Private Network 5g

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
https://5g.co.uk/guides/what-is-a-private-5g-network
07.02.2020 · What is a private 5G network? Also known as a local or non-public 5G network, a private 5G network is a local area network (LAN) that will use 5G …
https://www2.deloitte.com/.../2020/private-5g-networks.html
09.12.2019 · Unlike a public network, a private 5G network can be configured to a location’s specific needs, 2 and configurations can vary by site, depending on the type of work undertaken in each venue. A private network also allows companies to determine the network’s …
Private 5G networks – a gamechanger for your business | Verizon
5G - Private network for entreprises
Private 5G Network in Test Center from Siemens
Private 5G networks – a game changer for your business | Verizon
Private 5G networks – a game changer for your business | Verizon
https://www.sierrawireless.com/iot-blog/what-are-private-lte-networks
23.10.2020 · Private LTE and 5G networks (referred to as “non-public networks” by 3GPP, the mobile telecommunications standards organization) are networks that use licensed, shared, or unlicensed wireless spectrum and LTE or 5G cellular networking base stations, small cells, and other Radio Access Network …
https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2020/7/5g-private-network-operations
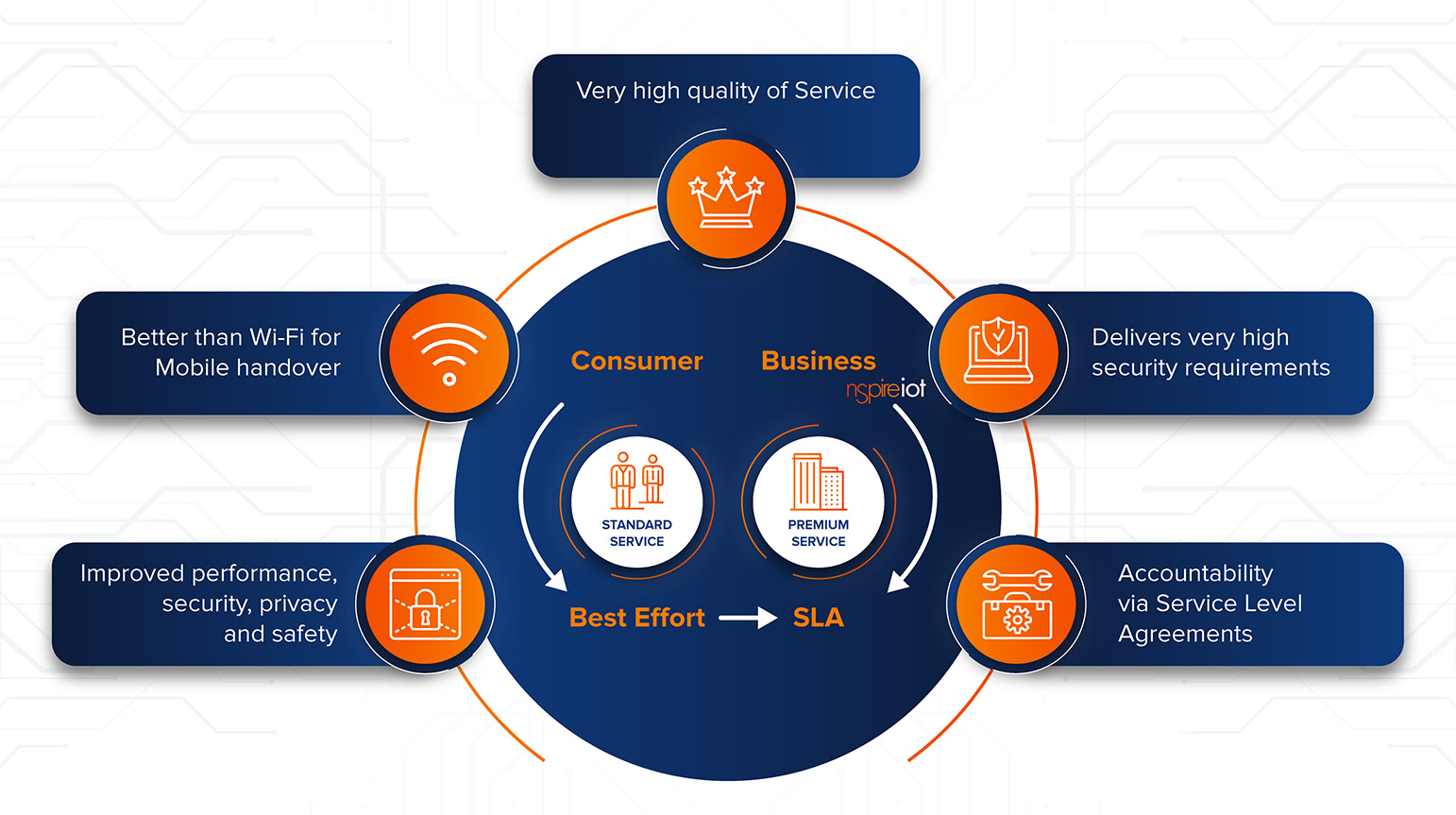
05.07.2020 · Ultra-high reliability, ultra-low latency, 99.999 percent availability, and very high security are some of the characteristics 5G private networks will be capable of. What are private networks …
https://innovationatwork.ieee.org/private-5g-networks
A private 5G network, also known as a local or non-public 5G network, is a local area network that provides dedicated bandwidth using 5G technology. Although the telecommunication industry is currently building the needed infrastructure and network gear to support 5G, …
What does it mean to have a private 5G network?
