Partial Vaginoplasty

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
Verywell Health's content is for informational and educational purposes only. Our website is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Ⓒ 2021 About, Inc. (Dotdash) — All rights reserved
Elizabeth Boskey, PhD, MPH, CHES, is a social worker, adjunct lecturer, and expert writer in the field of sexually transmitted diseases.
Medically reviewed by Maria M. LoTempio, MD on September 22, 2020
Maria M. LoTempio, MD, is double board-certified in plastic and reconstructive surgery and otolaryngology. She is an associate clinical professor at New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
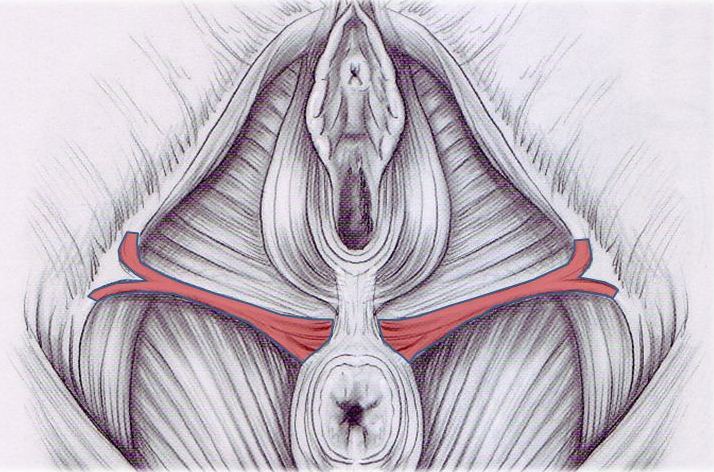
Vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure used to create a vagina. The surgery may be performed after a cisgender woman has had a vaginectomy for vaginal cancer. It may also be used to create a vagina for a woman born without one because of vaginal agenesis. In addition, vaginoplasty can be used to create a vagina for transgender women or individuals as a type of gender-affirming surgery.
Jessica Lia / DigialVision / Getty Images
For a patient who needs a vaginoplasty, there are several different types that may be offered. The type of vaginoplasty that is most appropriate depends on a number of factors. In particular, the type of vaginoplasty may be limited by the the patient's age and the indication for the vaginoplasty. The surgery appropriate for an adult transgender woman or individual would not be the same one indicated for a young cisgender girl. The main types of vaginoplasty are intestinal, peritoneal, McIndoe, buccal mucosa, and penile-inversion.
Sometimes when a vagina is created through vaginoplasty it is referred to as a neovagina. This literally means "new vagina."
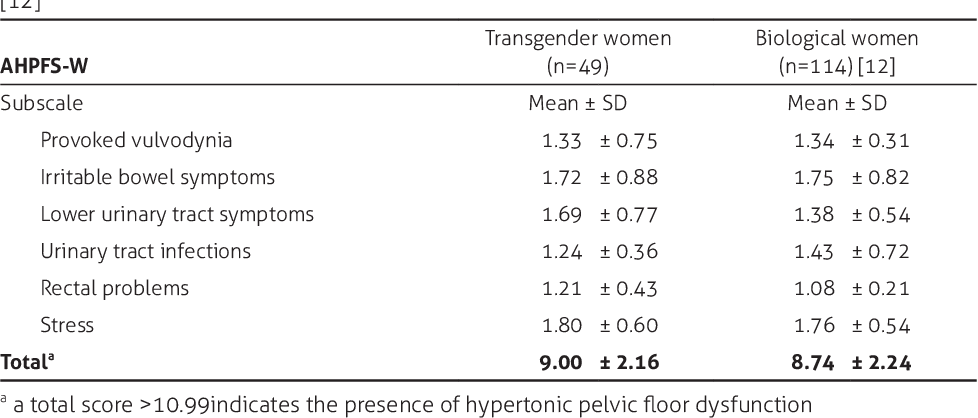
Intestinal vaginoplasty uses a section of the sigmoid colon to create the neovagina. This is usually done as laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic surgery is also often referred to as minimally invasive or keyhole surgery because there is only a small incision through the skin. For this surgery, a small piece of colon is detached and then rotated down to become the lining of the vagina. Then the surrounding colon is stitched together to restore its function.
There have been some criticisms that intestinal vaginoplasty can lead to excess mucus in the vagina and mucus with an unpleasant smell. However, these side effects have not been consistently reported.1
Some people see the mucus production by the intestinal tissue as an advantage. The healthy vaginal lining is also mucus-producing and self-lubricating. The colon segment is also stretchy in a way that is more similar to the regular vaginal lining than other tissue options used to line the neovagina.
