Metaverse: Structure, Capabilities, and Prospects
Maria SparkA Metaverse is a real sci-fi dream that came true. This is a holistic technology that digitalizes everything around us creating a completely new reality. Can you imagine driving your car, having a meal at your favourite restaurant, or travelling to Rome without leaving home? That becomes possible with the help of Metaverses.
What is it?
A Metaverse is a virtual reality space that operates on an ongoing basis and taps a lot of technologies that immerse users in the digital world. In a nutshell, this is a convergence of physical, augmented and virtual reality in a single online space. Factually, the Metaverse creates another reality with its own laws, economy, and infrastructure.

All events inside the universe occur in real time and do not depend on external factors. There is no limit to the number of participants so everyone can become part of the metaverse. It also has its own economy: people receive coins for the their work, own and dispose of property. In the metaverse, you can use elements of the real world, for example, work on your laptop in virtual space.
Data and digital assets from different platforms are combined. You can use things from Counter-Strike and Fortnite, buy a car from Need for Speed and sell it to friends on Facebook. The Metaverse is filled with "content and experiences" created by its users, both individuals and organizations.
History
Despite the fact that metaverse is only gaining popularity, such projects already existed but were called differently like OpenWorld games. The most popular is Second Life where the player is literally immersed into the "second world". The game was created in 2003 and now has over 1 million active users.
The idea of metaverses became popular in 2021 after Facebook`s transformation. In July, Mark Zuckerberg announced the start of work on a metaverse that would combine different digital platforms based on augmented and virtual reality technologies. The metaverse was meant to become a digital space where users can work, play and communicate.
Meta made a lot of fuss around the metaverse and inspired other business giants to try out the concept. Thus, Microsoft soon started to create its own metaverse, Nike decided to sell digital clothing for the metaverse, and other large IT companies began investing in real estate in the Decentraland gaming metaverse and other sites.
Why do we need a metaverse?
Social interaction
The Metaverse enables us to communicate with people from all over the world. This will help make new friends and keep in touch with relatives from remote places. In fact, the Metaverse will make us radically rethink our day-to-day communication providing new interaction opportunities.
Business
Perhaps, with the advent of a single digital space, many businesses will no longer need to create a physical office for employees, with workplaces and recreation areas. A considerable part of the work will be transferred to virtual reality, especially since the meetings will move from the video format of Zoom and Microsoft Teams services to the digital presence of avatars in a single space. The product visibility, group brainstorming sessions, and live discussions will be available for everyone.

Entertainment & shopping
The Metaverse aims to solve the problem of any entertainment platform providing a better experience than ever. It will be a place for everyone, including mere users, creators, and brands. If you manufacture cars, your brand's presence in the metaverse will not be an advertisement but a place where people will drive your cars.
Distant education
Virtual reality will allow us to get the best education online without leaving home. For example, by paying tuition and passing exams, you can become a student while being a metaverse avatar. This will provide numerous opportunities for students to practice various disciplines.
How does it work?
A Metaverse consists of 7 core components. Each of them is critical for the Metavers development and has a certain edge that technology must cross.
Hardware
It provides sales and support of technologies and devices for access, interaction and development of the Metaverse. This hardware includes equipment for users such as VR headsets, smartphones, tactile gloves and corporate equipment for creating VR or AR environments like industrial cameras, projection systems, sensors.
Networking
Ensuring the continuous operation of the metaverse in real time requires high bandwidth and decentralized data transmission.
Compute
To support the Metaverse, you need powerful systems capable of handling multiple functions. They involve object physics processing, rendering, data matching and synchronization, artificial intelligence, projections, motion capture and translation.
