Matplotlib Latex

⚡ 👉🏻👉🏻👉🏻 INFORMATION AVAILABLE CLICK HERE 👈🏻👈🏻👈🏻
https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/text/usetex.html
Перевести · 31.03.2021 · Text rendering With LaTeX¶. Matplotlib can use LaTeX to render text. This is activated by setting text.usetex: True in your rcParams, or by setting the usetex property to True on individual Text objects. Text handling through LaTeX is slower than Matplotlib's very capable mathtext, but is more flexible, since different LaTeX …
https://matplotlib.org/2.0.2/users/usetex.html
Перевести · 10.05.2017 · Text handling with matplotlib’s LaTeX support is slower than matplotlib’s very capable mathtext, but is more flexible, since different LaTeX …
Add math symbols to matplotlib figures with matplotlib LaTeX || Matplotlib Tips
Python Matplotlib Tutorial - How to Create Symbolic Titles with Latex
Add TEXT to MATPLOTLIB figures || Python matplotlib text with plt.text() || Matplotlib Tips
MATPLOTLIB in one video | Matplotlib Tutorial in Hindi (part-2): Bar Charts
Python Matplotlib Tutorial #3 - Scatter Plots
https://scipy-cookbook.readthedocs.io/items/Matplotlib_LaTeX_Examples.html
Перевести · Recent versions matplotlib break the psfrag functionality (see for example this discussion. That being said, one can use the usetex feature to render the LaTeX text …
https://sodocumentation.net/matplotlib/topic/2962/integration-with-tex-latex
Перевести · matplotlib Integration with TeX/LaTeX Remarks #. Matplotlib’s LaTeX support requires a working LaTeX installation, dvipng (which may be included with your...
https://www.alanshawn.com/tech/2021/03/27/matplotlib-latex-style.html
Перевести · 27.03.2021 · LaTeX distributions are shipped with TeX Gyre Termes’s OpenType version, which can be fed directly into matplotlib’s interactive backends. As a result, we can make the fonts in matplotlib more LaTeX-like by using TeX Gyre Termes. We also need to change matplotlib…
Is there a way to render LaTeX text in Matplotlib?
Is there a way to render LaTeX text in Matplotlib?
Recent versions matplotlib break the psfrag functionality (see for example this discussion . That being said, one can use the usetex feature to render the LaTeX text directly with very good results (if you are careful about choosing fonts). I will try to discuss this here further in the near future. -- MichaelMcNeilForbes
scipy-cookbook.readthedocs.io/items/Mat…
Is Matplotlib slower than Matplotlib?
Is Matplotlib slower than Matplotlib?
Text handling with matplotlib's LaTeX support is slower than matplotlib's very capable mathtext, but is more flexible, since different LaTeX packages (font packages, math packages, etc.) can be used. The results can be striking, especially when you take care to use the same fonts in your figures as in the main document.
matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/text/usetex.…
How to plot an array in Python using matplotlib?
How to plot an array in Python using matplotlib?
I am writing a script in Python (.py file) and I am using Matplotlib to plot an array. I want to add a legend with a formula to the plot, but I haven't been able to do it. I have done this before in IPython or the terminal.
stackoverflow.com/questions/14016217/ho…
What do you need to know about matplotlib and PGF?
What do you need to know about matplotlib and PGF?
Matplotlib’s pgf support requires a recent LaTeX installation that includes the TikZ/PGF packages (such as TeXLive), preferably with XeLaTeX or LuaLaTeX installed. TeX uses the backslash \ for commands and symbols, which can conflict with special characters in Python strings.
sodocumentation.net/matplotlib/topic/2962…
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30281485
Перевести · Using LaTeX in matplotlib. Ask Question Asked 5 years, 11 months ago. Active 5 years, 11 months ago. Viewed 5k times 0. 1. I try to make a table with a title in Python using LaTeX…
https://blog.csdn.net/jovahe/article/details/74780268
Перевести · Matplotlib 对 LaTeX 提供了很好的支持。只需要将 LaTeX 表达式封装在 美元符号 内,就可以在图的任何文本中显示了,比如 “ $ y=x^3$” 在 LaTeX 中常常会用到反斜杠,比如 \alpha 来产生符号 $ …
https://ru.stackoverflow.com/questions/811328/Ошибка-matplotlib-при...
