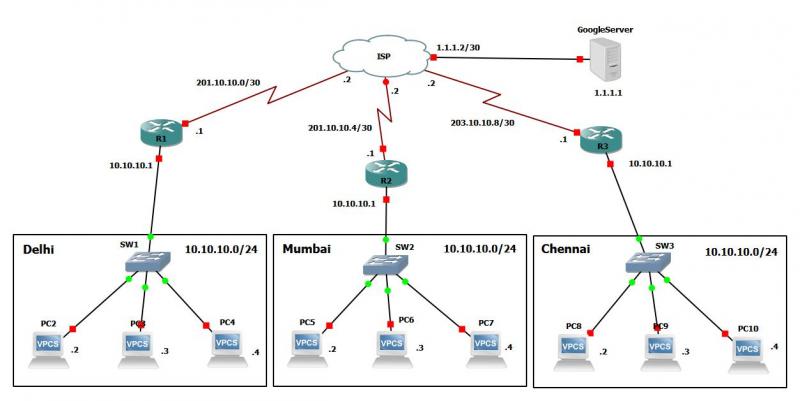
Private Ip Network

🛑 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
РекламаВыберите максимально качественный сервис прокси! 13 параметров в таблице. Сравните!
Все виды оплат · Скорость до 1Гбит/с
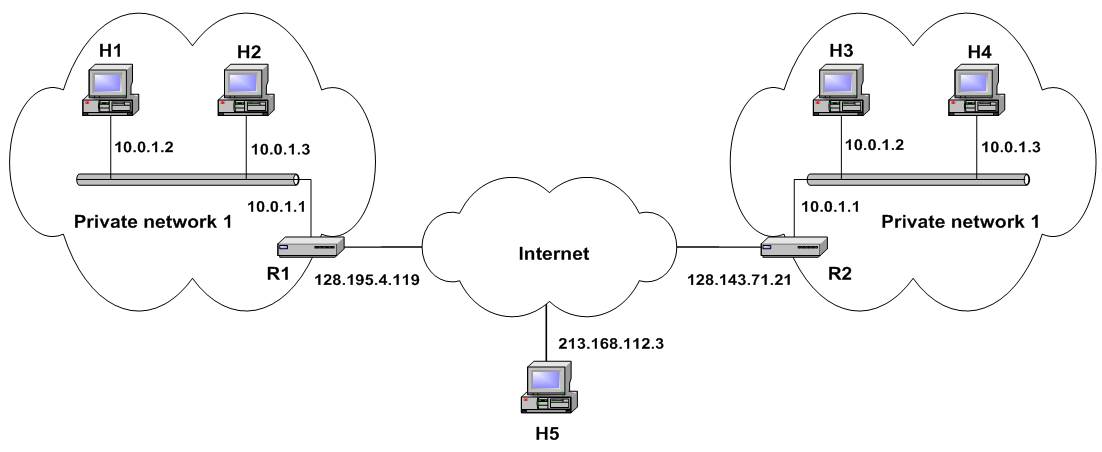
Private network. In IP networking, a private network is a computer network that uses private IP address space. Both the IPv4 and the IPv6 specifications define private IP address ranges. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments.
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network
What kind of IP address is used in a private network?
What kind of IP address is used in a private network?
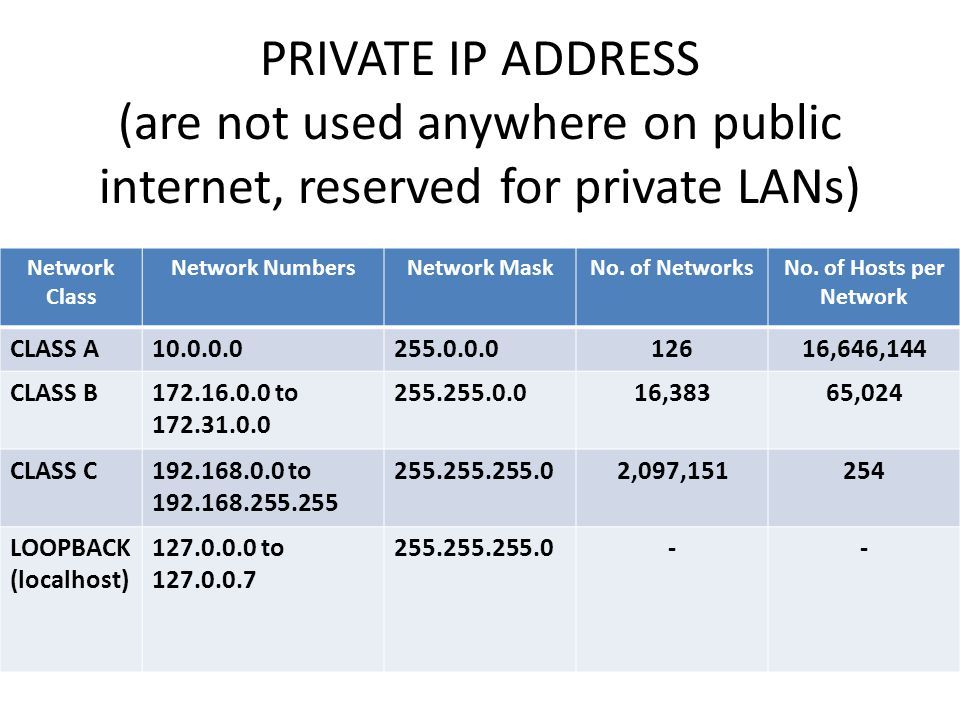
Private IP (Internet protocol) address blocks are the IP addresses most often used for private networks. Most networks use addresses in one of these ranges: Doug Lowe is the bestselling author of Networking For Dummies and Networking All-in-One Desk Reference For Dummies.