What does it mean to have a private 5G network?
What is a private 5G network? Also known as a local or non-public 5G network, a private 5G network is a local area network (LAN) that will use 5G technologies to create a dedicated network with unified connectivity, optimised services and a secure means of communication within a specific area.
5g.co.uk/guides/what-is-a-private-5g-netw…
What are the use cases for 5G technology?
What are the use cases for 5G technology?
An emerging use case for 5G is that of private 5G networks. In essence a private 5G network will be the next generation local area network (LAN), incorporating 5G technologies and enabling more advanced use cases than can be supported by current technologies.
5g.co.uk/guides/what-is-a-private-5g-netw…
What do you need to know about 5G operations?
What do you need to know about 5G operations?
Ericsson’s whitepaper, ‘ Critical capabilities for private 5G networks ’, stresses the importance of operations and lifecycle management (LCM) of a critical system. Operations are considered as important as the system itself, to guarantee automated deployment and maintenance throughout the network’s life.
www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2020/7/5g-priva…
Can a neutral host set up a 5G network?
Can a neutral host set up a 5G network?
Neutral Hosts: Similar to MNOs, neutral hosts are private LTE and 5G networks that supplement existing public wireless networks in a particular location. For example, a neutral host might set up a private cellular network in an airport, office building, stadium, or hotel.
www.sierrawireless.com/iot-blog/what-are-…
https://tmt.knect365.com/private-networks
About Private Networks in a 5G World. Back in-person, Private Networks in a 5G World is bringing the entire private network ecosystem together for two days of in-depth content, discussions, networking and more. Seize the opportunity to meet your next private network …
https://www.rimedolabs.com/blog/private-5g-networks-technology-architecture-and-deployment
04.01.2021 · A private mobile network is a 5G or LTE system optimized (tailored) for a specific industrial or enterprise use case (like Industrial Internet of Things, IIoT), where specific requirements play an important role (like QoS, latency, mobility, security). There are different options for the implementation of those local/dedicated networks.
https://telecoms.com/opinion/private-5g-networks-inside-the-operator-opportunity
13.07.2021 · Most private network deployments can fit into two categories: physically isolated or sharing the mobile operator’s public 5G network resources. In both cases, an enterprise can deploy a complete 5G network …
https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/news/252494178/Private-5G-networks-to-gain...
29.12.2020 · Published: 29 Dec 2020. In 2021, private 5G will gain momentum in industries as organizations with industrial IoT systems seek to improve …
РекламаНедорого! Подписка электронно Trimble SketchUp Pro Network Private server 1 year
РекламаСервис продаж ОСАГО для агентов — Работа с ТОП-16 СК — Подключись за 10 мин.!
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
A Comprehensive Set of IoT Solutions
Sierra Wireless simplifies the IoT, delivering you the device, software and service solutions to accelerate your data-driven transformation.
Octave:
The All-in-One Edge-to-Cloud Solution for Connecting Your Industrial Assets
Connectivity Services to Simplify your IoT Journey
Whether your machines or other assets are globally dispersed or regional, simplify how you connect and manage your IoT deployments.
Our solutions for asset tracking, offender monitoring & remote tank monitoring combine deep knowledge of each vertical with IoT expertise to resolve industry-specific issues.
Securely connect your devices globally at the highest speeds.
Ensure Always-on Connectivity for Your Critical Workers
Fully managed wireless connectivity, end-to-end wireless broadband solutions for permanent, temporary, and back-up
High Performance Multi-Network Vehicle Routers
The AirLink MG90 and MG90 5G are purpose-built to provide secure, always-on connectivity.
