Pi Hole Vpn

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
If you have a PC problem, we probably cover it!
If you have a PC problem, we probably cover it!
Time-saving software and hardware expertise that helps 200M users yearly. Guiding you with how-to advice, news and tips to upgrade your tech life.
Vlad might have a degree in Animal Husbandry and Livestock Management, but he's currently rocking anything software related, ranging from testing programs to writing in-depth reviews about them. He spent 3-4 years as a... Read more
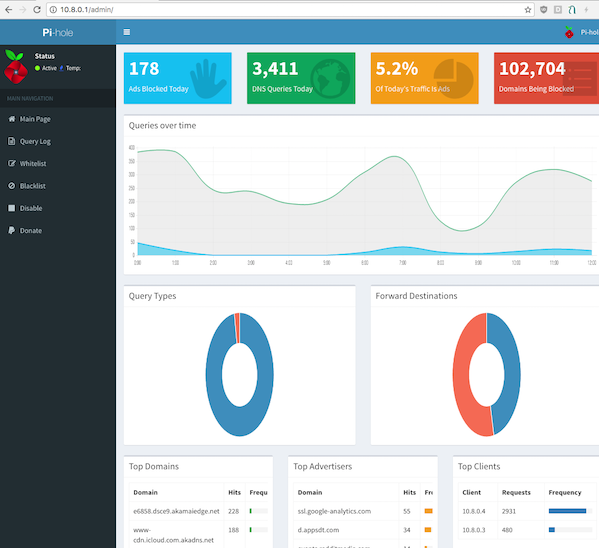
If you own a Raspberry Pi device, turning it into your personal, network-wide ad- and tracker-blocker with Pi-hole is one of the best things you can do with it.
However, if you plan on also appending a VPN to your network, you may run into a brick wall. Our guide will help you configure both services.
Check out our Raspberry Pi section for more guides and news about this awesome device.
Visit our VPN How-To Hub to discover more VPN troubleshooting guides on common issues.
If you recently invested in a Raspberry Pi device, you may probably know that a world of opportunities lies at the end of your fingers.
You can turn your RPi into a huge variety of things, but Pi-hole is arguably one of the most important uses for it.
It’s even possible to put a VPN on top of Pi-hole and use the whole ensemble as a whole. However, the guides you may find when querying various sites regarding this issue may put you off from even considering it.
Luckily, you have us. We’re going to tell you everything about the process.
However, it’s best if you come with just a smidge of previous rPi experience so that you won’t get stuck in the nomenclature (see, that’s a first example of what’s going to happen).
59% Off available for two-year plans
85% Off! Only 1.99$
per month for 15 months plan
83% Off (2.21$/Month)
+ 3 free Months
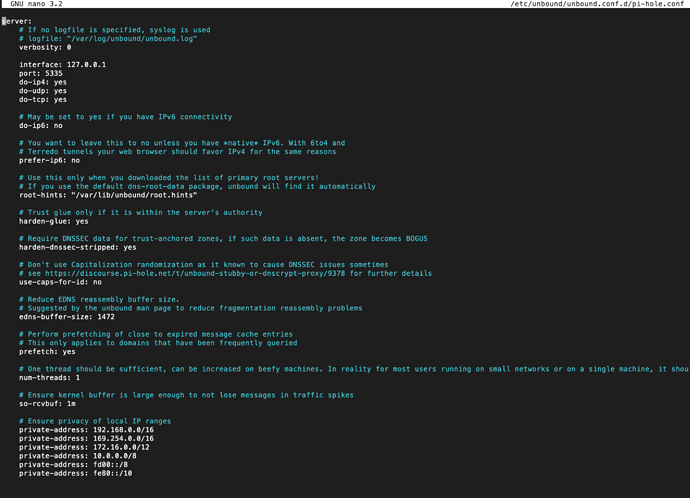
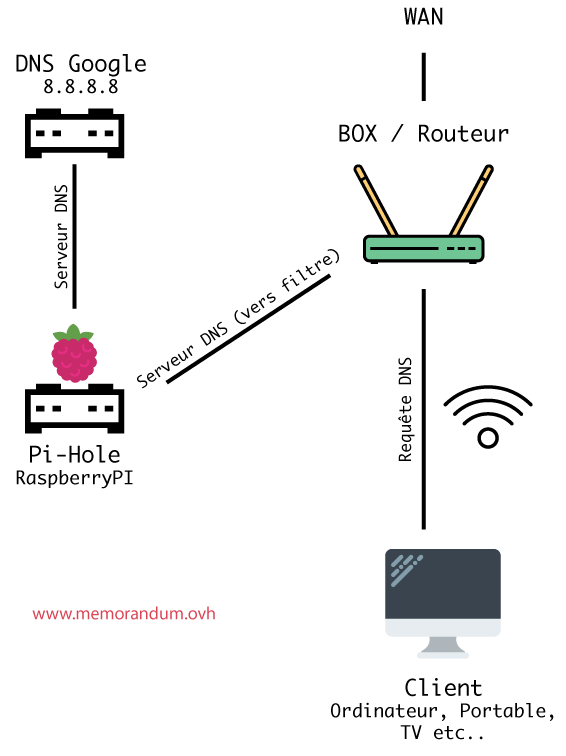
Pi-hole is a Linux-based application that you can install on your Raspberry Pi device. This service can help you block Internet trackers and advertisements on your entire network.