www.dummies.com/programming/networkin…
What is the definition of a private network?
What is the definition of a private network?
Private network. In the Internet addressing architecture, a private network is a network that uses private IP address space. Both, the IPv4 and the IPv6 specifications define private IP address ranges. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments.
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network
Is there a private network in IPv6?
Is there a private network in IPv6?
The concept of private networks has been extended in the next generation of the Internet Protocol, IPv6, and special address blocks are reserved. The address block fc00:: / 7 is reserved by IANA for Unique Local Addresses (ULA).
en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network
Can a PC connect to the Internet from a private IP address?
Can a PC connect to the Internet from a private IP address?
A PC in a private IP range can't be acccesed from the public internet. Devices in private range connecting to internet use a proxy or router/NAT device that replaces the local source IP for a single public IP address that redides in your router/NAT.
networkengineering.stackexchange.com/qu…
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network
In Internet networking, a private network is a computer network that uses private IP address space. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments. Both the IPv4 and the IPv6 specifications define private IP address ranges.
Private network addresses are not allocated to any specific organization. Anyone may use thes…
In Internet networking, a private network is a computer network that uses private IP address space. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments. Both the IPv4 and the IPv6 specifications define private IP address ranges.
Private network addresses are not allocated to any specific organization. Anyone may use these addresses without approval from regional or local Internet registries. Private IP address spaces were originally defined to assist in delaying IPv4 address exhaustion. IP packets originating from or addressed to a private IP address cannot be routed through the public Internet.