Fully Integrated IoT Solutions for Any Industry
Harness the power of the IoT for your business and deliver new levels of innovation and efficiency.
75% of Industrial IoT Projects Fail. Make Yours the Exception.
Learn how industrial companies can overcome complexity in IIoT development and commercialization.
Expanding the IoT into the Utility – Simply
Discover how Sierra Wireless Octave combined with Losant’s IoT Enterprise platform can be used to simplify the building of IoT applications for utilities.
The Fast, Cost-Effective Way to Deliver Telematics for Fleet Management
5 Key Trends in Public Safety & the Technology Implications
Discover trends shaping the future of first responders and what public safety agencies need to prepare for.
Liveable Cities Enables Smart City Traffic Management Via Street Light Infrastructure
Transforming Medical Care with Connectivity
Learn about using wireless technologies in hospitals and connecting high-value hospital assets.
Perto Veloh Smart Delivers Improved Speed and Ruggedness to Perto’s Retail Customers
Empowering businesses to transform and thrive in the connected economy.
Understanding the IoT for your Business
Resources to explore endless IoT applications.
Use the IIoT to converge your IT with OT in ways that empower you to create value in today’s connected economy.
Subscribe to the Sierra Wireless e-Newsletters
Receive regular updates on our latest innovations, product launches, customer stories, and news of wireless applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) space across all sectors and regions.
Open-Source Technologies Driving IoT Acceleration
Learn how to accelerate your Industrial IoT solution's time to market by nine months.
Strategies for Securing IoT Endpoints
Now there’s a solution for utilities that streamlines and increases communication capacity
Learn How Kii Corporation Yielded 5x ROI
Octave, The All-In-One Edge-to-Cloud Solution
Simplify IoT Deployments with Ready-to-Connect
Find the latest technical information related to Sierra Wireless products and solutions.
Building wireless solutions is in our DNA. We have the technology and the global team to deliver.
Shop online, talk with our experts, or find a distributor or reseller and learn more about our products and services.
by Warren Westrup, Director, Business Development, Utilities
For years, if an organization wanted to deploy a private wireless network at a factory, office building, transit hub, other facility, or over a utility service or other geographic area, its options were limited to Wi-Fi or proprietary network technologies like LoRa or Sigfox.
These legacy private networks were adequate for connecting laptops to the Internet and for other limited Industrial IoT (IIoT) use cases. However, the coverage and security limitations of these networks, their incompatibility with public cellular networks, as well as their high ongoing management costs, made it difficult for organizations to use these networks for many IIoT applications.
Recently, a new type of private network – private cellular networks that use 4G Long Term Evolution (LTE) and 5G technologies – have begun to be deployed by many companies. Because these networks use cellular technologies, and are compatible with public cellular networks, they offer organizations many of the coverage, security, and other capabilities they need for more advanced IIoT applications. In addition, the long-term management costs for these networks are often lower than other wireless technologies.
However, organizations face many questions as they consider whether they should deploy a private LTE or 5G network, including how these private networks work and what are specific advantages they offer over Wi-Fi and other private networks.
This blog will help answer these questions, along with providing information on additional resources organizations can use to learn if a private LTE or 5G network makes sense for their organization.
