Private Pem

🛑 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Private Pem
Products
Services
Support
Blog
About us
RSACryptoServiceProvider rsa = pem.ReadEncryptedPrivateKeyFromFile(
"EncryptedPrivateKey.pem" , // "EncryptedRSAPrivateKey.pem"
RSACryptoServiceProvider rsa = pem.ReadPrivateKeyFromFile( "PrivateKey.pem" );
RSACryptoServiceProvider rsa = pem.ReadPublicKeyFromFile( "PublicKey.pem" )
X509Certificate2 certificate = new X509Certificate2(
X509KeyStorageFlags.PersistKeySet)
using ( var rsa = (RSACryptoServiceProvider)certificate.PrivateKey)
X509Certificate2 certificate = new X509Certificate2( "certificate.cer" );
X509Certificate2 certificate = pem.ReadCertificateFromFile( "certificate.cer" );
Limilabs™ © 2004-2021. All rights reserved. |
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy
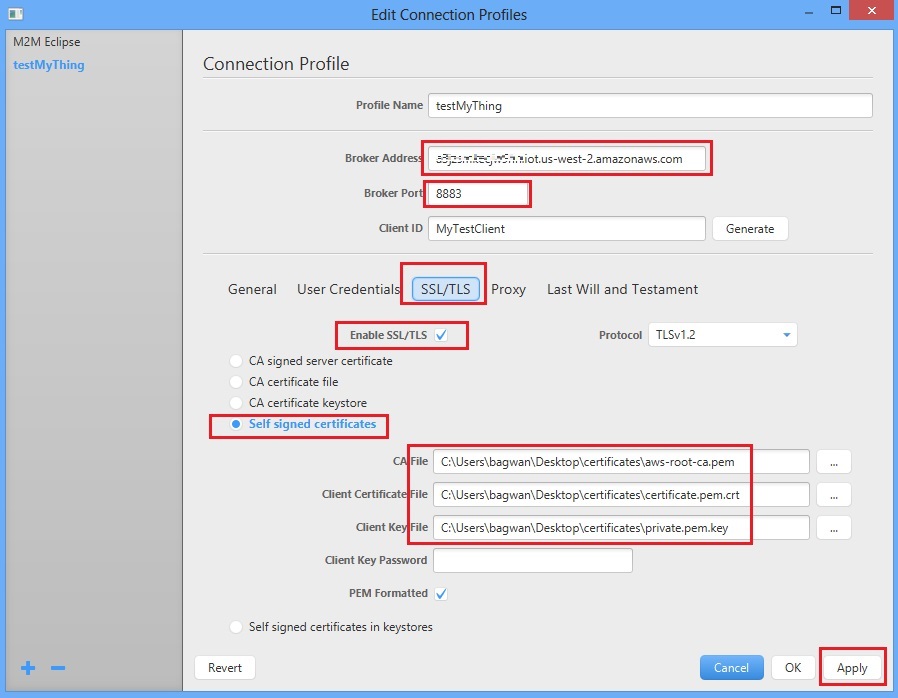
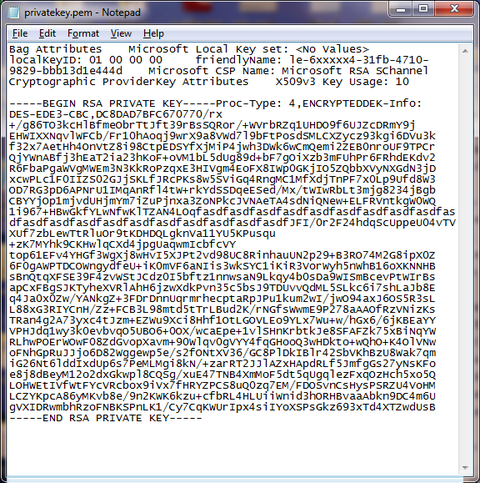
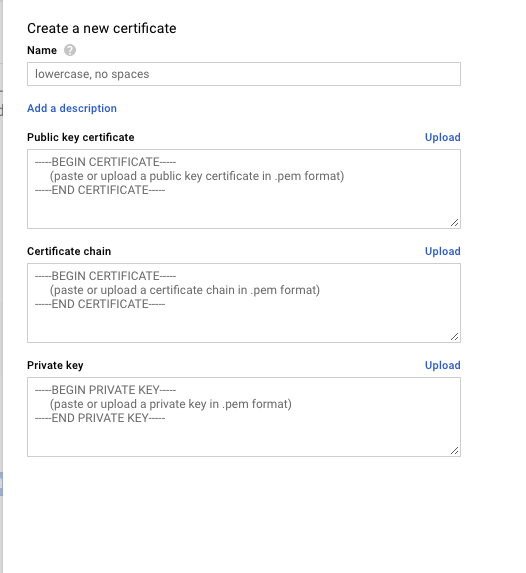
PEM stands for Privacy Enhanced Mail format. The PEM format is the most common format that Certificate Authorities issue certificates in. PEM certificates usually have extensions such as .pem, .crt, .cer, and .key. They are Base64 encoded ASCII files.
