OLD SARTELL BRIDGE
Go

Mississippi RiverThe Mississippi River is the primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, after the Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for 2,340 miles (3,766 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the world's tenth-largest river by discharge flow, and the largest in North America. Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Many were hunter-gatherers, but some, such as the Mound Builders, formed prolific agricultural and urban civilizations, and some practiced aquaculture. The arrival of Europeans in the 16th century changed the native way of life as first explorers, then settlers, ventured into the basin in increasing numbers. The river served sometimes as a barrier, forming borders for New Spain, New France, and the early United States, and throughout as a vital transportation artery and communications link. In the 19th century, during the height of the ideology of manifest destiny, the Mississippi and several tributaries, most notably its largest, the Ohio and Missouri, formed pathways for the western expansion of the United States. The river also became the subject of American literature, particularly in the writings of Mark Twain. Formed from thick layers of the river's silt deposits, the Mississippi embayment, and American Bottom are some of the most fertile regions of the United States; steamboats were widely used in the 19th and early 20th centuries to ship agricultural and industrial goods. During the American Civil War, the Mississippi's final capture by Union forces marked a turning point to victory for the Union. Because of the substantial growth of cities and the larger ships and barges that replaced steamboats, the first decades of the 20th century saw the construction of massive engineering works such as levees, locks and dams, often built in combination. A major focus of this work has been to prevent the lower Mississippi from shifting into the channel of the Atchafalaya River and bypassing New Orleans. Since the 20th century, the Mississippi River has also experienced major pollution and environmental problems, most notably elevated nutrient and chemical levels from agricultural runoff, the primary contributor to the Gulf of Mexico dead zone.

Sartell, MinnesotaSartell is a city in Benton and Stearns Counties in the U.S. state of Minnesota that straddles the Mississippi River. It is part of the St. Cloud Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 19,351 at the 2020 census, making it St. Cloud's most populous suburb and the fourth-largest city in central Minnesota, after St. Cloud, Elk River, and Willmar.
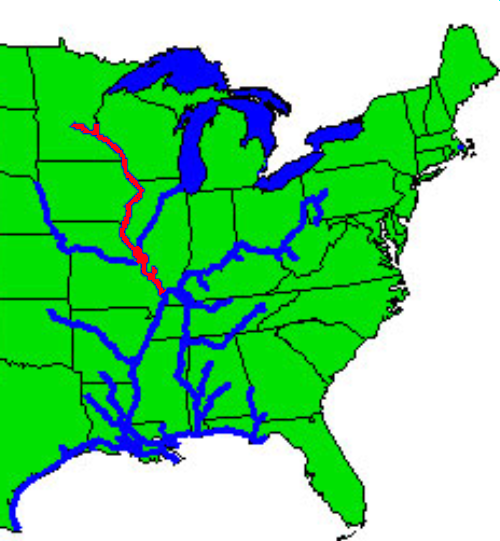
List of crossings of the Upper Mississippi RiverThis is a list of all current and notable former bridges or other crossings of the Upper Mississippi River which begins at the Mississippi River's source and extends to its confluence with the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois.

Minnesota State Highway 15Minnesota State Highway 15 (MN 15) is a 154.322-mile-long (248.357 km) highway in south-central and central Minnesota, which runs from Iowa Highway 15 at the Iowa state line and continues north to its northern terminus at its interchange with U.S. Highway 10 outside of Sartell and Sauk Rapids, north of St. Cloud.

Old Sartell BridgeThe Old Sartell Bridge is a bridge that spans the Mississippi River in the city of Sartell in the U.S. state of Minnesota. Though still standing, it is closed to traffic and was replaced by the Sartell Bridge constructed about 850 feet downstream. The bridge is around 1000 feet downstream of the Sartell Dam. The bridge was built during a six-month period in 1914, but over the years the bridge became congested and less able to carry heavy traffic. As early as 1957, heavy trucks were found to be too much for the span. When the new bridge was built in 1984, the old bridge was used as a pedestrian footbridge, but it became impractical for this use since there was a factory at the east end. The bridge carries utility lines and was reopened for pedestrian traffic on June 9, 2023 with lookouts for fishing. It is accessible to pedestrians from the west and closed on the east end. The Old Sartell Bridge is a three span pin connected camelback through truss. The camelback design is a specific type of Parker truss, where the polygonal top chord is composed of exactly five sections. Each span of the Old Sartell Bridge is composed of six panels. The bridge is supported by concrete piers and abutments.

Sartell BridgeThe Sartell Bridge is a bridge that spans the Mississippi River in the city of Sartell in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The bridge also spans a roadway, property belonging to the Sartell paper mill, and a rail line on the east side of the river.
Verso Paper Sartell MillThe Sartell Paper Mill, officially the Verso Paper Sartell Mill, was a paper mill located in the city of Sartell in the U.S. state of Minnesota, operating from 1905 until a disastrous explosion in 2012.
Quick Access
Tag Explorer
Discover Fresh Ideas in the Universe of aéPiot
MultiSearch | Search | Tag Explorer
SHEET MUSIC | DIGITAL DOWNLOADS