Multi Hole

💣 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 ALL INFORMATION CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
pokupki.market.yandex.ru/Опорная-тарелка-унив...
РекламаКэшбэк до 5% баллами и экономия до 99% для подписчиков Яндекс.Плюса. · Москва · 20482 · круглосуточно
vseinstrumenti.ru/Орбитальная-шлифовал...
РекламаВыгодные цены. Самовывоз/доставка. Сервис, гарантия! · Москва · пн-пт 8:00-20:00, сб-вс 9:00-18:00
Более 300 000 товаров · 15 лет на рынке
https://www.surreysensors.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Multihole-probes.pdf
2 Multi-hole probes 2.1 Seven-hole probes - current practice Seven-hole pressure probes operate on much the same principle as five-hole probes, though they do tend to be …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2238785419322690
Перевести · 01.05.2020 · Poly-drill head (PDH) or a multi-spindle system is a drilling system that can be used to increase productivity by drilling multiple holes simultaneously and thus, reducing the overall drilling time . Therefore, PDH is one way to produce a large number of holes …
https://certainerror.com/portfolio-view/multi-hole-pressure-probes
Перевести · 18.08.2016 · Multi-hole probe calibration methods are distinguished by the definitions of the four pressure coefficients. Error propagates from the measured …
www.alava-ing.es/repositorio/f9d8/pdf/2101/2/conventional-multiholes-probes.pdf?d=1
Conventional Multi-Hole Probes Introduction: Multi-hole probes are fluid mechanics instruments designed to measure the flow velocity and pressure through direct …
multi hole puncher testing on paper material
YouTube › Punching machine for plastic bag
CNC 3018 drill multi hole size and do board cut
Multi-hole Injector Simulations and Needle Transients
Multi hole punch machine for fruit bag packing
YouTube › Punching machine for plastic bag
multi hole punch machine on fruit bag packing
YouTube › Punching machine for plastic bag
Multi-hole Injector Simulations and Needle Transients
https://www.amazon.com/multi-hole-punch/s?k=multi+hole+punch
мая 07, 2021 · Amazon.com: multi hole pun…
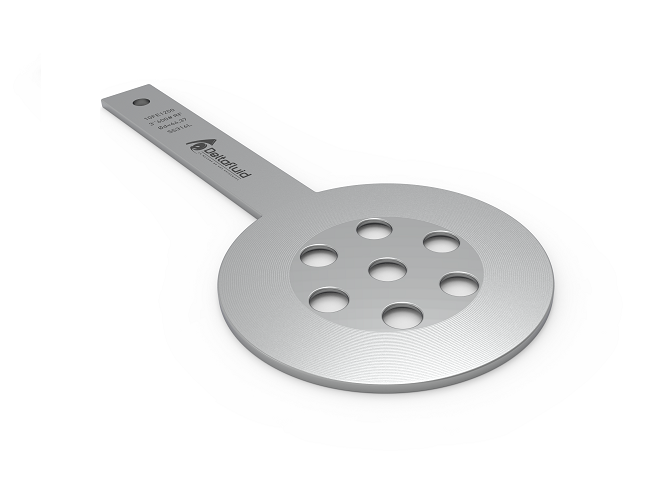
https://www.europages.com/filestore/product/3a/b1/Multi-hole-20orifice-20plate-20Rev.1...
ISO5167 standard The multi-holes orifice plate is a non-standardized flow element but is designed and manufactured according to ISO5167 standard requirements. The sizing of multi-holes …
https://www.althensensors.com/sensors/pressure-sensors/multi-hole-pressure-probes
Перевести · Multi-hole Pressure Probes Pressure Sensors Multi-hole Pressure Probes. Wide range of 5, 7 or 12 hole probes for flow measurement. View …
https://scarabeads.com/collections/multi-hole-beads
Перевести · Multi hole beads is a main trend in the beadwork recently. The beads have multi hole allow to create extraordinary things. The wide variety of multi hole …
https://www.sealconusa.com/products/liquid-tight-strain-relief-fittings/nylon/multihole/pg
Перевести · Строк: 67 · Nylon Multi Hole Strain Relief PG Thread | Cord Grip. Our Strain Reliefs also known as Cable Glands or Cord Grips fulfill the highest demands of quality …
pokupki.market.yandex.ru/Опорная-тарелка-унив...