Dedicated space for carrier-grade NAT deployment
Private use of other reserved addresses
https://www.verizon.com/business/en-gb/products/networks/connectivity/private-ip
Private IP is a VPN service based on MultiProtocol Label Switching (MPLS) that provides a simple network designed to grow with your business and help you consolidate your applications into a single network infrastructure. How does it help you? More flexible internal networks …
Частный IP-адрес (англ. private IP address), также называемый внутренним, внутрисетевым или локальным — IP …
Текст из Википедии, лицензия CC-BY-SA
https://www.dummies.com/programming/networking/private-ip-address-ranges-for-networks
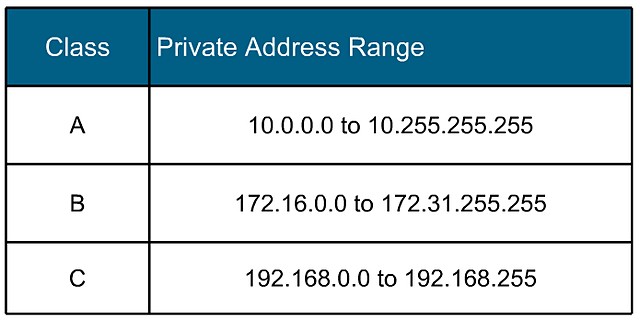
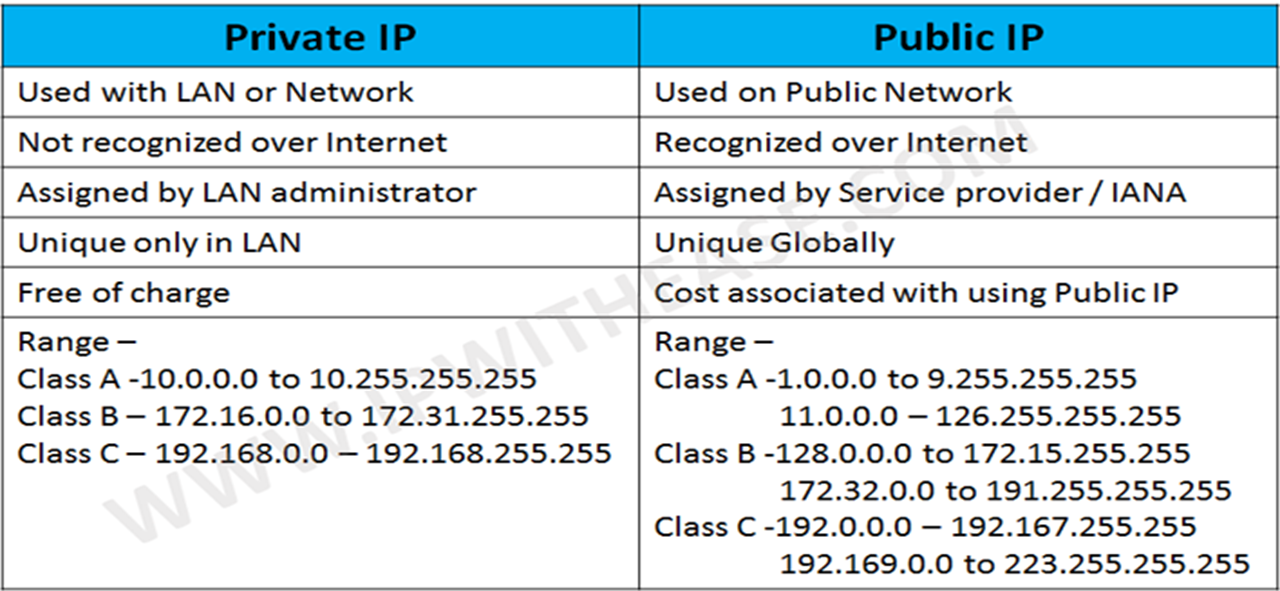
Private IP (Internet protocol) address blocks are the IP addresses most often used for private networks. Most networks use addresses in one of these ranges: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255. …
https://ccnatutorials.in/network-fundamentals-ccna-200-301/private-ip-address-in...
03.04.2020 · In this section we discuss on necessity and importance of private IP address in computer networking. IP address is the identity of any device in a network. Without IP address …
Private versus Public IP Addresses (archived)
Private vs Public IP Address (Version 4)
Find the Private IP Addresses Question
Private IP Addresses (RFC 1918) Tutorial
https://www.wikihow.com/Set-up-a-Private-Network
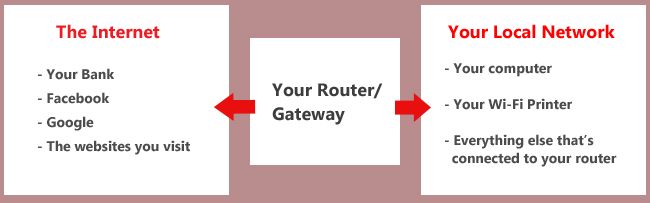
11.10.2020 · A private network is one which either does not connect to the internet, or is connected indirectly using NAT (Network Address Translation) so its addresses do not appear on the public network. However, a private network allows you to connect to other computers that are on the same physical network. This allows a set of computers to share files and printers, while limiting internet connectivity. This wikiHow teaches you how to set up a private network.
https://www.linguee.com/english-russian/translation/private+ip+network.html
Many translated example sentences containing "private ip network" – Russian-English dictionary and search engine for Russian translations.