Peritoneal vaginoplasty is also referred to as the Luohu operation. It uses the lining of the abdominal cavity, the peritoneum, to create the vagina. Like intestinal vaginoplasty, peritoneal vaginoplasty is usually a laparoscopic procedure.2
Patients who have this procedure do not necessarily need to use dilation to maintain their vaginal opening. That is particularly true if they are having regular sexual intercourse.
There is a risk of rectovaginal fistula with peritoneal vaginoplasty and with other types of vaginoplasty. A rectovaginal fistula is when the rectum and vagina have a hole between them. Fistulas are usually treatable with surgery.
The McIndoe technique, McIndoe procedure, or McIndoe vaginoplasty are quite different from the peritoneal and intestinal vaginoplasty procedures. Unlike with peritoneal and intestinal vaginoplasties, the McIndoe technique does not require abdominal surgery to create the lining.
Instead, McIndoe vaginoplasty lines the vagina with a skin graft.3 That skin graft is placed on a vaginal mold and then placed into the space that has been opened to become the vagina. In peritoneal and intestinal vaginoplasty, no such mold is used. The mold is used consistently for the first several months after surgery (removing it for regular cleaning) in order to promote healing of the vagina into an open cavity suitable for intercourse.
Unlike the peritoneum and the intestine, the skin is not a mucosal tissue. Therefore, it does not self lubricate. This also increases the risk that the vaginal opening will close. Because of that, those who have a McIndoe procedure, and do not have regular sexual intercourse, will need to commit to dilating their vaginas for the rest of their lives.
Buccal mucosa is the tissue lining the mouth. It is quite similar to the lining of the vagina. Both tissues are hairless and create mucus.3 Therefore, in some ways, it is an ideal lining for a neovagina created during vaginoplasty.
However, buccal vaginoplasties are not as common as other vaginoplasty procedures for several reasons. Only a relatively small area of tissue is available. People may be concerned about side effects in the mouth and cheek. In addition, the inside of the mouth is not an area most gynecologists are used to working on. Therefore, they may have to collaborate with facial surgeons in order to harvest tissue appropriately.
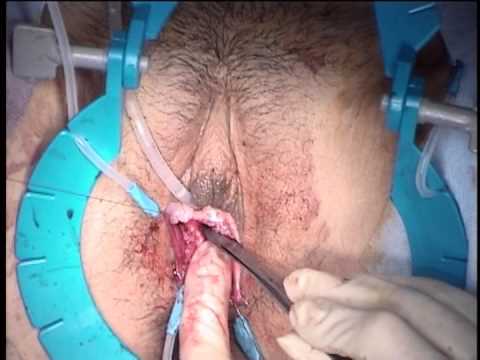
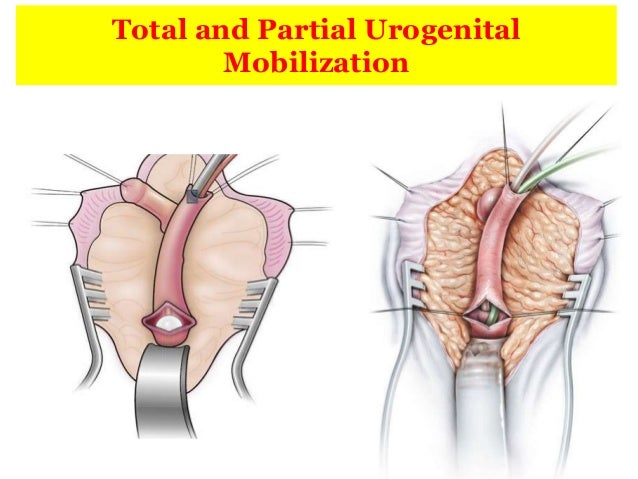
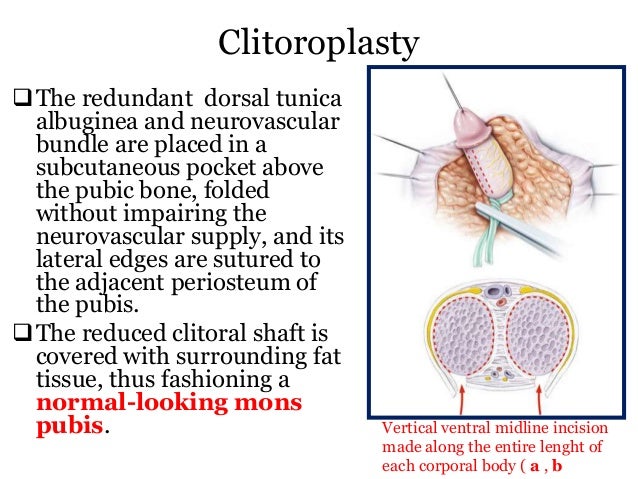
Penile inversion vaginoplasty is only used in transgender women.4 In this procedure, the skin from the outside of the penis is removed and inverted to create the lining of the vagina. The head of the penis is also reshaped to create a clitoris. Finally, scrotal skin is used to create the labia majora and minora.
