Private Class Public Class

🔞 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Private Class Public Class
Select your preferred language English (US) Español Français 日本語 한국어 Polski Русский 中文 (简体) Change language
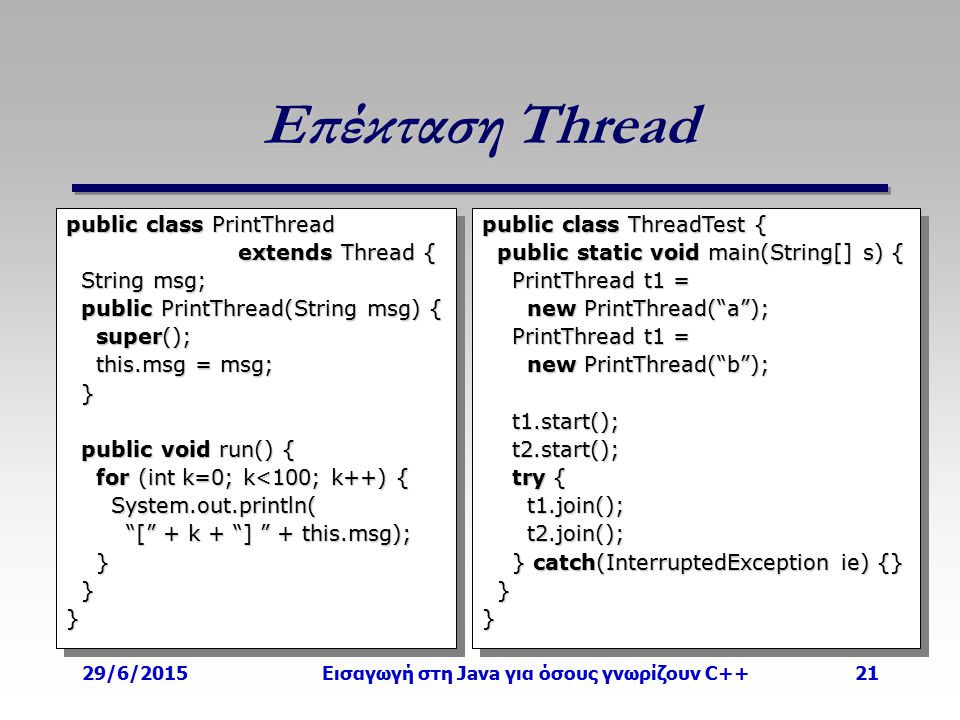
class ClassWithPrivateField {
#privateField
}
class ClassWithPrivateMethod {
#privateMethod ( ) {
return 'hello world'
}
}
class ClassWithPrivateStaticField {
static # PRIVATE_STATIC_FIELD
}
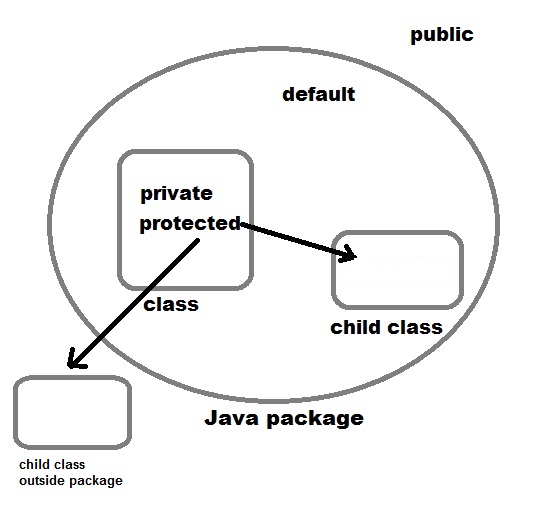
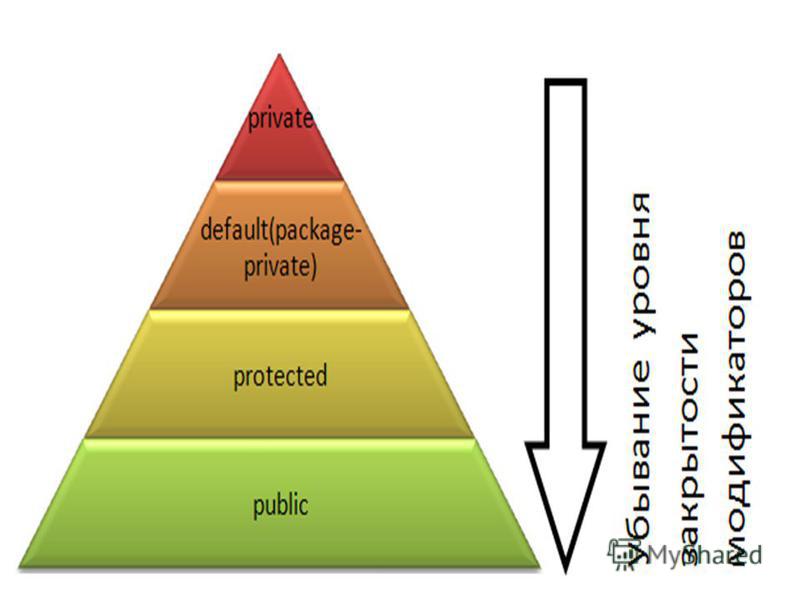
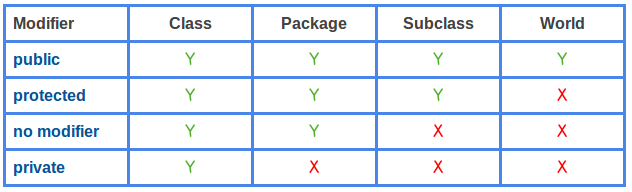
Class properties are public by default and can be examined or modified outside the
