PLINIAN ERUPTION
https://search.headlines-world.com/search.html?q=PLINIAN%20ERUPTIONMultiSearch Tag Explorer
aéPiot
Go

Mount Vesuvius ( viss-OO-vee-əs) is a somma–stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about 9 km (5.6 mi) east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes forming the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera, resulting from the collapse of an earlier, much higher structure. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD destroyed the Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum, Oplontis, Stabiae and other settlements. The eruption ejected a cloud of stones, ash and volcanic gases to a height of 33 km (21 mi), erupting molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of 6×105 cubic metres (7.8×105 cu yd) per second. More than 1,000 people are thought to have died in the eruption, though the exact toll is unknown. The only surviving witness account consists of two letters by Pliny the Younger to the historian Tacitus. Vesuvius has erupted many times since. It is the only volcano on Europe's mainland to have erupted in the last hundred years. It is regarded as one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world because 3,000,000 people live near enough to be affected by an eruption, with at least 600,000 in the danger zone. This is the most densely populated volcanic region in the world. Eruptions tend to be violent and explosive; these are known as Plinian eruptions.
In connection with: Mount Vesuvius
Title combos: Mount Vesuvius
Description combos: metres mi Europe the Pliny structure The volcanoes cloud

1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
In March 1980, a series of volcanic explosions and pyroclastic flows began at Mount St. Helens in Skamania County, Washington, United States. A series of phreatic blasts occurred from the summit and escalated until a major explosive eruption took place on May 18, 1980, at 8:32 a.m. The eruption, which had a volcanic explosivity index of 5, was the first to occur in the contiguous United States since the much smaller 1915 eruption of Lassen Peak in California. It has often been considered the most disastrous volcanic eruption in U.S. history. The eruption was preceded by a series of earthquakes and steam-venting episodes caused by an injection of magma at shallow depth below the volcano that created a large bulge and a fracture system on the mountain's north slope. An earthquake at 8:32:11 am PDT (UTC−7) on May 18, 1980, caused the entire weakened north face to slide away, a sector collapse which was the largest subaerial landslide in recorded history. This allowed the partly molten rock, rich in high-pressure gas and steam, to suddenly explode northward toward Spirit Lake in a hot mix of lava and pulverized older rock, overtaking the landslide. An eruption column rose 80,000 feet (24 km; 15 mi) into the atmosphere and deposited ash in 11 U.S. states and various Canadian provinces. At the same time, snow, ice, and several entire glaciers on the volcano melted, forming a series of large lahars (volcanic mudslides) that reached as far as the Columbia River, nearly 50 miles (80 km) to the southwest. Less severe outbursts continued into the next day, only to be followed by other large, but not as destructive, eruptions later that year. The thermal energy released during the eruption was equal to 26 megatons of TNT. About 57 people were killed, including innkeeper and World War I veteran Harry R. Truman, photographers Reid Blackburn and Robert Landsburg, and volcanologist David A. Johnston. Hundreds of square miles were reduced to wasteland, causing over $1 billion in damage (equivalent to $3.4 billion in 2023), thousands of animals were killed, and Mount St. Helens was left with a crater on its north side. At the time of the eruption, the summit of the volcano was owned by the Burlington Northern Railroad, but afterward, the railroad donated the land to the United States Forest Service. The area was later preserved in the Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument and due to the eruption, the state recognized the month of May as "Volcano Awareness Month" and events are held at Mt. St. Helens, or within the region, to discuss the eruption, safety concerns, and to commemorate lives lost during the natural disaster.
