Nurses Know How To Give People Injections

👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
‘The few positives that have come out of the pandemic must be retained’
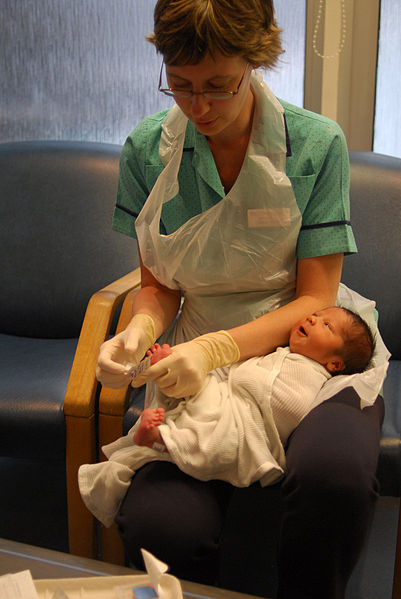
Injection technique 1: administering drugs via the intramuscular route
Part 1 of this two-part series on injection techniques describes the evidence base and procedure for administering an intramuscular injection
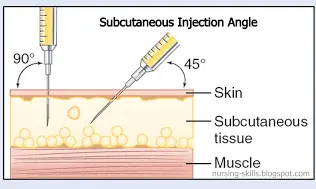
The intramuscular route allows the rapid absorption of drugs into the circulation. Using the correct injection technique and selecting the correct site will minimise the risk of complications. This is part 1 of a two-part series on injection techniques. Part 2 covers the subcutaneous route.
Citation: Shepherd E (2018) Injection technique 1: administering drugs via the intramuscular route. Nursing Times [online]; 114: 8, 23-25.
Author: Eileen Shepherd is clinical editor at Nursing Times.
Drugs administered by the intramuscular (IM) route are deposited into vascular muscle tissue, which allows for rapid absorption into the circulation (Dougherty and Lister, 2015; Ogston-Tuck, 2014).
Complications of poorly performed IM injection include:
These complications can be avoided if the site for injection is accurately identified and a skilled evidence-based technique is used (Greenway, 2014).
