PERLES CONFIGURATION
https://search.aepiot.ro/search.html?q=PERLES%20CONFIGURATIONMultiSearch Tag Explorer
aéPiot
Go
Divine Proportions: Rational Trigonometry to Universal Geometry
Divine Proportions: Rational Trigonometry to Universal Geometry is a 2005 book by the mathematician Norman J. Wildberger on a proposed alternative approach to Euclidean geometry and trigonometry, called rational trigonometry. The book advocates replacing the usual basic quantities of trigonometry, Euclidean distance and angle measure, by squared distance and the square of the sine of the angle, respectively. This is logically equivalent to the standard development (as the replacement quantities can be expressed in terms of the standard ones and vice versa). The author claims his approach holds some advantages, such as avoiding the need for irrational numbers. The book was "essentially self-published" by Wildberger through his publishing company Wild Egg. The formulas and theorems in the book are regarded as correct mathematics but the claims about practical or pedagogical superiority are primarily promoted by Wildberger himself and have received mixed reviews.
In connection with: Divine Proportions: Rational Trigonometry to Universal Geometry
Title combos: Proportions Trigonometry Divine Proportions Universal Universal Rational Geometry Divine
Description combos: have his about Wildberger standard standard geometry Rational proposed
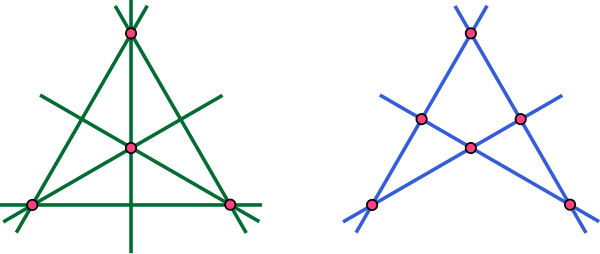
In mathematics, specifically projective geometry, a configuration in the plane consists of a finite set of points, and a finite arrangement of lines, such that each point is incident to the same number of lines and each line is incident to the same number of points. Although certain specific configurations had been studied earlier (for instance by Thomas Kirkman in 1849), the formal study of configurations was first introduced by Theodor Reye in 1876, in the second edition of his book Geometrie der Lage, in the context of a discussion of Desargues' theorem. Ernst Steinitz wrote his dissertation on the subject in 1894, and they were popularized by Hilbert and Cohn-Vossen's 1932 book Anschauliche Geometrie, reprinted in English as Hilbert & Cohn-Vossen (1952). Configurations may be studied either as concrete sets of points and lines in a specific geometry, such as the Euclidean or projective planes (these are said to be realizable in that geometry), or as a type of abstract incidence geometry. In the latter case they are closely related to regular hypergraphs and biregular bipartite graphs, but with some additional restrictions: every two points of the incidence structure can be associated with at most one line, and every two lines can be associated with at most one point. That is, the girth of the corresponding bipartite graph (the Levi graph of the configuration) must be at least six.
In connection with: Configuration (geometry)
Title combos: Configuration geometry
Description combos: Thomas as in popularized by planes theorem introduced 1849
Perles may refer to Perles, Aisne, a commune in the Aisne department in Picardie in northern France Perles-et-Castelet, a commune in the Ariège department in southwestern France Perles, the French name for Pieterlen, Switzerland Alfred Perlès (1897–1990), Austrian-British writer George Perles (1934–2020), American football coach Joseph Perles (1835–1894), Hungarian rabbi Micha Perles, Israeli mathematician Perles configuration Tessalon Perles
In connection with: Perles
Description combos: may Perles commune Perles in department in Perles Austrian
In computing, especially computational geometry, a real RAM (random-access machine) is a mathematical model of a computer that can compute with exact real numbers instead of the binary fixed-point or floating-point numbers used by most actual computers. The real RAM was formulated by Michael Ian Shamos in his 1978 Ph.D. dissertation.
In connection with: Real RAM
Title combos: Real RAM
Description combos: binary with of especially actual access dissertation especially fixed

In geometry, the Perles configuration is a system of nine points and nine lines in the Euclidean plane for which every combinatorially equivalent realization has at least one irrational number as one of its coordinates. It can be constructed from the diagonals and symmetry lines of a regular pentagon, and their crossing points. All of the realizations of the Perles configuration in the projective plane are equivalent to each other under projective transformations. The Perles configuration is the smallest configuration of points and lines that cannot be realized with rational coordinates. It is named after Micha Perles, who used it to construct an eight-dimensional convex polytope that cannot be given rational number coordinates and that have the fewest vertices (twelve) of any known irrational polytope.
In connection with: Perles configuration
Title combos: configuration Perles
Description combos: one points points which of the of their number
Micha Asher Perles (Hebrew: מיכה פרלס) is an Israeli mathematician working in geometry, a professor emeritus at the Hebrew University. He earned his Ph.D. in 1964 from the Hebrew University, under the supervision of Branko Grünbaum. His contributions include: The Perles configuration, a set of nine points in the Euclidean plane whose collinearities can be realized only by using irrational numbers as coordinates. Perles used this configuration to prove the existence of irrational polytopes in higher dimensions. The Perles–Sauer–Shelah lemma, a result in extremal set theory whose proof was credited to Perles by Saharon Shelah. The pumping lemma for context-free languages, a widely used method for proving that a language is not context-free that Perles discovered with Yehoshua Bar-Hillel and Eli Shamir. Notable students of Perles include Noga Alon, Gil Kalai, and Nati Linial.
In connection with: Micha Perles
Title combos: Perles Micha
Description combos: contributions plane the not Shamir under configuration students Ph
In the mathematical theory of matroids, a matroid representation is a family of vectors whose linear independence relation is the same as that of a given matroid. Matroid representations are analogous to group representations; both types of representation provide abstract algebraic structures (matroids and groups respectively) with concrete descriptions in terms of linear algebra. A linear matroid is a matroid that has a representation, and an F-linear matroid (for a field F) is a matroid that has a representation using a vector space over F. Matroid representation theory studies the existence of representations and the properties of linear matroids.
In connection with: Matroid representation
Title combos: Matroid representation
Description combos: analogous matroid existence representation theory linear is that representations
Quick Access
Tag Explorer
Discover Fresh Ideas in the Universe of aéPiot
MultiSearch | Search | Tag Explorer
SHEET MUSIC | DIGITAL DOWNLOADS
© aéPiot - MultiSearch Tag Explorer. All rights reserved.
Hosted by HOSTGATE