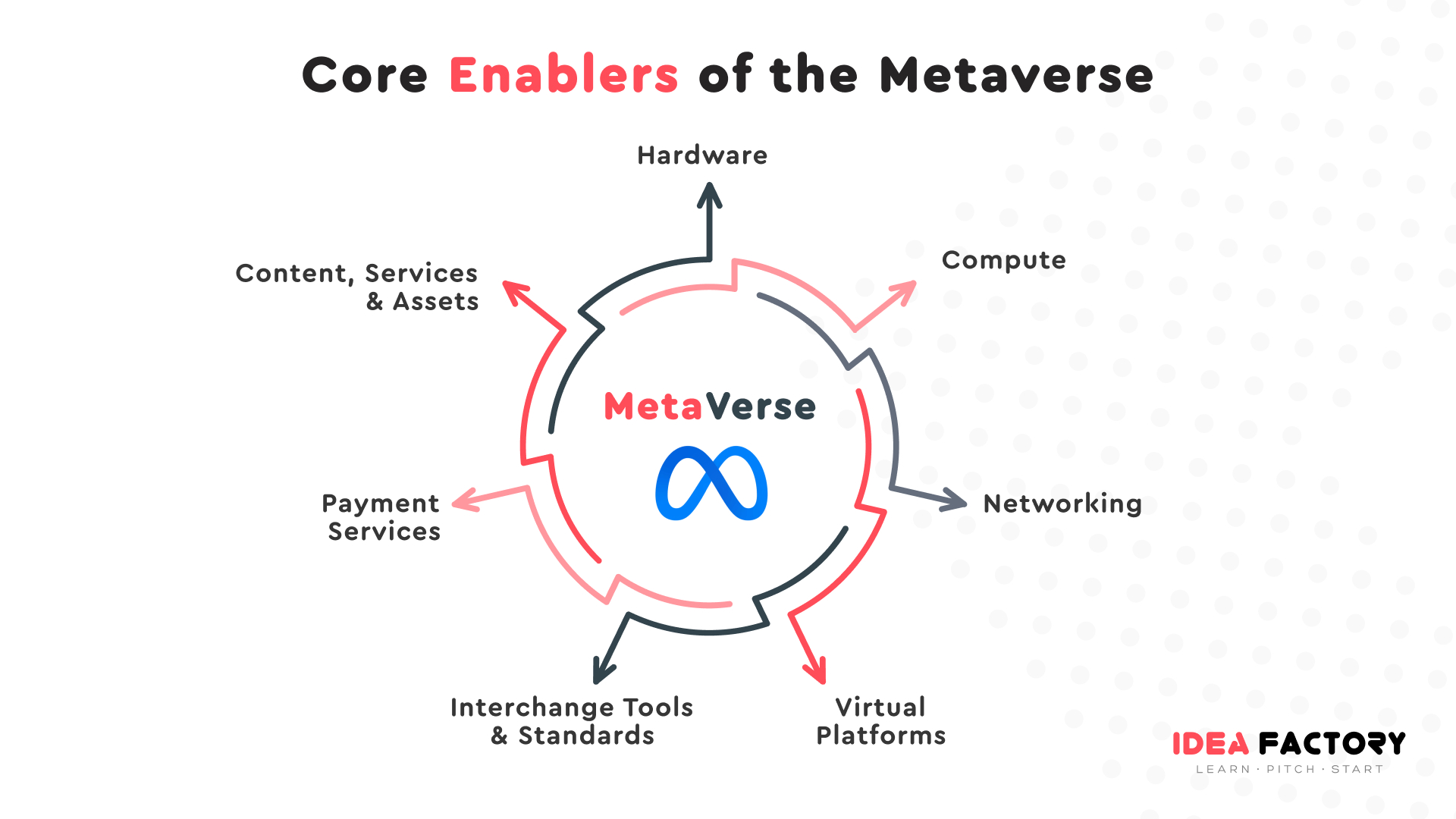
Virtual platforms
They provide the development and support of immersive digital three-dimensional simulations and environments. Virtual platforms help people and companies create, communicate and participate in various events, from car races and studies to listening to music and painting. Economic activity will have a big impact. Unlike traditional online games, there is a large ecosystem of developers and content creators in the metaverse who make money in it.