Box 1. How to reduce pain caused by injection technique
Source: Dougherty and Lister (2015)
The procedure for IM injection has been discussed widely in the literature but there are concerns that nurses are still performing outdated and ritualistic practice relating to site selection, aspirating back on the syringe (Greenway, 2014) and skin cleansing.
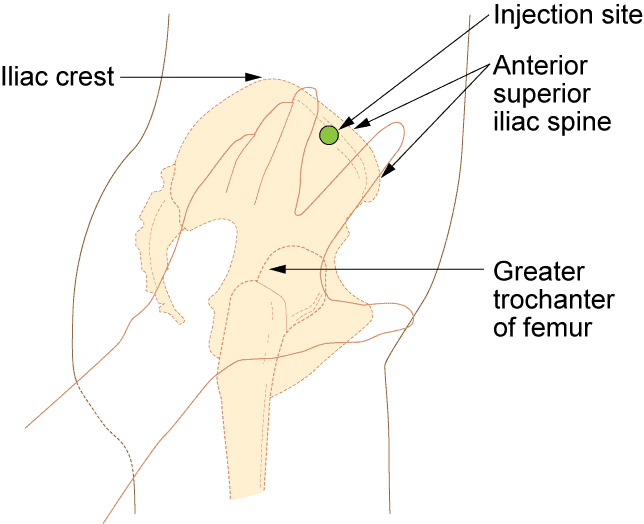
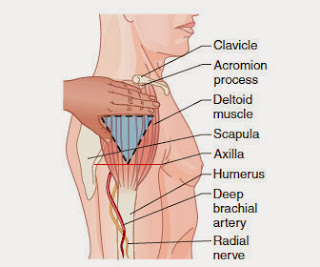
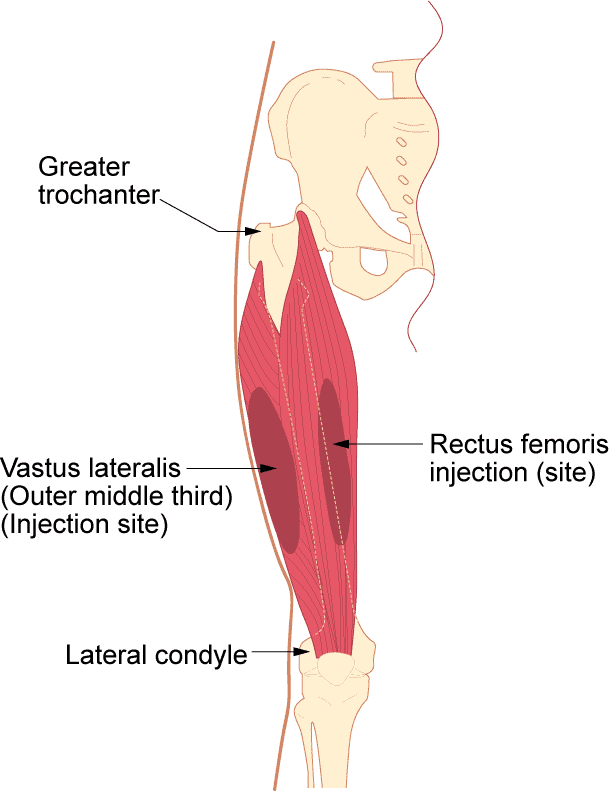
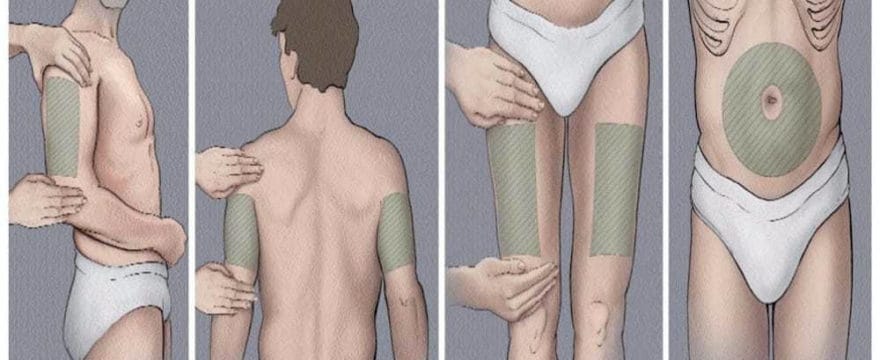
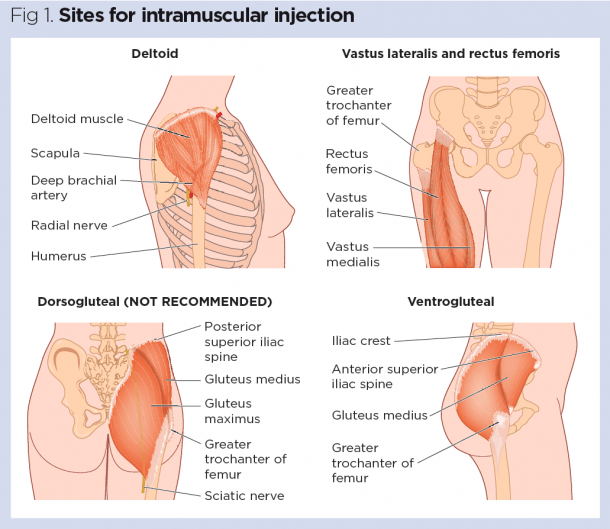
Four muscle sites are recommended for IM administration (Fig 1, Table 1):
Traditionally the dorsogluteal (DG) muscle was used for IM injections but this muscle is in close proximity to a major blood vessel and nerves, with sciatic nerve injury a recognised complication (Small, 2004). In addition, drug absorption from the DG muscle may be slower than other sites and this can lead to a build-up of drugs in the tissues and risk of overdose (Malkin, 2008). Many patients find the use of the DG site intrusive and are reluctant to undress to give access to the relevant area. For these reasons, the DG muscle is no longer recommended for IM injections – in spite of this, many nurses continue to use it (Ogston-Tuck,2014; Walsh and Brophy, 2011; Malkin, 2008).