Pi-hole acts as a DNS sinkhole, which basically means that it provides systems looking for DNS info with fake results. Furthermore, this application can also work as a DHCP server, which can be used (preferably) on a private network.
Long story short, if you need a hardware, network-wide ad- and tracker-blocker, Pi-hole is exactly what you’re looking for. As opposed to traditional software ad-blockers, Pi-hole can keep ads from spawning on other devices on your network, such as smartphones or Smart TVs.
Note that it can be installed on other devices other than Raspberry Pi, just as long as they have network capabilities and they run on Linux.
PiVPN is the easiest way to deploy VPN on your Raspberry Pi device. You just have to fire up a terminal and run the following command:
curl -L https://install.pivpn.io | bash
Alternatively, if you access your Raspberry Pi remotely through SSH, you can use the SSH console and type the very same command we used above.
After you run this command, you’ll be greeted by a text-based GUI where additional instructions will be provided to you.
For instance, you have to confirm that turning your rPi into an OpenVPN server is what you want to do.
The instructions are pretty much straightforward if you have a bit of previous experience with rPi and OpenVPN. If not, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered.
Note: selecting a network interface can be done with the Spacebar button. If you hit the Enter key on your keyboard, the default selection will be loaded and you’ll be taken to the next screen.
If you plan on using a commercial-grade VPN such as Private Internet Access, it would be best to install it on your router. That way, your entire network traffic will be routed through PIA and remain private.
However, you should know that not many routers accept external VPN services.
Need a VPN for your router? Check out Private Internet Access.
In this case, you may either have to purchase a more expensive router that accepts outgoing VPN traffic natively or try to install custom firmware on your router, such as Tomato, Open WRT, or DD-WRT.
Note that each router model/brand has its own configuration, so there’s no universal way to deploy VPNs that works on any router. Check out our complete guide on setting up VPN on Netgear routers and try to adapt our recommendations to your gear.
If you don’t have the option to install PIA on your home router, you’ll have to turn your Pi-hole into a VPN gateway. This way, all traffic on your network will pass through your Pi-hole device and the VPN.
However, note that this method has some shortcomings, including bandwidth throttling or even packet loss, as it depends entirely on the performance of your Pi-hole host device.
If none of these steps look appealing to you, there’s one more thing you can do. If you plan on using a VPN on your computer and want to also benefit from Pi-hole’s DNS sinkhole capabilities, you’ll have to disable the DNS leak protection feature on your VPN.
The reason why the two (VPN‘s DNS leak protection and Pi-hole) can’t work together is quite obvious and easy to understand.
While your VPN‘s DNS leak protection is active, your device can’t use other DNS addresses other than the ones your VPN provides you with.
This means that Pi-hole can no longer block sites/domains effectively, which would expose you to tracking and advertisements once more.
We don’t recommend you to use this method, since it would make your DNS requests visible. And that completely defeats the purpose of using an anonymization tool such as a VPN.
Whether you want to configure a VPN server on your Pi-hole host and connect to it remotely or using Pi-hole side-to-side with your favorite consumer VPN, there are ways to do it.
However, you shouldn’t rush into it if you don’t fully understand the implications of your actions. Some of the methods we’ve explained in this article can have quite an impact on your privacy if implemented haphazardly.
