Private Git Repository

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
You've probably heard about the growth of edge computing, but what is edge? And what does it mean- especially for OpenShift admins? By moving workloads to the edge of the network, devices spend less ...
In this three-part blog series, I discuss the challenges that organizations face when managing multicluster OpenShift deployments and examine how they affect security and compliance in large ...
AWS PrivateLink provides private connectivity between VPCs, AWS services, and your on-premises networks, without exposing your traffic to the public internet. AWS PrivateLink makes it easy to connect ...
August 31, 2017 | by
Graham Dumpleton
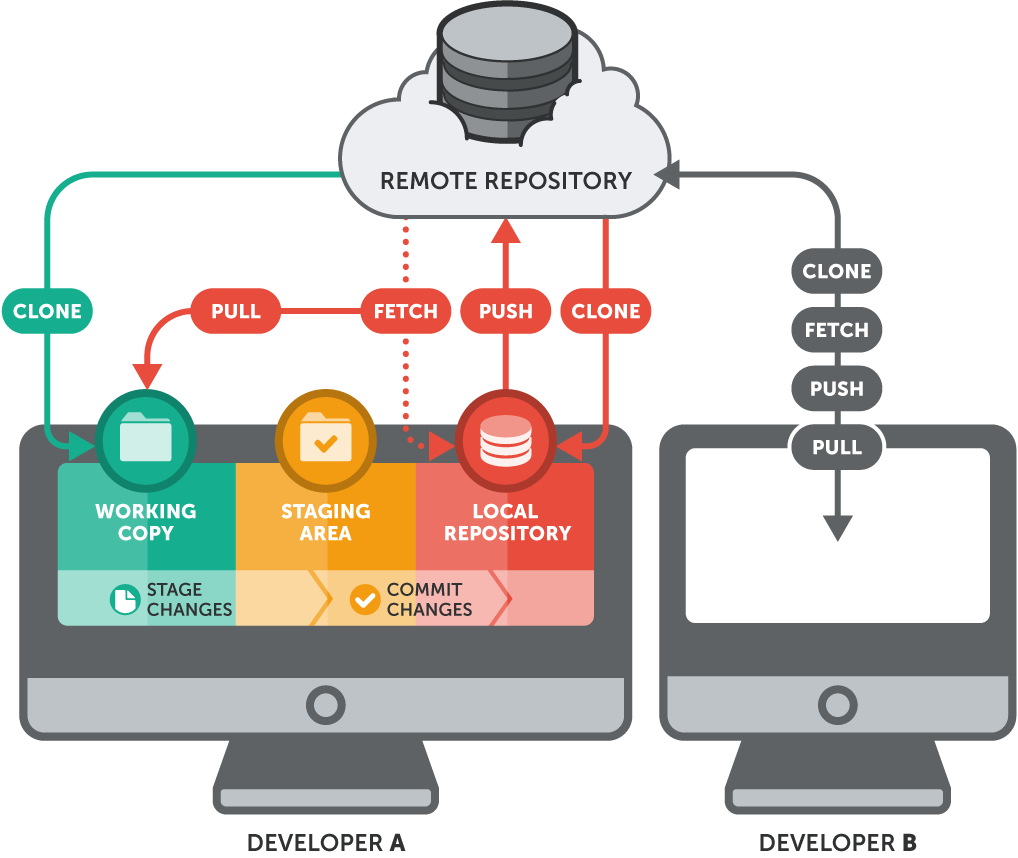
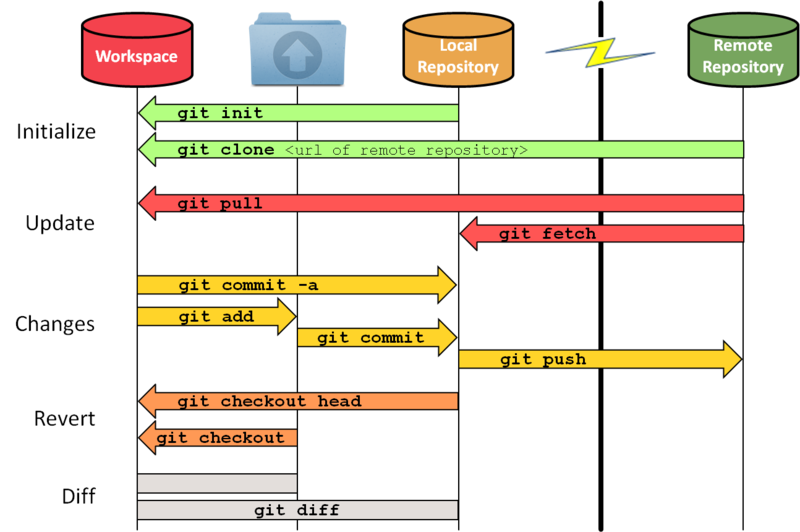
When you deploy applications to OpenShift from source code, you will typically provide the source code by specifying a URL to a repository managed by a Git hosting service such as GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket. When the build process runs to create the image for your application, the first step will be to pull down the source code from that hosted Git repository.