Safety needles should be used for IM injections to reduce the risk of needle-stick injury (Health and Safety Executive, 2013).
Needle size is measured in gauges (diameter of the needle). A 21G is commonly used but selection depends on the viscosity of the liquid being injected (Dougherty and Lister, 2015). Public Health England (2013) recommends 23G or 25G needle for IM vaccines.
Needles need to be long enough to ensure the drug is injected into the muscle; length depends on:
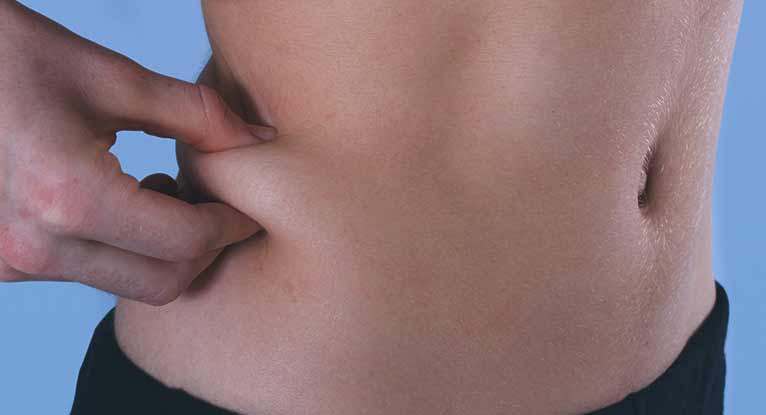
Women have more subcutaneous fat than men (Zaybak et al, 2007) and consideration needs to be given to using longer needles for patients who are obese. PHE (2013) recommends that a 25mm or 38mm needle is used in adults.
Traditionally nurses have been taught to leave a few millimetres between the skin and the hub of the needle in case the needle breaks off during the injection. This practice is not evidence based, may cause medication to be delivered into the subcutaneous fat layer and, with modern single-use needles, is no longer necessary (Greenway, 2014).
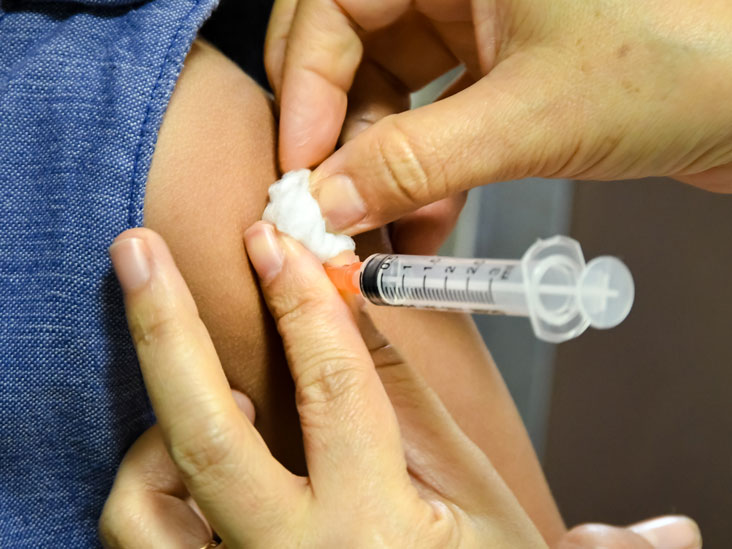
There is some debate about using alcohol-impregnated swabs to clean injection sites. PHE (2013) suggests that, if a patient is physically clean and generally in good health, swabbing the skin is not required.
In older or immunocompromised patients, skin preparation using an alcohol-impregnated swab may be recommended (70% isopropyl alcohol) (Dougherty and Lister, 2015). Follow local policy.
It is common practice to draw back on a syringe after the needle is inserted to check whether it is in a blood vessel. While it is important to aspirate if the DG muscle site is used – because of proximity to the gluteal artery – it is not required for other IM injection sites (PHE, 2013; Malkin, 2008).