This code handles following formats:
PKCS #8 EncryptedPrivateKeyInfo Encrypted Format:
-----BEGIN ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----
MIICojAcBgoqhkiG9w0BD .....
Private Key (Traditional SSLeay RSAPrivateKey format) Encrypted:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
Proc-Type: 4,ENCRYPTED
DEK-Info: DES-EDE3-CBC,24A667C253F8A1B9
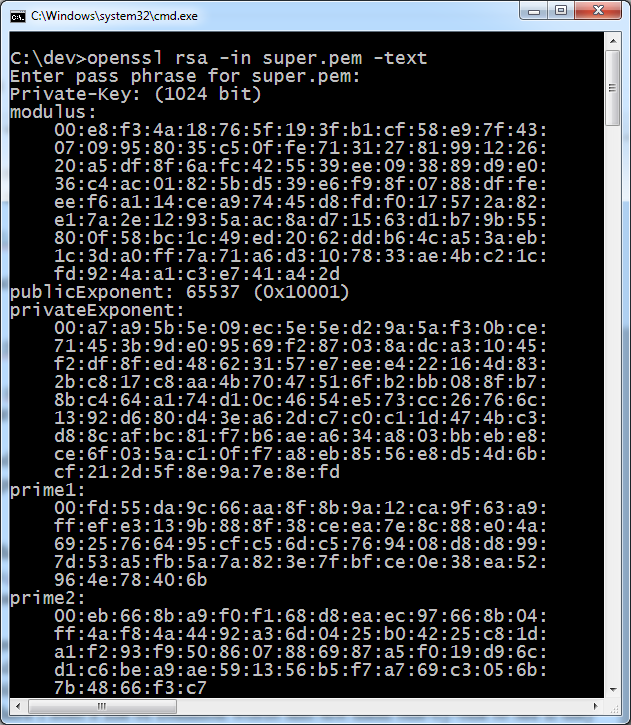
You can remove the passphrase from the private key using openssl:
openssl rsa -in EncryptedPrivateKey.pem -out PrivateKey.pem
This code handles following formats:
PKCS #8 PrivateKeyInfo Unencrypted:
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
MIICdgIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0B ......
Private Key (Traditional SSLeay RSAPrivateKey format) Unencrypted:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIICXQIBAAKBgQCcHVm .....
This code handles following formats:
Public Key (SubjecPublicKeyInfo):
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEB .....
Note: The private key is never stored in a .pem/.cer certificate file.
This code handles following formats:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFsTCCA5mgAwIBAgIKYQ .....
VAT: PL 5213195875
Regon: 145938780
Pulawska 115/18
02-707 , Warsaw Poland
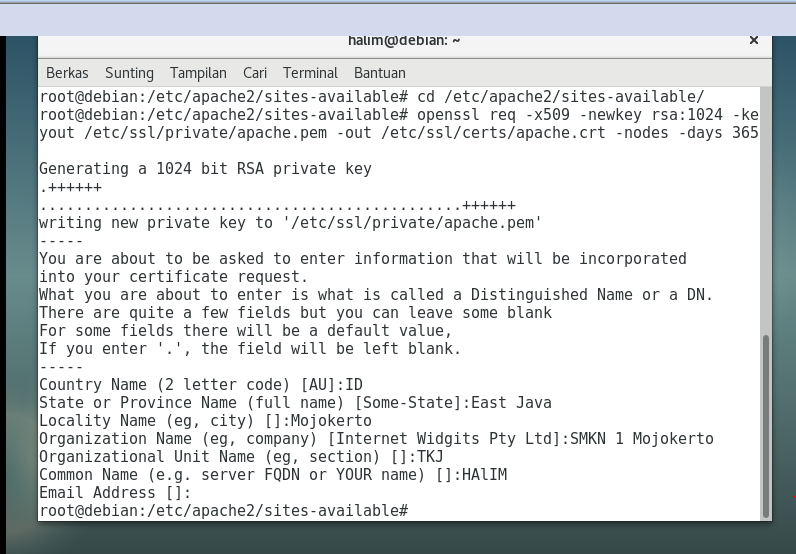
Convert private key to PEM format
Import certificate, private or public keys ( PEM , CER, PFX) | Limilabs
How to Read PEM File to Get Public and Private Keys | Baeldung
PHP: openssl_ private _encrypt - Manual
tls - Private key to PEM - Information Security Stack Exchange
I just announced the new Learn Spring Security course, including the full material focused on the new OAuth2 stack in Spring Security 5:
>> CHECK OUT THE COURSE
I just announced the new Learn Spring Security course, including the full material focused on the new OAuth2 stack in Spring Security 5:
>> CHECK OUT THE COURSE
In public-key cryptography (also known as asymmetric cryptography), the encryption mechanism relies upon two related keys, a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt the message while only the owner of the private key can decrypt the message.
