Net Spread

⚡ ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
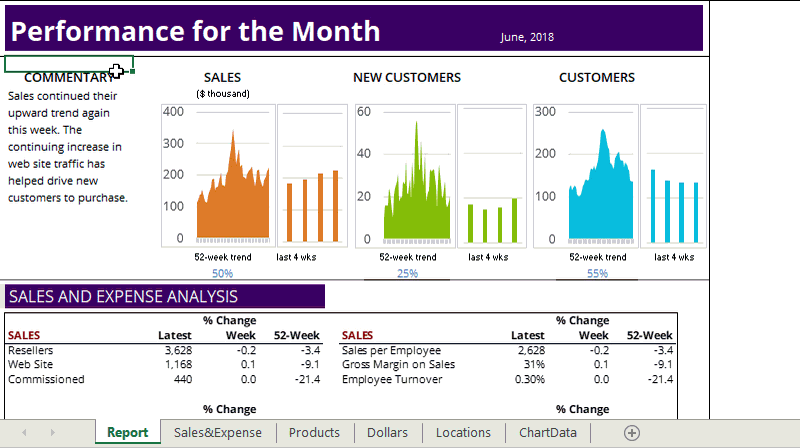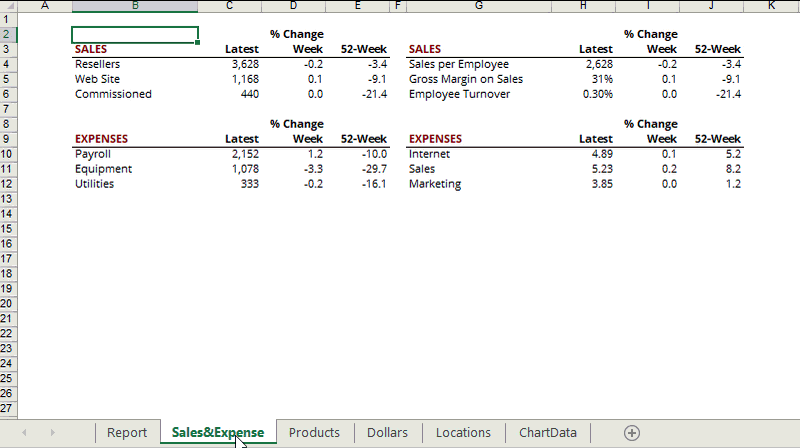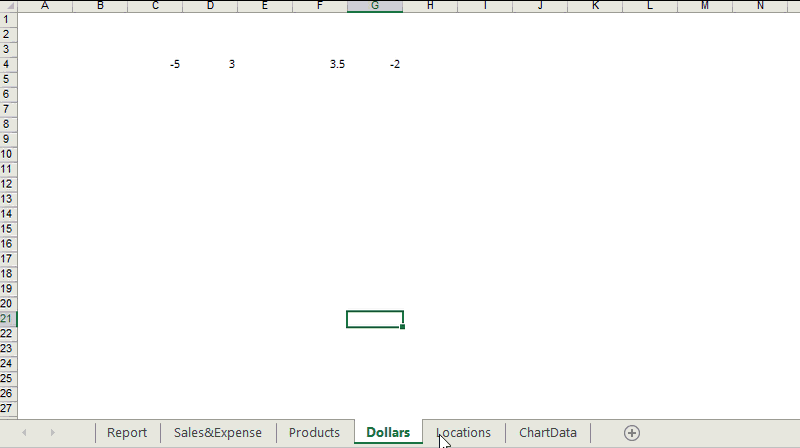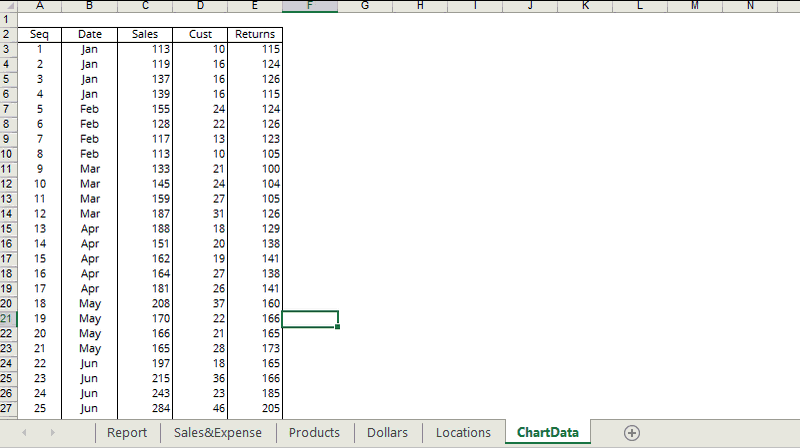
Net Spread
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Net interest spread refers to the difference in borrowing and lending rates of financial institutions (such as banks) in nominal terms. It is considered analogous to the gross margin of non-financial companies.