The disadvantages of this procedure are similar to those when the skin is used for a McIndoe vaginoplasty. Hair must be fully removed to make certain there is no hair growing on the inside of the vagina. The vagina requires a lifetime of dilation for maintenance. It is also not self-lubricating.
Although only transgender women or individuals can get a penile inversion vaginoplasty, that is not the only type of vaginoplasty they can get. These patients may also be offered an intestinal vaginoplasty either as a primary surgery or if they need a surgical revision. At least one transgender woman or individual has also had a peritoneal vaginoplasty, but they are not widely available for this population.
Depending on the technique used, patients may or may not need to dilate their neovagina for the rest of their lives.
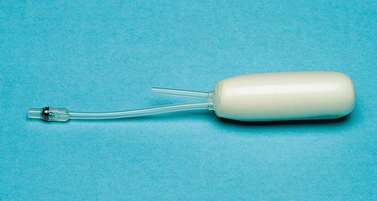
Dilation involves inserting a silicone dilator—a rod with a curved end—into the vagina and leaving it in place for a short period of time (usually around 10-15 minutes).
Dilation can be used to increase the depth and width of the vagina through gentle stretching. This can help those who have difficulty with intercourse after vaginoplasty. Dilation is also necessary to maintain the vaginal opening when the skin is used to line the neovagina, such as in penile inversion or McIndoe vaginoplasty. The frequency of dilation needed depends on the type of procedure and how long it has been since the surgery was completed.5
Sign up for our Health Tip of the Day newsletter, and receive daily tips that will help you live your healthiest life.
Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
Bhaskar V, Sinha RJ, Mehrotra S, Mehrotra CN, Singh V. Long-term outcomes of sigmoid vaginoplasty in patients with disorder of sexual development - our experience. Urol Ann. 2018;10(2):185-190. doi:10.4103/UA.UA_88_17
Mhatre P, Mhatre J, Sahu R. New laparoscopic peritoneal pull-through vaginoplasty technique. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2014;7(3):181-6. doi:10.4103/0974-1208.142478
Salim A, Poh M. Gender-Affirming Penile Inversion Vaginoplasty. Clin Plast Surg. 2018;45(3):343-350. doi:+10.1016/j.cps.2018.04.001
Johns Hopkins Medicine. FAQ: vaginoplasty.
Bouman MB, van Zeijl MC, Buncamper ME, Meijerink WJ, van Bodegraven AA, Mullender MG. Intestinal vaginoplasty revisited: a review of surgical techniques, complications, and sexual function. J Sex Med. 2014 Jul;11(7):1835-47. doi:10.1111/jsm.12538
Chan JL, Levin PJ, Ford BP, Stanton DC, Pfeifer SM. Vaginoplasty with an Autologous Buccal Mucosa Fenestrated Graft in Two Patients with Vaginal Agenesis: A Multidisciplinary Approach and Literature Review. J Minim Invasive Gynecol.2017 May - Jun;24(4):670-676. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2016.12.030.
Horbach SE, Bouman MB, Smit JM, Özer M, Buncamper ME, Mullender MG. Outcome of Vaginoplasty in Male-to-Female Transgenders: A Systematic Review of Surgical Techniques. J Sex Med. 2015 Jun;12(6):1499-512.doi: 10.1111/jsm.12868.
Li FY, Xu YS, Zhou CD, Zhou Y, Li SK, Li Q. Long-term outcomes of vaginoplasty with autologous buccal micromucosa. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 May;123(5):951-6. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000161.
Qin C, Luo G, Du M, Liao S, Wang C, Xu K, Tang J, Li B, Zhang J, Pan H, Ball TW, Fang Y. The clinical application of laparoscope-assisted peritoneal vaginoplasty for the treatment of congenital absence of vagina. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016 Jun;133(3):320-4. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2015.11.015.
What to Expect on the Day of Your Vaginoplasty
Why Intercourse Can Be Painful After Menopause and What You Can Do
A Rectovaginal Exam Can Identify Ovarian Abnormalities and Cancer
Ask an Expert: What Types of Procedures Treat Fibroids?