https://community.spiceworks.com/topic/2279429-connect-to-a-private-ip-from-internet
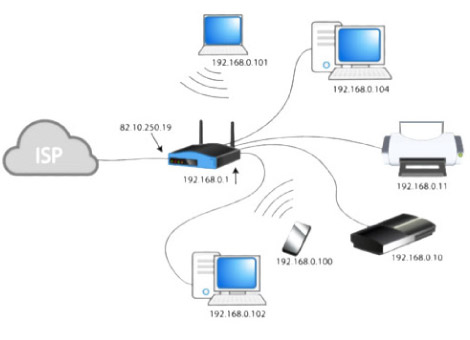
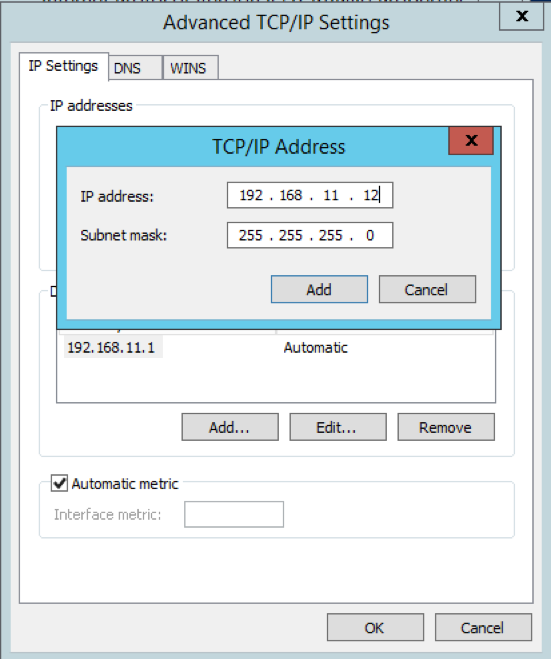
06.07.2020 · The 192.168.0 network as well the 10. networks are all private networks, not including any public IP address. Only the 203.... IP address is a public one of your provider.
https://networkengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/42957
Your PC has the private IP address 192.168.2.3 and is connected to an internet router that has the public IP 54.239.25.200. Now, if you open the port 80 in the router then anyone in the public …
РекламаНедорого! Подписка электронно Trimble SketchUp Pro Network Private server 1 year
РекламаСервис продаж ОСАГО для агентов — Работа с ТОП-16 СК — Подключись за 10 мин.!
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
In Internet networking, a private network is a computer network that uses a private address space of IP addresses. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments. Both the IPv4 and the IPv6 specifications define private IP address ranges.[1][2]
Private network addresses are not allocated to any specific organization. Anyone may use these addresses without approval from regional or local Internet registries. Private IP address spaces were originally defined to assist in delaying IPv4 address exhaustion. IP packets originating from or addressed to a private IP address cannot be routed through the public Internet.
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) has directed the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to reserve the following IPv4 address ranges for private networks:[1](p4)
In practice, it is common to subdivide these ranges into smaller subnets.
In April 2012, IANA allocated the block 100.64.0.0/10 (100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255, netmask 255.192.0.0) for use in carrier-grade NAT scenarios.[4]
This address block should not be used on private networks or on the public Internet. The size of the address block (222, approximately 4 million addresses) was selected to be large enough to uniquely number all customer access devices for all of a single operator's points of presence in a large metropolitan area such as Tokyo.[4]
The concept of private networks has been extended in the next generation of the Internet Protocol, IPv6, and special address blocks are reserved.
The address block fc00::/7 is reserved by IANA for Unique Local Addresses (ULA).[2] They are unicast addresses, but contain a 40-bit random number in the routing prefix to prevent collisions when two private networks are interconnected. Despite being inherently local in usage, the IPv6 address scope of unique local addresses is global.
The first block defined is fd00::/8, designed for /48 routing blocks, in which users can create multiple subnets, as needed.
fdxx:xxxx:xxxx:yyyy:zzzz:zzzz:zzzz:zzzz
A former standard proposed the use of site-local addresses in the fec0::/10 block, but because of scalability concerns and poor definition of what constitutes a site, its use has been deprecated since September 2004.[5]
Another type of private networking uses the link-local address range. The validity of link-local addresses is limited to a single link; e.g. to all computers connected to a switch, or to one wireless network. Hosts on different sides of a network bridge are also on the same link, whereas hosts on different sides of a network router are on different links.
In IPv4, link-local addresses are codified in RFC 6890 and RFC 3927. Their utility is in zero configuration networking when Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services are not available and manual configuration by a network administrator is not desirable. The block 169.254.0.0/16 was allocated for this purpose. If a host on an IEEE 802 (Ethernet) network cannot obtain a network address via DHCP, an address from 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255[Note 2] may be assigned pseudorandomly. The standard prescribes that address collisions must be handled gracefully.
In IPv6, the block fe80::/10 is reserved for IP address autoconfiguration.[6] The implementation of these link-local addresses is mandatory, as various functions of the IPv6 protocol depend on them.[7]
Private addresses are commonly used in residential IPv4 networks. Most Internet service providers (ISPs) allocate only a single publicly routable IPv4 address to each residential customer, but many homes have more than one computer or other Internet connected device, such as smartphones. In this situation, a network address translator (NAT/PAT) gateway is usually used to provide Internet connectivity to multiple hosts.
Private addresses are also commonly used in corporate networks, which for security reasons, are not connected directly to the Internet. Often a proxy, SOCKS gateway, or similar devices are used to provide restricted Internet access to network-internal users.
