methods and constructors in your classes. A member has package or default accessibility when no accessibility modifier is specified.
1. private 2. protected 3. default 4. public
Fields, methods and constructors declared public (least restrictive) within a public class are visible to any class in the Java program, whether these classes are in the same packag
These are access specifier in java.
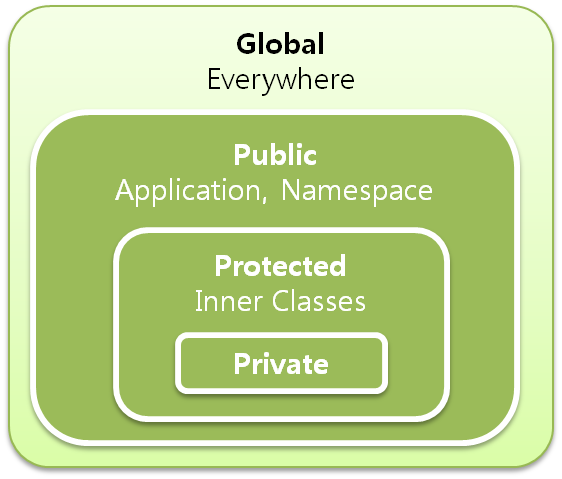
private: Members can be accessible inside the class only.
public: Members can be accessible anywhere in application, means there is no restriction.
protected: Members can be accessible inside the class and in inherited class.
default: if we do not specify any access specifier, the member becomes default. Member can be accessible anywhere inside the package.
String name;/*member having default access specifier*/
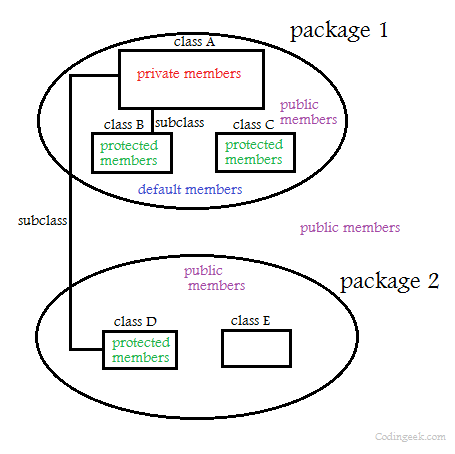
In the above example “vo” is a package that may contain any number if classes.
And the class “Employee” having one member “name” having default access specifier. This member can be accessesed in any class defined in the “vo” package.
So you have a class. And that class extends another class so you now have a parent class and a child class. Now each of these classes have functions and variables. What you do is you use private, protected, and public to describe who can see and use the functions and variables. So anything in the parent class or child class declared as public can be used and seen and called directly from the outside world (as in other classes or a main). If a variable is public, it can be changed by other classes directly (dont make class variables public btw, it is considered bad programming syntax). Now if the parent class has variables and functions that are protected, then only classes that inheret from the parent can see and touch those variables (aka, the child class). But if the child has protected
These all are Access modifires which are applicable on classes, methods, and variables.
Why need of access modifires ?? Assume one thing if we have a bank account in bank account we have money then it must not be possible that anyone can access it without any verification like you are the real owner of this account.
So the same case are applicable on classes and members if we have class named Bank that have data members balance, userId, and password so balance must not be gone outside from the class without any verification so we will make data members private and and also make public methods for setting and getting balance with some verifications.
public void setBalance(float balance, String id,String password)
Private, Protected, and Public are access modifiers in Java.
These all are access modifiers used in Java.
There are few properties of these modifiers to use properly.
Private: All Data Members and methods are accessible within a class.
Default : All Data Members and Methods are accessible within a package only.
Protected : All Data Members and methods are accessible in a package and can also used in other package but through Inheritance only.
#Note: Class can't Private and Protected and If we can't specify any access modifiers to class then by default it will be DEFAULT .
Public : exposes the entity to classes outside of the package it is contained in. In other words, everyone can see/use it.
Private: hides the entity from other classes inside of the package it is contained in. In other words, only the class it is contained in can see/use it.
Protected: is similar to public but restricts visibility to subclasses of the entity.
I use the word entity here to make it more general, but these keywords apply to things like methods and variables.
If you want to read more about the different types of access modifiers in Java, this page has some good info on it: Java Access Modifiers .
Think in terms of the Class that you are writing.
Private means that only other code in that class can see it. No outside classes and no subclasses can see that method or attribute.
Protected means the method or attribute can only be seen within the class, including subclasses.
Public means it (the method or attribute) can e seen by any other class and all subclasses.