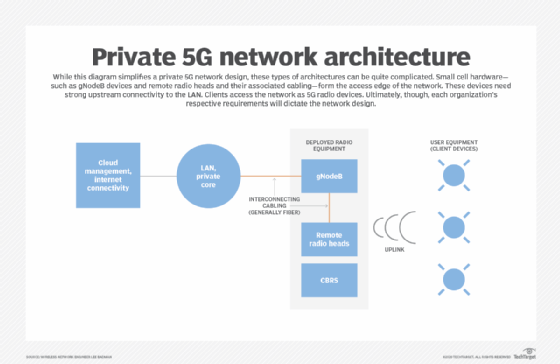
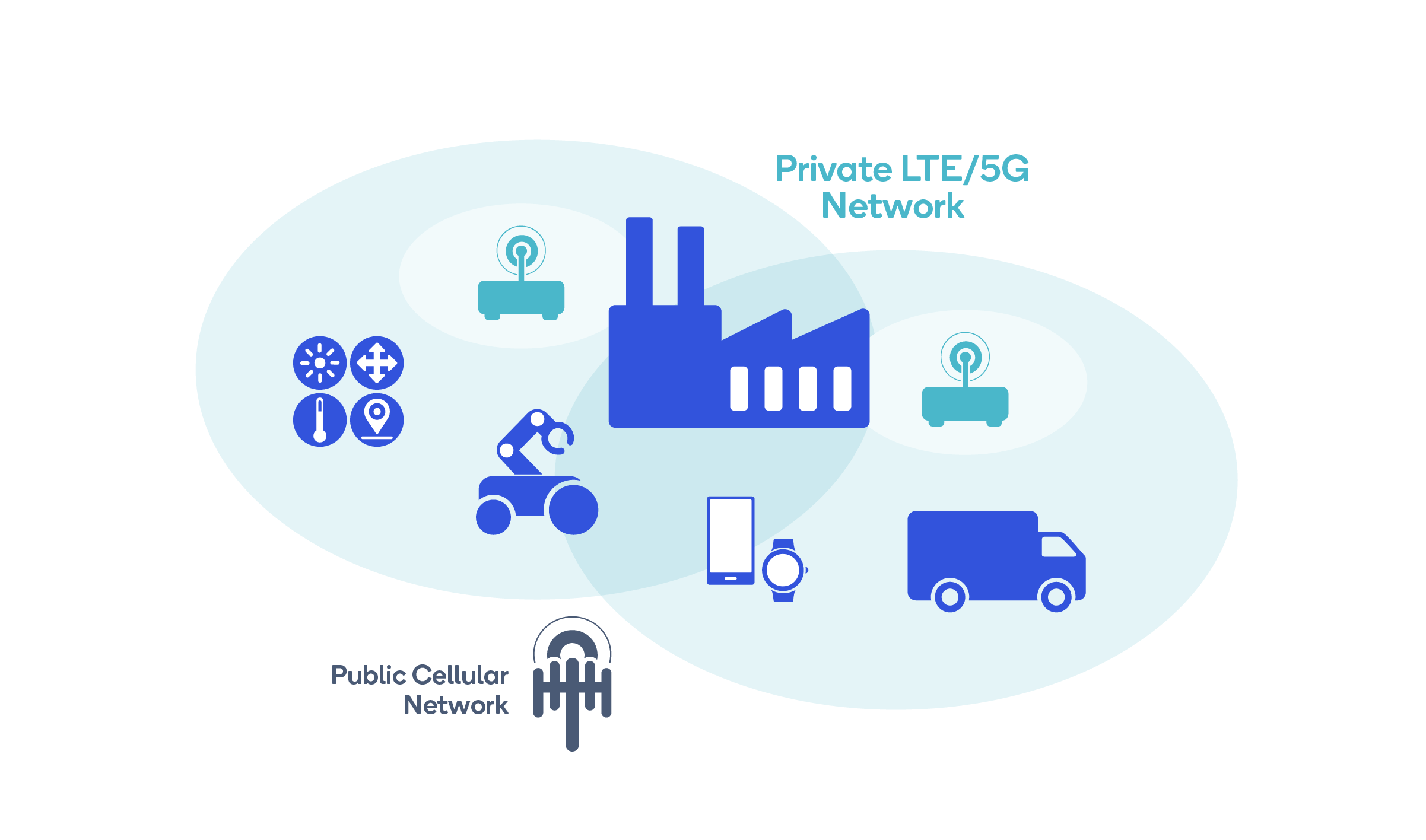
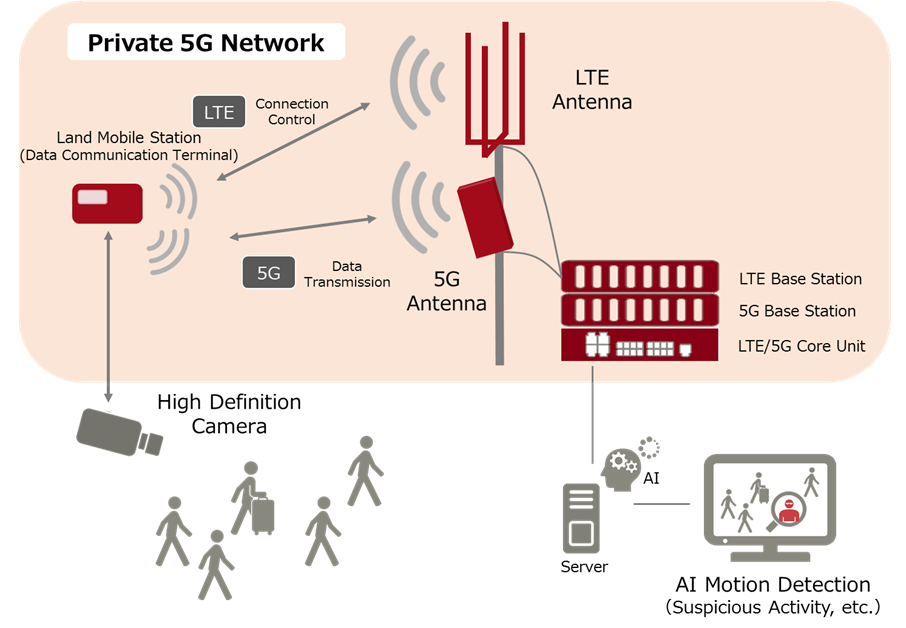
Private LTE and 5G networks (referred to as “non-public networks” by 3GPP, the mobile telecommunications standards organization) are networks that use licensed, shared, or unlicensed wireless spectrum and LTE or 5G cellular networking base stations, small cells, and other Radio Access Network (RAN) infrastructure to transmit voice and data to edge devices, including smart phones, embedded modules, routers, and gateways.
