Pregnant Pain

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Advertisement - Continue Reading Below
Advertisement - Continue Reading Below
Advertisement - Continue Reading Below
The Centers for Disease Control has updated their risk assessment regarding Coronavirus during pregnancy. The CDC previously stated your risk…
The First-Trimester Screening is an early optional non-invasive evaluation that combines a maternal blood screening test with an ultrasound evaluation…
Preeclampsia is a condition that occurs only during pregnancy. Some symptoms may include high blood pressure and protein in the…
Subscribe to our week-by-week Pregnancy Newsletter
What week is your pregnancy in?
Week 1-2
Week 3
Week 4
Week 5
Week 6
Week 7
Week 8
Week 9
Week 10
Week 11
Week 12
Week 13
Week 14
Week 15
Week 16
Week 17
Week 18
Week 19
Week 20
Week 21
Week 22
Week 23
Week 24
Week 25
Week 26
Week 27
Week 28
Week 29
Week 30
Week 31
Week 32
Week 33
Week 34
Week 35
Week 36
Week 37
Week 38
Week 39
Week 40
Donate
Partner With Us
Corporate Sponsors
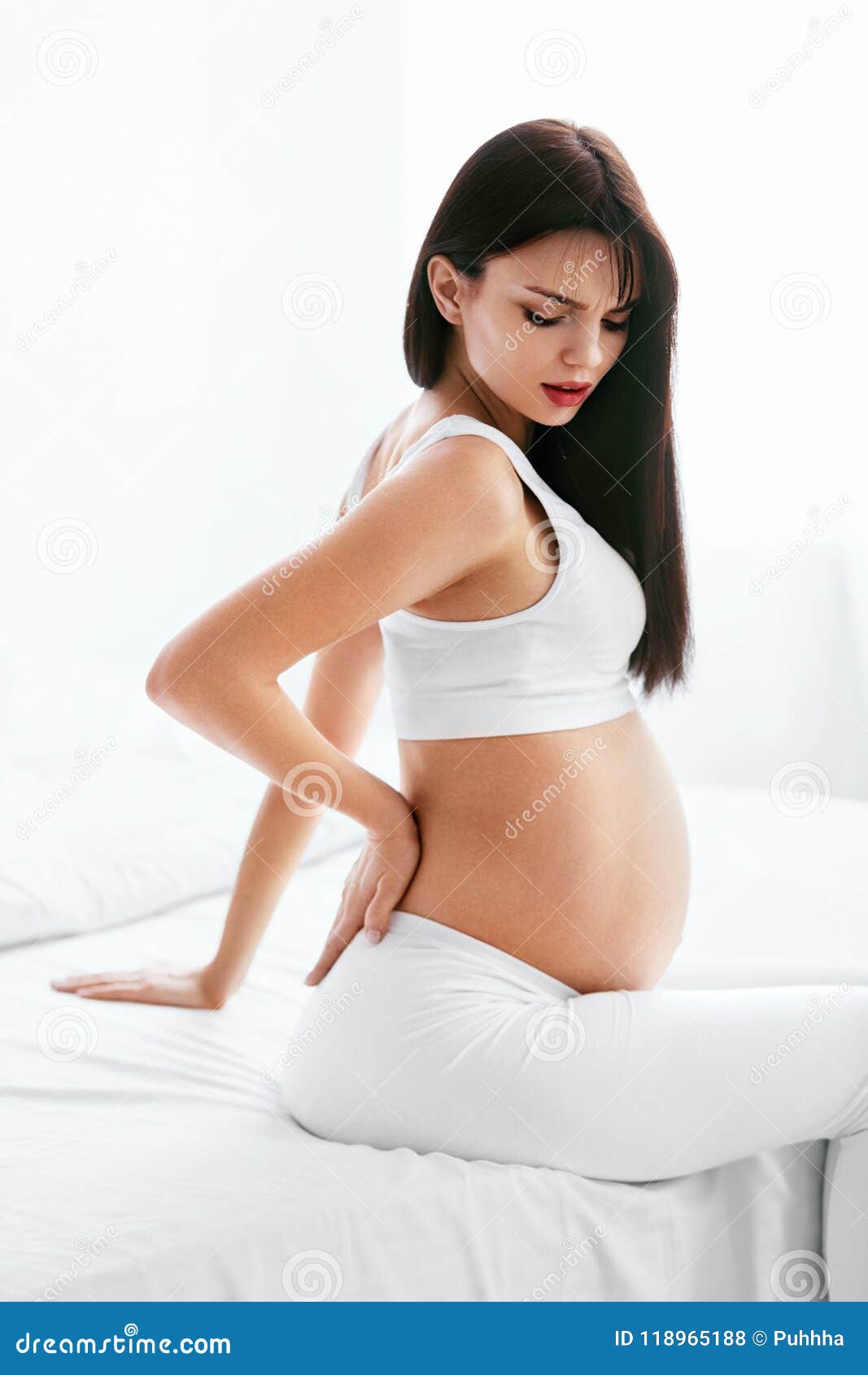
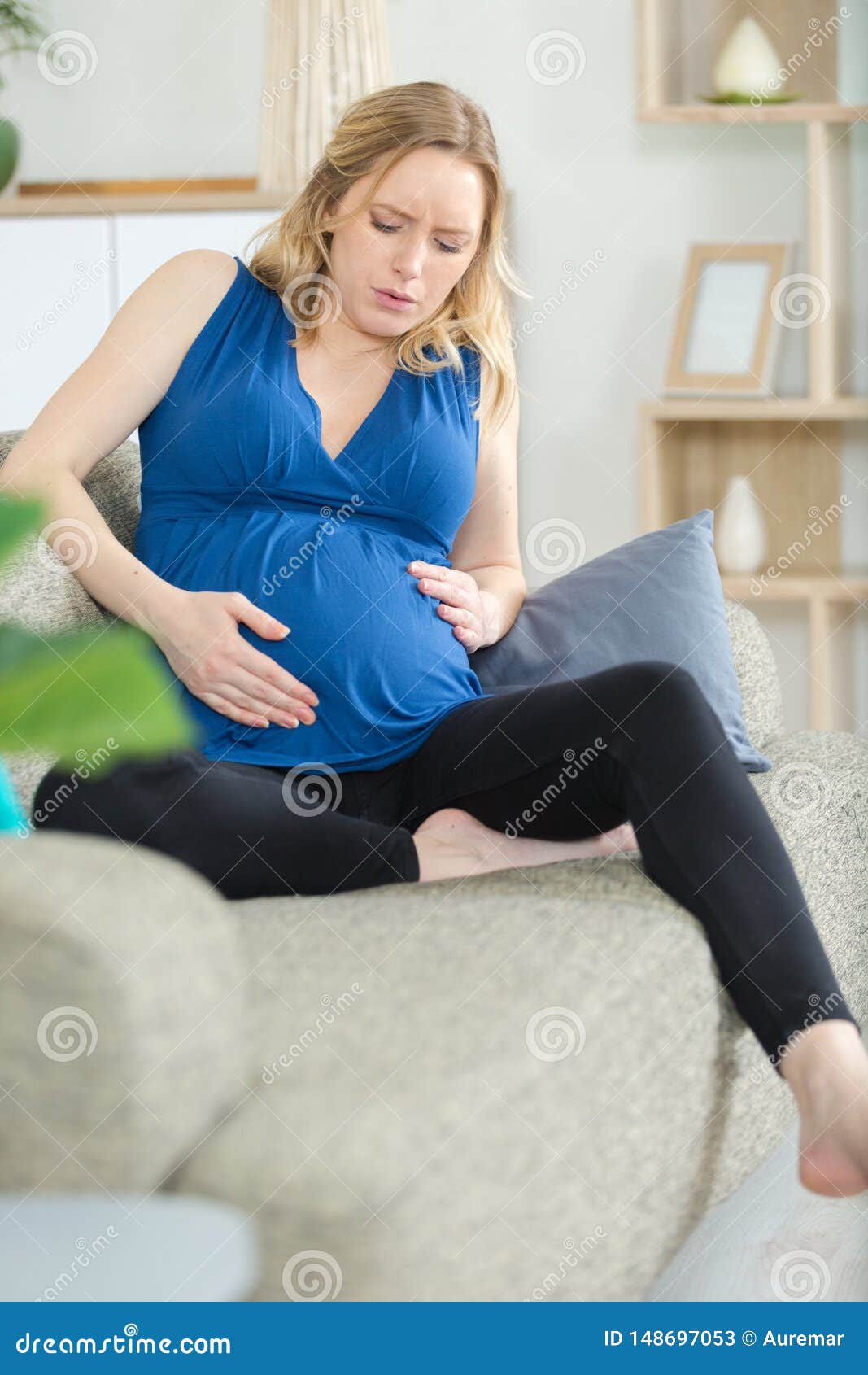
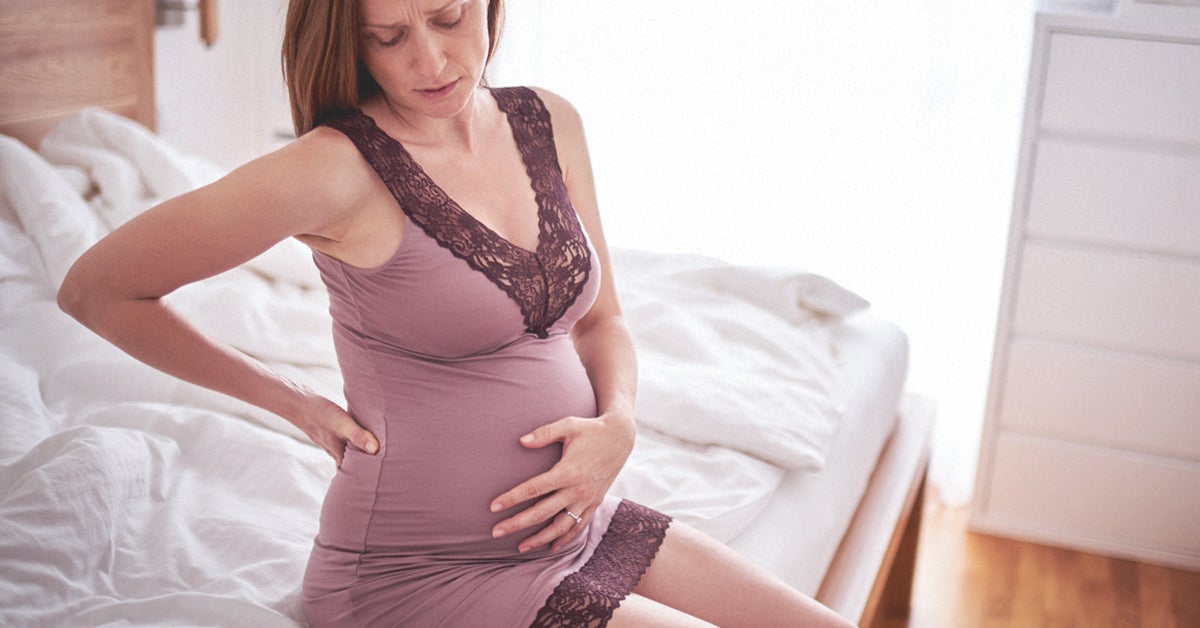
It can be stressful, especially for first-time mothers, to discern between normal pregnancy pains and when there is a possible complication from a sharp pain during pregnancy. During pregnancy, your body will undergo many changes as it adapts to the growing life inside of you. You will gain weight and your body will grow to accommodate your new baby. While this is natural and necessary, it can cause some discomfort.