This article covers:Topics:
raspberry pi
VPN
Save information for future comments
I agree with the Privacy Policy regarding my personal data
Our team tests various VPN brands and we recommend them to our users by:
Server numbers and availability
Attention to privacy and encryption
Pricing
Premium security Visit NordVPN 68% OFF
Easy to use Visit CyberGhost 85% OFF
4 best VPNs for Apex Legends to reduce ping and lag
If you have high ping, lags, delays or latency while playing Apex Legends, use a VPN to reduce ping and improve your connection speed. Read More
Is Virgin Media blocking your VPN? Try 3 options that work
If Virgin Media blocked your VPN connection, read this guide to learn what are the best VPN tools to use on this platform. Read More
Best VPN for Korean Netflix to watch K-Dramas from anywhere
Few VPNs can unblock Netflix KR. Discover the best VPN for Korean Netflix so that you can watch K-Dramas, movies, and TV series from anywhere in the world. Read More
4 best VPNs for Factorio to fix multiplayer lag & ping
If you can't enjoy Factorio multiplayer due to lag spikes, high ping, and latency issues, use a fast VPN to optimize your network connection for gaming. Read More
I agree with the Privacy Policy regarding my personal data
© Copyright Windows Report 2021. Not associated with Microsoft
By clicking or navigating this website site, you agree to allow our collection of information on Scaleway to offer you an optimal user experience and to keep track of statistics through cookies. Learn more about our Cookie Policy.
How to create an ad-blocking VPN using Pi-hole and OpenVPN
Pi-hole® is a DNS sinkhole that protects your devices from unwanted content, such as advertisements, without installing any client-side software. It comes with an easy-to-use interactive installer and is even able to block content in non-browser locations, such as mobile apps and smart TVs. This can help to reduce data consumption on mobile plans.
To secure the connection, we use the PiVPN tool to install an OpenVPN virtual private network that routes all traffic over a Scaleway Virtual Cloud Instance.
This tutorial consists of four steps:
1 . Login to your Scaleway Console and create a new Virtual Instance. For this tutorial we use a DEV1-S instance running on Ubuntu Focal Fossa (20.04 LTS).
2 . Log into the newly created instance using SSH.
3 . Update the cache of the apt package manager and upgrade the software already installed on the server:
1 . Download the Pi-hole installer and run it:
curl -sSL https://install.pi-hole.net | bash
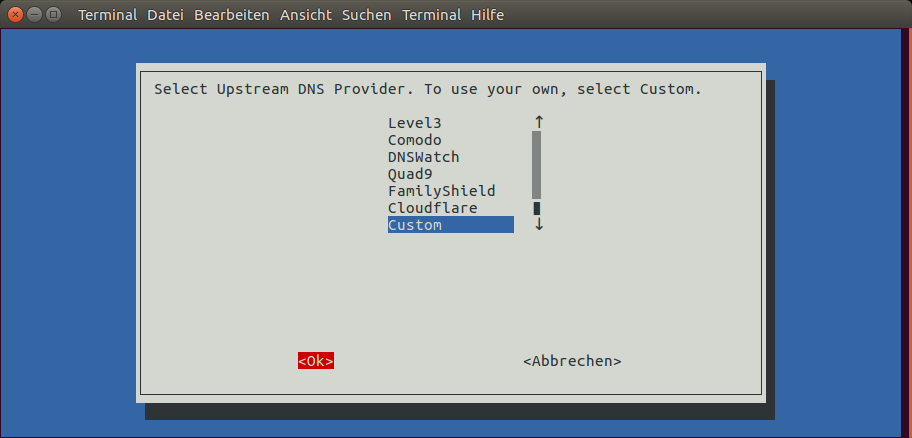
2 . The installer does some checks, and then gives you a series of prompt questions to answer. Choose OK or answer positively to all of them, until you are being asked choose an upstream DNS provider.
3 . Select one of the proposed upstream DNS servers from the list or specify a custom DNS server. Once selected, use the TAB key to move to the OK button and confirm by pressing ENTER.
4 . Pi-hole uses third party filter lists. Select the list you want to use and confirm by pressing the OK button:
5 . Choose whether you want to filter both IPv6 and IPv4 traffic and confirm by pressing the OK button.
6 . Confirm the network settings by navigating to the YES button. You will be guided through two more network prompts. Confirm them by by pressing the OK button.
7 . Choose whether you want to enter the Pi-hole web interface and confirm by pressing the OK button:
8 . The Pi-hole installer proposes the automatic installation of a webserver and its dependencies. If you are not using another web server, select to install it and confirm by pressing the OK button:
9 . Choose whether you want to log queries and confirm by pressing the OK button:
10 . Select a privacy mode for FTL and confirm by pressing the OK button:
11 . The Pi Hole installer proceeds with the automatic installation of the required software. Once the installation is complete, the URL to the admin interface and your password are displayed in a prompt. Take a note of the password and leave the prompt by pressing the OK button.