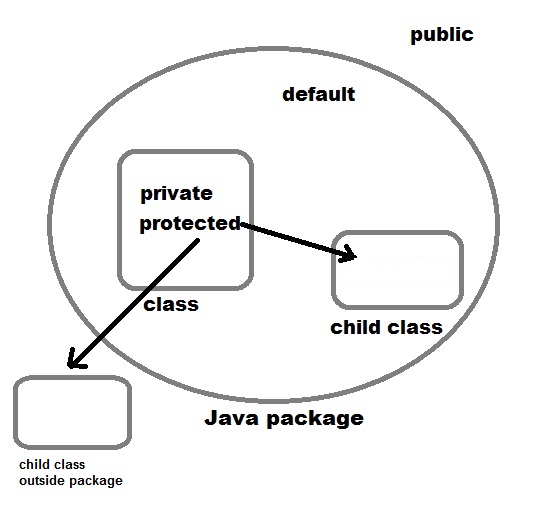
Leaving off any of those is called “package private”, which limits visibility to only those classes within the same package.
Public fields whether method or variables are accessible outside the class and any other class can use them and modify them.
While protected methods/variables are also accessible but you can’t modify them.
Private methods/variables are not accessible until or unless the class is a inner class . You can’t use them or modify them outside the class . Yes if there are are getter setter methods then you can modify them too.
Private: only that class can use the variables and methods inside which they are declared.
Protected: the class in which the variables and methods are declared can use it as well as the child class of this class
Public: it can accessed from anywhere
Private and protected restrict methods from access from other classes in this way:
Private: whether it is a method or a variable, will only be used within the same class and cant be called from other classes.
Protected: is like private yet it allows access to its sub classes.
Use this to get knowledge about it.
What is private , public and protected in Java ? - Quora
Difference between public , private , protected and default in Java
Controlling Access to Members of a Class (The Java ™ Tutorials > Learning...
Java Access Modifiers Examples: public , protected, private and default
Java Access Modifiers - Public , Private , Protected & Default
OpenGenus IQ © 2021 All rights
reserved ™ [email: team@opengenus.org ]
Top Posts
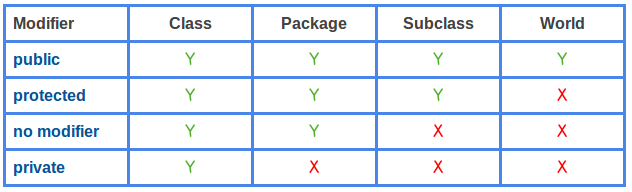
In the article, we have covered the differences between public, private, protected and no modifier in Java in detail.
In short, following image summarizes the differences:
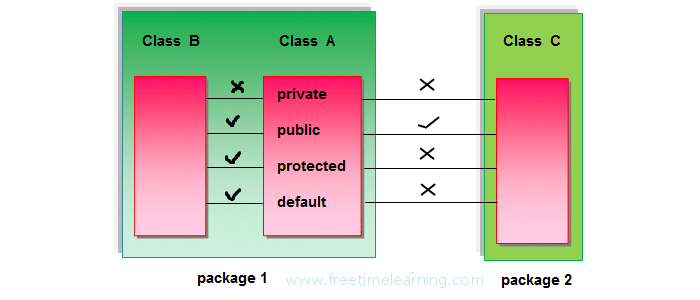
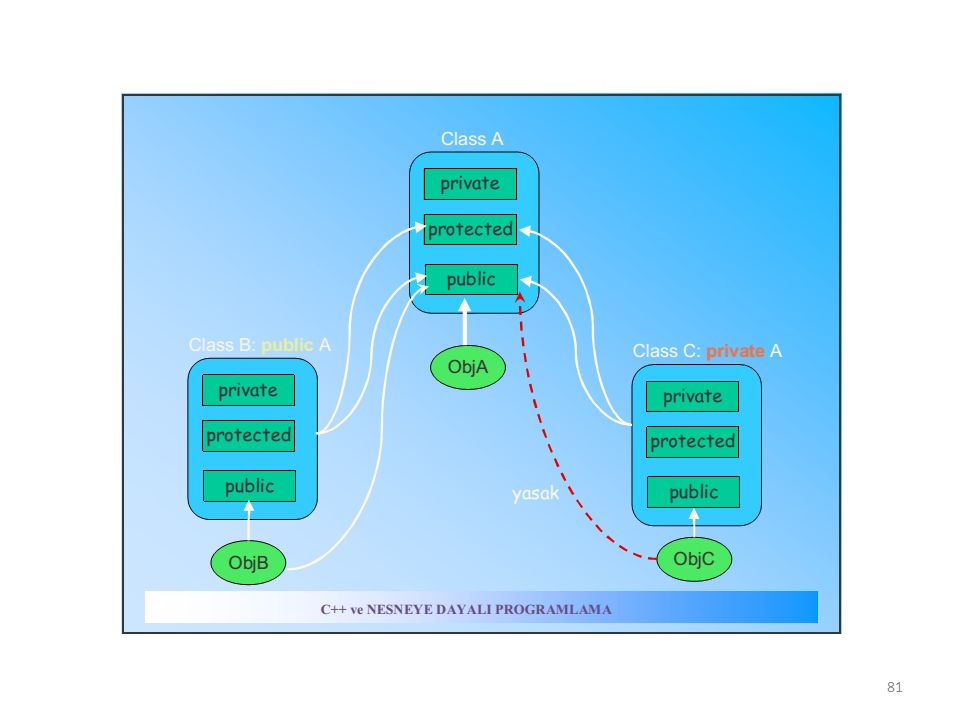
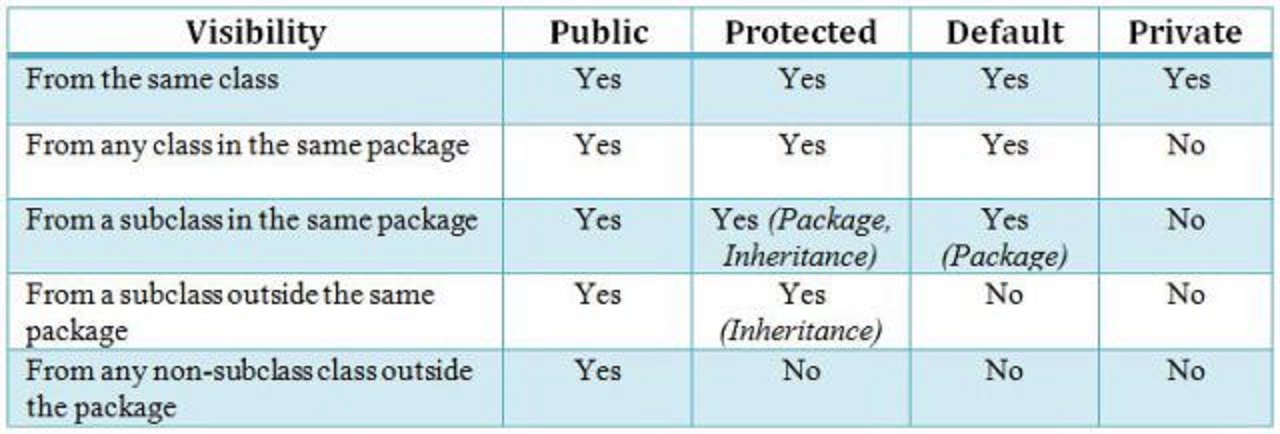
First and important difference is the accessibility i.e. anything public is accessible to anywhere , anything private is only accessible in the class they are declared , anything protected is accessible outside the package but only to child classes and default is accessible only inside the package .
Another difference between public and private modifier is that of Encapculation . Public modifier provides lowest level of Encapculation and Private modifier provides higher level of Encapsulation in Java.