class. There is however a
stage 3 proposal to allow defining private class fields using a hash
# prefix.
Private fields are accessible on the class constructor from inside the class
declaration itself.
The limitation of static variables being called by only static methods still holds.
Private static fields are added to the class constructor at class evaluation time.
There is a provenance restriction on private static fields. Only the class which
defines the private static field can access the field.
This can lead to unexpected behavior when using this .
Private instance fields are declared with # names (pronounced
" hash names "), which are identifiers prefixed with # . The
# is a part of the name itself. It is used for declaration and accessing as
well.
The encapsulation is enforced by the language. It is a syntax error to refer to
# names from out of scope.
Like their public equivalent, private static methods are called on the class itself,
not instances of the class. Like private static fields, they are only accessible from
inside the class declaration.
Private static methods may be generator, async, and async generator functions.
This can lead to unexpected behavior when using this . In
the following example this refers to the Derived class (not
the Base class) when we try to call
Derived.publicStaticMethod2() , and thus exhibits the same "provenance
restriction" as mentioned above:
Private instance methods are methods available on class instances whose access is
restricted in the same manner as private instance fields.
Private instance methods may be generator, async, or async generator functions. Private
getters and setters are also possible:
BCD tables only load in the browser
Last modified: Jan 9, 2021 , by MDN contributors
© 2005- 2021 Mozilla and individual contributors. Content is available under these licenses .
c# - Private class with Public method? - Stack Overflow
Private class fields - JavaScript | MDN
Public , Protected and Private Inheritance in C++ Programming
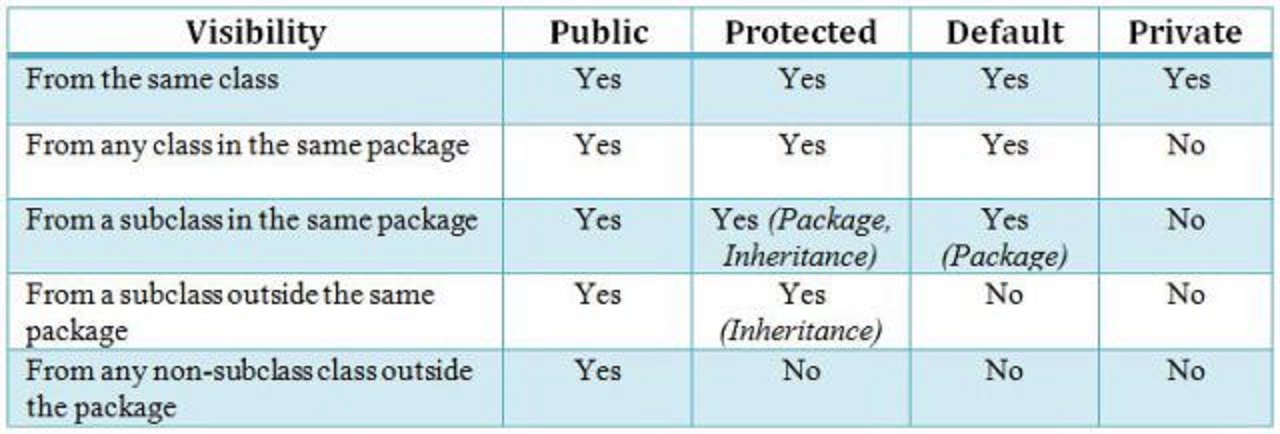
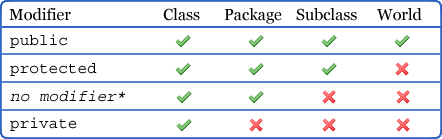
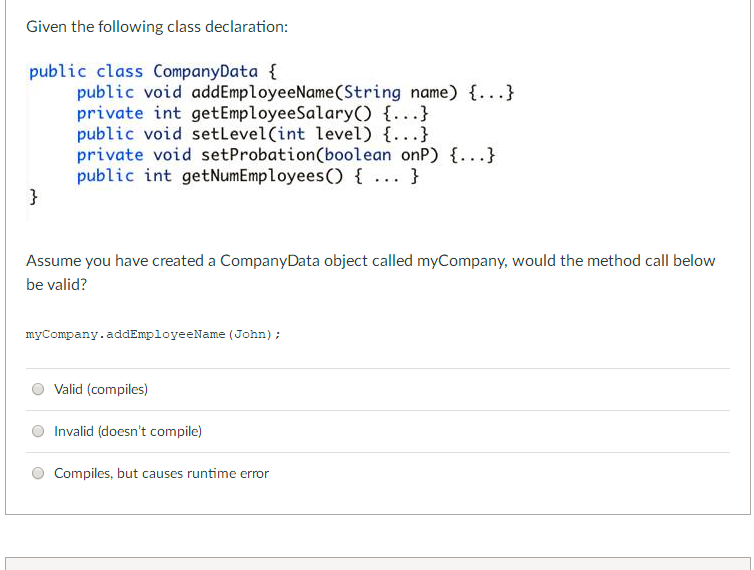
Java. Encapsulation of data in class . Modifiers private , protected, public
PHP: Область видимости - Manual | Пример #1 Объявление свойства класса
Join our newsletter for the latest updates.
Join our newsletter for the latest updates.
Examples
Python Examples
JavaScript Examples
C
Examples
Java Examples
Kotlin Examples
C++ Examples
Company
Change Ad Consent
Do not sell my data
About
Advertising
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
Contact
Blog
Youtube
Apps
Learn Python
Learn C Programming
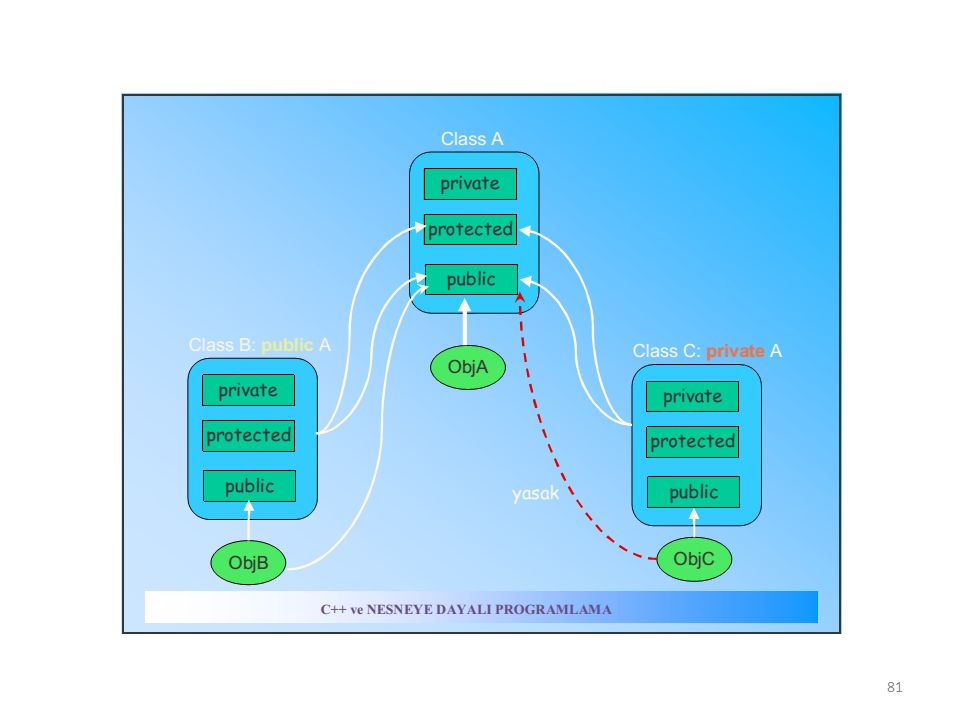
In this tutorial, we will learn to use public, protected and private inheritance in C++ with the help of examples.