One of the most common sharp pains that women report is a stabbing pain in and around the uterus, stomach or groin area. While this can be uncomfortable, in many cases it can be explained by normal changes that occur during pregnancy.
Some common causes include:
Although the above conditions are part of normal pregnancy, they typically don’t cause sharp pain. If the sharp pain you are experiencing is localized on one side, it could be indicative of an ectopic pregnancy . This is a serious condition and requires urgent medical attention.
A pending miscarriage can also result in a sharp pain from the cramping. This raises concerns for expecting mothers who want to know the difference between normal cramping associated with the expanding uterus and cramping from a pending miscarriage.
Contacting your healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms is always the right choice.
Despite the fact that sharp pain can be the result of normal pregnancy change, there are some warning signs that you need to watch out for in case the sharp pain is the result of a complication.
If you experience any of the above symptoms contact your healthcare provider immediately.
If you are experiencing sharp or stabbing pain during pregnancy, there are some possible solutions that you can try to alleviate the pain:
Again, if the pain becomes too intense or prevents you from doing day-to-day activities, contact your health care provider immediately. Consult with your doctor for more pregnancy-safe pain management ideas.
Get the Fetal Life App for Apple and Android endorsed by the American Pregnancy Association. It features meal recommendations, kicks counter, blood glucose tracking, and more.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Gibbs, R. (2008). Prenatal Care. In Danforth’s obstetrics and gynecology (10th ed., p. 18). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Harms, R. (2004). Mayo Clinic guide to a healthy pregnancy (1st ed.). New York: HarperResource.
Jordan, R. (2014). Exercise, Recreational and occupational issues, and intimate relationships in pregnancy. In Prenatal and postnatal care: A woman-centered approach (pp. 274-279). Oxford: Wiley Blackwell.
Copyright © 2021 American Pregnancy Association Web Design by Edesen
EM Resident
EMRA Match
Publications
Media Kit
Benefits
Join/Renew EMRA
LOGIN
Benefits
Meet Your Board & Staff
History
Governing Docs
Publications
Advertise with Us
Benefits
Become A Member
AHC Relias Learning EM Reports
Doctors Without Quarters
EBMedicine
EM:RAP
EMedHome
emCareers.org
EMRAfied
Hippo EM
Integrated WealthCare
Laurel Road
New Member Kits
PEER
PEPID
Rosh Review
Visual DX
Fellowships
Career Planning
Financial Planning
Legal
EMRA Match
Administrative Fellowships
Critical Care Fellowships
Education Fellowships
EMS Fellowships
Global EM Fellowships
Health Policy Fellowships
Hyperbaric Fellowships
Pediatric EM Fellowships
Simulation Fellowships
Toxicology Fellowships
Sports Medicine Fellowships
Ultrasound Fellowships
Wilderness Fellowships
Advising Resources
Med Student Council
Medical Student Forum
Emergency Medicine Interest Groups (EMIG)
EMRA Match
Special Populations
EMRA Hangouts
Advising Guide - Match
Apply for Away Rotations
Interviews
Reading Recommendations
Research Resources
Advice for 1st and 2nd Year MS
Effective Consultation In Emergency Medicine
Global EM Student Leadership Program
Tips for Success as a MS3
Patient Presentations
Preparing for a Successful Fourth Year of Med School
Program Director Video Interviews
Fourth Year Schedule
Seek, Develop a Mentor Relationship
Skill Demonstration Videos and Topics Pertaining to EM
Student Advising Task Force Advising Resource List
Student Resident Mentorship Program
Transitions of Care
Awards & Scholarships
Committees
Events & Activities
Be an EMRA Leader
Be an Advocate
Share an Idea
Write for EM Resident
Awards FAQ
All Awards
EMRA 25 Under 45
EMRA 45 Under 45
Winter Awards
Summer Awards
EMRA Award Application Form
Regional Meeting Grant
Tools and Aids
Model of EM Clinical Practice
A - F
G - M
N - O
P - S
T - Z
Search External Content
EM Resident
EMRA Books
EMRA Videos
EMRA*Cast
EMRA Reference Cards
Mobile Applications
Skill Demonstration Videos and Topics Pertaining to EM
Recommended Blogs and Podcasts
Login to maximize your experience!