What Causes Postmenopausal Bleeding? Is It Serious?
Verywell Health's content is for informational and educational purposes only. Our website is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Ⓒ 2021 About, Inc. (Dotdash) — All rights reserved
Verywell Health is part of the Dotdash publishing family.
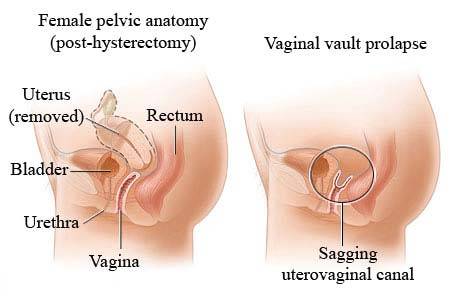
Vaginoplasty is a surgical procedure that tightens the vaginal opening and walls. In some cases, it is performed in order to reconstruct a vagina after a woman has undergone a vaginectomy for vaginal cancer. In other instances, women may elect to have vaginoplasty if they have experienced a natural loss of tone and tightness as a result of aging, hormonal changes, childbirth, or birth defects. Often referred to as vaginal rejuvenation, vaginoplasty has grown in popularity. Weakened vaginal muscles can result in physical discomfort and emotional insecurity for many women. In addition, the weakened walls can be the cause of displeasure or pain during intercourse. Some women may experience a loss of femininity. They may experience a loss of sexual pleasure and sensitivity as the walls of the vagina weaken, resulting in self-conscious feelings about their partner’s experience during intercourse. For millions of women who undergo vaginoplasty, a restored sense of femininity and sexual pleasure is a benefit.
This procedure is also sometimes referred to as vaginal rejuvenation. While most often performed to tighten weakened vaginal muscles, this procedure is also sometimes undergone to correct birth defects or create a vagina for transgender sex reassignment surgery. Some vaginoplasty procedures require removal of tissue or grafting from tissue taken from other parts of the body. In instances when vaginoplasty is performed to create a vagina, it is sometimes referred to as a neovagina, which quite literally means “new vagina.”
For women who elect to undergo a vaginoplasty procedure, a few different types of the procedure may be discussed. The most appropriate choice depends on various factors, such as a woman’s age or reason for undergoing the surgery. The particular type appropriate for a young, cisgender girl who needs the procedure to correct a birth defect would not be the same type of procedure indicated for an older woman who wishes to have her vaginal walls tightened after childbirth and aging has weakened them. The primary types of vaginoplasty are:
This particular type of procedure creates a new vagina by utilizing a section of the sigmoid colon. Often performed as a laparoscopic surgery, this minimally invasive procedure requires only a small incision. For an intestinal vaginoplasty, a piece of the colon is removed and rotated to become the vaginal lining. The surrounding colon is then stitched together to restore its proper function.
Some criticisms of this type of vaginoplasty have been expressed, stating that it can result in excessive mucus in the vaginal cavity that creates an unpleasant odor. These side effects have not been significantly reported, and some see this excess mucus production as an advantage since it is self-lubricating. Additionally, the elasticity of the colon segment bears more similarity to a regular vaginal lining than some other tissue options used to line the neovagina.
Peritoneal vaginoplasty, sometimes called the Louhu operation, is also usually completed as a laparoscopic procedure. This type of vaginoplasty utilizes the lining of the abdominal cavity, or the peritoneum, to create the new vagina.
As with all types of vaginoplasty, there is a risk of recto-vaginal fistula development, or a hole between the rectum and vagina. However, this risk is slightly greater with peritoneal vaginoplasty. Fistulas are easily treated with surgery.
An added benefit to this type of vaginoplasty is that women who undergo this procedure do not necessarily need to maintain dilation of the vaginal opening. This is particularly true if they are maintaining sexual intercourse on a regular basis.
McIndoe Vaginoplasty, or the McIndoe technique, uses a skin graft to create the walls of the vagina. Unlike the above two mentioned procedures, this method does not require abdominal surgery to create a lining. Instead, skin grafted from another area on the patient’s body is placed on a vaginal mold which is then placed into the area that has been opened to create the vagina. Necessary precautions to remove all hair and hair follicles from this piece of skin must be made in order to prevent future hair growth in the new vagina. The mold is used for several months and removed only for regular cleaning in an effort to promote healing.
Since skin is not a mucosal tissue, it does not self-lubricate. This increases the risk of the vaginal opening closing up. As a result, women who undergo a McIndoe procedure, and are not sexually active on a regular basis, will need to dilate the vagina regularly for the rest of their lives.