Следующий код используется для отображения LaTeX формул в Matplotlib: def latex_draw(tex, ri, eq=False): ''' :param tex: TeX code :param ri: random number for save …
https://ru.stackoverflow.com/questions/815671/matplotlib-latex-не...
Мне нужно при помощи Python3 и MatPlotLib отобразить русские символы. Я использую следующий код, он работает с английскими символами, но не работает с русскими: import matplotlib matplotlib…
Не удается получить доступ к вашему текущему расположению. Для получения лучших результатов предоставьте Bing доступ к данным о расположении или введите расположение.
Не удается получить доступ к расположению вашего устройства. Для получения лучших результатов введите расположение.
2017-07-13 (last modified), 2006-05-11 (created)
This page describes several ways to produce publication quality graphics with LaTeX.
This section describes a technique following the ["Cookbook/Matplotlib/UsingTex"] guidelines.
Here is the outline of the LaTeX file used to include the figure (example for `REVTeX4` for publication is APS physics journals with a two column format.)
\documentclass[prl,10pt,twocolumn]{revtex4}
\usepackage{graphicx} % Used to import the graphics
\begin{document}
%...
\begin{figure}[t]
\begin{center}
\showthe\columnwidth % Use this to determine the width of the figure.
\includegraphics[width=\columnwidth]{fig1.eps}
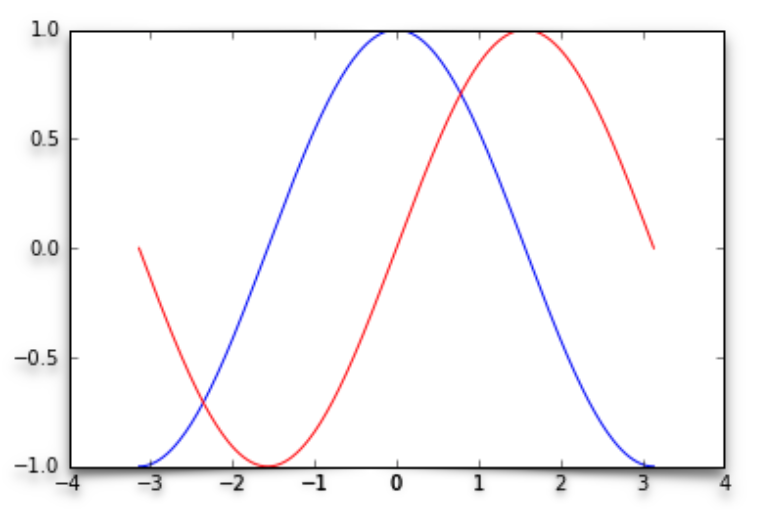
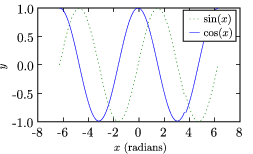
\caption{\label{fig:sin_cos} Plot of the sine and cosine functions.}
\end{center}
\end{figure}
%...
\end{document}
The first step is to determine the size of the figure: this way, when the graphic is included, it will not be resized, and the fonts etc. will be exactly as you set them rather than scaled (and possibly distored). This can be done in LaTeX by explicitly setting the width of the figure and using the `\showthe` command to print this width. (In the example above, the figure width is set to the `\columnwidth`.)
When the file is processed by LaTeX, look at the output. The example above produces the following output (Note: LaTeX will pause after the `\showthe` command, press enter to continue):
This is TeX, Version 3.14159 (Web2C 7.4.5)
LaTeX2e <2001/06/01>
...
> 246.0pt.
l.8 \showthe\columnwidth
% Use this to determine the width of the figure.
?
[1] (./tst.aux) )
...
Thus, the figure will be 246.0pt wide. There are 1 inch = 72.27pt (in [La]TeX), so this means that the figure width should be 3.40390 inches. The heigth depends on the content of the figure, but the golden mean may be used to make a pleasing figure. Once this is determined, the `figure.figsize` property can be used to set the default figure size.
#!python numbers=disable
fig_width_pt = 246.0 # Get this from LaTeX using \showthe\columnwidth
inches_per_pt = 1.0/72.27 # Convert pt to inches
golden_mean = (sqrt(5)-1.0)/2.0 # Aesthetic ratio
fig_width = fig_width_pt*inches_per_pt # width in inches
fig_height =fig_width*golden_mean # height in inches
fig_size = [fig_width,fig_height]
Since the figure will not be scaled down, we may explicitly set the font sizes.