РекламаКэшбэк до 5% баллами и экономия до 99% для подписчиков Яндекс.Плюса. · Москва · 20482 · круглосуточно
vseinstrumenti.ru/Орбитальная-шлифовал...
РекламаВыгодные цены. Самовывоз/доставка. Сервис, гарантия! · Москва · пн-пт 8:00-20:00, сб-вс 9:00-18:00
Более 300 000 товаров · 15 лет на рынке
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
Volume 9, Issue 3, May–June 2020, Pages 3994-4006
Poly-drill heads are used in mass production to increase productivity when a large number of holes are required. In this work, drilling experiments on Al5083 aluminium alloy were carried out using a poly-drill head to measure the thrust force and assess hole quality. Analysis of chip formations and post-machining tool condition were evaluated using optical microscopy. Additional drilling tests were conducted using one-shot drilling and results obtained from the two drilling techniques were evaluated against each other. The results showed that the average thrust forces obtained from poly-drill head were slightly lower than those from one-shot drilling. Improvement in hole quality in terms of surface roughness and reduction in chip length were achieved using the poly-drill head. Furthermore, visual inspection of the tools showed that adhesion and built-up edges on drills used in the poly-drill head were lower as compared to drills used in the one-shot drilling. The contribution of input parameters on the measured outputs was determined using an ANOVA statistical tool.
The drilling process constitutes a large portion of all machining processes in several manufacturing industries [1]. In the aerospace industry, drilling is one of the most commonly used machining processes during all manufacturing stages of an aircraft, especially prior to the joining process where a large number of rivets are required for assembly of different structures [2], [3], [4], [5], [6]. A large commercial aircraft wing is joined together by almost 750,000 bolts and rivets [7]. According to Felkins et al. [8], large ships contained well over a million rivets before they were replaced entirely by welding after the 1950’s. The RMS Titanic which sank back in 1912 contained three million rivets. This shows the significance of drilling in the industry. Accordingly, single hole (one-shot) drilling might not be economically feasible in such large structures that require a large number of holes, where alternatives are needed to increase the productivity of the hole making process using multi-spindle heads also known as poly drill heads.
Poor hole quality reduces strength against fatigue due to stress concentration and can result in hole crack initiation within a material. Indeed, it is estimated that poor hole quality is responsible for 60% of all part rejections during final assembly of an aircraft [9]. Furthermore, De Lacalle et al. [10] have noted in their studies that drilling process needs to be monitored and controlled to be used systematically in industrial applications.
Giasin et al. [11] have also reported that drilling concerns arise due to poor hole quality, which subsequently affects dimensional accuracy and surface roughness (Ra). Liu et al. [12] have concluded that the surface quality of a hole deteriorates due to tool-chip friction, which causes fatigue cracks initiation due to the formation of stress concentration zones. According to Uddin et al. [13] burr formation negatively affects the dimensional accuracy, which leads to reworking, additional costs and sometimes damage due to fatigue in assembly. Therefore, deburring is required for the functional reliability of components, where it has been reported by Niknam et al. [14] that deburring accounts for nearly 30% of the total fabrication costs in an aircraft’s fuselage assembly. Furthermore, Nouari et al. [15] have stated that the deterioration of tool condition is another problem due to the formation of built-up edges, which weakens tool edges and ultimately results in fracture failure. Accordingly, manufacturing industries are sensitive to their investments, since using improper machine tools can negatively affect productivity. Thus, drilling is the most challenging and necessary process in different industries and requires further research to reduce incidences of the above problems leading to improvement of hole quality [16].