LTE is a 4G cellular networking technology that offers secure, reliable, and fast connectivity. It is the same technology that you use today when you use your smart phone to call friends and family, check your email, play games, or watch videos.
5G is a new cellular network technology. 5G offers many performance advantages over LTE, including faster data transmission, lower latency, and the ability to connect to more edge devices. To learn more about 5G, and how some of the performance advantages it offers will be evolutionary while others will be revolutionary, read our previous blog, A Closer Look at the Five Waves of 5G.
Technically, private LTE and 5G networks work the same as public LTE and 5G networks operated by Verizon, AT&T, Vodafone, and other Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). Edge devices use wireless spectrum to transmit data to nearby cellular base stations, access points and other network infrastructure. The infrastructure then carries this data to the enterprise’s internal network over a secured wired connection. Using this secured connection, data from the edge devices can be sent to various cloud services and applications. To transmit data back to the edge devices, the same process happens in reverse.
The difference between public and private LTE and 5G networks resides in who has a license or priority access to the wireless spectrum, and who owns and operates the network’s base stations and infrastructure.
With public LTE and 5G networks, the MNO owns and operates the spectrum and the network infrastructure. In addition, generally all of the MNO’s customers (outside of first responders or similar public safety organizations) have the same access rights to the network.
With private LTE and 5G networks, private organizations own, operate, or have some level of priority access to the network’s infrastructure or spectrum. The amount of network infrastructure and spectrum owned and operated can vary greatly.
With Full Private LTE and 5G networks (which we will focus on in this blog) the organization owns the wireless spectrum it uses for the network, as well as the network base stations and other infrastructure. This provides it with full control over the network and allows it to completely isolate its users from other MNO public networks.
However, there are other types of private networks. With Private Shared and Hybrid Private LTE and 5G networks, parts of the network are either owned, shared, or operated by the MNO or another organization.
Pretty much any organization can set up and operate their own private LTE or 5G network if they want to, just as anyone can set up and operate their own Wi-Fi network. They just need spectrum, network infrastructure equipment, and edge devices that can connect to this equipment.
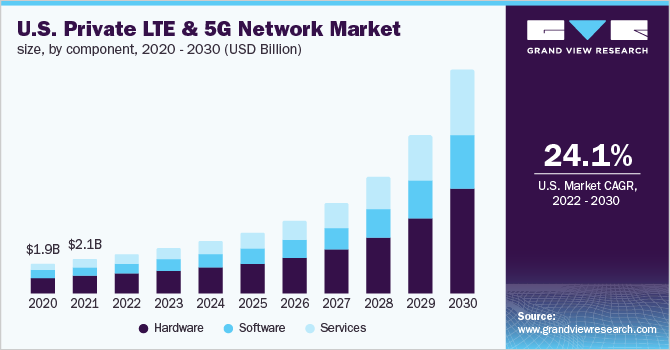
Full Private LTE and 5G networks require a higher initial capital investment than Wi-Fi and other networks. This is why organizations that are deploying or are considering deploying private LTE or 5G networks are generally organizations that need to provide connectivity to a large number of users and devices, or need to cover a large geographic area for IIoT applications.