#!python numbers=disable
'font.size' : 10,
'axes.labelsize' : 10,
'font.size' : 10,
'text.fontsize' : 10,
'legend.fontsize': 10,
'xtick.labelsize' : 8,
'ytick.labelsize' : 8,
With these smaller plot sizes, the default margins are not enough to display the axis labels, so we need to specify large margins. We do this with an explicit call to the `axes()` function. In this example, we only have one axis. The typeset LaTeX document will have whitespace on either side of the figure, so we do not need to include this in the figure. Thus, we keep just a bit of whitespace at the top and to the right so that the labels do not extend beyond the bounding box, and add more space to the bottom for the x label:
#!python numbers=disable
pylab.axes([0.125,0.2,0.95-0.125,0.95-0.2])
Here is the python file that generates the plots.
#!python
import pylab
from pylab import arange,pi,sin,cos,sqrt
fig_width_pt = 246.0 # Get this from LaTeX using \showthe\columnwidth
inches_per_pt = 1.0/72.27 # Convert pt to inch
golden_mean = (sqrt(5)-1.0)/2.0 # Aesthetic ratio
fig_width = fig_width_pt*inches_per_pt # width in inches
fig_height = fig_width*golden_mean # height in inches
fig_size = [fig_width,fig_height]
params = {'backend': 'ps',
'axes.labelsize': 10,
'text.fontsize': 10,
'legend.fontsize': 10,
'xtick.labelsize': 8,
'ytick.labelsize': 8,
'text.usetex': True,
'figure.figsize': fig_size}
pylab.rcParams.update(params)
# Generate data
x = pylab.arange(-2*pi,2*pi,0.01)
y1 = sin(x)
y2 = cos(x)
# Plot data
pylab.figure(1)
pylab.clf()
pylab.axes([0.125,0.2,0.95-0.125,0.95-0.2])
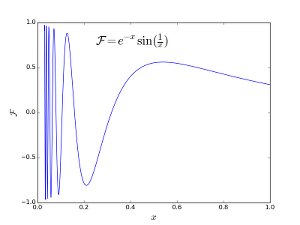
pylab.plot(x,y1,'g:',label='$\sin(x)$')
pylab.plot(x,y2,'-b',label='$\cos(x)$')
pylab.xlabel('$x$ (radians)')
pylab.ylabel('$y$')
pylab.legend()
pylab.savefig('fig1.eps')
An obvious solution is to greyscale convert your figure, but for readibility, adding dashes is often better.. This maybe implemented for an example of a SigmoidalFunctions with
Note: This section is obsolete. Recent versions matplotlib break the psfrag functionality (see for example this discussion. That being said, one can use the usetex feature to render the LaTeX text directly with very good results (if you are careful about choosing fonts). I will try to discuss this here further in the near future. -- MichaelMcNeilForbes
To ensure that your graphics use exactly the same fonts as your document, you can have LaTeX generate and substitute the text for your graph using the psfrag package. This is a good option if you have problems with the `text.usetex` method (for example, if the appropriate fonts cannot be found.)
To do this, simply use plain text for the labels and then replace them using the psfrag package. Here are the modified files to make use of this method:
\documentclass[prl,10pt,twocolumn]{revtex4}
\usepackage{graphicx} % Used to import the graphics
\usepackage{psfrag}
\begin{document}
%...
\begin{figure}[t]
\begin{center}
\psfrag{sin(x)}{$\sin(x)$}
\psfrag{cos(x)}{$\cos(x)$}
\psfrag{x (radians)}{$x$ (radians)}
\psfrag{y}{$y$}
{\footnotesize % Replace tick-lables with smaller font.
\psfrag{1.0}{1.0}
\psfrag{0.5}{0.5}
\psfrag{0.0}{0.0}
\psfrag{-0.5}{-0.5}
\psfrag{-1.0}{-1.0}
\psfrag{-8}{-8}
\psfrag{-6}{-6}
\psfrag{-4}{-4}
\psfrag{-2}{-2}
\psfrag{0}{0}
\psfrag{2}{2}
\psfrag{4}{4}
\psfrag{6}{6}
\psfrag{8}{8}
\showthe\columnwidth % Use this to determine the width of the figure.
\includegraphics[width=\columnwidth]{fig2.eps}
} % Note that the psfrag commands only work in the top-most environment.