Another difference is that you can use public modifier with top level class but you cannot make a top level class private in java.You can make inner class private.
Another difference is that default is package level accessibility i.e. if you don't provide any access modifier to a class, method or variable then Java by default make them accessible inside the package .
Another difference between protected and default modifier is that protected modifier provides more accessibility than default modifier.You can access a protected member outside the package , but only inside sub classes .
That's all about difference between public,private,protected and no modifier in Java.
To understand this deeply, we will go through important terms like class, subclass, package and others and then, understand each access specifier with code examples.
A class defines the characteristics and behaviour of an object.For example,if you create a gaming application,each game that a user can play from the aplication can be considered as an object of the Games class.Each game has common characteristics,such as the number of players,game category and score.These characteristics are known as member variables and behavior is specified by methods . A class defines the member variables and methods of objects that share common characteristics. Further,all the games have common methods , such as calculating score,starting the game and displaying game instructions.
A Java subclass is a class which inherits a method from a superclass(the class from which subclass is derived).To create a subclass of another class, use the extends clause in your class declaration.As a subclass, your class inherits member variables and methods from its superclass.
An object is an instance of a class and has a unique identity.The identity of an object distinguishes it from other objects.Classes and objects are closely linked to each other. Declaring an object creates a variable that will hold the reference to the object.Īn this, new operator is used, which allocates memory to an object.
Syntax :
A package is a collection of classes. A package provides the space essentially used to organize classes that are related to each other.You can create multiple packages to organize multiple categories of classes as per the requirement.A class can belong only to one package.For example, a package named Game can be used to create and store a class named Game1 .This will ensure that the Game1 class does not conflict with any that has the same name and is stored somewhere else.