Buccal mucosa is the tissue lining of the mouth and is quite similar to that of the vagina in that both create mucus and are hairless. These similarities make it an ideal lining for a neovagina that is created during vaginoplasty.
While Buccal mucosa may seem like an ideal option at first, this type of vaginoplasty is not as common as some others. This primarily is because only a small amount of tissue is available. Thus, patients are concerned about side effects that may result in the mouth and cheeks. Additionally, most gynecologists are not as familiar with the inside of the mouth. As such, collaboration with a facial surgeon may be necessary.
Penile inversion is a type of vaginoplasty surgery only performed on transgenders. This procedure involves removing skin from the outside of the penis and inverting it to create the lining for the neovagina. A clitoris is then shaped from the head of the penis, and scrotal skin is utilized to create the labia majora and labia minora.
This procedure requires a lifetime of dilation and is not self-lubricating. As with the McIndoe vaginoplasty, precautions must be made to ensure no hair follicles remain.
Vaginoplasty is generally only recommended for women with vaginal defects or who have undergone surgery for vaginal cancer. In some instances, it may be recommended to correct vaginal looseness caused by childbirth. Even in these instances, a variety of natural alternatives may be explored before resorting to surgery.
In cases of gender transition, surgery should never be the first step. A number of other social and medical transition options should be thoroughly explored before considering a vaginoplasty procedure. Individuals who do choose to have vaginoplasty generally do not do so until they have taken other steps, such as supplemental hormones. In order o qualify for vaginoplasty as a transitional surgery, most doctors and hospitals require the individual to meet certain age requirements.
The overall cost of vaginoplasty will vary depending on a number of factors, such as the location of the medical facility and physician, the type of procedure needed, other medical procedures that might be necessary, insurance requirements, and other factors. In all, the overall cost can range anywhere from a few thousand dollars to a hundred thousand or more, depending upon your particular circumstances. For example, the average penile inversion vaginoplasty generally costs around $20,000 on average. However, a secondary labiaplasty may be necessary.
The majority of health insurance plans do not cover vaginoplasty as an elective plastic surgery rather than a medically necessary procedure. Only if the procedure can be deemed medically necessary will most insurance companies cover the surgery.
After the correct amount of tightening has been determined, a wedge is marked to indicate what extra skin
is to be removed from inside the vaginal area. The tissues under the skin are then tightened with sutures. After the vaginal canal is tightened, the mucosal skin is also sutured closed. Once this part of the procedure has been completed, any visible external skin protruding from the area can be reduced.
A significant length of recovery time, as well as ongoing self-care, is necessary after a vaginoplasty procedure. One can expect to spend approximately a week or more in the hospital after the surgical procedure has been completed. After being discharged from the hospital, a patient must return for follow-up appointments for some time until the area is completely healed and your doctor releases you from care. The healing process can take a good length of time. As such, you should not engage in any strenuous physical activities or do any heavy lifting for at least six weeks following the vaginoplasty surgery.
You should also expect to use a catheter for urination for one or two weeks after the procedure. You will be provided with detailed instructions on care and maintenance of the catheter. Additionally, your doctor will instruct you on how to check for signs of infection around the surgical site. You most likely will be able to perform light activities and walk around normally after about a week or so. Within six to eight weeks, you should be recovered enough to go back to normal activities. Complete healing, however, can take as much as a year to two years.
Depending upon the type of vaginoplasty surgery you are scheduled for, your pre-op instructions can vary. Your doctor should go over these instructions with you carefully. In addition to specific instructions related to the procedure, you should follow a list of generalized pre-operative instructions. Following are some examples of basic pr-op instructions you can expect to follow:
Cl
Aria Lee Xxx Vse 2021
Mature Porno Granny Group
Suck A Nigga Dick
Huge Boobs Gym
Female Outfit Replacer With Vanilla Shoes 4.3
A Guide To Vaginoplasty | Vaginal Rejuvenation, Costs ...
Vaginoplasty - Wikipedia
Creation of a Neovagina by Laparoscopic Modified Davydov ...
Vulvoplasty: Zero Depth Vaginoplasty in Male-to-female Surgery
MTF Vaginoplasty: What Patients Need To Know Before Having ...
Is Rectosigmoid Vaginoplasty Still Useful?
Partial Vaginoplasty






































/GettyImages-1194482310-0a87ed68602a477b9be05d217ef736f0.jpg)