12 . Set the listener of the Pi-hole web interface to local to avoid it being accessible from the public Internet:
13 . Optionally, you can customize the password of your Pi-hole’s web interface, run the following command:
To direct Internet traffic via our Pi-hole instance, we install OpenVPN using the PiVPN project. It provides a very easy way to install OpenVPN and Wireguard on the instance. In this tutorial we are using OpenVPN.
1 . Create a new non-root user for OpenVPN:
2 . Run the following command from a SSH shell on your instance to download and launch the PiVPN installer:
curl -L https://install.pivpn.io | bash
3 . A series of prompts displays. Validate them by pressing the OK button until you are asked under which user the OpenVPN application should run. Select the previously created openvpn user and validate by pressing the OK button:
4 . Choose the OpenVPN protocol in the prompt and validate by pressing the OK button:
5 . PiVPN provides a default configuration, accept it by pressing Yes:
6 . Keep the value for the UDP transport protocol unless you have specific requirements and validate by pressing the OK button:
7 . You can leave the default OpenVPN port 1194 unless your network configuration requires another port. Confirm by pressing the OK button:
8 . The PiVPN installer automatically detects the presence of Pi-hole and asks to use it. Validate the prompt by confirming with the Yes button:
9 . The Pi-hole installer asks you if you want to use a custom search domain. Keep the default value and press the No button unless you have specific requirements:
10 . The following prompt asks you if you want to use the instance’s IP address or a custom domain name to connect to your VPN. Keep the default setting, using the public IP address of your instance and validate by pressing the OK button.
11 . During the installation, PiVPN prompts you if you want to use Elliptic Curves to provide higher connection speed and improved security over RSA. Confirm by pressing the Yes button. If you are using some devices using legacy OpenVPN clients not supporting this feature, select No.
12 . Select the desired key size for the certificate. In this tutorial we use the recommended size of 256 bit. Confirm by pressing the OK button:
13 . The following prompt informs you that the server key and HMAC key are now being generated. Confirm by pressing the OK button.
14 . The installer now prompts you to enable unattended upgrades, which allow to update the software on your server automatically to make sure it is using the latest version of the software available in the repository. Validate by pressing the Yes button.
15 . The installation of PiVPN is now complete. You can reboot your instance as suggested by the installer by pressing the Yes button.
You can now add users to your filtered VPN service. It is recommended to create a user profile for each device you want to connect to the VPN. Sharing profiles between devices is not recommended for security reasons.
1 . Run the pivpn add command to launch the interactive user creation wizard.
2 . Enter each parameter of the user and validate by pressing the Enter key on your keyboard:
Enter a Name for the Client: client <- the identifier of your user
How many days should the certificate last? 1080 <- the validity of the user's certificate. You can leave the default value
Enter the password for the client: <- a secret password for your user (Note: the password is not shown when you type for security reasons)
Enter the password again to verify: <- enter the password again to confirm it
The certificate and user profile is now generated and once it is ready, the following message displays:
========================================================
Done! client.ovpn successfully created!
client.ovpn was copied to:
/home/openvpn/ovpns
for easy transfer. Please use this profile only on one
device and create additional profiles for other devices.
========================================================
3 . Download the generated *.ovpn configration file on your device and import it into your OpenVPN client.
4 . Connect to your VPN to use your secure and filtered Internet connection.