|
Pain Management
|
Pain in Pregnancy
Rachel E. Bridwell, MD | Brooke Army Medical Center Alex Koyfman, MD | UT Southwestern Medical Center Brit Long, MD, FACEP | San Antonio Uniformed Services Health Education Consortium
Headaches, back pain, and abdominal/pelvic pain are the most common presenting pregnancy-related pain complaints in the emergency setting, and under 15% of pregnant women receive opioid prescriptions for these pregnancy-related complaints at some point during their pregnancy. 3 Given the frequency of these presentations, a concern for opioid-overuse, and the additional concern for fetal safety, it is essential that emergency providers be adept at managing pain in this unique population.
Before considering the more common (benign) causes of pain, it is essential to consider the can't-miss diagnoses that often masquerade during pregnancy. Example include:
Once the life-threatening causes have been thoroughly considered and ruled out, efforts can focus on treating the underlying cause of pain.
Headaches: Headaches are frequent during pregnancy and most notable in the first trimester. Whereas a history of similar headaches may provide reassurance, new-onset headaches during pregnancy (particularly at >20 weeks' gestation) should raise a red flag. Particular attention should be given to headaches unresponsive to analgesia prior to ED arrival. A full assessment of visual acuity, vital signs, and basic labs should be conducted for further assessment. A lumbar puncture may also be warranted.
Back pain: Occurring in half of all pregnancies, low back pain is common and the result of regular physiologic changes of pregnancy, secondary to growth of the gravid uterus and subsequent lumbar lordosis. In combination with the release of increased relaxin, which causes ligamentous laxity, the increased mechanical and gravitational load placed on the paraspinal muscle beds adds to the stress to the lower lumbar spine. 4 Radicular symptoms may be present as the gravid uterus compresses spinal roots. Evaluation is generally elicited through history and examination with symptom relief with heat, mechanical offloading, and massage and avoiding aggravation with axial loading. Careful evaluation should be directed at both evaluations for cauda equina syndrome, as well as sacroiliitis, highlighted by unilateral low lateral spinous pain. 5 While MRI is considered safe during pregnancy, there are currently no studies to evaluate long term effects of ferromagnetic exposure on a fetus, and thus imaging should be conducted with extreme caution. 4
Abdominal/pelvic pain : Abdominal pain is a common symptom during mid to late pregnancy. Fetal growth and round ligament stretching are associated with the sensation of contractions and self-resolving pain. However, moderate to severe pain associated with fever, vital sign abnormalities (tachycardia, hypotension, respiratory distress), syncopal episodes, or vaginal bleeding warrants further consideration of the previousl
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-complications/sharp-pain-pregnancy/
https://www.emra.org/books/pain-management/pain-in-pregnancy/
Being Muslim
Porno Young 18 Old
St Private Tours
Sharp Pregnancy Pain - Causes & Symptoms | American ...
Pain in Pregnancy EMRA
Pregnancy Pains: What's Normal And What's Not
First Trimester Pregnancy Pains: When to Call Your Doctor ...
Vaginal Pain and 7 Other Common Pregnancy Pains | SELF
7 common pregnancy aches and pains | BabyCenter
Pregnancy Vaginal Pain - Causes & Tips for Relief ...
INTENSE PREGNANCY PAIN! - YouTube
Abdominal Pain and Other Pregnancy Pains You Shouldn’t ...
21 Uncomfortable Symptoms of Pregnancy & Their Causes
Pregnant Pain