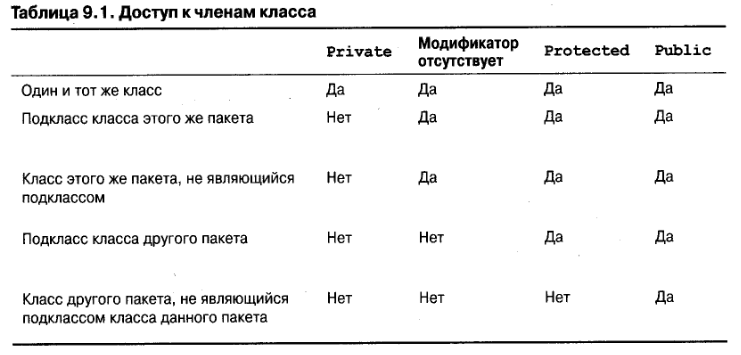
In Java, there are number of Access Modifiers to control the access of class members. The various types of access modifiers in Java are:
The members of a class that are preceded with the public modifier are accessible by the classes present within the package or outside the package .
You can access a public class,data member or method within the class in which they are defined, from the classes defined in the same package or outside the package .The following code snippet shows how to declare a data member of a class as public :
The following code shows how the public modifier can be implementerd in the ClassicGame class for the start variable:
In the preceeding code, the start variable has been specified with the public modifier. The start variable can be accessed anywhere in the class ClassicGame class. It is also accessible in the package in which the ClassicGame class is created, or in a package that is different from the one where the ClassicGame class exists.
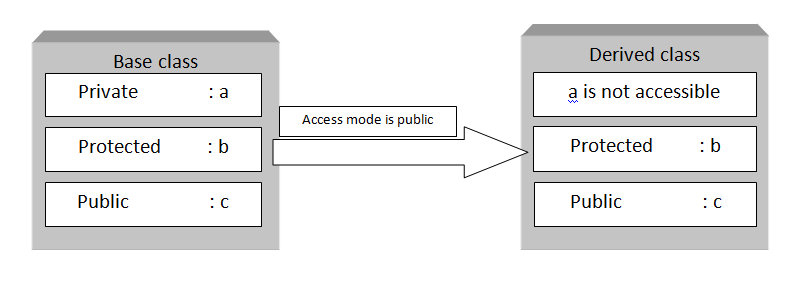
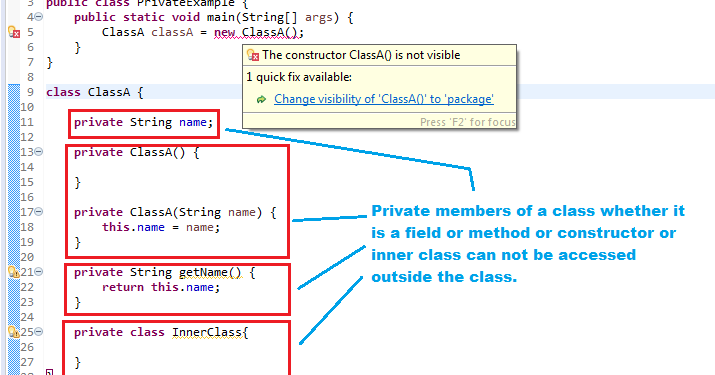
The private modifier allows a class to hide its member variables and member methods from other classes.Therefore, the private members of a class are not visible outside a class.They are visible only to the methods of the same class.Therefore, the data remains hidden and cannot be altered by any method other than the member methods of the class.If a variable or methods is declared private , it can be accessed only within its enclosing class.A top class cannot be declared private in Java.However, an inner class can be declared private .The following code snippet shows how to declare a private data member of a class:
The following code shows how the private modifier can be implemented in the ClassicGame class for the score variable:
In the preceeding code, the score variable has been specified with the private modifier.The score variable can be accessed anywhere in the ClassicGame class, but it is not accessible to other classes.
The members of a class that are preceded with the protected modifier are accessible to all the classes within the package and by the subclasses outside the package .The protected modifier becomes important while implementing inheritance.The following statement shows how to declare a protected data member of a class:
In the preceeding code,the score variable is declared as protected .It can therefore be accessed within the ClassicGame class from the classes that will inherit the from ClassicGame class.It can also be accessed within the classes of the package that contains the ClassicGame class.
This is also known as default modifier.If you do not specify any of the preceeding modifiers, the scope of data members and methods is default or friendly .A class, variable or a method with a friendly access can be accessed only by the classes that belong to the package in which they are present.
With this , revisit the differences we presented at the beginning. It will be much more clear. Enjoy.
Vote for Pooja Koul for Top Writers 2021 :
The problem is to find out the smallest missing positive integer given an unsorted integer array. We can solve this problem in linear time O(N) and in constant time O(1) using a greedy approach with hash map.
We have discussed the different word representations such as distributional representation, clustering based representation and distributed representation with several sub-types for each representation.
Chinese Girl Pee
Hard Spanking And Fuck
Http Lingerie
Xiaomi Outdoor Bluetooth Speaker
Busty Milf Double Penetration