Mass hole production can be achieved by using poly-drill heads. Poly-drill head (PDH) or a multi-spindle system is a drilling system that can be used to increase productivity by drilling multiple holes simultaneously and thus, reducing the overall drilling time [17]. Therefore, PDH is one way to produce a large number of holes with significant time and cost savings, as well as less operator fatigue [18].
Aluminum and its alloys are extensively used in aerospace, automotive and marine applications [19]. Aluminium 5083 (Al5083) alloy is resistance to salt water corrosion making it suitable for marine applications. This alloy is currently used in marine hulls, shipbuilding and drilling rigs due to its excellent corrosion resistance properties and excellent performance in extremely cold environments [1]. Some researchers who have investigated the machining of aluminium Al5XXX alloys are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Summary of previous studies on machining of Al5XXX alloys.
The surface texture was affected more by Vc, the peripheral relief angle, and the core diameters.
Cutting forces were decreased up to 12% using coolant when the thickness of the undeformed chips was up to 0.282 mm. High f increased C.
Ra is directly influenced by f and drill diameter, however, the increase in rotation speed decreased Ra. The decrease in point angle resulted in built-up edges on the tool which ultimately increased Ra.
The cutting forces and the tool-
tip temperatures increased when the undeformed chip thickness increased in both dry and wet machining. However, at high Vc, the cutting forces in dry machining of Al5038 were lower than wet machining.
The best surface quality is possible when the cutting fluid pressure ranging 2.5–3.5 bars and f of 0.41–0.45 m/min.
Symbols: C: cutting forces, F: feed force, W: tool wear, T: drilling temperature, feed rate: f, cutting speed: Vc.
An overview of recently cited papers in Table 1 shows that only a handful of studies have been presented on the machining of Al5083. In addition, there are no systematic studies available in open literature that analyze Al5083 using multi-hole drilling techniques. Kechagias et al. [20] have conducted end-milling tests using two flute mill cutters to study the surface finish of Al5083. The tested parameters were cutting speed (Vc), depth of cut, flute angle, rake angle, peripheral relief angles, tool feed and core diameter. They concluded that Vc, the peripheral relief angle, and core diameters have more influence on the surface texture of Al5083. Davoodi et al. [21] have worked on orthogonal cutting process using Al5083 to study cutting and feed forces. They found reduction in cutting forces up to 12% when using coolant and when the thickness of the undeformed chips was up to 0.282 mm. Furthermore, High feed (f) also increased cutting forces. Bahçe et al. [22] have concluded in their study that Ra is directly influenced by f and drill diameter; however, increases in rotation speed led to decreases in Ra. The decrease in point angle resulted in built-up edges on the tool which ultimately increased Ra. They used drilling process; however, the material was Al5005. In another study by Davoodi et al. [23], the influence of cutting parameters on Al5083 was investigated using a turning process. Their findings showed that cutting forces had a direct relation to undeformed chip thickness during both dry and wet machining. Their results also showed that dry machining of Al5083 performs better at high Vc and produces lower cutting forces than in wet cutting. Khorasani et al. [24] have used different machining parameters and coolant pressure to minimize Ra of Al5083 using a high speed milling operation. They concluded that the best surface quality is possible when the cutting fluid ranges between 2.5–3.5 bars and f between 0.41–0.45 m/min.
According to Totten et al. [25] aluminium alloys are ranked into five groups: A, B, C, D, and E in order of increasing length of the chip to decreasing order of surface quality. Al5083 is ranked in group D, which means it has poor machinability. Furthermore, researchers have focused on finding optimized machining processes using one-shot drilling (OSD). None of the previous studies reported the impact of multi-spindle drilling on hole quality in aluminium alloys in general or Al5083 in particular to the authors’ knowledge. Therefore, in this work, a PDH with three adjustable spindles in the assessment of the drilling process is used and compared with OSD in terms of generated thrust force (Fz), average Ra, chips analysis and post-machining tool conditions. The study also evaluates the impact of Vc, f on Fz, Ra, chip formation and post-machining tool conditions. Furthermore, ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is employed to determine the contribution of drilling inpout parameters on output parameters.