The World Health Organization (2010, 2009) states that gloves need not be worn for this procedure if the health worker’s and patient’s skin are intact. It also notes that gloves do not protect against needle-stick injury. Nurses need to risk assess individual patients (Royal College of Nursing, 2018) and be aware of local policies for glove use.
Box 2. ‘Five rights’ of medicines administration
Ağaç E, Güneş UY (2011) Effect on pain of changing the needle prior to administering medicines intramuscularly: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Advanced Nursing; 67: 3, 563-568.
Dougherty L, Lister S (2015) The Royal Marsden Hospital Manual of Clinical Nursing Procedures. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Greenway K (2014) Rituals in nursing: intramuscular injection. Journal of Clinical Nursing; 23: 23-24, 3583-3588.
Health and Safety Executive (2013) Health and Safety (Sharp Instruments in Healthcare) Regulations 2013: Guidance for Employers and Employees.
Malkin B (2008) Are techniques used for intramuscular injection based on research evidence? Nursing Times; 104: 50/51, 48-51.
Ogston-Tuck S (2014) Intramuscular injection technique: an evidence-based approach. Nursing Standard; 29: 4, 52-59.
Public Health England (2013) Immunisation Procedures: The Green Book, Chapter 4.
Royal College of Nursing (2018) Tools of the Trade: Guidance for Health Care Staff on Glove Use and the Prevention of Contact Dermatitis.
Small SP (2004) Preventing sciatic nerve injury from intramuscular injections: literature review. Journal of Advanced Nursing; 47: 3, 287-296.
Walsh L, Brophy K (2011) Staff nurses’ sites of choice for administering intramuscular injection to adult patients in the acute care setting. Journal of Advanced Nursing; 67: 5, 1034-1040.
World Health Organization (2010) WHO Best Practices for Injections and Related Procedures Toolkit.
World Health Organization (2009) WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care.
Zaybak A et al (2007) Does obesity prevent the needle from reaching muscle in intramuscular injections? Journal of Advanced Nursing; 58: 6, 552-556.
Sign in or Register a new account to join the discussion.
Please remember that the submission of any material is governed by our Terms and Conditions and by submitting material you confirm your agreement to these Terms and Conditions. Links may be included in your comments but HTML is not permitted.
News about identification of genetic variants may be a hot topic but…
Dorset HealthCare University NHS Foundation Trust
EMAP Publishing Limited Company number 7880758 (England & Wales) Registered address: 7th Floor, Vantage London, Great West Road, Brentford, United Kingdom, TW8 9AG
We use cookies to personalize and improve your experience on our site. Visit our Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy to learn more. You can opt out of some cookies by adjusting your browser settings. More information on how to do this can be found in the cookie policy. By using our site, you agree to our use of cookies. Accept
To support you through the pandemic we have made all coronavirus clinical content free to registered users. Our clinical zone will aid your practice while our news coverage will keep you up to date. Plus free online CPD including infection control and patient isolation
https://slate.com/human-interest/2021/01/how-nurses-give-injections-what-makes-a-good...
Перевести · 14.01.2021 · If it’s upside down, it’s actually harder to get it in. “Bevel up” is something that you teach when you teach people how to give injections. The other thing is to be quick. The …
https://www.who.int/occupational_health/activities/1bestprac.pdf
How to give injections safely: Outline • Eliminate unnecessary injections • Use sterile injection equipment and sharps • Prepare and give injections without contamination or needle-sticks • Dispose of sharps to prevent reuse and harmful waste
https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/assessment-skills/injection-technique-1...
Introduction
Evidence Base
Equipment
Procedure
Drugs administered by the intramuscular (IM) route are deposited into vascular muscle tissue, which allows for rapid absorption into the circulation (Dougherty and Lister, 2015; Ogston-Tuck, 2014). Complications of poorly performed IM injection in…
https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44298/9789241599252_eng.pdf;sequence=1
WHO best practices for injections and related procedures toolkit. WHO/EHT/10.02 1.Injections – adverse effects. 2.Injections – standards. 3.Needlestick injuries – prevention and control. …
https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/diabetes-clinical-archive/injection...