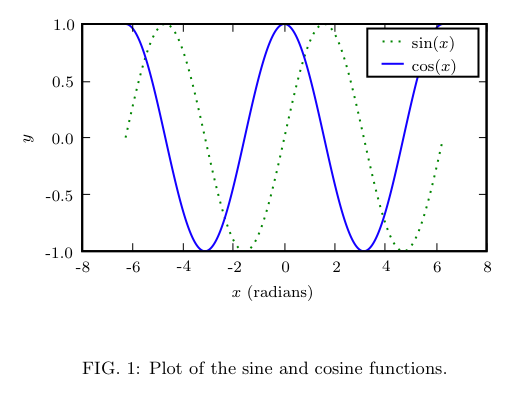
\caption{\label{fig:sin_cos} Plot of the sine and cosine functions.}
\end{center}
\end{figure}
%...
\end{document}
#!python
import pylab
from pylab import arange,pi,sin,cos,sqrt
fig_width_pt = 246.0 # Get this from LaTeX using \showthe\columnwidth
inches_per_pt = 1.0/72.27 # Convert pt to inch
golden_mean = (sqrt(5)-1.0)/2.0 # Aesthetic ratio
fig_width = fig_width_pt*inches_per_pt # width in inches
fig_height = fig_width*golden_mean # height in inches
fig_size = [fig_width,fig_height]
params = {'backend': 'ps',
'axes.labelsize': 10,
'text.fontsize': 10,
'legend.fontsize': 10,
'xtick.labelsize': 8,
'ytick.labelsize': 8,
'text.usetex': False,
'figure.figsize': fig_size}
pylab.rcParams.update(params)
# Generate data
x = pylab.arange(-2*pi,2*pi,0.01)
y1 = sin(x)
y2 = cos(x)
# Plot data
# Plot data
pylab.figure(1)
pylab.clf()
pylab.axes([0.125,0.2,0.95-0.125,0.95-0.2])
pylab.plot(x,y1,'g:',label='sin(x)')
pylab.plot(x,y2,'-b',label='cos(x)')
pylab.xlabel('x (radians)')
pylab.ylabel('y')
pylab.legend()
pylab.savefig('fig2.eps')
Another way to set the legend fonts after the legend has been drawn is to use, for example:
from matplotlib.font_manager import fontManager, FontProperties
font= FontProperties(size='x-small');
pylab.legend(loc=0, prop=font);
If you have very complex images such as high-resolution contour plots or three-dimensional plots, saving these to vector graphic formats like PDF or EPS can result in unacceptably large files (though with the ability for stunning zooms). One solution is to selectively convert parts of the plot (not the text labels) to a rasterized image. This can be done with the so-called "mixed-mode rendering" capability in recent versions of matplotlib. Here is an example as it should probably work:
#!python
from pylab import meshgrid, sin, cos, linspace, contourf, savefig, clf
x, y = meshgrid(*(linspace(-1,1,500),)*2)
z = sin(20*x**2)*cos(30*y)
c = contourf(x,y,z,50)
savefig('full_vector.pdf')
clf()
c = contourf(x,y,z,50,rasterized=True)
savefig('rasterized.pdf')
however, {{{contourf}}} currently does not support the {{{rasterized}}} option (which is silently ignored). Some other plot elements do however. I am looking into a solution for this. -- MichaelMcNeilForbes
Section author: MichaelMcNeilForbes, Unknown[100], GaelVaroquaux, Unknown[101], EmmanuelleGouillart, Unknown[102], LaurentPerrinet, Unknown[8], Christian Gagnon
© Copyright 2015, Various authors Revision 5e2833af.
Latex References
Dreamroll Max Latex
Anime Latex Bondage
Latex Suit Porn
Latex Forums
Text rendering With LaTeX — Matplotlib 3.4.1 documentation
Text rendering With LaTeX — Matplotlib 2.0.2 documentation
Matplotlib: latex examples — SciPy Cookbook documentation
matplotlib - Integration with TeX/LaTeX | matplotlib Tutorial
matplotlib: High Quality Vector Graphics for LaTeX Paper ...
Matplotlib 对 LaTeX 的支持_jovahe的专栏-CSDN博客
python 3.x - Ошибка matplotlib при отрисовке TeX текста ...
python - MatPlotLib LaTeX не отрисовывает русские символы ...
Matplotlib Latex