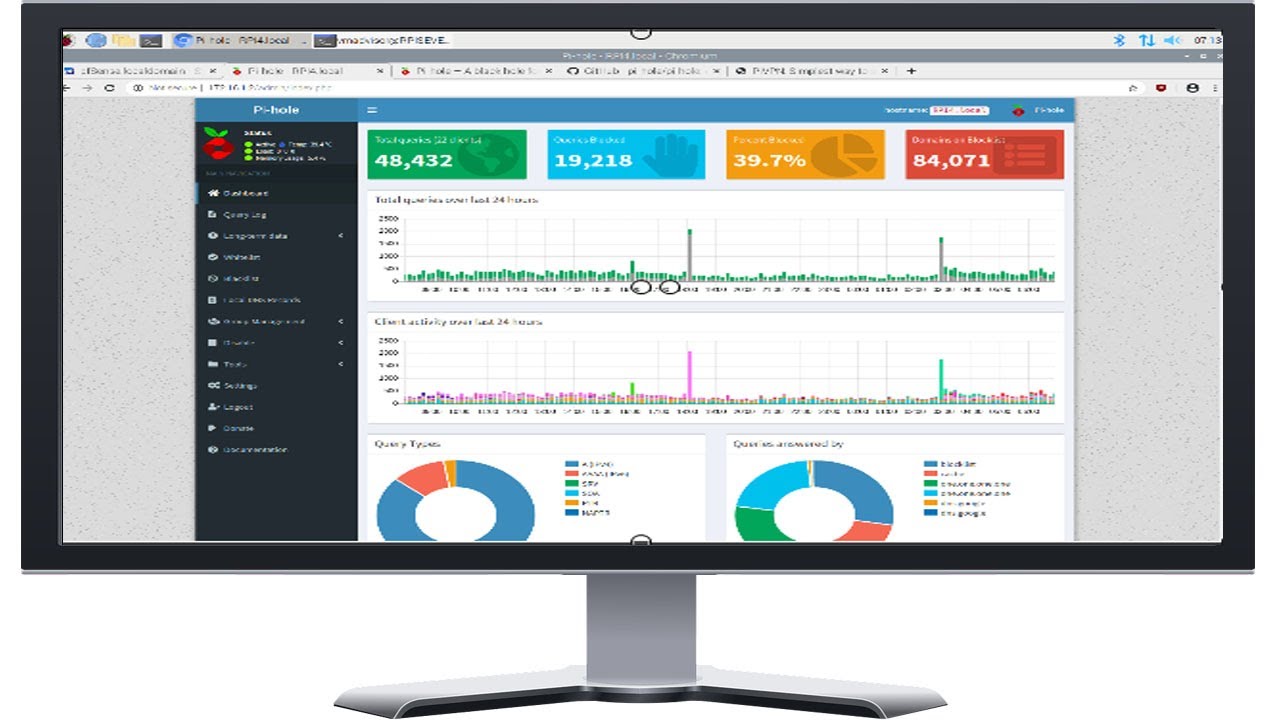
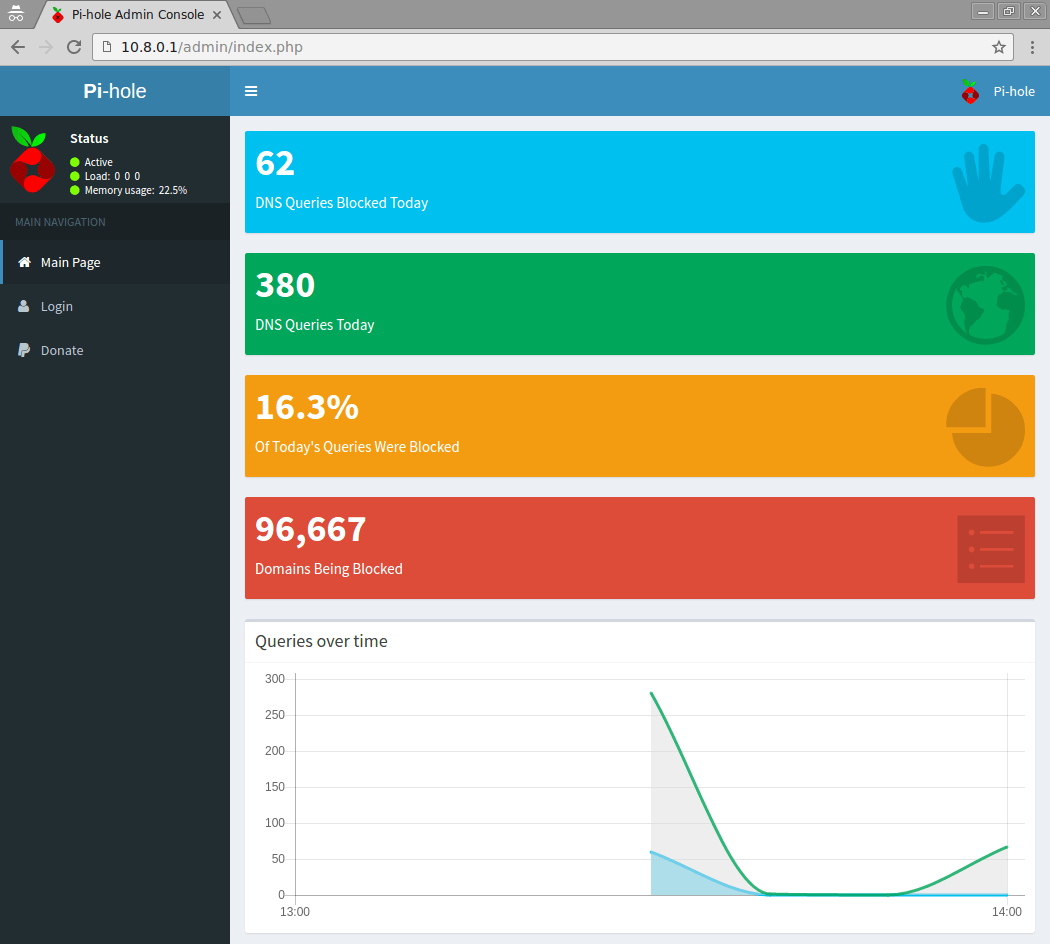
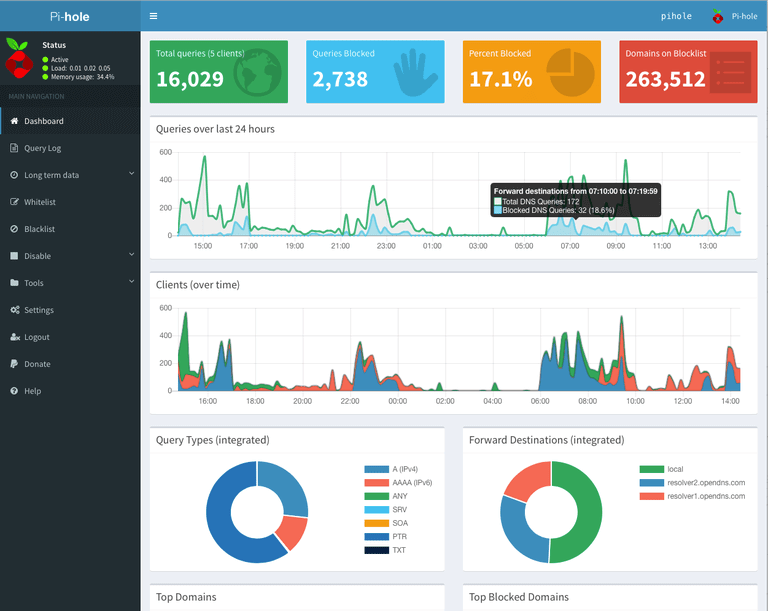
5 . Open the following URL in your web browser to connect to the Pi-hole webinterface: http://10.8.0.1/admin/. The web interface allows you to further configure Pi-hole and to view statistics about your DNS requests:
To avoid keeping an open DNS resolver on the Intenet, we restrict the requests from outside of our infrastructure. This is very important, as unprotected DNS servers can be abused and participate in DNS Amplification attacks.
1 . From your Scaleway console, click on Instances in the Compute section of the side menu.
2 . Click on the Security Groups tab. A list of your existing security groups displays.
3 . Click Create a security group to go the Security Group creation page:
4 . Enter the details for your new Security Group:
Your configuration should look like the following example:
You instance is now protected against requests to the DNS server running on it from external hosts. For more information about Security Groups, refer to our dedicated documentation.