Interchange tools & standards
These mean various formats, services, engines and other mechanisms for human interaction, as well as the creation, operation, and continuous development of the metaverse. They support copyrights, export and import of data, rendering technologies, AI, and physics.
Payments services
Metaverses support digital payment services and platforms for the exchange of digital and fiat currencies, and other financial services.
Content, services, and assets
The system also provides the development, sale, resale, storage, protection and management of digital assets in the form of money, real estate, or goods.
Statistics
In 2020, the Metaverse market was estimated at nearly $500 billion. According to Statista, it is expected to reach $800 billion by 2024. The primary market for online game makers and gaming hardware may exceed $400 billion in 2024 while opportunities in live entertainment and social media make up the remainder.
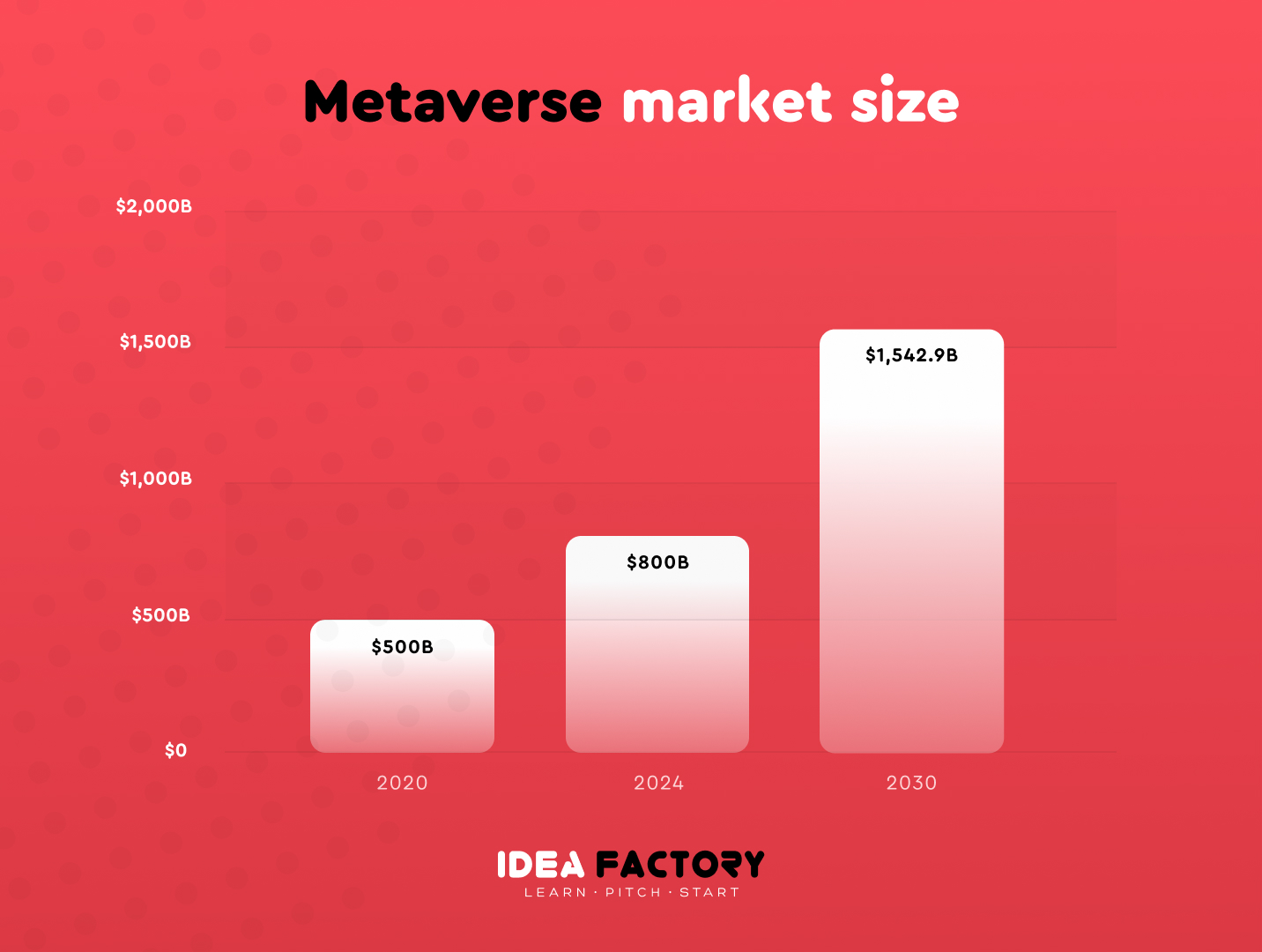
Revenue from live entertainment businesses that can become part of the Metaverse concept – films, live music and sports – can reach $200 billion in 2024, as these businesses gradually recover from the Covid-19 pandemic.