The drilling experiments for both the OSD and PDH were performed on a vertical turret milling machine with a maximum spindle speed of 3500 rpm and a feed of 0.04, 0.08 and 0.14 mm/rev. Fig. 1 illustrates the experimental setup of the drilling tests. The pattern of holes using a PDH is given in Fig. 2. The same pattern was used for OSD for consistency of results.
Fig. 1. Experimental setup (a) one-shot drilling (b) poly-drill head.
The thrust force (Fz) was measured using a 3-component piezoelectric dynamometer (KISTLER 9257BA) with a built-in 3-channel charge amplifier. The charge amplifier was connected to the control unit Type 5233A1; where a type 5697A2 Kistler data acquisition system was used for interfacing and controlling charge amplifiers in force measurement. The system was connected via a USB 2.0 port and controlled by DynoWare software type: 2825A through a computer that was used to process the data in a force-time graph plot. The dynamometer was mounted on the machine bed and a support plate with a size of 20 mm × 200 mm × 150 mm was placed on the top of the dynamometer. The workpiece was fixed and bolted on a supporting plate as shown in Fig. 1. A SUNHER PDH type MH 30/13 was used for one-shot multiple drilling.
An Al5083 plate with a thickness of 10 mm and a size of 150 × 200 mm2 was used in this work. The material was purchased from Robert Cameron & Co Pty Ltd, Burswood, Western Australia. The chemical compositions and some other properties of the Al5083 alloy are given in Tables 2 and 3, respectively.
Table 2. Chemical compositions of in Al5083 in wt% [26].
Table 3. Mechanical and physical properties of Al5083 [26].
The recommended point angles for drilling aluminium alloys are 115°–140° depending on the silicon content in the aluminium alloy discussed by Geier et al. [7]. Therefore, 6 mm uncoated high-speed steel (HSS) twist drills with a point angle of 118° and a helix angle of 30° were used for both OSD and PDH. Additional details regarding the drills are provided in Table 4.
Table 4. Description of the drill bit.
The cutting parameters used in these experiments are summarized in Table 5. These combinations were considered based on previous studies and limitations of the vertical milling machine that has three fixed feed rates and a maximum spindle speed of 3500 rpm. A new tool was used to confirm the initial conditions of each drilling trial and to minimize any effect arising from tool wear. All the drilling processes were carried out under dry cutting conditions. The reason for choosing dry cutting conditions relate to the environmental risks, reduction in cost and problems related to recycling of chips that also encouraged industries in favour of dry machining [27]. Furthermore, in aircraft industries cutting fluids are eliminated or reduced in order to avoid the need for cleaning the structures before placing the rivets to achieve high-quality holes, especially ones free from burrs or to eliminate the need to deburr before riveting [28].
The surface roughness (Ra) of the holes was measured using a portable surface roughness tester TR200 equipped with a natural diamond stylus having a 90° cone angle and a 5 µm tip radius. Ra was measured at 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270° around the hole wall by rotating the sample along its edges, where average values were taken as similar to previous studies [29].
A digital optical microscope was utilized to check the hole quality. All images were taken on a scale of 1 mm. In addition, the analyses of tool wear were done using an optical microscope.
ANOVA is a statistical technique that is used to determine the highest influence that each design parameter presents [30]. ANOVA gives the percent contribution which is used to show how much effect each process parameter has on output responses. In ANOVA, the P-value shows that values less than 0.05 have no effect [31] and F-value is used to check the design parameters with a significant impact on the quality characteristic [32]. The confidence interval chosen in this study is 95% (α = 0.05). Therefore, ANOVA has been applied in this study to measure the importance of each of the process parameters on Fz and Ra in both the drilling process including OSD and PDH.