In connection with: 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
Title combos: of Helens 1980 eruption of St Mount of eruption
Description combos: earthquake World northward was an of of am column

Plinian eruptions or Vesuvian eruptions are volcanic eruptions characterized by their similarity to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which destroyed the ancient Roman cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii. The eruption was described in a letter written by Pliny the Younger, after the death of his uncle Pliny the Elder. Plinian eruptions eject columns of volcanic debris and hot gases high into the stratosphere, the second layer of Earth's atmosphere. They eject a large amount of pumice and have powerful, continuous gas-driven eruptions. Eruptions can end in less than a day, or continue for days or months. The longer eruptions begin with production of clouds of volcanic ash, sometimes with pyroclastic surges. The amount of magma ejected can be so large that it depletes the magma chamber below, causing the top of the volcano to collapse, resulting in a caldera. Fine ash and pulverized pumice can be deposited over large areas. Plinian eruptions are often accompanied by loud sounds. The sudden discharge of electrical charges accumulated in the air around the ascending column of volcanic ashes also often causes lightning strikes, as depicted by the English geologist George Julius Poulett Scrope in his painting of 1822 or observed during 2022 Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha'apai eruption and tsunami. The lava is usually dacitic or rhyolitic, rich in silica. Basaltic, low-silica lavas rarely produce Plinian eruptions unless specific conditions are met (low magma water content <2%, moderate temperature, and rapid crystallization); a recent basaltic example is the 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera on New Zealand's North Island.
In connection with: Plinian eruption
Title combos: Plinian eruption
Description combos: eruption the their North painting large collapse in lightning

Peléan eruptions are a type of volcanic eruption. They can occur when viscous magma, typically of rhyolitic to andesitic type, is involved, and share some similarities with Vulcanian eruptions. The most important characteristic of a Peléan eruption is the presence of a glowing avalanche of hot volcanic ash, called a pyroclastic flow. Formation of lava domes is another characteristic. Short flows of ash or creation of pumice cones may be observed as well. The initial phases of eruption are characterized by pyroclastic flows. The tephra deposits have lower volume and range than the corresponding Plinian and Vulcanian eruptions. The viscous magma then forms a steep-sided dome or volcanic spine in the volcano's vent. The dome may later collapse, resulting in flows of ash and hot blocks. The eruption cycle is usually completed in a few years, but in some cases may continue for decades, like in the case of Santiaguito. The 1902 eruption of Mount Pelée (VEI-4) is the first described case of a Peléan eruption; the term is derived from the name of the volcano. Other examples of Peléan eruptions include: the 1948–1951 eruption of Hibok-Hibok; (VEI-3) the 1951 eruption of Mount Lamington, which remains the most detailed observation of this kind; (VEI-4) the 1968 eruption of Mayon Volcano (VEI-3) The 2021 eruption of La Soufrière (VEI-4)
In connection with: Peléan eruption
Title combos: Peléan eruption
Description combos: is and vent Peléan of the lower tephra initial

A volcanic eruption occurs when material is expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series. There are three main types of volcanic eruptions. Magmatic eruptions involve the decompression of gas within magma that propels it forward. Phreatic eruptions are driven by the superheating of steam due to the close proximity of magma. This type exhibits no magmatic release, instead causing the granulation of existing rock. Phreatomagmatic eruptions are driven by the direct interaction of magma and water, as opposed to phreatic eruptions, where no fresh magma reaches the surface. Within these broad eruptive types are several subtypes. The weakest are Hawaiian and submarine, then Strombolian, followed by Vulcanian and Surtseyan. The stronger eruptive types are Pelean eruptions, followed by Plinian eruptions; the strongest eruptions are called ultra-Plinian. Subglacial and phreatic eruptions are defined by their eruptive mechanism, and vary in strength. An important measure of eruptive strength is the Volcanic Explosivity Index an order-of-magnitude scale, ranging from 0 to 8, that often correlates to eruptive types.