Metaverse benefits & challenges
Prospect of remote travelling
In the Metaverse, the real and virtual worlds merge together. Thus, travelling acquire unimaginable dimensions such as time travel, trips to virtual cities, and expeditions to the digital jungle.
Virtual projections in the real world, smart gloves generating impulses, suits projecting wind, heat and virtual effects on the body – all these will make virtual journeys as realistic as possible.
Stronger retailer customer connections
Retail in the Metaverse provides new opportunities to access and present products in a way that hasn`t existed before. When users put on VR goggles, they can not only see what their room would look like with different furniture but also experience how it all fits together. The metaverse enables customers to experience physical goods in the virtual world to get an immersive experience before buying any goods.
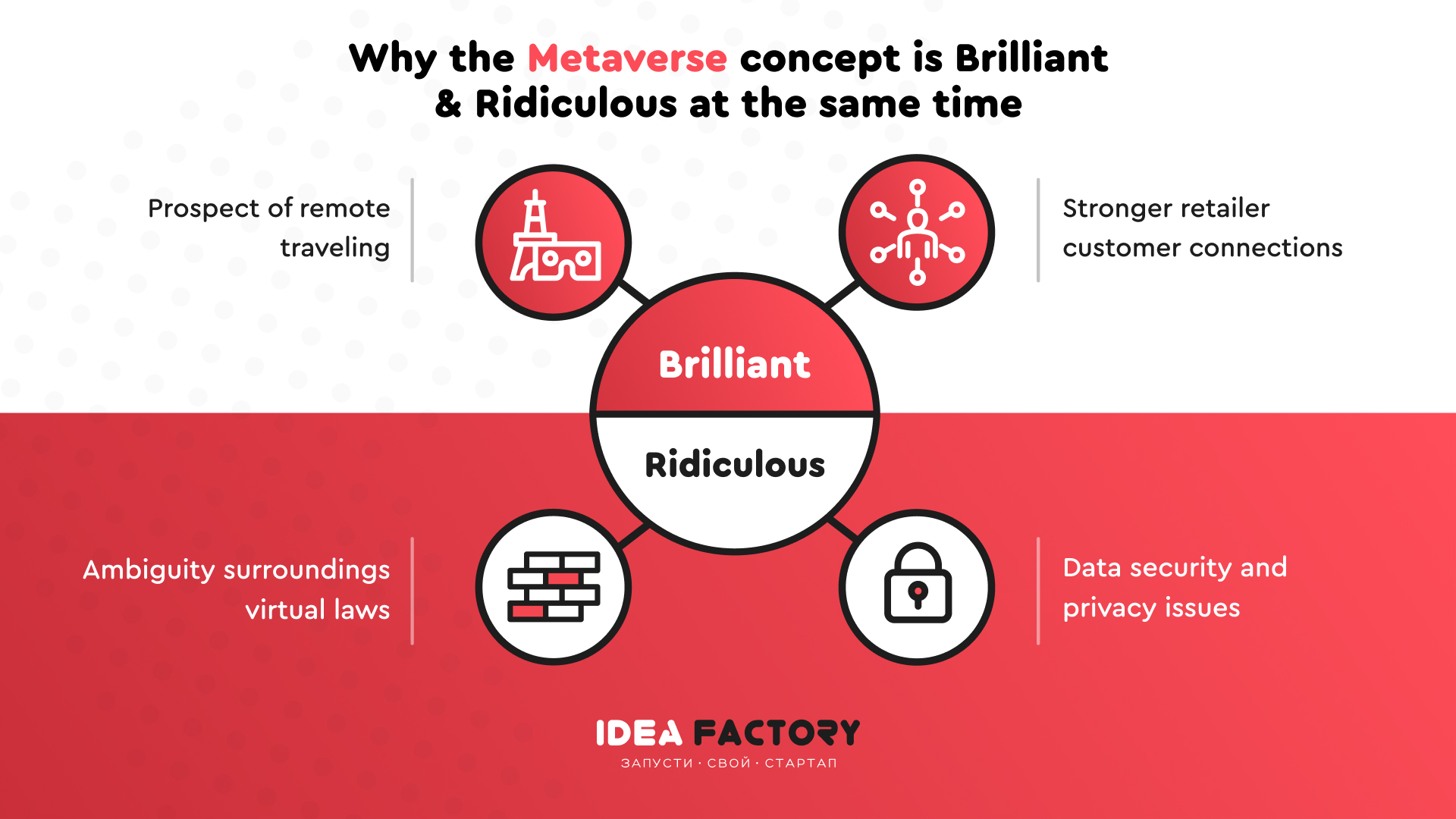
Ambiguity surroundings virtual laws
On the one hand, Metaverses are easy to control with the help of rules/user agreements/terms of use. Such rules, in fact, are no different from those we now accept before launching any game or registering on any site.
Difficulties arise when government agencies notice a new phenomenon and decide to investigate the compliance of the organizers of the metaverse with applicable laws and public interests.
For example, there may be a limit on the maximum time allowed to spend in the metaverse. Also, labor legislation can be extended to metaverses, at least in part of the working time. There may well be restrictions on authorization in the metaverse. To pass it, you will need to provide passport or other data, or log in through government portals.
Data security and privacy issues
Cybersecurity problems become more considerable within a Metaverse. It is likely to be funded by NFT tokens, which may attract cybercriminals. For them, laundering illegally acquired money and turning fraudulent schemes will become much easier. Frauders will be able to block people, their avatars and assets.
As for data security, the matters can get much worse as well. In the process of interacting with the Metaverse, users will generate much more data than they do now. The risk of theft or loss of biometric data will increase, which is fraught with much more serious consequences than a password loss.
Trends in the Metaverse
Machine Intelligence
Users are at the center of the metaverse, and the accuracy of your avatar will determine the quality of the experience for you and other participants. The AI engine can analyze users' 2D images or 3D scans to come up with a very realistic simulated interpretation.
It can then create different facial expressions, emotions, hairstyles, aging-induced features, etc. to make the avatar more dynamic. Companies like Ready Player Me are already using it to create avatars for the metaverse, and Meta is working on its own version of the technology.
Low-code platforms
They provide higher-level abstractions like visual scaffolding and drag-and-drop tooling to replace the hand-coding of processes. The key advantage is that even people who don`t possess program skills can create platforms.
The thing is the large amount of automation happens underneath the visual layer: the automation of workflow, deployment, security, scaling, and integration with various data endpoints.