In a drilling operation, Fz is one of the main force components which represents the interaction of the tool-chip and tool-machined surface as described by Xu et al. [33]. Liu et al. [34] have suggested that Fz depends on input parameters such as Vc, f, tool geometry, tool materials and coatings, number of holes, tool wear and drilling operation. The impact of different cutting parameters on drilling force using OSD has been widely researched [11], [29], [32], [35], [36], [37], [38], [39], [40], [41]. Therefore, in this study, simultaneous drilling using a PDH with three adjustable drills is used. Fig. 3 shows the signals of the Fz of OSD and PDH for one of the drilled-holes. The signals for Fz were obtained from the dynamometer under the time domain by monitoring the feed motion of the tool from the time it entered the workpiece until it exited. It is evident from Fig. 3 that as the drilling process started, there was no force recorded because the tool was not in contact with the workpiece. Soon the tool came in contact with the workpiece, Fz started processing and a sharp increase was recorded. As the tool continued to advance into the workpiece, Fz gradually increased until it reached a steady-state maximum value. When the tool approached the bottom of the workpiece, Fz began to decrease due to lower resistance of the workpiece and ultimately reached to zero value with the completion of the hole drilling.
Fig. 4 shows the average Fz at different cutting parameters. The results indicate that Fz increased with increasing f while no significant impact of Vc on the Fz was noted and only a slight decrease was observed when Vc has increased. Beranoagirre et al. [42] have developed predictive cutting forces mechanistic models in which it was also noticed in both experimental and predictive model that Fz can be increased as f increases. Therefore, the impact of f on Fz was more dominant than Vc which is in agreement with Faraz et al. [43]. This is because the chip thickness which is cut per unit time increases and thus, the material showed resistance against rupturing leading to a higher Fz [44]. Therefore, an increase in f resulted in higher thickness of chips which not only increased Fz but also increased Ra and hence, affected t
Shemale Fuck Guy New
Hair Pulling And Play Seks
Teen Sister Handjob
Sex Free Porn Film
Panty Gagged Mouth Domina
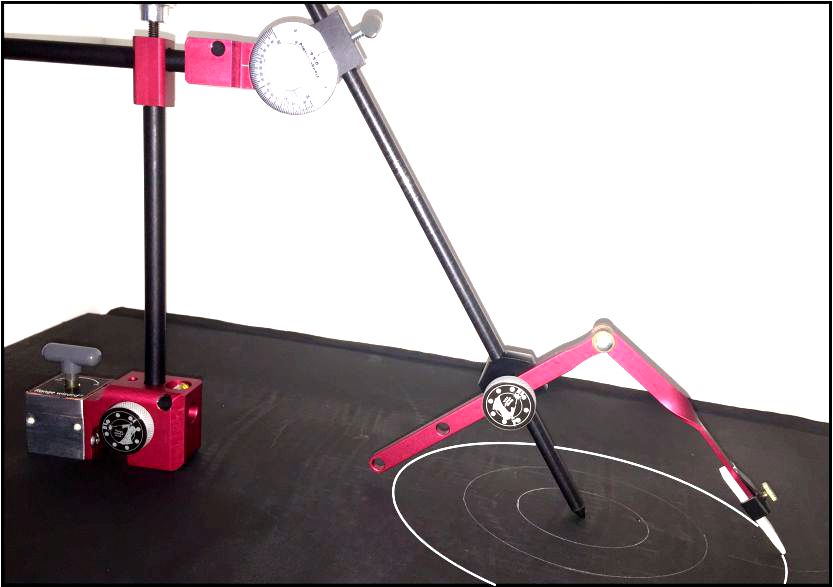
Multi-hole pressure probes - Surrey Sensors
Multi-hole simultaneous drilling of aluminium alloy: A ...
Multi-hole Pressure Probes | CertainError
Conventional Multi-Hole Probes - alava-ing.es
Amazon.com: multi hole punch
Datasheet Orifice plate – multi-holes
Multi-hole Pressure Probes | Althen Sensors
Multi Hole Beads — ScaraBeads US
Multi Hole Strain Relief, Cord Grips, Cable Glands, PG ...
Multi Hole