In connection with: Volcanic eruption
Title combos: eruption Volcanic
Description combos: eruptions eruptions water only fissure types Phreatic type by

Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD
In 79 AD, Mount Vesuvius, a stratovolcano located in the modern-day region of Campania, erupted, causing one of the deadliest eruptions in history. Vesuvius violently ejected a cloud of super-heated tephra and gases to a height of 33 km (21 mi), ejecting molten rock, pulverized pumice and hot ash at 1.5 million tons per second, ultimately releasing 100,000 times the thermal energy of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The event gives its name to the Vesuvian type of volcanic eruption, characterised by columns of hot gases and ash reaching the stratosphere, although the event also included pyroclastic flows associated with Peléan eruptions. The event destroyed several Roman towns and settlements in the area. Pompeii and Herculaneum, obliterated and buried underneath massive pyroclastic surges and ashfall deposits, are the most famous examples. Archaeological excavations have revealed much of the towns and the lives of the inhabitants, leading to the area becoming Vesuvius National Park and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The total population of both cities was over 20,000. The remains of over 1,500 people have been found at Pompeii and Herculaneum. The total death toll from the eruption remains unknown.
In connection with: Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD
Title combos: in Eruption Mount Eruption Vesuvius in 79 Eruption Vesuvius
Description combos: and unknown area Mount hot ultimately volcanic stratovolcano the
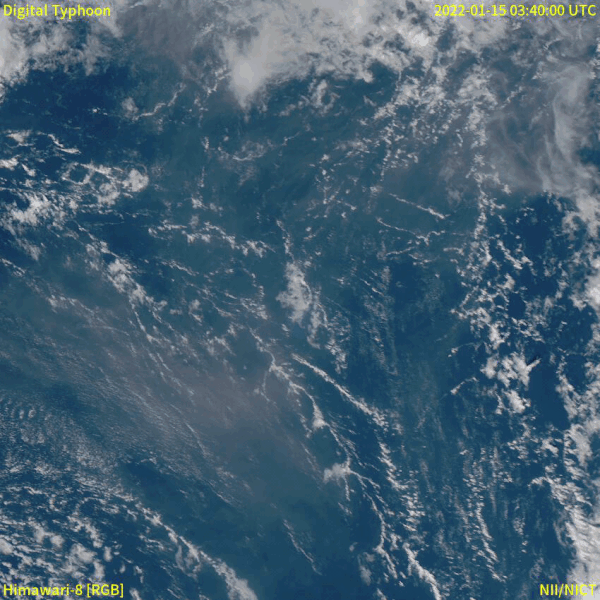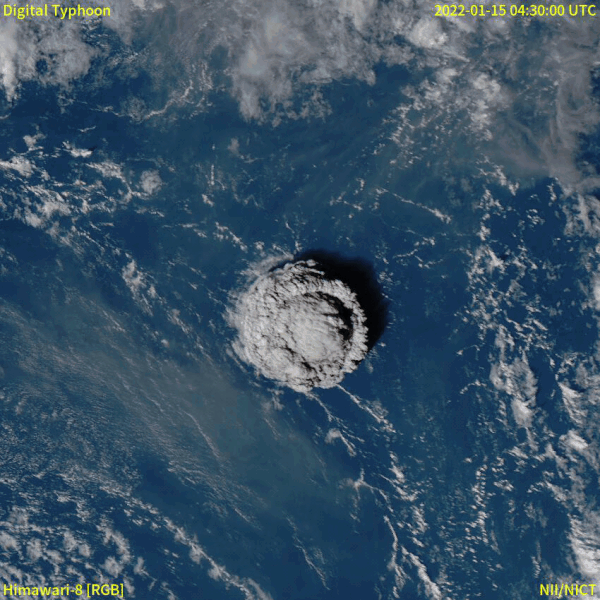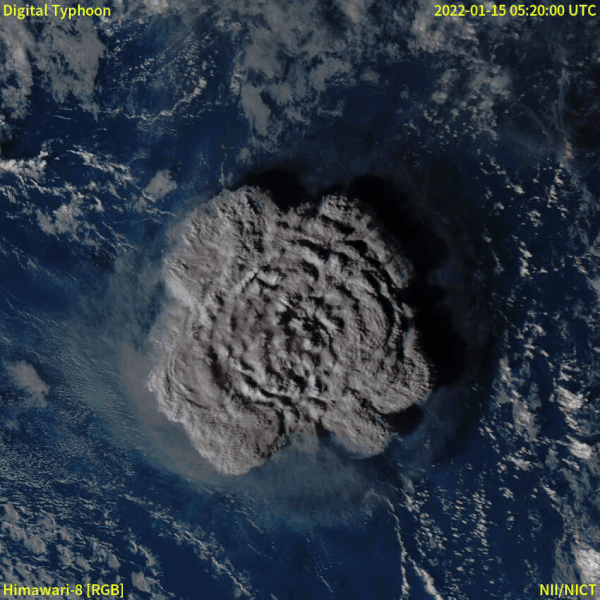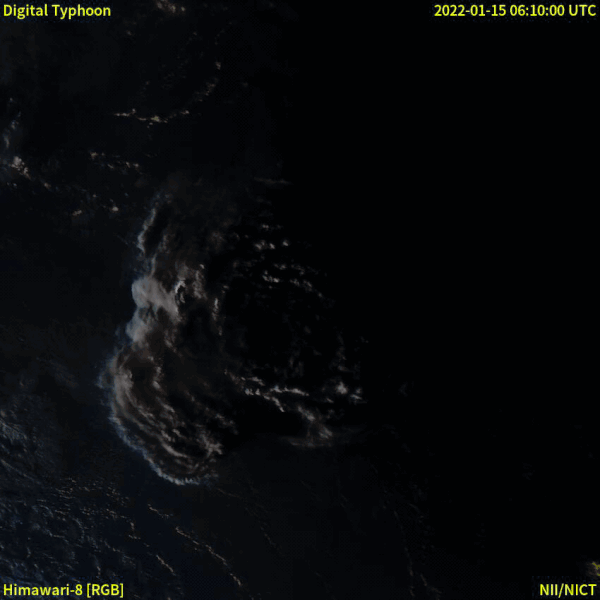
2022 Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai eruption and tsunami