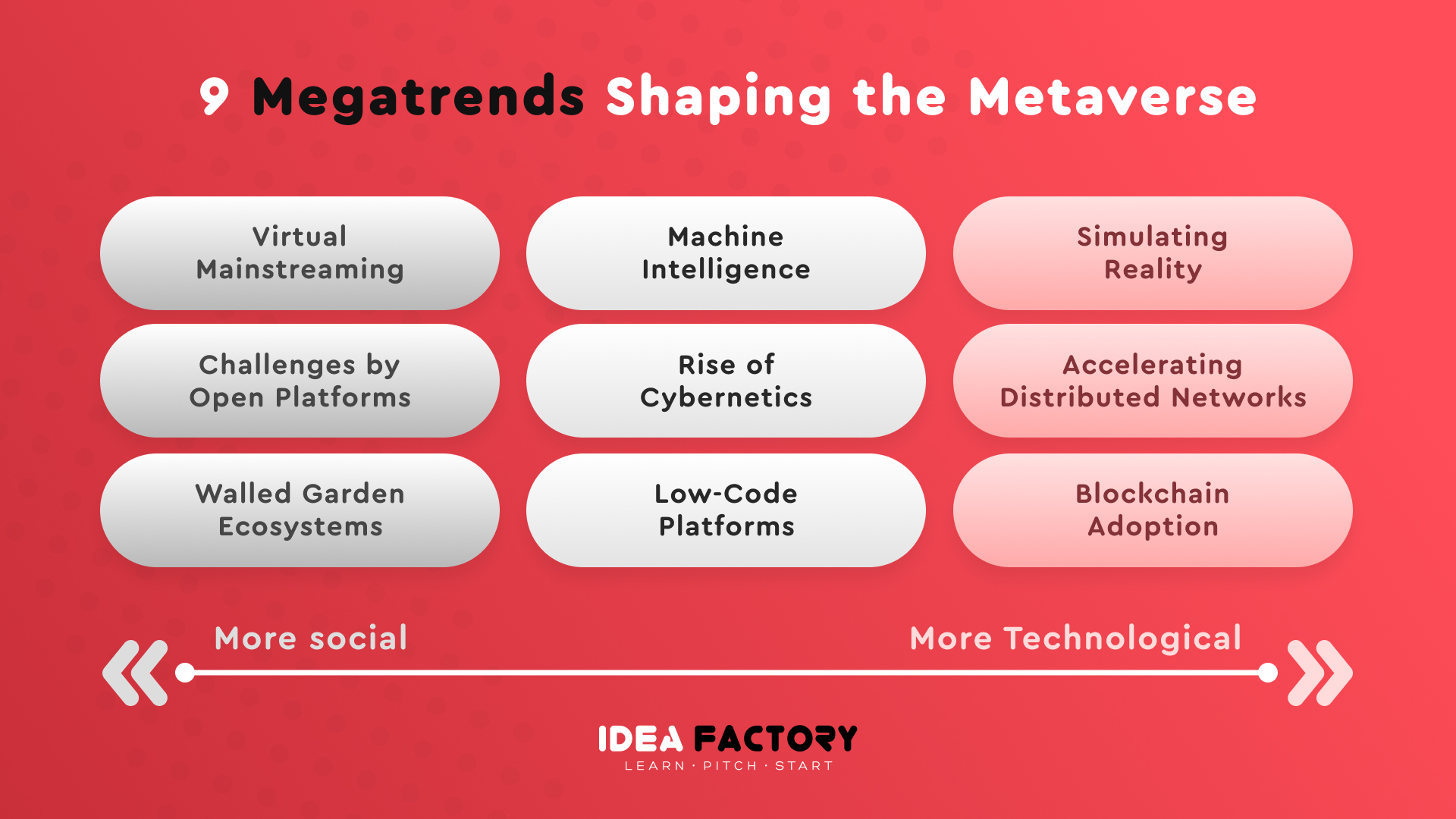
Blockchain adoption
In the Metaverse, Blockchain provides data exchanges; decentralized authority, a record of history and provenance, provable scarcity of assets. When decentralized, a blockchain allows for permissionless participation, or governance through a decentralized autonomous organization.