If the hosted Git repository is publicly accessible, there is nothing else to do. If, however, you want to use a private Git repository, you will need to provide to OpenShift access credentials which the build process can use when accessing the Git repository.
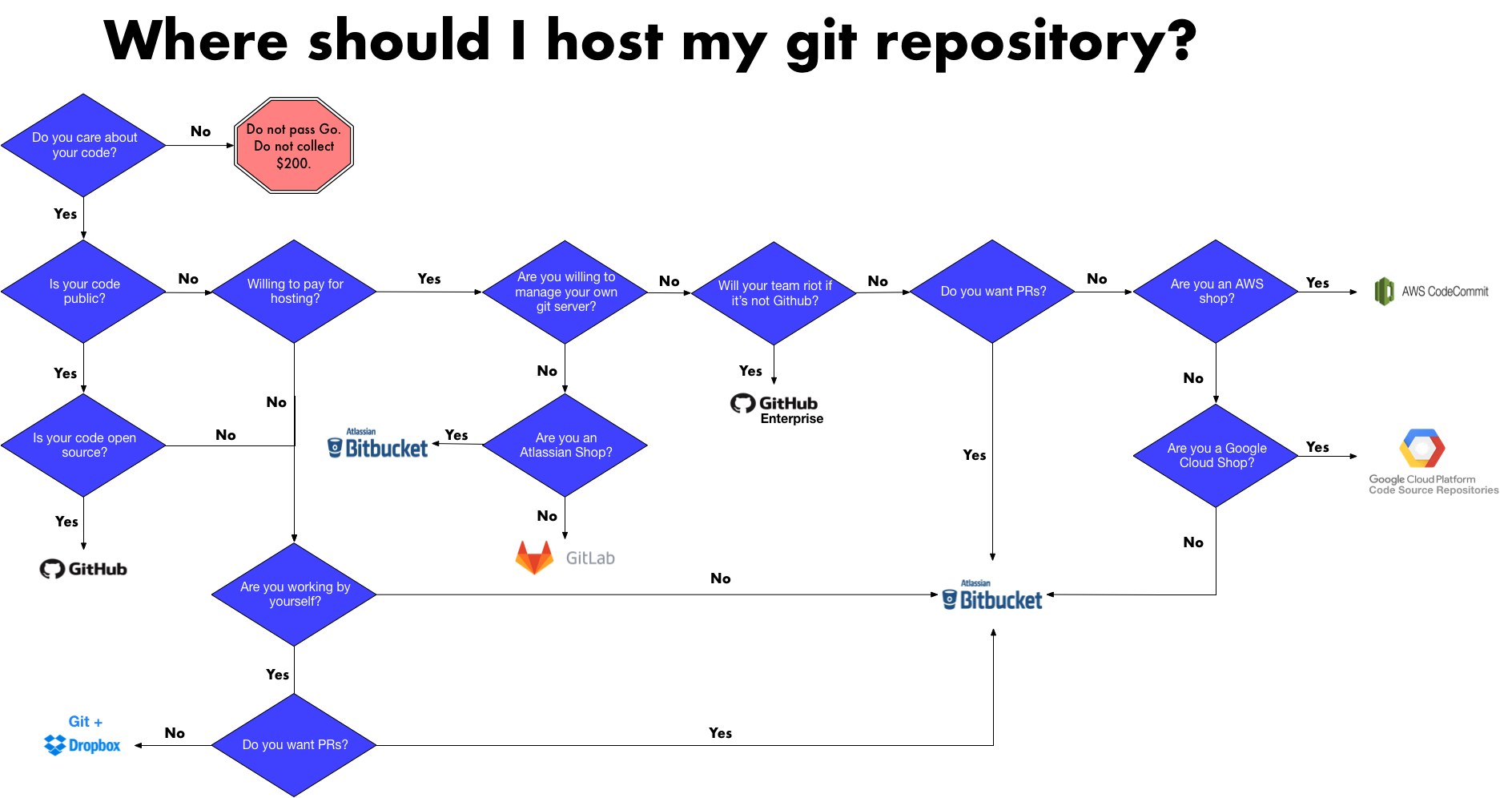
The principles of using private Git repositories with OpenShift have been covered in a number of prior posts:
These looked at key generation and setting up a build configuration to use it, however, beyond these basics there are additional features in OpenShift which make using private Git repositories easier. There are also various best practices you can adopt to ensure you are using the most secure mechanism possible, without risking your most important access credentials.