MNOs: Many MNOs are considering deploying private networks to supplement their existing wireless services in areas where there is high demand, or they have limited licensed spectrum. For example, with private LTE networks, they can provide additional service to customers outside of the licensed LTE spectrum they already have. In addition, some MNOs set up and manage private LTE or 5G networks on behalf of organizations that want a private cellular network, but don’t want to own or operate the private cellular network infrastructure themselves.
Neutral Hosts: Similar to MNOs, neutral hosts are private LTE and 5G networks that supplement existing public wireless networks in a particular location. For example, a neutral host might set up a private cellular network in an airport, office building, stadium, or hotel. The neutral host network can provide faster and better connectivity to the travelers, office workers, sports fans, or hotel guests at the location. The facility owner will pay the neutral host network provider for improved connectivity in their facility. MNOs may also compensate the neutral host provider for offering connectivity to their public LTE or 5G networks in facilities where the MNO’s own coverage is limited.
Private Enterprises: Practically any type of organization – manufacturing company, mining company, university, transportation agency, utility, etc. – can install and operate a private LTE or 5G network to provide connectivity to their factory, mine, campus, airport, or utility service area. To do this, the organization needs:
Organizations around the world have deployed or are in the process of deploying private LTE and private 5G networks.
Though private LTE and 5G networks use the same cellular technology as MNOs for their public LTE and 5G networks, you can’t just turn on your LTE or 5G smartphone, embedded module, router, or other edge device and expect it to connect to a private cellular network.
First, your device needs to be able to operate on the wireless spectrum utilized by the private network. Second, it will need a unique Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card that identifies it and allows it to securely communicate over the private cellular network. If the private network is operated by an MNO, or by a neutral host or other organization with an operating agreement with the MNO, the device typically can use the MNO’s SIM to connect to the network (there might be charges from the MNO).
Organizations with Full Private LTE or 5G networks that do not connect their private LTE network to an MNO will need a unique SIM card that connects to their own private LTE network. SIM cards are inexpensive and easy to obtain from network equipment providers.
In addition, Smart SIM cards are available that enable devices to connect to a private cellular network when they are in private network coverage, and then switch to public cellular networks when they can no longer connect to their private network.
In the United States the Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) is a band of wireless spectrum that has been made available by the FCC for private LTE networks. Edge devices -- including smartphones, embedded modules, routers -- that have been certified to use the CBRS band by the FCC can connect to these private CBRS LTE networks.
More and more edge devices are becoming available that have been certified for use with private wireless spectrum. For example, Apple’s new iPhones supports CBRS, and Sierra Wireless’s AirPrime EM7511 module along with several gateways have been certified for CBRS.
As mentioned above, a private LTE CBRS network is a private LTE network using CBRS wireless spectrum. Though the FCC auctioned some CBRS licenses, called Priority Access Licenses (PALs), companies can still use General Authorized Access (GAA) CBRS spectrum without obtaining a license, sharing this spectrum with PAL license owners (who have priority access to the spectrum) and other GAA users. This allows both PAL license owners and GAA users to build and operate private LTE networks in the United States using the CBRS 3.5 GHz band of wireless spectrum.
In addition to private LTE CBRS networks, organizations interested in building their own private LTE networks in the U.S. have other spectrum options beyond CBRS. For example, the FCC recently approved rules that will allow a 900 MHz band of spectrum owned by Anterix to be used for private networks.
In addition, many governments in Europe and elsewhere around the world allow companies to purchase wireless spectrum for private LTE or private 5G networks. For example, Germany has allocated spectrum in the 3.4–3.8GHz band for private 5G networks. In France, frequencies in the 2.57-2.62 GHz band have been offered to businesses for private cellular networks.
Organizations around the world can also use unlicensed spectrum in the 5 GHz band for private LTE and 5G networks.
As mentioned above, there are various pros and cons to consider when comparing Wi-Fi vs. private LTE and private 5G networks.
Private LTE and private 5G networks ty
Lesbian Tickling Orgasm
Russian Shemale Porno Pics
Cfg Cs Go 2021 Private
Busty Porno Free
Female Casting Hd
What is a private 5G network?
Private 5G networks | Deloitte Insights
What are Private 5G and LTE Networks? (2021) | Sierra Wirel…
5G private network operations: What you need to know ...
Private 5G Networks - IEEE Innovation at Work
Private Networks in a 5G World - KNect365
Private 5G Networks - Technology, Architecture, and …
Private 5G networks: inside the operator opportunity ...
Private 5G networks to gain momentum in 2021
Private Network 5g





















/factory-internet-c8d09407d7f64f70abbcca4684b9b761.png)