You now have configured a secure and filtered OpenVPN connection to the Internet. Pi-hole automatically filters unwanted advertisings and and helps to save bandwidth on metered plans. The web interface allows you to view detailed statistics about the DNS requests made and you can white or blacklist additional entries.
Discover the Cloud That Makes Sense
SCALEWAY SAS, a simplified stock corporation (Société par actions simplifiée) with a working capital of €214.410,50, subsidiary of the Iliad group, registered with the Paris Corporate and Trade Register number RCS PARIS B 433 115 904, VAT number FR 35 433115904, represented by : Cyril Poidatz, Arnaud de Brindejonc de Bermingham.
Contact: SCALEWAY SAS, BP 438, 75366 PARIS CEDEX 08, FRANCE – Fax: +33 (0)899 173 788 (€1.35 per call then €0.34/min) – Phone: +33 (0)1 84 13 00 00
© 1999-2020 – Scaleway SAS
Alternative Point Spread Bet365
Czech Swingers Vk
Little Girl Lingerie
Found Doctors Cum Wife
Shake Your Ass Porno
Pi-hole – Network-wide protection
How to create an ad-blocking VPN using Pi-hole and OpenVPN ...
Installing Pi-hole with PiVPN – Sylvain Durand
Installing Pi-Hole, an OpenVPN server and an IPsec VPN ...
Pi Hole with a VPN : pihole
PiHole with OpenVPN the easy way - Pi-hole Userspace
Vpn with pi hole : pihole
Pi Hole Vpn