In December 2021, an eruption began on Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai, a submarine volcano in the Tongan archipelago in the southern Pacific Ocean. The eruption reached a very large and powerful climax nearly four weeks later, on 15 January 2022. Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai is 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of Tongatapu, the country's main island, and is part of the highly active Tonga–Kermadec Islands volcanic arc, a subduction zone extending from New Zealand to Fiji. On the Volcanic Explosivity Index scale, the eruption was rated at least a VEI-5. Described by scientists as a "magma hammer", the volcano at its height produced a series of four underwater thrusts, displaced 10 cubic kilometres (2.4 cu mi) of rock, ash and sediment, and generated the largest atmospheric explosion recorded by modern instrumentation. The eruption produced a volcanic tsunami that affected Tonga, Fiji, American Samoa, Vanuatu, New Zealand, Japan, the United States, the Russian Far East, Chile and Peru. At least four people were killed, some were injured, and some remain possibly missing in Tonga from tsunami waves up to 20 m (66 ft) high. Tsunami waves with run-up heights up to 45 m (148 ft) struck the uninhabited island of Tofua. Two people drowned in Peru when 2 m (6 ft 7 in) waves struck the coast, while another died of indirect causes in Fiji. It was the largest volcanic eruption since the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo. NASA determined that the eruption was "hundreds of times more powerful" than Little Boy. The eruption was the largest explosion recorded in the atmosphere by modern instrumentation, far larger than any 20th-century volcanic event or nuclear bomb test. It is thought that in recent centuries, only the Krakatoa eruption of 1883 rivalled the atmospheric disturbance produced.
In connection with: 2022 Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai eruption and tsunami
Title combos: Haʻapai Tonga 2022 and Hunga eruption Hunga Haʻapai tsunami
Description combos: the zone Peru another eruption 65 volcanic causes island
Quick Access
Tag Explorer
Discover Fresh Ideas in the Universe of aéPiot
MultiSearch | Search | Tag Explorer
SHEET MUSIC | DIGITAL DOWNLOADS
© aéPiot - MultiSearch Tag Explorer. All rights reserved.
Hosted by HOSTGATE