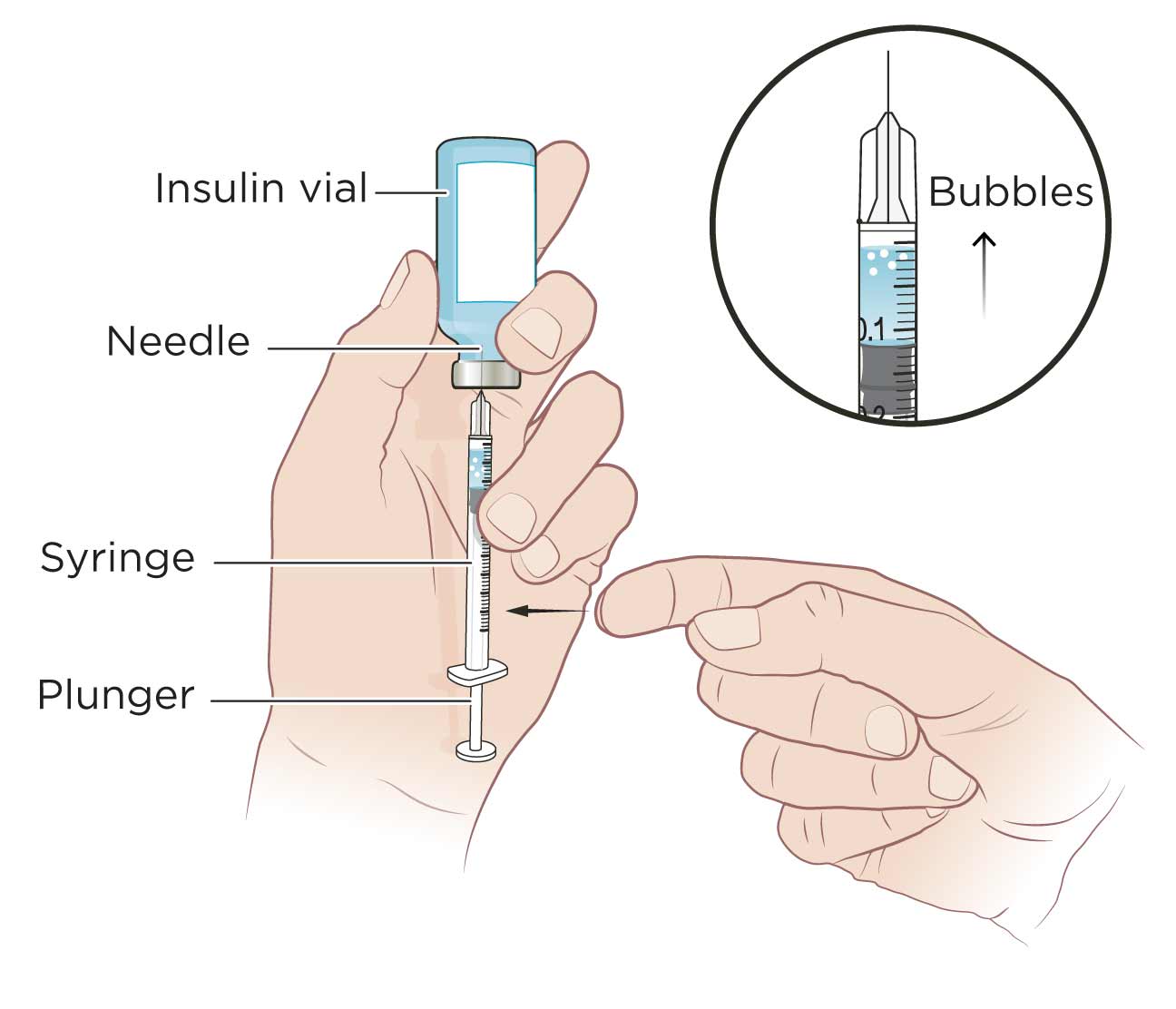
Перевести · 02.03.2012 · Sequence for injecting. The optimal sequence for injection technique should be: Make a lifted skin fold if necessary; Insert the needle into the skin at a 90° angle; Administer insulin; Leave the needle in the skin for at least 10 seconds after the insulin has been injected; Withdraw the needle from the skin;
Who guide for nurses who give injections?