In this series of posts I will look again at the topic of accessing private Git repositories, but explore new and more recommended ways of using OpenShift, and hosting services such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, to best secure access to your source code.
To access a hosted Git repository, a number of different protocol types are supported.
For more information about communicating with a Git repository using these protocols see the hosted version of the Pro Git book .
When accessing a repository, Git repository hosting services such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket support using both the HTTPS and SSH protocols. The terminology for each can vary, but the credential types offered by these hosting services then fall into the following categories:
When using a private Git repository with OpenShift, you should always aim to use a unique repository SSH key and ensure it has read-only access to the repository. This is because you will need to upload the private key of the key-pair to OpenShift.
When setting up a repository SSH key you should not use your primary identity SSH key. This is because you should never upload its private key to a system you do not control or which can be accessed by others. Using a primary identity key carries additional risk as it is likely used for other purposes, such as gaining secure shell access over SSH to other hosts. If someone were able to get the private key, they could access those other systems.
One saving grace is that OpenShift will not allow you to use a key-pair where the private key has a passphrase. A best practice, which I am sure you are following, is that your primary identity SSH key should always have a passphrase; this will prevent you from inadvisedly using your primary identity SSH key.
So repository SSH keys and accessing a repository over the SSH protocol is the preferred method of accessing a repository. One situation where this will not work though is where the OpenShift instance you are using sits behind a firewall, and that firewall blocks SSH connections to an external Git hosting service.
In this situation, you would have to fallback to using a personal access token over a HTTPS connection. Although the access rights of personal access tokens can be limited to read-only access, they cannot be linked to just a single repository and could be used with any repository accessible to the user account. If you are deploying a personal project to OpenShift, this may be acceptable. However, if this were a project of your company hosted on the hosting service under an organization, you should not rely on using a personal access token of a specific developer. If that developer were to leave you now have the problem that your builds are linked to that developer's account and they could revoke the access token and break the builds. The developer also puts themselves at risk, as the access token could be used to access other private repositories they have which are not related to their work at the company.
If you cannot use the SSH protocol and must use a personal access token with the HTTPS protocol, for a company it would be better to create a separate machine user account on the Git repository hosting service and use it as the owner of the personal access token.
In this post we have covered the different protocols and credential types you can use to access a hosted Git repository, as well as listed some best practices around the credential type used. In the next post in this series, we will look at setting up a repository SSH key, using the GitHub hosting service as an example.
Access the rest of the series here:
OpenShift Container Platform ,
How-tos ,
OpenShift Dedicated ,
OpenShift Online
Contents:
Pull code from a private Git repository
Using multiple private Git repositories
; Add private repository from GitHub
projects[module_private][type] = module
projects[module_private][subdir] = "contrib"
projects[module_private][download][type] = git
projects[module_private][download][branch] = dev
projects[module_private][download][url] = "git@github.com:guguss/module_private.git"
Let’s say you’re building a module ( or theme, library… ) which is stored in a private Git repository that you have access to, and you want to use it on your project. Platform.sh allows you to include code dependencies that are stored in external private Git repositories.