In this tutorial, we’re going to see how to read public and private keys from a PEM file.
First, we’ll study some important concepts around public-key cryptography. Then, we’ll learn how to read PEM files using pure Java.
Finally, we’ll explore the BouncyCastle library as an alternative approach.
Before we start, let’s understand some key concepts.
X.509 is a standard defining the format of public-key certificates. So, this format describes a public key among other information.
DER is the most popular encoding format to store data like X.509 certificates, PKCS8 private keys in files. It's a binary encoding and the resulting content cannot be viewed with a text editor.
PKCS8 is a standard syntax for storing private key information. The private key can be optionally encrypted using a symmetric algorithm.
Not only can RSA private keys can be handled by this standard, but also other algorithms. The PKCS8 private keys are typically exchanged through the PEM encoding format.
PEM is a base-64 encoding mechanism of a DER certificate. PEM may also encode other kinds of data such as public/private keys and certificate requests.
A PEM file also contains a header and a footer describing the type of encoded data:
Let’s start by reading the PEM file and storing its content into a string:
We’re going to build a utility method that gets the public key from the PEM encoded string:
Let’s suppose we receive a File as a parameter:
As we can see, first we need to remove the header, the footer, and the new lines as well. Then, we need to decode the Base64-encoded string into its corresponding binary format.
Next, we need to load the result into a key specification class able to handle a public key material. In our case, we’re going to use the X509EncodedKeySpec class.
Finally, we can generate a public key object from the specification using the KeyFactory class.
Now that we know how to read a public key, the algorithm to read a private key is very similar.
We're going to use a PEM encoded private key in PKCS8 format. Let's see what the header and the footer look like:
As we learned previously, we need a class able to handle PKCS8 key material. The PKCS8EncodedKeySpec class fills that role.
We’re going to explore the BouncyCastle library and see how it can be used as an alternative to the pure Java implementation.
There are a few important classes that we need to be aware of when using BouncyCastle:
Moreover, let's see another approach that wraps the Java's classes ( X509EncodedKeySpec, KeyFactory ) into BouncyCastle's own class ( JcaPEMKeyConverter ):
We're going to see two examples that are very similar to the ones showed above.
In the first example, we just need to replace the X509EncodedKeySpec class with the PKCS8EncodedKeySpec class and return an RSAPrivateKey object instead of an RSAPublicKey :
Now, let's rework a bit the second approach from the previous section in order to read a private key:
As we can see, we just replaced SubjectPublicKeyInfo with PrivateKeyInfo and RSAPublicKey with RSAPrivateKey .
There are a couple of advantages provided by the BouncyCastle library.
One advantage is that we don’t need to manually skip or remove the header and the footer. Another one is that we’re not responsible for the Base64 decoding either. Therefore, we can write less error-prone code with BouncyCastle.
Moreover, the BouncyCastle library supports the PKCS1 format as well. Despite the fact that PKCS1 is also a popular format used to store cryptographic keys (only RSA keys), Java doesn't support it on its own.
In this article, we learned how to read public and private keys from PEM files.
First, we studied a few key concepts around public-key cryptography. Then, we saw how to read public and private keys using pure Java.
Finally, we explored the BouncyCastle library and learned that it’s a good alternative since it provides a few advantages as compared to the pure Java implementation.
The full source code for both Java and BouncyCastle approaches is available over on GitHub.
Learn the basics of securing a REST API with Spring
Overwatch Cat
Chubby Missionary Porno
Overwatch Mercy X
King Orgasmus One
Txxx Dona Maria