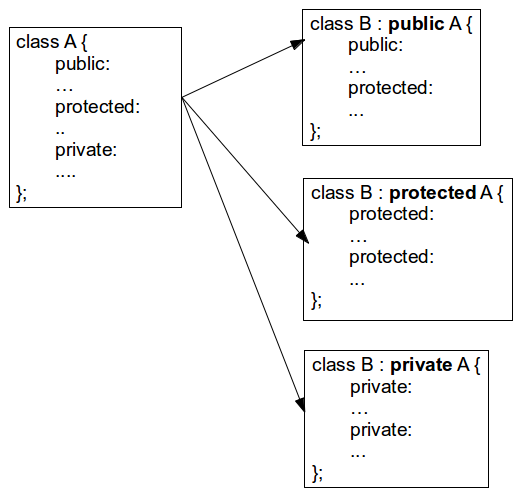
In C++ inheritance , we can derive a child class from the base class in different access modes. For example,
Notice the keyword public in the code
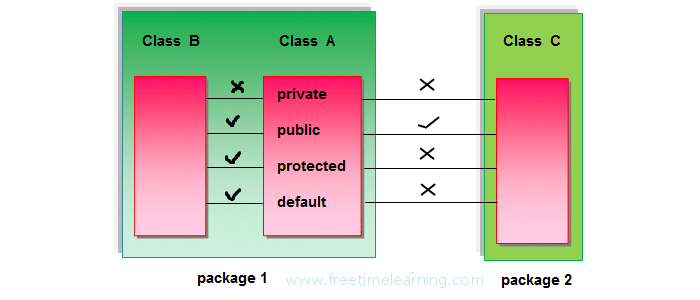
This means that we have created a derived class from the base class in public mode . Alternatively, we can also derive classes in protected or private modes.
These 3 keywords ( public , protected , and private ) are known as access specifiers in C++ inheritance.
public , protected, and private inheritance have the following features:
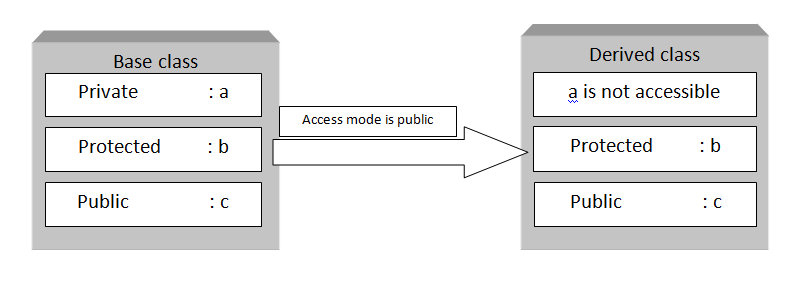
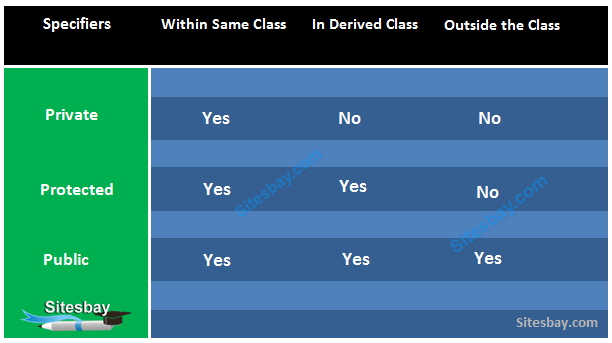
Note: private members of the base class are inaccessible to the derived class.
Here, we have derived PublicDerived from Base in public mode .
Since private and protected members are not accessible, we need to create public functions getPVT() and getProt() to access them:
Here, we have derived ProtectedDerived from Base in protected mode .
As we know, protected members cannot be accessed directly.
As a result, we cannot use getPVT() from ProtectedDerived . That is also why we need to create the getPub() function in ProtectedDerived in order to access the pub variable.
Here, we have derived PrivateDerived from Base in private mode .
As we know, private members cannot be accessed directly.
As a result, we cannot use getPVT() from PrivateDerived . That is also why we need to create the getPub() function in PrivateDerived in order to access the pub variable.
C++ friend Function and friend Classes
© Parewa Labs Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Yes (inherited as protected variables)
Yes (inherited as private variables)
Yes (inherited as private variables)
Young Nudist Tube
Pov Oral Porn
Piercing Pussy Fisting Beach
Naked Silver
Family Nudist Galleries