NeRF-Supervised Deep Stereo
https://t.me/reading_ai, @AfeliaN🗂️ Project Page
📄 Paper
📎 GitHub
🗓 Date: 9 Jun 2023
Main idea
- Motivation: training deep stereo networks requires a lot of data. To solve this problem self-supervised methods are presented, but they are usually not so effective at dealing with ill-posed stereo settings (e.g. occlusions, non-Lambertian surfaces, etc.).
- Solution: Using NeRF it is possible to render stereopairs to generate the new dataset and provide rendered depth to supervise training process.
Pipeline

- Step one: image collection
Firstly the authors collected multi-view images from multiple static scenes and using COLMAP the camera poses and intrinsic were calculated.
2. Step two: learn NeRF for each scene
3. Step three: stereo pairs rendering
- generate a set of stereo extrinsic parameters (rotation is the identity matrix and translation b - vector representing translation along an x-axis)
- render two novel views (for +- b translations). This creates a stereo triplet in which the three images are perfectly rectified

- the disparity is extracted from rendered depth

4. Step four: NeRF-Supervised Training Regime
To train the model the authors use several losses
- Triplet Photometric loss
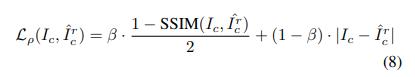
where \hat{I^r_c} - is the reconstructed image from the predicted disparity.
- To deal with occlusions the authors compute the same loss but for the third image. So final results can be estimated as following:

- Loss between predicted and rendered disparities

But as depth maps rendered by NeRF usually contain artifacts the authors additionally use the Ambient Occlusion to measure the confidence of rendered depth and use a filtering mechanism to preserve only the most reliable pixels
The final loss can be written as following:

Implementation details
Models:
- Dataset criation: Instant NGP, COLMAP
- Stereo-models: RAFT-Stereo, PSMNet, CFNet
Evaluation datasets: KITTI, Midd-A, Midd-21
Metrics: PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, KID scores
Compared with: MfS with 3 different Stereo networks
Pros and cons
- Pros: the idea of using NeRF to supervise training or generate new data is very promising for depth estimation problem
- Limitations: Samples collected so far are limited to small-scale, static scenes.
Results