Who guide for nurses who give injections?
World Health Organization International Council of Nurses A guide for nurses and others who give injections The World Health Organization (WHO) defines a safe injection to be one that does not harm the recipient, does not harm the health care worker, and does not harm the community
www.who.int/occupational_health/activitie…
Is the IM injection still performed by nurses?
Is the IM injection still performed by nurses?
The procedure for IM injection has been discussed widely in the literature but there are concerns that nurses are still performing outdated and ritualistic practice relating to site selection, aspirating back on the syringe (Greenway, 2014) and skin cleansing. Ventrogluteal.
www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/ass…
What are who best practices for injections and related procedures?
What are who best practices for injections and related procedures?
WHO best practices for injections and related procedures toolkit. WHO/EHT/10.02 1.Injections – adverse effects. 2.Injections – standards. 3.Needlestick injuries – prevention and control. 4.Syringes – utilization. 5.Needles – utilization. 6.Cross infection – prevention and control. 7.Guidelines.
apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/…
Can nurses deliver intravitreal drug injections?
Can nurses deliver intravitreal drug injections?
He and his colleagues are now offering training to the increasing number of other hospitals which are also going down the route of using nurses to deliver intravitreal drug injections. However, they are also very clear that setting up a service involves more than simply training nurses in a technique.
www.rnib.org.uk/nb-online/nurses-take-ch…
https://www.rnib.org.uk/nb-online/nurses-take-charge-needles
Перевести · 09.06.2015 · Originally the official position, including the Royal College of Ophthalmologists (RCOPth) guidelines, was that these injections should be delivered only by doctors …
https://www.portea.com/nursing/injection
Перевести · Getting injection service at home with the assistance of trained and experienced nurses comes with several benefits. Find below some of the prominent benefits of having injections …
HOW TO GIVE IVF INJECTIONS | NURSE TIPS
YouTube › World Health Organization (WHO)
How to Prepare and Give Subcutaneous Injections
How to give Intramuscular Vitamin B12 Injections
How to Give an IM Intramuscular injection in the Buttocks | Dorsogluteal Hip Injection Technique
https://www.nurses.co.uk/nursing/blog/how-to-fully-prepare-for-your-first-nursing...
Перевести · 1. Watch as many injections as possible. So, using injections as an example, I would recommend you watch as many injections as you possibly can. And obviously, this is going to …
https://nypost.com/2020/12/19/travel-nurses-are-making-11k-a-week-to-give-covid-vaccines
Перевести · 20.12.2020 · One local RN said she was recruited to do COVID-19 vaccinations at a rate of $70 an hour for a 40-hour week plus a stipend of $2,200 for a total of $5,000 a week. But she said she met other nurses ...
РекламаPeople you know за 449 руб. Только сегодня! Бесплатная доставка.
Гарантия низкой цены · Мега скидки до 70%
РекламаООО "Техноспринт Нева" - Ваш сервисный партнер по ремонту промышленной электроники · будни 9:00-17:30
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Lick Pussy Teens Hd
Aidra Fox Ryan Madison Jean Fucking
Teen Handjob Vk
Pussy Licking Videos Vk
John Updike Ace In The Hole
How nurses give injections: What makes a good shot.
Giving safe injections - WHO
Injection technique 1: administering drugs via the ...
WHO best practices for injections and related procedures ...
Nurses are the new injection service - RNIB - See differently
Nurse for Injection Solutions At Home | Portea
How to fully prepare for your first nursing ... - Nurses.co.uk
Nurses Know How To Give People Injections






















/healthcare-medical-job-titles-2061494-v2-db29fe9c11264511ba1737aeb7f2f1a9.png)















%3amax_bytes(150000)%3astrip_icc()/how-to-give-an-insulin-injection-1087305-453dfccdebb448918053b400119fcbe1.png)