In both cases, private addresses are often seen as enhancing network security for the internal network, since use of private addresses internally makes it difficult for an Internet (external) host to initiate a connection to an internal system.
It is common for packets originating in private address spaces to be misrouted onto the Internet. Private networks often do not properly configure DNS services for addresses used internally and attempt reverse DNS lookups for these addresses, causing extra traffic to the Internet root nameservers. The AS112 project attempted to mitigate this load by providing special blackhole anycast nameservers for private address ranges which only return negative result codes (not found) for these queries.
Organizational edge routers are usually configured to drop ingress IP traffic for these networks, which can occur either by misconfiguration, or from malicious traffic using a spoofed source address. Less commonly, ISP edge routers drop such egress traffic from customers, which reduces the impact to the Internet of such misconfigured or malicious hosts on the customer's network.
Since the private IPv4 address space is relatively small, many private IPv4 networks unavoidably use the same address ranges. This can create a problem when merging such networks, as some addresses may be duplicated for multiple devices. In this case, networks or hosts must be renumbered, often a time-consuming task, or a network address translator must be placed between the networks to translate or masquerade one of the address ranges.
IPv6 defines unique local addresses in RFC 4193, providing a very large private address space from which each organization can randomly or pseudo-randomly allocate a 40-bit prefix, each of which allows 65536 organizational subnets. With space for about one trillion (1012) prefixes, it is unlikely that two network prefixes in use by different organizations are the same, provided each of them was selected randomly, as specified in the standard. When two such private IPv6 networks are connected or merged, the risk of an address conflict is therefore virtually absent.
Despite official warnings, historically some organizations have used other parts of the reserved IP addresses for their internal networks.[citation needed]
^ Classful addressing is obsolete and has not been used in the Internet since the implementation of Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), starting in 1993. For example, while 10.0.0.0/8 was a single class A network, it is common for organizations to divide it into smaller /16 or /24 networks. Contrary to a common misconception, a /16 subnet of a class A network is not referred to as a class B network. Likewise, a /24 subnet of a class A or B network is not referred to as a class C network. The class is determined by the first three bits of the prefix.[3]
^ The first and last /24 subranges of the subnet (addresses 169.254.0.0 through 169.254.0.255 and 169.254.255.0 through 169.254.255.255) are reserved for future use by RFC 3927
^ a b Y. Rekhter; B. Moskowitz; D. Karrenberg; G. J. de Groot; E. Lear (February 1996). Address Allocation for Private Internets. Network Working Group IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1918. BCP 5. RFC 1918.
^ a b R. Hinden; B. Haberman (October 2005). Unique Local IPv6 Unicast Addresses. Network Working Group IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4193. RFC 4193.
^ Forouzan, Behrouz (2013). Data Communications and Networking. New York: McGraw Hill. pp. 530–31. ISBN 978-0-07-337622-6.
^ a b J. Weil; V. Kuarsingh; C. Donley; C. Liljenstolpe; M. Azinger (April 2012). Reserved IPv4 Prefix for Shared Address Space. IETF. p. 8. doi:10.17487/RFC6598. ISSN 2070-1721. BCP 153. RFC 6598.
^ C. Huitema; B. Carpenter (September 2004). Deprecating Site Local Addresses. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC3879. RFC 3879.
^ R. Hinden; S. Deering (February 2006). IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture. Network Working Group, IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4291. RFC 4291. Updated by RFC 5952, RFC 6052, RFC 7136, RFC 7346, RFC 7371, RFC 8064.
^ S. Thomson; T. Narten; T. Jinmei (September 2007). IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration. Network Working Group, IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4862. RFC 4862. Updated by RFC 7527.
Content is available under CC BY-SA 3.0 unless otherwise noted.
Video Porn Private Amateur
Private Erotic Films
Www Son And Daughter Xnxx
Adult Video Handjob Standing
Booty Farm 5.2 Mod
Private network - Wikipedia
Private IP Network | Verizon
Private IP Address Ranges for Networks - dummies
Private IP address in computer networking explained - CCNA ...
How to Set up a Private Network: 11 Steps (with Pictures)
private ip network - Russian translation – Linguee
connect to a private ip from internet - Networking ...
Private Ip Network




.jpg)



%3amax_bytes(150000)%3astrip_icc()/ipconfig-private-address-5b7496e246e0fb0050464441.png)






















/192-168-1-0-818388-e4e6538cfb554e209588ab3be9c48e5f.png)












.jpg)