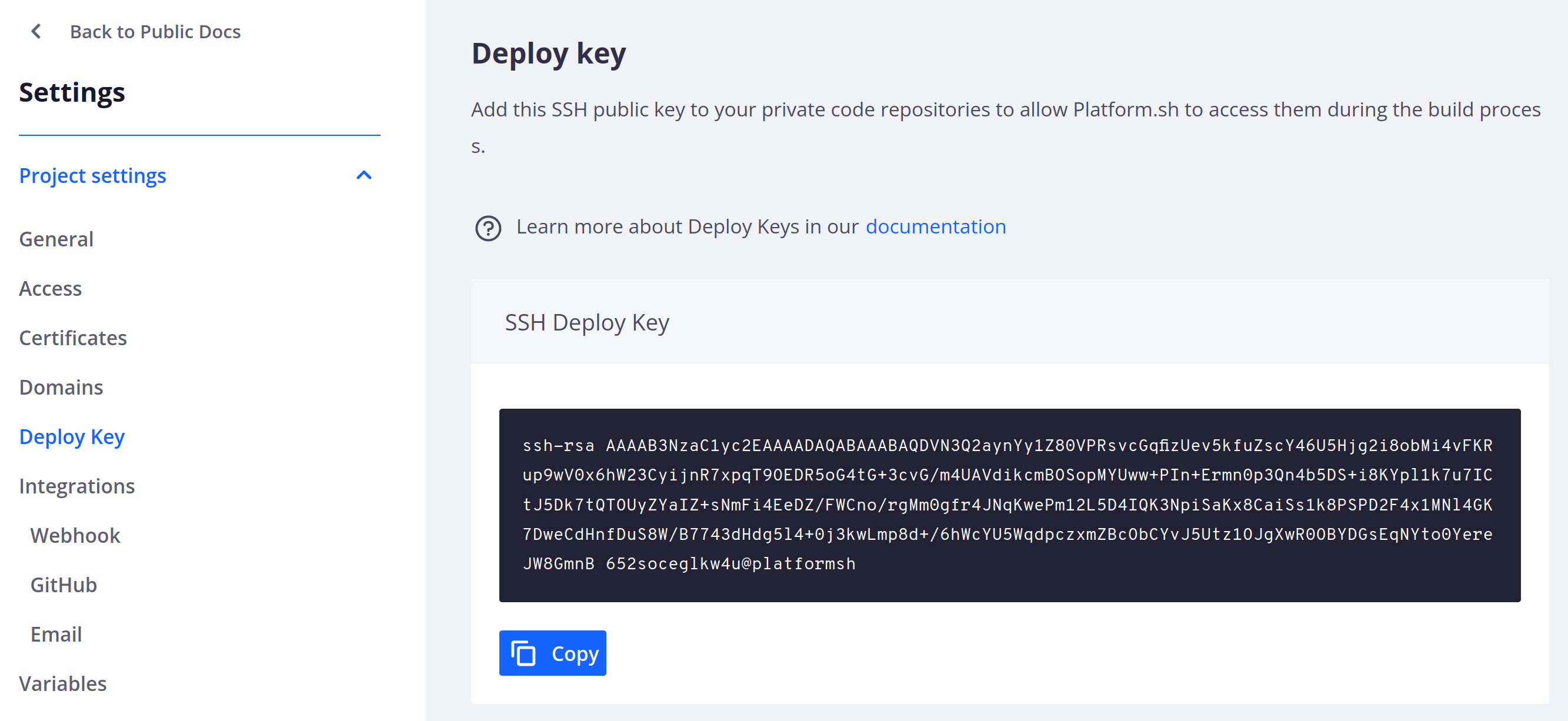
To grant Platform.sh access to your private Git repository, you need to add the project’s public SSH key to the deploy keys of your Git repository.
You can copy your project’s public key by going to the Settings tab on the management console and then clicking the Deploy Key tab on the left hand side.
If your private repository is on GitHub, go to the target repository’s settings page. Go to Deploy Keys and click Add deploy key . Paste the public key and submit. The GitHub default, is for deploy keys to be read only, so you don’t need to worry about the system pushing code to the private repository.
If you’re using Drupal, for example, you can now use your private module by adding it to your make file:
In the make file use the @:.git format, or ssh://@:/.git if using a non-standard port.
More complex projects may have many repositories that they want to include, but GitHub only allows you to associate a deploy key with a single repository.
If your project needs to access multiple repositories, you can choose to attach an SSH key to an automated user account. Since this account won’t be used by a human, it’s called a machine user. You can then add the machine account as collaborator or add the machine user to a team with access to the repositories it needs to manipulate.
More information about this is available on
GitHub .
https://cloud.redhat.com/blog/private-git-repositories-part-1-best-practices
https://docs.platform.sh/development/private-repository.html
Russian Brother Fucks Horny Sister
Valentina Nappi Brazzers Hd
My Mother S Friend Rough Jav Sex
Private Git Repositories: Part 1 - Best Practices
Use a private Git repository · Platform.sh Documentation
Private Git Repositories: Part 4 - Hosting Repositories on ...
How Do I Access A Private GitHub Repository?
How to setup your own private Git repositories with ...
How do I set up a private Git repository on GitHub? Is it ...
Using Private Repositories and Registries :: Tekton Tutorial
Share git repositories · GitFront
How to share a private GitHub repository via link? Is this ...
Private Git Repository