Net interest spread is expressed as interest yield on earning assets (any asset, such as a loan, that generates interest income) minus interest rates paid on borrowed funds.
Net interest spread is similar to net interest margin ; net interest spread expresses the nominal average difference between borrowing and lending rates, without compensating for the fact that the amount of earning assets and borrowed funds may be different.
For example, a bank has average loans to customers of $100, and earns gross interest income of $6. The interest yield is 6/100 = 6%. A bank takes deposits from customers and pays 1% to those customers. The bank lends its customers money at 6%. The bank's net interest spread is 5%.
Successful Bank Asset/Liability Management: A Guide to the Future Beyond Gap, John W. Bitner, Robert A. Goddard, 1992, p. 185.
There are several popular commercial net interest spread software packages to help banks manage and grow their net interest spread effectively. Among these are:
Download NET Spreadsheet | Spread . NET
Net interest spread - Wikipedia
Net Interest Rate Spread Definition
FreshPorts -- net / spread : The Spread Group Communication System...
net spread 🎓 перевод с английского на русский
The net interest rate spread is the difference between the interest rate a bank pays to depositors and the interest rate it receives from loans to consumers. The net interest rate spread is instrumental to a bank’s profitability. It can be useful to think of the net interest rate as a profit margin.
Sponsored
Compete Risk Free with $100,000 in Virtual Cash
Put your trading skills to the test with our
FREE Stock Simulator.
Compete with thousands of Investopedia traders and trade your way to the top! Submit trades in a virtual environment before you start risking your own money.
Practice trading strategies
so that when you're ready to enter the real market, you've had the practice you need.
Try our Stock Simulator today >>
Cost of funds refers to the interest rate paid by financial institutions for the funds that they deploy in their business.
Discount window is a central bank lending facility meant to help banks manage short-term liquidity needs.
The Wall Street Journal Prime Rate is an average of 10 banks' prime rates on short-term loans and published in WSJ.
A subprime loan is a loan offered at a rate above prime to individuals who do not qualify for prime-rate loans.
Federal funds rate is the target interest rate set by the Fed at which commercial banks borrow and lend their excess reserves to each other overnight.
Adjustment credit is a short-term loan, which a Federal Reserve Bank extends to a smaller commercial bank.
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
Investopedia is part of the Dotdash publishing family.
The net interest rate spread is the difference between the average yield that a financial institution receives from loans—along with other interest-accruing activities—and the average rate it pays on deposits and borrowings. The net interest rate spread is a key determinant of a financial institution’s profitability (or lack thereof).
Loan-granting institutions, such as commercial banks , receive interest income from a number of sources. Deposits (often called core deposits ) are a primary source, generally in the forms of checking and savings accounts or certificates of deposit (CDs). These are often obtained at low rates. Banks also obtain funds through shareholder equity, wholesale deposits, and debt issuance. Banks issue a variety of loans—such as mortgages on property, home equity lending, student loans, car loans, and credit card lending—that are offered at higher interest rates.
The primary business of a bank is managing the spread between the interest rate on deposits that it pays consumers and the rate it receives from their loans . In other words, when the interest that a bank earns from loans is greater than the interest it pays on deposits, it generates income from the interest rate spread. In simple terms, net interest rates spreads are like profit margins .
The greater the spread, the more profitable the financial institution is likely to be. However, this is just the basic view, and financial institutions work on creative customer acquisition, customer retention and loyalty and principal investing strategies. Their individual strategies help them compete and differentiate themselves from other financial institutions.
The federal (“fed") funds rate is an important component in determining the net interest rate spread.
Most commercial banks (such as savings and loans ) generate their main source of profits through net interest rates spreads. For instance, they may credit depositors 1.25% on their money while issuing a mortgage to a home buyer charging 4.75%. In this case the net interest rate spread would be 3.5%, minus any fees or costs incurred by the bank in effecting both transactions.
Although we won’t delve into how rates are determined in the market, several factors drive rates, including monetary policy set by the Federal Reserve Bank and the yields on U.S. Treasuries . While open-market activities ultimately shape the net interest rate spread, the federal (“fed") funds rate plays a large role in determining the rate at which an institution lends immediate funds. Indeed, according to the U.S. Federal Reserve, the federal funds rate is “the interest rate at which depository institutions lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight.”
This applies to the biggest, most creditworthy institutions as they maintain the mandated amount of reserve required . Thus, the fed funds rate is a base interest rate, one by which all other interest rates in the U.S. are determined. The fed funds rate is a key indicator of the health of the U.S. economy.
Advanced Technical Analysis Concepts
Sex Logan Pierce
Real Secretary Porno
Milf Fuck Missionary
Oral Sex Jones Jay Com
Mom Son Sleep Porn